Ap Macroeconomics Unit 1 Test Questions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Capital
answer
Produced goods that can be used as inputs for further production, such as factories, machinery, tools, computers and buildings
question
Ceteris Paribus
answer
A Latin term meaning "all other things constant", or "nothing else changes". The assumption in economics that nothing else changes in a given situation except for the stated change.
question
Complements
answer
Two goods that are used jointly in consumption.
question
Consumers' Surplus
answer
The difference between the maximum price a buyer is willing and able to pay for a good or service and the price actually paid.
question
Marginal Analysis (Decisions at the Margin)
answer
Decision making characterized by weighing the additional benefits of a change against the additional costs of a change with respect to current conditions.
question
Demand
answer
The willingness and ability of buyers to purchase different quantities of a good at different prices during a specific time period.
question
Demand Schedule
answer
The numerical tabulation of the quantity demanded of a good at different prices.
question
Disequilibrium
answer
A state of either surplus of shortage in a market.
question
Economic System
answer
The way in which society decides to answer key economic questions- in particular those questions that relate to production and trade.
question
Economics
answer
The science of scarcity; the science of how individuals and societies make choices because of scarcity.
question
Entrerpreneurship
answer
The particular talent that some people have for organizing the resources of land, labor and capitol to produce goods, seek new business opportunities, and develop new ways of doing things.
question
Equilibrium
answer
The price-quantity combination from which there is no tendency for buyers or sellers to move away.
question
Equilibrium Price (Market Clearing Price)
answer
The price at which quantity demanded of the good equals quantity shipped.
question
Equilibrium Quantity
answer
The quantity at which the amount of the good that buyers are willing and able to buy equals the amount that sellers are willing and able to sell, and both equal the amount actually bought and sold.
question
Labor
answer
The physical and mental talents people contribute to the production process.
question
Land
answer
All natural resources, such as minerals, forests, water, and unimproved land.
question
Law of Demand
answer
As the price of a good rises, the quantity demanded of the good falls, and as the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded of the good rises, Ceteris Paribus.
question
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
answer
For a given time period, the marginal utility or satisfation gained by consuming equal successive units of a good will decline as the amount consumed increases, Ceteris Paribus.
question
Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs
answer
As more of a good is produced, the opportunity costs of producing that good increases, Ceteris Paribus.
question
Law of Supply
answer
As the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied of the good rises, and as the price of a good falls, the quantity supplied of the good falls, Ceteris Paribus.
question
Macroeconomics
answer
The branch of economics that deals with human behavior and choices as they relate to highly aggregate markets or the entire economy.
question
Microeconomics
answer
The branch of economics that deals with human behavior and choices as they relate to relatively small units - an individual, a firm, an industry, a single market.
question
Normative Economics
answer
The study of "what should be" in economic matters.
question
Opportunity Costs
answer
The most highly valued opportunity or alternative forfeited when a choice is made.
question
Positive Economics
answer
The study of "what is" in economic matters.
question
Price Ceiling
answer
A government-mandated maximum price above which legal trades cannot be made.
question
Price Floor
answer
A government-mandated minimum price below which legal trades cannot be made.
question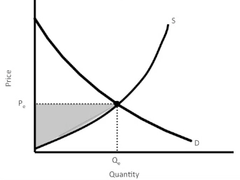
Producers' Surplus

answer
The difference between the price sellers receive for a good and the minimum or lowest price for which they would have sold the good.
question
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
answer
Represents the possible combinations of the two goods that can be produced in a certain period of time, under the conditions of a given state of technology and fully employed resources.
question
Productive Efficiency
answer
The situation that exists when a firm produces its output at the lowest possible per unit cost.
question
Scarcity
answer
The condition in which our wants are greater than the limited resources available to satisfy those wants.
question
Shortage
answer
A condition in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied. Shortages occur only at prices below equilibrium price.
question
Substitutes
answer
Two goods that satisfy similar needs or desires.
question
Supply
answer
The willingness and ability of sellers to produce and offer to sell different quantities of a good at different prices during a specific time period.
question
Supply Schedule
answer
The numerical tabulation of the quantity supplied of a good at different prices. A supply schedule is the numerical representation of the law of supply.
question
Surplus
answer
A condition in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded. Surpluses occur only at prices above equilibrium price.
question
Comparative Advantage
answer
The situation where a country can produce a good at lower opportunity cost than another country can.
question
Absolute Advantage
answer
The ability of a party (an individual, or firm, or country) to produce a greater quantity of a good, product, or service than competitors, using the same amount of resources.
question
Resource
answer
Anything that can be used to produce something else.
question
Trade-Offs
answer
All options given up in order to have the the option chosen.
question
Efficiency
answer
the use of resources in such a way as to maximize the output of goods and services.
question
Technology
answer
The technical means for producing goods and services.
question
Trade
answer
Providing good(s), service(s) or money to others and receiving good(s), service(s) or money in return.
question
Gains from Trade
answer
Getting more of what is wanted/needed through trade than what could be gained if a country tried to be self-sufficient.
question
Specialization
answer
A situation in which each person engages in a task that he or she is good at performing.
question
Quantity Demanded
answer
The amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a specific price.
question
Demand Curve
answer
A graphical representation of the demand schedule. It shows the inverse relationship between quantity demanded and price.
question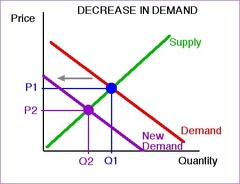
Change in Demand

answer
A shift of the demand curve, caused by an "outside the market" shift, which changes the quantity demanded at any/all given prices.
question
A Movement along the Demand Curve
answer
A change in the quantity demanded of a good that is the result of a change in that good's price.
question
Normal Good
answer
A good for which, other things equal, an increase in income leads to an increase in demand & a decrease in income leads to a decrease in demand.
question
Inferior Good
answer
A good for which, other things equal, an increase in income leads to a decrease in demand & a decrease in income leads to an increase in demand.
question
Quantity Supplied
answer
The actual amount of a good or service producers are willing to sell at a specific price.
question
Supply Curve
answer
Shows the positive relationship between quantity supplied and price.
question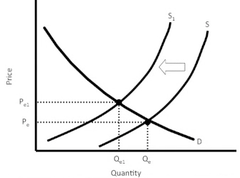
Change in Supply

answer
A shift of the supply curve, caused by an "outside the market" shift, which changes the quantity supplied at any/all given prices.
question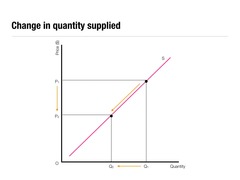
A Movement along the Supply Curve

answer
A change in the quantity supplied of a good that is the result of a change in that good's price.
question
Price Controls
answer
Legal restrictions on how high or low a market price may go.
question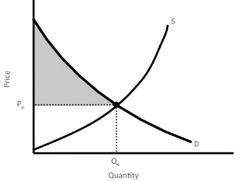
Consumer Surplus

answer
The amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it.
question
Production Possibilities Curve
answer
An economic model of a simplified economy (an economy producing only 2 goods) to show trade-offs graphically.
question
Competitive Market
answer
A market in which there are many buyers and sellers of the same good or service, none of whom can influence the price at which the good is sold.
question
Supply and Demand Model
answer
A model of how a competitive market works. A way of showing the behaviors and interactions of buyers and sellers.



