Integument System Vet. Anatomy and Physiology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Epidermis
answer
The most superficial layer of the skin, composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
question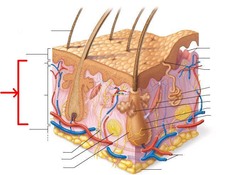
Dermis

answer
Middle layer of the skin, tough, leathery layer composed of dense fibroelastic connective tissue, also called the corium
question
Hypodermis/Subcutaneous
answer
Deepest layer of the skin, acts as a thermoinsulator and a mechanical shock absorber
question
Arrector Pili
answer
Smooth muscles that connect hair follicles and create "goosebumps"
question
Sebaceous Gland
answer
An exocrine gland in the dermis or subcutaneous layer that produces oil (sebum)., in sheep it is called lanolin
question
Sudoriferous Glands
answer
Sweat glands which are located in the dermis with their ducts opening onto the epidermis. They consist of the eccrine and apocrine glands.
question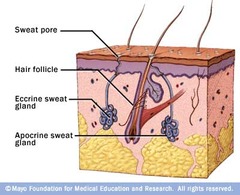
Apocrine Sweat Glands

answer
A simple coiled tube located in the dermis or hypodermis with a single excretory duct that empties into hair follicles
question
Melanin
answer
One factor that determines skin color. It is a brownish black pigment found in some parts of the body such as the skin, retina, and hair.
question
Keloid
answer
Overgrowth of scar tissue that is benign and not contagious. Sometimes accompanied by severe itchiness, pain, and changes in texture. Can occur in anyone but are more common in darker-skinned individuals.
question
Lesion
answer
any abnormal damage or change in the tissue, usually caused by disease or trauma
question
Mammary Glands
answer
Gland that produces milk
question
Keratin
answer
Protein that makes up hair and nails
question
Exocrine Gland
answer
Glands whose secretions pass into a system of ducts that lead ultimately to the exterior of the body
question
Endocrine Gland
answer
Glands whose secretions pass into the internal environment - the blood.
question
Connective Tissue
answer
Adipose Tissue, Cartilage, Blood, Bone
question
Epithelial Tissue
answer
A sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity.
question
Membrane
answer
Cover, protect, or separate other structures or tissues in the body
question
Mucous Membrane
answer
Membrance that lines the body cavities that open to the exterior, such as the digestive, respiratory, reproductive, and urinary tracts
question
Serous Membrane
answer
Tissue that lines certain internal cavities of the body, forming a smooth, transparent, two-layered membrane lubricated by a fluid derived from serum. The peritoneum, pericardium, and pleura are serous membranes.
question
Pleura
answer
lining the lung cavity and covering the lungs
question
Peritoneum
answer
lining the abdominal cavity and and covering the abdominal organs
question
Pericardium
answer
lining the heart cavity and covering the heart
question
Synovial Membrane
answer
Connective tissue that surround the cavity of joints, filling the space with the synovial fluid that they make that lubricates the ends of the bones allowing them to move freely
question
Cutaneous Membrane
answer
Layer of stratified squamous (epidermis) firmly attached to a thick layer of dense connective tissue; the technical term for our skin.
question
Keratinocytes
answer
produce keratin, located in the basement membrane
question
Melanocytes
answer
Located within the lower epidermis and produces melanin
question
Merkel cells
answer
Aid in tactile sensory functions, found in the epidermal-dermal junction
question
Langerhans cells
answer
The macrophages of the epidermis that phagocytize invading microorganisms and produce antigens
question
Stratum germinativum (stratum basale or basal layer)
answer
Base layer of the epidermis, composed of a single layer of cubiodal cells
question
Stratum spinosum (spiny layer)
answer
contains prickle cells, weblike layer of epidermis dense with intercellular attachments (desmosomes)
question
Stratum granulosum
answer
Middle layer, composed of 2-4 layers of flattened, diamond-shaped keratinocytes
question
Stratum lucidum (clear layer)
answer
only in very thick skin, composed of flattened, dead cells
question
Stratum cornium (horny layer)
answer
outermost layer, up to 3/4 of epidermal thickness, contains anucleated and keratinized cells
question
Haired skin
answer
Has 3 layers, basale (germinativum), spinosum, and corneum
question
epidermal papillae
answer
associated with a tactile hair called tylotrich hairs that are associated with the perception of touch
question
Dermis (Corium)
answer
contains blood vessels, glands, nerve endings, smooth muscle, and hair follicles, composed of dense irregular connective tissue that contains collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers
question
fibroblasts, adipocytes, and macrophages
answer
located in the dermis
question
Papillary layer
answer
beneath the epidermal layer of the epidermis, composed of loose connective tissue
question
dermal papillae
answer
projections that rise up into the epidermis to help cement the epidermis and dermis together
question
Meissner's corpuscles
answer
located in the papillary layer, pain and touch receptors
question
Reticular layer
answer
second dermal layer, composed of dense irregular connective tissue
question
Hypodermis
answer
A loose layer of areolar tissue that contains adipose tissue, blood and lymphatic vessels, and nerves
question
Pacinian corpuscles
answer
touch receptors located in the hypodermis
question
Paw Pads
answer
Contains thick layers of fat and connective tissue, has all 5 layers of the epidermis, conical papillae, contains sweat glands
question
Planum Nasale
answer
The nose of dogs, cats, pigs, and sheep, has 3 edpidermal layers: basal (stratum germinativum), spinosum, and corneum
question
Planum Nasolabiale
answer
The muzzle of horses and cattle
question
Ergots (Dark horny Structure)
answer
Found in the long, caudal hairs of the fetlock of horses
question
Chestnuts (Dark horny Structure)
answer
Found on the medial aspect of each leg at the carpus of the forearm and the tarsus (hock) or the hind leg
question
Cutaneous Pouches
answer
In sheep, Infoldings of skin found in sheep found in three primary locations: infraorbital, interdigital, and inguinal pouches; contain fine hairs and numerous sebaceous and oil glands
question
Hair shaft
answer
part that is visible above the skin
question
Hair root
answer
part that is buried within the skin
question
Hair follicle
answer
Tube-like invaginations of the epidermis that transverse through the dermis into the connective tissue, where the hair is rooted; located near arrector pilli and sebaceous glands
question
Root hair plexus
answer
The arrangement of sensory nerves located at the root of the hair follicle that enable it to sense touch
question
Medulla
answer
innermost layer of hair, contain flexible, soft keratin
question
Cortex
answer
surrounds the medulla of the hair, composed of hard keratin
question
Cuticle
answer
surface of the hair, composed of hard keratin
question
Anagen
answer
the active phase of hair growth, stops when maximum length is achieved
question
Catagen
answer
phase between anagen and telogen phases
question
Telogen
answer
Resting phase of hair growth, can last years
question
Telogen effluvium
answer
"blowing" the coat
question
Primary (guard) hairs
answer
Straight or arched; thick and long
question
Secondary (wool-type) hairs
answer
softer and shorter hairs, the undercoat
question
Sinus (tactile) hairs (Vibrissa)
answer
whiskers, used as probes and feelers, contains large blood sinus
question
Eccrine Sweat Glands
answer
A simple coiled tube located in the dermis or hypodermis that is connected to the surface of the skin by a long duct
question
Circumoral glands
answer
found on the lips of cats, used for marking territory
question
Tail Glands
answer
Located at an oval region at the dorsal base of the tail in dogs and cats, used in scent recognition
question
Claws
answer
Hard, keratinized, pigmented outer coverings of the distal digits
question
Declawing
answer
Surgical procedure that removes the entire third (distal) phalanx
question
The Hoof (Ungula) Cows, Sheep, Goats
answer
Weight bearing hooves are the third and fourth digits, dewclaws are the second and fifth digits
question
The Hoof (Horse)
answer
Weight bearing hoof is the third digit
question
Outer hoof (horny hoof (epidermis))
answer
Modified keratinized epithelial layer
question
Corium (dermis)
answer
Sensitive, well innervated tissue found under the hooves and claws, firmly attached to the periosteum of the phalanx
question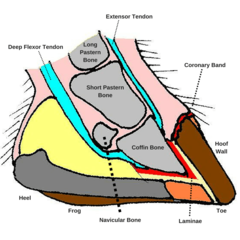
Laminar Corium

answer
between hoof wall and phalanx, connects lateral and dorsal side of phalanx to hoof wall, provides nutrients to the stratum internum
question
Perioplic Corium
answer
Continuous with the dermis of the skin, Located in the perioplic sulcus and supplies nutrients the the overlaying periople
question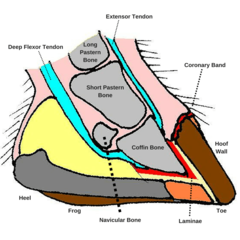
Coronary Corium

answer
Found in the coronary sulcus (grove) and provides nutrients to the stratum externum and medium
question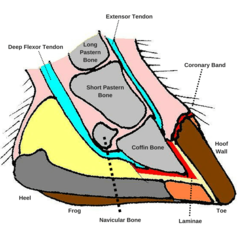
Sole Corium

answer
The dermis underlying the horny sole. provides nutrients to the sole
question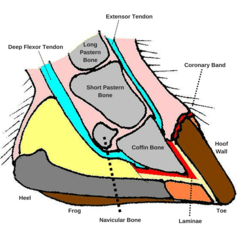
Frog Corium

answer
The dermis underlying the frog
question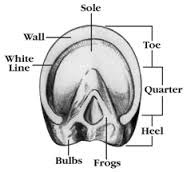
Three Parts of the Equine Hoof

answer
Wall, Sole, Frog
question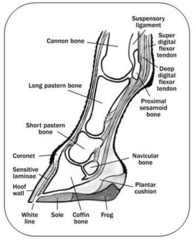
Wall

answer
The convex, external portion of the hoof that is visible from the anterior, lateral, and medial views; divided into the toe, quarters, heel
question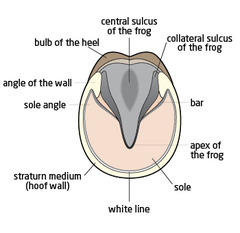
Sole

answer
plantar/palmar surface of hoof, Concave and fills the space bordered by the wall and the bars
question
Angle
answer
part of the sole that immediately surrounds the bars
question
White Line
answer
the junction of the sole and hoof wall, where the sensitive laminae is located
question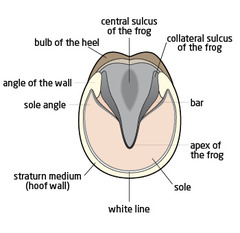
Frog

answer
Triangular, horny structure located between the heels on the underside of the hoof
question
Central sulcus
answer
a central depression that divides the frog
question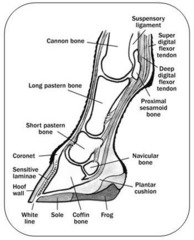
Navicular bone

answer
The distal sesamoid bone
question
Coffin bone
answer
The third phalanx
question
Laminae
answer
Interdigitations formed between the hoof and the corium
question
Lateral cartilages
answer
Two large bands of cartilage that extend proximally from the distal phalanx and form structural support for the foot
question
Collateral grooves
answer
grooves lateral to the frog
question
Periople
answer
Waxy, shiny layer the covers the outer surface of the hoof
question
Hoof Growth
answer
grows down from the coronary band, 1/4 inch per month
question
Thrush
answer
An infection of the frog associated with dirty conditions
question
Gravel
answer
A draining tract resulting from a crack in the white line



