Ap Human Geography Chapter 2 Test Questions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Demographic Transition model:
answer
the steps through which a society progresses *The Demographic Transition model helps me understand this concept better.
question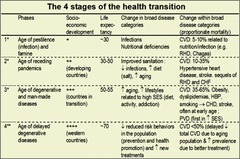
Epidemiological transition

answer
The a distinctive cause of death in each stage of the demographic transition. Explains how countries' population changes **Black Plaque " fleas on rats"
question
gravity model
answer
A model that holds the potential use of a service at a particular location is directly related to the number of people in a location and inversely related to the distance people must travel to reach the service *Starbucks in NYC
question
Agricultural revolution

answer
the development of farming people didn't have to rely on hunting and gathering *Plows
question
Census

answer
A complete enumeration of a population * Census is redone every decade
question
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)

answer
The number of live births yearly per 1,000 people in a population. *(natality)
question
Crude Death Rate (CDR)

answer
The number of deaths yearly per 1,000 people in a population * the CDR in LDC's are higher than in MDCs
question
Demography
answer
the scientific study of population characteristics Look statistically at how people are distributed spatially by age, gender, occupation, fertility, and health *The Demography of people who use snapchat is 13-30
question
Dependency ratio

answer
the number of people who can't work *0-14 and over 65
question
Doubling Time
answer
the time it takes for an area's population to double *increase by 100%
question
Ecumene
answer
the area of land occupied by humans * How much space we are taking up
question
Epidemiology

answer
The branch of medical science concerned with the incidents, distribution, and control of diseases that affect large number of people * science that is concerned with disease
question
Industrial Revolution
answer
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transforms the process of manufacturing goods *Machines
question
Infant Mortality Rate
answer
The total number of deaths in a year among infants under one year old for every 1000 live births in a society *much higher in LDCs because of lack of medical
question
Life Expectancy

answer
A figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live *My life expectancy is 100 :)
question
Medical Revolution

answer
the leap of medical knowledge in stage 2 of the demographic transition *Hopefully the next medical revolution will be the cure of cancer
question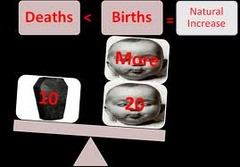
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)

answer
Natural Increase Rate (NIR) Population growth measured as the excess of live births over deaths; does not reflect either emigrant or immigrant movements *More Population naturally
question
Overpopulation
answer
too many people in one place for the resources available *occurs when the number of people exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living. *Can be a threat to some regions in the world, but not others.
question
Pandemic

answer
Disease that occur over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of the population * Fleas on rats
question
Population Pyramids

answer
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex * Can go either way
question
Sex ratio
answer
the ratio of men to women *without balance, population will be affected
question
Total Fertility rate
answer
the average number of children a woman has *1.9 in the US 6 in LDC
question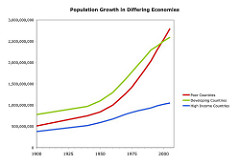
Zero population growth (ZPG)

answer
Where natural birth rate declines to equal crude birth rate and the natural rate of population approaches 0 *NO change
question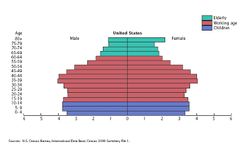
Age distribution

answer
The proportion of individuals of different ages within a population. You can use an age distribution to estimat survival by calculating the difference in proportion of individuals in succeeding age classes *Baby Boomers
question
carrying capacity

answer
the maximum number of organisms of a particular species that can be supported indefinitely in a given environment *resources
question
cohort

answer
measures refer data to a population group unified by a specified common characteristic *squads
question
Demographic equation
answer
NIR = CBR - CDR *simple math
question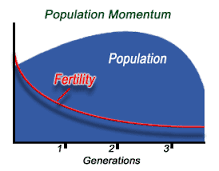
Demographic momentum

answer
is the tendency for growing population to continue growing after a fertility decline because of their young age distribution. This is important because once this happens a country moves to a different stage in the demographic transition model * rollercoaster
question
Demographic regions

answer
Regions grouped together by the stage of the demographic transition model that most countries in the region are in. Sections/Countries that are in the same stage
question
diffusion of fertility control

answer
Shows how many children a mother is having. *baby average
question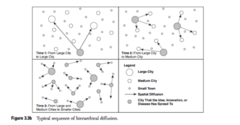
disease diffusion

answer
There are two types, contagious and hierarchical. Hierarchical is along high density areas that spread from urban to rural areas. Contagious is spread through the density of people. This is important in determining how the disease spread so you can predict how it will spread. *How Disease spreads
question
gendered space

answer
areas or regions designed for men or women. *Specific space for each
question
J-curve
answer
The shape of a line graph of population graph when growth is exponential *Huge increase
question
maladaptaion

answer
s a trait that is (or has become) more harmful than helpful, i All organisms, from bacteria to humans, display maladaptive and adaptive traits. * bad habits
question
Malthus, Thomas (Thomas Malthus)

answer
British economist of late 1700's. considered the first to predict a population crisis * Overpopulation will cause us to run out of food
question
Mortality
answer
the rate at which people die *Medical gains are helping to make that age higher
question
Natality

answer
*birth rate CBR
question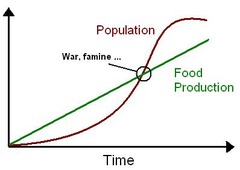
Neo-Malthusians

answer
group who built on Malthus' theory and suggested that people wouldn't just starve for lack of food, but would have wars about food and other scarce resources * first Apocalypse believers :)
question
Population Density

answer
A measurement of the number of people per given unit of land *Population
question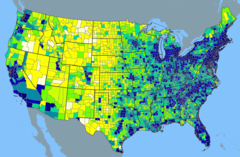
Population Distribution

answer
Description of locations on Earth's surface where populations live *Where people choose to live
question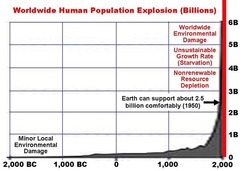
Population Explosion

answer
The rapid growth of the world's human population during the past century, attended by ever- shorter doubling times and accelerating rates of increase. *The world is getting populated quicker
question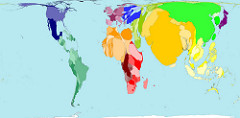
Population Projection

answer
Estimation of future population growth, by extrapolating current trends and known growth factors *Hypothesis about the future Populations
question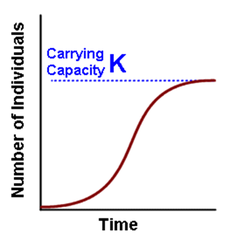
S curve

answer
the horizontal bending, or leveling, of an exponential or J-curve *leveling off
question
Standard of living
answer
The goods a services and their distribution within a population * the standard of living in my house is good :)
question
Sustainability
answer
The level of development that can be maintained without depleting resources * recycle, reuse, renew
question
underpopulation (Is that even a real word??)

answer
A drop or decrease in a region's population *Last man on earth
question
• Study of population is important for 3 reasons:
answer
1. More people are alive at this time (7 billion+) 2. The world's population increased at a faster rate during the 2nd half of the 20th century. 3. Virtually all global population growth is concentrated in developing countries.
question
How is Population distributed
answer
by examining 2 basic properties. **Concentration and density
question
How many population clusters
answer
4 South Asia East Asia Southeast Asia Europe
question
East Asia
answer
1⁄4 of the world's people lives here. ▫ Eastern China, Japan, Korean Peninsula, & Taiwan. • People's Republic of China: most populous country and the 4th largest country in land area. ▫ Population clustered near Pacific Coast and several fertile river valleys. ▫ Most interior is sparsely inhabited mountains and deserts. ▫ 1⁄2 live in rural areas (farmers) • 3⁄4 of Japanese and Koreans live and work in urban areas (industrial or service jobs
question
South Asia
answer
• 1⁄4 of world's people live here ▫ India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, island of Sri Lanka,. • Largest concentration of people live along a corridor from Lahore, Pakistan through India and Bangladesh to the Bay of Bengal. • Population clustered along the plains of the Indus and Ganges Rivers • India: ▫ Heavy clustering along the Arabian Sea to the west and the Bay of Bengal to the East. • Most people rural (farmers
question
Southeast Asia
answer
• 600 million people lives here. ▫ Series of islands that lie between the Indian and Pacific oceans. • Indonesia: • ▫ 13,677 islands ▫ World's 4th most populous country. ▫ Largest concentration on island of Java. High population concentration in the Philippines ▫ Population clustered along river valleys and deltas at the SE tip of Asian mainland (Indochina) • Farmers
question
Europe
answer
Includes 4 dozen countries ▫ Monaco (.7 square miles) to Russia (world's largest land area) • 3⁄4 people live in cities • Fewer than 10% are farmers • Highest population concentration: ▫ Major rivers and coalfields of Germany and Belgium ▫ London and Paris (Capitol cities)
question
2 other clusters
answer
Largest population concentration in the Western Hemisphere is in the northeaster United States and Southeastern Canada. • Atlantic Coast from Boston to Newport News, Virginia and westward along the Great Lakes to Chicago. •Africa: • Largest cluster is along the Atlantic Coast • Nigeria most populous country. • West Africans work in agriculture
question
Dry lands
answer
too dry for farming occupy 20% of the Earth's surface. •Deserts lack sufficient water to grow crops that could sustain a population. •Contain oil reserves
question
Wet lands
answer
receive very high levels of precipitation •Located near the equator •Combination of rain and heat rapidly depletes nutrients from the soil.
question
cold Lands
answer
Much of the land nearer the North and South poles covered with ice or permafrost. •Unsuitable for agriculture. •Few animals and humans survive climate.
question
Highlands
answer
mountains are steep, snow covered, sparsely settled. •High altitude: densely populated. •Low latitude: densely populated where agriculture is possible.
question
Agricultural density
answer
• Arable: land suited for agriculture. •Importance: • Helps account for economic differences. • Developed: lower agricultural densities because technology and finance. • Geographers examine physiological and agricultural densities together .
question
How can we explain population increase
answer
Population increases in places where more people are born then die. It also increases when people move into places.
question
Where is virtually all of the worlds NIR (Natural Increase rate)
answer
. More than 95% of he NIR are clustered in LDC's. ¼ is in Saharan Africa, 1/3 in South Asia
question
What is the world's TFR ( total fertility rate)
answer
2.6, 6.0 in LDC 1.9 in Europe
question
Where is the worlds highest IMR (infant Mortality Rate)
answer
The Highest IMR is also in LDC's The IMR reflects the countries healthcare system, Lower IMR's are in countries with well trained doctors and nurses and large supplies of medicine
question
What is today's NIR (Natural Increase rate)
answer
1.2 The population of the world is growing by 1.2%
question
What was the global NIR (Natural Increase rate) at its peak
answer
2.2% in 1963
question
How many people are added to the world each year
answer
80 million
question
In what region is the most growth occuring
answer
LDC's ¼ is in Saharan Africa, 1/3 in South Asia
question
Mortality rates globally
answer
MDC 80 years old LDC's 50 years old
question
industrial revolution
answer
a series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods
question
medical revolution
answer
medical technology invented in Europe and North America that is diffuse to the poorer countries of latin America, Asia, and Africa. Improved medical practices have eliminated many of the traditional causes of death in poorer countries and enabled more people to live longer and healthier lives.



