Macroeconomics Exam 1 (CH 1, 2, 3) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Economics
answer
the study of how people, individually and collectively, manage resources
question
Microeconomics
answer
the study of how individuals and firms manage resources
question
Macroeconomics
answer
the study of the economy on a regional, national, or international scale
question
Rational Behavior
answer
making choices to achieve goals in the most effective way possible
question
Scarcity
answer
the condition of wanting more than we can get with available resources
question
Opportunity Cost
answer
the value of what you have to give up in order to get something; the value of your next-best alternative
question
Marginal Decision Making
answer
comparison of additional benefits of a choice against the additional costs it would bring, without considering related benefits and costs of past choices
question
Sunk Costs
answer
costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered or refunded
question
Incentive
answer
something that causes people to behave in a certain way by changing the trade-offs they face
question
Efficiency
answer
use of resources in the most productive way possible to produce the goods and services that have the greatest total economic value to society
question
Correlation
answer
a consistently observed relationship between two events or variables
question
Positively Correlated
answer
If both events or variables tend to occur at the same time or move in the same direction
question
Negatively Correlated
answer
If one event or variable increases while a related event or variable decreases
question
Causation
answer
a relationship between two events in which one brings about the other
question
Circular Flow Model
answer
represents a basic economy
question
Positive Statement
answer
a factual claim about how the world actually works Ex. A nuclear weapon with the explosive power of 10 kilotons of TNT will have a fallout radius of up to 6 miles.
question
Normative Statement
answer
a claim about how the world should be (an opinion) Ex. The United States was right to use nuclear weapons in World War II.
question
Model
answer
* A simplified representation of the important parts of a complicated situation *Show how people, firms, and governments make decisions about managing resources, and how their decisions interact
question
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
answer
A line or curve that shows all the possible combinations of two outputs that can be produced using all available resources
question
Efficient Points
answer
combinations of production possibilities that squeeze the most output possible from all available resources
question
Absolute Advantage
answer
the ability to produce more of a good or service than others can with a given amount of resources
question
Comparative Advantage
answer
the ability to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than others
question
Specialization
answer
spending all of your time producing a particular good
question
Gains from trade
answer
the improvement in outcomes that occurs when producers specialize and exchange goods and services
question
Market Economy
answer
an economy in which private individuals, rather than a centralized planning authority, make the decisions
question
Market
answer
*buyers and sellers who trade a particular good or service *located locally, globally, or virtually
question
Competitive Market
answer
market in which fully informed, price-taking buyers and sellers easily trade a standardized good or service
question
4 Characteristics of perfectly competitive market
answer
1. Standardized good 2. Full information 3. No transaction costs 4. Participants are price takers
question
Standardized good
answer
a good for which any two units have the same features and are interchangeable
question
Full Information
answer
marker participants know everything about the price and features of the good
question
No Transaction Costs
answer
there is no cost to participation in exchanges in the market
question
Participants are Price Takers
answer
neither buyers nor sellers have the power to affect the market price
question
Transaction Costs
answer
the costs incurred by buyer and seller in agreeing to and executing a sale of goods or services
question
Price Taker
answer
a buyer or seller who cannot affect the marker price
question
Quantity Demanded
answer
the amount of a particular good that buyers will purchase at a given price during a specified period
question
Law of Demand
answer
a fundamental characteristic of demand which states that, all else equal, quantity demanded rises as price falls
question
Demand Schedule
answer
a table that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that consumers will purchase (demand) at various prices
question
Demand Curve
answer
a graph that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that consumers will demand at various prices
question
Shifts in Demand Curve
answer
*When demand increases, demand curve shifts right (all good things shift right) *When demand decreases, demand curve shifts left (all bad things shift left)
question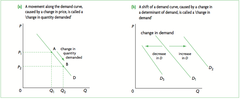
Shifts vs. Movements

answer
*If non-price determinant changes, then demand curve SHIFTS *If the price decreases, then the quantity demanded increases and there is MOVEMENT along the demand curve
question
5 most important non-price determinants of demand
answer
1. Preferences 2. Number of buyers 3. Incomes 4. Expectations 5. Price of related goods
question
Consumer Preferences
answer
the personal likes and dislikes that make buyers more or less inclined to purchase a good
question
Substitutes
answer
goods that serve a similar-enough purpose that a consumer might purchase one in place of the other (Ex. Purchasing salmon because they're out of trout)
question
Complements
answer
goods that are consumed together, so that purchasing one will make consumers more likely to purchase the other (Ex. Peanut butter ; jelly)
question
Normal Goods
answer
goods for which demand increases as income increases
question
Inferior Goods
answer
goods for which demand decreases as income increases
question
Quantity Supplied
answer
the amount of a particular good or service that producers will offer for sale at a given price during a specified period
question
Law of Supply
answer
a fundamental characteristic of supply which states that, all else equal, quantity supplied rises as price rises
question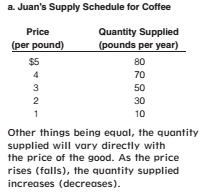
Supply Schedule

answer
a table that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that producers will supply at various prices
question
Supply Curve
answer
a graph that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that producers will supply at various prices
question
5 Determinants of supply
answer
1. Technology 2. Number of producers 3. Price of inputs 4. Expectations 5. Price of related goods
question
Shifts in the supply curve
answer
*When supply increases, the supply curve shifts right *When supply decreases, the supply curve shifts left
question
Equilibrium

answer
the situation in a market when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded; graphically, this convergence happens where the demand curve intersects the supply curve
question
Equilibrium Price
answer
the price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded
question
Equilibrium Quantity
answer
the quantity that is supplied and demanded at the equilibrium price
question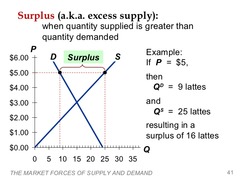
Surplus (Excess Supply)

answer
a situation in which the quantity of a good that is supplied is higher than the quantity demanded
question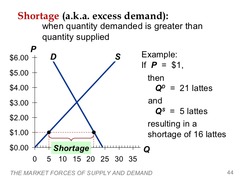
Shortage (Excess Demand)

answer
a situation in which the quantity of a good that is demanded is higher than the quantity supplied
question
Shifts in Demand (Graph)
answer
`
question
Marginal Cost
answer
change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented by one unit
question
Free Trade
answer
international trade left to its natural course without tariffs, quotas, or other restrictions
question
Economic Analysis
answer
A systematic approach to determining the optimum use of scarce resources, involving comparison of two or more alternatives in achieving a specific objective under the given assumptions and constraints.



