Anesthesia Basics – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Who first conclusively demonstrated the clinical use of ether in a surgical setting and where? *
answer
-William T.G. Morton, a dentist, used ether at Massachusetts General Hospital on Oct. 16, 1846 in the ether dome. - Tried to patent ether but too many others assuming credit. -Lived in poverty died of a seizure.
question
Who is credited with introducing cleanliness, good ventilation and adequate nurtition in hospitals during the Crimean War?*
answer
Florence Nightengale "Hospitals don't have to be pest houses"
question
What two physicians hypothesized that infection spread by the health care provider was the main cause of pueperal fever, and reccomended hand washing?
answer
Oliver Wendell Holmes & Ignaz Phillip Semmelweis (Semmelweis noticed mid-wives infection rates were lower than medical students and that mid-wives washed their hands between patients.)
question
When did the germ theory become widely accepted?
answer
1880's
question
Occasional Anesthestists
answer
Physicians did not frequently choose to go into anesthesia due to poor pay. Anesthesia was provided poorly, morbidity & mortality were high. In the 1890's Europe & the US recognized a need for devoted anesthesia professionals. England chose a physician model, the US did not choose. Surgeons began to encourage nurses at the Catholic Hospital Sisters to train as nurse anesthetists.
question
Beginnings of Nurse Anesthesia
answer
Civil War Franco-Prussian War The need for health care created by wars led to use of nurses as anesthetists in the US.
question
First Nurse Anesthetists
answer
Sisters of St. Joseph Franscisican Sisters at St. John's trained and sent out several nurse anesthetists.
question
St. Mary's
answer
-Edith & Dinah Graham became anesthetists under direction of Charles Mayo. Alice Magraw took over Dinah Graham's position as anesthetist. -Magraw implemented record keeping and published findings making anesthesia safer. Magraw is known as "Mother of Anesthesia". The country began adopting nurses as anesthetists and hospitals and surgeons began employing them.
question
Agatha Hodgins*
answer
Canadian nurse Dr. George Crile's nurse anesthetist Founder of the AANA Lakeside Hospital Trained nurses in France during the war. Pioneered early anesthsia machines and nitrous and oxygen use. First president of NANA
question
Anne Penland
answer
Nurse with Presbyterian Hospital Base 2 Went to British front British were impressed, began training their own nurse anesthetists
question
Before WW1 what four formalized nurse anesthesia programs opened?
answer
St. Vincent's- Portland OR (1909) St. John's- Springfield IL (1912) New York Post Graduate Hospital- NYC (1912) Long Island College Hospital- Brooklyn (1914)
question
Francis Hoeffer
answer
Stated that nurse ansethesia was illegal as they were practicing medicine. Crile (from Lakeside) challenged Ohio legislature and 1919 amendment stated nurses could practice under supervision of a physician.
question
Dagmar Nelson
answer
Charged with practicing medicine in California court. Court decided in favor of Nelson.
question
WW2 & Nurse Anesthetists
answer
AANA began certification exam US trained 2000 nurse anesthetists Nurse anesthetists outnumbered anesthesiologists 17:1
question
American Society of Anesthesiologists
answer
Founded in 1936 Changed anesthetist to anesthesiologist and stated it wanted to eliminate nurse anesthetists and make anesthesia an all physician practice. Made working with anesthetists or training them unethical... Stated campaign against nurse anesthetists, AMA, American College of Surgeons & American Hospital Association came to CRNA's defense.
question
Beecher & Todd
answer
Followed over 600,000 anesthetic procedures and found the following mortality rates. Anesthesiologists: 1:890 Nurse Anesthetists: 1:1800
question
Edward L.T. Lyon
answer
First US Army male anesthetist Proposed bills which allowed males to be nurses in the army in April 1966.
question
The 1960's and Nurse Anesthesia
answer
Medicaid & Medicare introduced Anesthesiologists met, did not include anesthetists Not enough anesthesia providers Nursing as a profession ASA & AANA began working together, ASA withdrew statement of support... Recognized need for bachelor's program as prerequisite and academic move from hospitals Some states attempted to expand their scope of practice for CRNA's Codification in legislative bills
question
AANA & Federal Involvement in 1970's
answer
Acquired DC lobbyist ASA started study that asked for CRNA's addresses, places of work. Stated it was in cooperation with AANA and need for anesthesiologists to be more involved with credentialing for nurse anesthetists. Set into motion higher standard of education for CRNA's and Council for Higher Education Accreditation. 2 Anesthesiologist Assistant programs opened in 1974 about 1,000 practice today.
question
TEFRA Tax Equity & Fiscal Responsibility Act of 1982
answer
Effort to contain hospital costs Anesthesiologists billing for services when not present or performed.
question
Health Care Financing Administration
answer
HCFA came up with 7 standards for anesthesiologist reimbursement. 1- perform pre-anesthesia evaluation 2- prescribe the anesthesia plan 3- personally participate in induction & emergence 4- Monitor anesthesia at frequent intervals 5- Remain physically available 6- Provide needed postanesthesia care 7- Refrain from personally performing anesthetic procedure when purporting to be engaged in medical direction REQUIRED PHYSICIAN SUPERVISION under Medicare reimbursements
question
Hyde vs. Jefferson Parish Hospital
answer
Based on whether an exclusive contract for anesthesiologist was violating Sherman anti-trust laws. Derogatory statements against CRNA's, alerted AANA to the need to revitalize its public relations program and watch for attempts to discredit the profession.
question
Medicare Payment System for Hospital Services
answer
Prospective Payment System (PPS) introduced diagnostic related groups (DRG) as form of payment. AANA proposed & acquired: 1- temporary pass through of hospitals CRNA costs 2- single exception to the unbundling provisions questionable if anesthesiologists would be reimbursed for CRNA services 3- direct reimbursement for all CRNAs under Medicare Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act: Direct reimbursement of CRNA's enacted into law. Two payment schedules: 1) with anesthesiologist 2) independent
question
Quality of Care Studies
answer
US House of Representatives studied VA. W.H. Forrest, Anesthesiologist, Stanford Center for Health Care research, looked at primarily CRNA and primarily anesthesiologist hospitals. Both studies found NO DIFFERENCE in anesthesia outcomes based on provider.
question
ASA Anesthesia Care Team (ACT) Statement
answer
Implies CRNA's are technicians AANA does not agree, restrictive of practice, inhibits productivity of providers and is wasteful of anesthesia personnel.
question
Surgeon liability for CRNA action
answer
Only under 2 circumstances: 1- surgeon dictates what CRNA does (e.g. regional vs. GA) 2- hospital policies mandate a degree of supervision "Captain of the Ship" null and void
question
Study by Pine, Holt & Yu
answer
Medicare data from over 400,000 patients in 22 states found that patients were equally safe under CRNA, anesthesiologist, or ACT.
question
When was the AANA founded?
answer
1931 AANA has more than 36,000 members, more than 90% of CRNA's are members. It establishes guidelines for nurse anesthesia practice.
question
What are the three requirements to become a CRNA?
answer
1- unrestricted RN license 2- COA accredited program graduate 3- pass CCNA boards
question
Scope of Practice for CRNA's
answer
1- Performing & documenting a preanesthetic assessment and evaluation of the patient, including requesting consultations and diagnostic studies; selecting, obtaining, ordering, and administering preanesthetic medications & fluids; and obtaining informed consent for anesthesia. ASSESS, LABS, MEDS & CONSENT
question
Task 2
answer
Developing & implementing an anesthetic plan. CARE PLAN
question
Task 3
answer
Initiating the anesthesia technique, which may include general, regional & local anesthesia & sedation. METHOD of ANESTHESIA DELIVERY
question
Task 4
answer
Selecting, applying & inserting appropriate noninvasive and invasive monitoring modalities for continuous evaluation of the patient's physical status. MONITOR VS
question
Task 5
answer
Selecting, obtaining & administering the anesthetics, adjuvant and accessory drugs, and fluids necessary to manage the anesthetics. GIVE 'EM DRUGS
question
Task 6
answer
Managing a patient's airway and pulmonary status using current practice modalities. PULSE OX & ETCO2
question
Task 7
answer
Facilitating emergence and recovery from anesthesia by selecting, obtaining, ordering, and administering medications, fluid, and ventilatory support. RECOVERY
question
Task 8
answer
Discharging the patient from a postanesthesia care area and providing postanesthesia follow up and care. DISCHARGE
question
Task 9
answer
Implementing acute and chronic pain management modalities. MANAGE PAIN
question
Task 10
answer
Responding to emergency situations by providing airway management, administration of emergency fluids and drugs, and using basic or advanced cardiac life-support techniques. EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT
question
Tasks 1-10 Scope of Practice
answer
1-Assess, labs, meds and consent 2- Care plan 3-Method of Anesthesia delivery 4- Monitor VS 5- Give drugs 6- Pulse ox & ETCO2 7- Recovery 8- Discharge 9- Manage pain 10- Emergency management
question
Council of Accreditation of Nurse Anesthesia Educational Programs (COA)
answer
Accreditation of Educational Programs Educational Standards including didactic curriculum Implemented monitoring of pass rates
question
Certification of Nurse Anesthetists (CCNA)
answer
Certification of CRNA's Requirements, guidelines & prerequisites for certification Exam eligibility Grants initial certification
question
Council on Recertification of Nurse Anesthetists (COR)
answer
Evaluation & recertification of CRNA's Formulate, adopt & evaluate eligibility criteria for recertification.
question
Council for Public Interest in Anesthesia (CPIA)
answer
Composed of anesthesia providers & representatives of the public concerned with issues that involve public safety in anesthesia care. Monitor social and health care trends and issues from viewpoint of public.
question
International Federation of Nurse Anesthetists (IFNA)
answer
International members, more than 50,000 members worldwide. Standards for education, practice, monitoring and a code of ethics.
question
AANA Vision Statement
answer
Vision Statement: recognized leaders in anesthesia care
question
AANA Mission Statement
answer
Mission Statement: Advancing patient safety and excellence in anesthesia.
question
AANA Core Values
answer
Core Values: Integrity, professionalism, advocacy & quality
question
AANA Motto
answer
Motto: Supporting our members- protecting our patients.
question
Helen Lamb
answer
Founder Barnes school of Anesthesia Developed initial method for approving schools which led to method of accreditation.
question
1945 Essentials of an Acceptable School for Graduate Registered Nurses
answer
Developed proper training programs and standard curriculum in response to poor programs in the US in preparation of WW2.
question
Bolton Act of 1943
answer
Offered financing of graduate nurses through established civilian schools of anesthesia.
question
How many anesthetics must be performed to meet COA standards?
answer
550 The average student performs 800 anesthetics.
question
Joseph Priestly*
answer
1772-1774 Leeds, England Nitrous oxide for recreational use Discovered oxygen & nitrous oxide
question
Horace Wells*
answer
-1844 -Dentist -Social use of nitrous -No credit (suicide)
question
1840's Ether Frolics Crawford Long*
answer
- Ether frolics & small cyst removal - Injured themselves in frolics and couldn't recall - Died in an insane asylum
question
James Young Stimpson*
answer
-England - Gave chloroform to Queen Victoria during childbirth in 1853 & 1857
question
Anesthesia Problems
answer
-Main surgical problem was infection - Main anesthesia problem was unskilled or "occasional anesthetist" -Limited prestige, low pay
question
Who were some of the first anesthetists in the US?
answer
Mrs. Harris & Catherine Lawrence* Used chloroform and stimulants at the Battle of Gettysburg during the Civil War Sister Mary Bernard*: "first anesthetist" in the US
question
Who was Carl Koller?*
answer
- Ophthalmologist who used topical cocaine for anesthesia of the eye
question
Who was August Bier?*
answer
-Gave the first spinal anesthetic in 1898, 3ml of .5% cocaine IT. -Bier Block in 1908
question
Who is Charles Mayo?*
answer
- Opened the Mayo clinic with nurse anesthesia instruction - Role in the UN, appointed by Eisenhower -Died in MVA on his 70th birthday
question
Who is John Snow?*
answer
-First anesthesiologist or "physician anesthetist" - Died from stroke at 45, after spending his last years conducting experiments on himself.
question
Who is known as the "Mother of Anesthesia"?*
answer
-Training program in 1900's - Alice Magraw -14,000 anesthetics without a death - Late 1800's to early 1900's
question
1990's
answer
-1996 Anesthesiologist outnumber CRNA 1.2:1 -55% of anesthesiology residents were international medical graduates
question
2000's
answer
-2007: 38,000 CRNAs in the US -40% of practicing CRNAs have been practicing for more than 20 years. - SRNA graduates number 800/year in 2000 (84 schools) - 1,100 CRNAs on active duty in the military
question
2013
answer
-2,200 graduates/year (118 schools) -40,000 CRNA's -Median salary $150,000, starting usually $110-130K
question
ASA I
answer
Patients are considered to be normal and healthy. Patients are able to walk up one flight of stairs or two level city blocks without distress. Little or no anxiety. Little or no risk. This classification represents a "green flag" for treatment.
question
ASA II
answer
Patients have mild to moderate systemic disease or are healthy ASA I patients who demonstrate a more extreme anxiety and fear toward dentistry. Patients are able to walk up one flight of stairs or two level city blocks, but will have to stop after completion of the exercise because of distress. Minimal risk during treatment. This classification represents a "yellow flag" for treatment. Examples: History of well-controlled disease states including non-insulin dependent diabetes, prehypertension, epilepsy, asthma, or thyroid conditions, smoker, overweight; ASA I with a respiratory condition, pregnancy, and/or active allergies. May need medical consultation. Note: Patients who demonstrate a more extreme anxiety and fear toward dentistry have a baseline of ASA II even before their medical history is considered; that situation raises the classification system
question
ASA III
answer
Patients have severe systemic disease that limits activity, but is not incapacitating. Patients are able to walk up one flight of stairs or two level city blocks, but will have to stop enroute because of distress. If dental care is indicated, stress reduction protocol and other treatment modifications are indicated. This classification represents a "yellow flag" for treatment. Examples: History of angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, or cerebrovascular accident, congestive heart failure over six months ago, slight chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and controlled insulin dependent diabetes or hypertension. Will need medical consultation.
question
ASA IV
answer
Patients have severe systemic disease that limits activity and is a constant threat to life. Patients are unable to walk up one flight of stairs or two level city blocks. Distress is present even at rest. Patients pose significant risk since patients in this category have a severe medical problem of greater importance to the patient than the planned dental treatment. Whenever possible, elective dental care should be postponed until such time as the patient's medical condition has improved to at least an ASA III classification. This classification represents a "red flag" ‑ a warning flag indicating that the risk involved in treating the patient is too great to allow elective care to proceed. Examples: History of unstable angina pectoris, myocardial infarction or cerebrovascular accident within the last six months, severe congestive heart failure, moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and uncontrolled diabetes, hypertension, epilepsy, or thyroid condition. If emergency treatment is needed, medical consultation is indicated
question
ASA V
answer
Patients are moribund and are not expected to survive more than 24 hours with or without an operation. These patients are almost always hospitalized, terminally ill patients. Elective dental treatment is definitely contraindicated; however, emergency care, in the realm of palliative treatment may be necessary. This classification represents a "red flag" for dental care and any care is done in a hospital situation.
question
ASA VI
answer
Clinically dead patients being maintained for harvesting of organs.
question
ASA-E
answer
Emergency operation of any variety (used to modify one of the above classifications, i.e., ASA III-E).
question
Appendectomy
answer
GA-OETT Supine Inpatient 30mins
question
Arm Fracture
answer
GA-OETT, LMA or MAC Regional Block: brachial Supine Out patient 45 mins-6h
question
BMT (bilateral myringotomy) /PE (pressure equalization) Tubes
answer
Mask Supine Outpatient 5 minutes
question
Breast Biopsy
answer
MAC supine 10-30 minutes
question
Broken Jaw
answer
GA-Nasal intubation or fiberoptic intubation protocol Supine Inpatient 1-3 hours
question
BTL p CS (Bilateral tubal ligation after cesarean section)
answer
SAB or epidural Steep trendelenberg, supine, lithotomy Inpatient 15-25 mins
question
Bunion repair
answer
MAC Supine Outpatient 30 minutes
question
CABG
answer
GA-OETT Supine Inpatient 3-4 hours
question
Cardioversion
answer
MAC Supine Outpatient <30 minutes
question
Carotid Endarectomy
answer
GA-OETT, MAC Supine Inpatient 1-2 hours
question
Carpal Tunnel Release
answer
MAC Bier block, axillary or brachial Supine Home 30-90 minutes
question
Cataracts
answer
MAC Retrobulb-peribulbular block Supine Outpatient 15-60 minutes
question
C-section
answer
GA-OETT, SAB, epidural Supine with left lateral tilt Inpatient 20-90 minutes
question
Craniotomy
answer
GA or MAC Supine, sitting, lateral or prone Inpatient 3-5 hours
question
Colon Resection
answer
GA-OETT, epidural Supine, modified lithotomy Inpatient 1-3 hours
question
Colporrhaphy (bladder repair)
answer
GA-OETT, LMA* Lithotomy In or outpatient 1-4 hours
question
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
answer
MAC Supine Outpatient <10 minutes
question
Endometriosis Ablation (Laparascopic)
answer
GA-OETT Dorsal lithotomy, stirrups or steep trendelenberg Outpatient or 1 day admit 45 mins- 4 hours
question
Hemorrhoidectomy
answer
GA-OETT, MAC, SAB Prone, lateral decubitus, lithotomy, jack-knife Outpatient 10-90 minutes
question
Hip Fracture
answer
GA-OETT, SAB or epidural Supine, left decubitus Inpatient 3-6 hours
question
Hysterectomy
answer
GA-OETT, LMA, spinal or epidural Supine, lithotomy Inpatient 45 mins- 2 hours
question
Inguinal Hernia
answer
GA-OETT, LMA, MAC, SAB Supine In or Outpatient 3 hours
question
Knee Scope
answer
GA-OETT, LMA, SAB, regional Supine Outpatient 2 hours
question
Laporascopic BTL
answer
GA-OETT Supine, lithotomy Outpatient 20-35 minutes
question
Mastectomy
answer
GA-OETT, LMA, regional Supine Inpatient 1-3 hours
question
Microdiscectomy
answer
GA-OETT Prone, kneeling Inpatient (24 hours) 1-2 hours
question
MRI of Brain/Neck
answer
GA-OETT, LMA, MAC Supine Outpatient ≥ 1 hour
question
Nissan Fundoplication
answer
GA-OETT (GERD=no LMA) Supine Inpatient 1-2 hours
question
Oral Surgery
answer
GA-OETT Supine Out or inpatient ½-3 hours
question
Prostate Biopsy
answer
MAC Supine Outpatient 15 minutes
question
Prostate Resection
answer
GA-OETT, LMA, SAB or epidural Lithotomy Inpatient 1-2 hours
question
Rotator Cuff Repair (RCR)
answer
GA-OETT, regional Lateral decubitus, beach chair Outpatient 1-4 hours
question
Sinus Surgery
answer
GA-OETT, MAC, HOB 30° or supine Outpatient 1-4 hours
question
Thoracoscopy
answer
GA-OETT (double lumen tube), thoracic epidural Lateral Inpatient ½-1½ hours
question
Thyroidectomy
answer
GA-OETT Supine 24 hours inpatient 1-2 hours
question
Tonsillectomy
answer
GA- nasal ETT Supine Outpatient 10-60 minutes
question
Vaginal Delivery
answer
SAB, epidural Lithotomy Inpatient Time varies
question
Thoracotomy
answer
GA-OETT, thoracic epidural Lateral Inpatient 1-3 hours
question
Pre-op anesthetic
answer
Interview Review of Systems Review labs EKG Old charts Discuss prior experiences with patient/family, discuss options, benefits & risks. CRNA's can order any lab test or medication that is pertinent to the anesthetic. EG: pain meds, EKG, anti-emetic, labs *Include caveat that GA may be required.
question
Intra-op anesthetic
answer
Do what you said you would. Have back-up plans, be vigilant. Expect the worst, hope for the best. Be prepared for the unexpected.
question
Post-op anesthetic
answer
PONV Pain control Morbidity (cut lips, damaged teeth, sore neck, limbs, nerve damage, sore throat, scratched eyes etc.) Exit interview a few days later.
question
Which factors affect the absorption of inhalational anesthetics?
answer
CO, respiratory rate
question
Advantages of Local Anesthetic
answer
- Don't have the risks involved with GA - If they come to OR it is monitored anesthesia care
question
Disadvantages of Local Anesthetic
answer
-Physician can do independent of CRNA, "straight local"
question
Advantages of MAC
answer
-Light to moderate to deep sedation similar to general - May need oral airway -Spinal, epidural or regional
question
Disadvantages of MAC
answer
- Sometimes people are uncomfortable so they require GA anyway.
question
Advantages of GA
answer
-A progressive depression of the CNS -Controlled passage through stage 1 and 2 to arrive in stage 3. - Patient cooperation not absolutely essential - Unconscious -Amnesia - Rapid onset of action - Titration possible
question
Disadvantages of GA
answer
-Loss of protective airway reflexes - Depression of VS - Advanced training required - Additional personnel required - Special Equipment/setting -Need recovery room - Greater risk of intra-op complications -Post-anesthetic complications -More extensive pre-op evaluation, including lab work Indications: extreme anxiety or fear, mentally/physically disabled adults or children, poor patient cooperation, infants & children, traumatic procedures Contraindications: lack of adequate training by doctor or personnel, lack of equipment, facilities or medically compromised patient
question
Mask
answer
-Oral airway or nasal airway -Nasal avoided, bleeding -Short-term case
question
LMA
answer
Most common airway manipulation -Must be spontaneously breathing - LMA at induction, ventilate until propofol wears off -Reflux not a candidate
question
ETT
answer
OETT: oral endotracheal tube NETT: nasal endotracheal tube DLT: double lumen tube (one lung ventilation- thoracic cases) Most secure airway.
question
Advantages of TIVA
answer
-Used with allergies to gas/MH history - Quick stages of anesthesia -TIVA is a general anesthetic -used for neuro cases (rapid awakening)
question
Advantages of Epidural/Neuraxial
answer
-Pain control 12-24 hours post surgery (duramorph) - no respiratory issues - Used with older or compromised patients
question
Disadvantages of Epidural/Neuraxial
answer
- Urinary retention - Immobile, pad immobile extremities
question
Advantages of Regional Block
answer
- Somewhat awake, will hear things - MAC cases
question
Disadvantages of Regional Block
answer
- Need to be asleep with tourniquet because it is uncomfortable - Patient can remain awake
question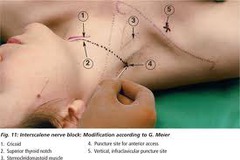
Interscalene

answer
Indications for interscalene nerve block include the following: Shoulder surgery, such as rotator cuff repair, acromioplasty, hemiarthroplasty, and total shoulder replacement Humerus fracture Other arm surgery that does not involve the medial aspect of the forearm or hand
question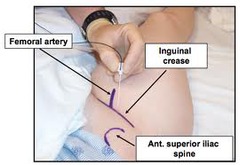
Femoral

answer
Indications: Anterior thigh and knee surgery Landmarks: Femoral (inguinal) crease, femoral artery pulse Nerve Stimulation: Twitch of the patella (quadriceps) at 0.2-0.5 mA current Local anesthetic: 20 mL Complexity level: Basic
question
Bier Block
answer
Indications: Surgery on the wrist, hand and fingers. Local anesthetic: 15 mL of 2% lidocaine (up to 40ml) Complexity level: Basic
question
Malignant Hyperthermia Cause
answer
-Open ryanodine receptor allows continuous release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. -Triggers: all anesthetic gases -Nitrous is safe.
question
MH S/S and treatment
answer
Trigger: all halogenated anesthetics and succinylcholine (nitrous is safe) Increasing CO2, hyperthermia Treat: dantrolene 2.5 mg/kg every 5 minutes up to 10mg/kg Anesthetic plan: MAC, regional, TIVA (for general) Flush machine, new absorber, new circuit
question
Stages of Anesthesia: Stage 1
answer
Stage 1: Analgesia Stage 2: Delerium Stage 3: Surgical Anesthesia Stage 4: Overdose (medullary paralysis) Stage 1: -Beginning of induction drug to loss of consciousness -dizzy, loses sense of reality -lessened sensitivity to touch and pain -hearing is increased, response to noise intensified
question
Stage 2
answer
Delirium or excitement phase: loss of consciousness to onset of rhythmicity of VS into entry of surgical anesthesia -Struggling, ↑ muscle tone, jaw sets, eyelids closed, may breath hold and retch , nystagmus -Reflexes are hyperactive -Respiratory pattern is irregular -"Goofy" disconjugate eyes - NEVER EXTUBATE (laryngospam)
question
Stage 3
answer
Surgical or Operative Stage: -End of stage 2 to cessation of respirations - Respirations regular, patient likely intubated or LMA There are 4 planes of anesthesia in Stage 3. -Most surgical procedures occur in plane 2.
question
Stage 4
answer
Death... cessation of respiration to death, respiratory and circulatory arrest. Circulatory collapse. -all reflexes absent - flaccid paralysis - marked hypotension - weak irregular pulse
question
IV anesthetics & pregnancy
answer
-Most are safe - Versed avoided but may be ok -Fentanyl & propofol frequently used
question
Inhalational Anesthetics & pregnancy
answer
All gas anesthetics: -depress the uterus, ↑ risk of miscarriage - may increase blood loss during intrauterine procedures - reduced MAC required due to higher circulating blood volume hemodilution
question
Benefit of continuous infusion of opioids
answer
-Used for maintenance of general anesthesia -Balanced technique -Morphine, fentanyl, alfentanil, sufentanil, remifentanil, demerol
question
Which factors lower MAC requirements?
answer
↑ age Hypothermia Depressant medications α₂ agonists Acute ethanol consumption Metabolic acidosis Hypoxemia Anemia Hypotension Hyponatremia Pregnancy N₂O, ketamine, lidocaine, clonidine, lithium
question
Which factors raise MAC requirements?
answer
Kids (higher metabolism/RR) Hyperthermia Hyperthyroidism Hypernatremia Chronic alcohol consumption MAO Inhibitors Cocaine, levodopa
question
What is the mechanism of action of local anesthetics?
answer
- Block Na channels preventing depolarization of the cells.
question
Which medications reverses narcotics?
answer
- Narcan .04-4mg IV q 3 minutes
question
Which medications reverses benzodiazepines?
answer
- Flumazenil -Competitive agonist at receptor binding sites. Sole benzodiazepine antagonist. - 0.2 mg doses (2ml) titrated up gradually to desired LOC, up to 1mg
question
Which medications reverse paralytics?
answer
-Neostigmine .04-.07mg/kg up to 5mg (combine with robinul because neostigmine will increase salivation) - Endrophonium .5-1mg/kg (combine with atropine to block muscarinic cholinergic effects)
question
Desflurane Advantages & Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: quick, rapid uptake & elimination, minimal metabolism Disadvantages: pungent, respiratory irritant, expensive, tachycardia
question
Desflurane dosing & metabolism
answer
Dosing: 3-9% induction, 2-6% maintenance Metabolism: <0.1%
question
Isoflurane Advantages & Disadvantages
answer
Advantages:cheap, minimal metabolism Disadvantages: pungent, respiratory irritant, slow uptake & distribution, coronary steal
question
Isoflurane dosing & metabolism
answer
Dosing: 1-4% induction, .5-2% maintenance Metabolism: <1%
question
Sevoflurane Advantages & Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: not respiratory irritant, rapid uptake & distribution non-pungent Disadvantages: metabolized, compound A, expensive, ↑ fluoride ion concentration
question
Sevoflurane Dosing & Metabolism
answer
Dosing: 4-8% induction 1-4% maintenance Metabolism: 3-6% by liver
question
What are each anesthetic agents blood/gas solubility coeffcient? What does this number tell you?
answer
Des:0.42 Iso:1.4 Sevo: 0.6 N₂O: .47 SPEED -The proportion of the anesthetic that will be soluble in the blood. -The more soluble the drug, the slower the uptake. (The gas is "tied" up and unable to get to brain.) - Poorly soluble = rapid uptake
question
What are the MAC values of each anesthetic? What does this number mean?
answer
Des: 5.8 Iso: 1.15 Sevo: 2 N₂O: 105 DOSE
question
What are the oil/gas values of each anesthetic? What does this number mean?
answer
Des: 18.7 Iso: 99 Sevo: 50 N₂O: 105 POTENCY
question
What is the second gas effect?
answer
Simultaneous administration of a relatively slow agent, such as iso, and a faster agent, such as N₂O will speed the onset of the slower agent.
question
Nitrous Oxide Advantages & Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: moderate analgesia, rapid uptake & elimination, non pungent, does not ↓BP Disadvantages: expansion of closed air spaces, ↑PONV, immune supression, teratogenic, supports combustion, weak
question
Nitrous Oxide Dosing & Metabolism
answer
Dosing: 50-70% induction & maintenance Metabolism: <1%
question
Benzodiazepines
answer
-Versed- quick on and off .25 mg for elderly people, 1mg-2mg for most others
question
MAC of a Halogenated Anesthetic
answer
-The dose is expressed as minimum alveolar concentration necessary to produce anesthesia on surgical stimulation. -Faster the lung and therefore brain concentrations rise the faster the anesthesia is achieved.
question
MAC defined
answer
-MAC awake 1/3 (amnesia) -MAC bar 1.5 (block adrenergic receptors) usually goal for start of surgery -MAC intubation 2 (ETT, very stimulating)
question
Ventilation Effect
answer
The faster and more deeply a patient breathes or is ventilated the faster the patient loses consciousness and emerges. Ventilation/perfusion deficits or poor lung function hinders inhalation drug administration. Affects fast drugs the most.
question
Uptake into the Blood
answer
Vessel Rich: heart, liver, kidneys, brain, to a lesser degree muscle Vessel Poor: fat ↑ in CO slows uptake. Pediatric uptake is faster than adults (kids have higher alveolar ventilation per weight ratio).
question
Concentration Effect and Over-pressurizing
answer
-Concentration effect: A loading dose is given to speed initial uptake & turn up the flows ↑Fi% -"Over-pressurizing" is the process of significantly increasing a volatile anesthetic delivered to a patient to increase the alveolar concentration and therefore the amount dissolved in the blood, to speed uptake. Henry's Law
question
Diffusion hypoxia
answer
-Occurs during emergence - High concentrations of nitrous have been given - Nitrous is turned off - Nitrous exits the body quickly through the lungs and is replaced by nitrogen in the air - Results in transient dilution of oxygen and carbon dioxide - Administration of 100% FIO₂ for several minutes will prevent
question
Placement guidelines for Epidural
answer
-Intercristal/Tuffier's line - Feel iliac crest, guide placement of epidural - mark L3/L4 space, have patient arch back - "heavy" on solutions mean hyperbaric, goes down -Isobaric same as CSF, hypobaric lower than CSF -Marcain .5-.75% in dextrose commonly used
question
Which of the following correctly describes ketamine dose for IV induction? IM
answer
- 2-3 mg/kg IV for induction - 4-6 mg/kg IM Mixed with atropine to counteract salivation. -Maintenance: 15-45mcg/kg/min (1-3 mg/min)
question
What is the longest acting local anesthetic?
answer
- Tetracaine with epinephrine
question
What is a normal dibucaine number?
answer
-80, 80% of the PChE inhibited by dibucaine - Dibucaine Inhibition Test
question
ER, ORIF for finger reduction, ETOH
answer
- ETOH lowers MAC requirement with acute intoxication (already at .2-.3 MAC) - Chronic ETOH with raise MAC requirements (noticeable with propofol)
question
What causes bradycardia in kids?
answer
-Succinylcholine -Mix with atropine to counteract bradycardia
question
If eyes are midline which stage are they in?
answer
- Stage 1 or 3
question
During what stage do you NEVER extubate?
answer
Stage 2 -Delirium, prone to laryngospasm
question
Why are paralytics avoided in kids?
answer
- Want to maintain airway, respiratory drive - Succinylcholine causes MH, bradycardia - Use demerol and propofol for induction -Avoid reversals
question
What do narcotics do to pupils? Atropine?
answer
- Pinpoint: narcotics - Dilate: atropine
question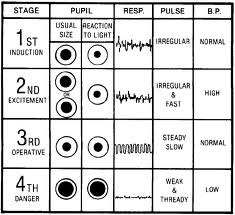
Stages of Anesthesia

answer
...
question
What medication can you use when a patient on ACE inhibitor is not responding to ephedrine or neosynephrine?
answer
- few units of vasopressin
question
Most adults use which size of MAC blade?

answer
3
question
Most adults use which size Miller blade?

answer
2 ( used ages 2+)
question
What is the size for oral airways? Colors?

answer
8- green 9- yellow, most often used 10-red
question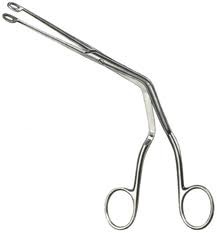
What are Mcgill forceps used for?

answer
-Nasal intubation
question
Epiglottis hangs down so which blade works better?
answer
Usually Miller blade, although Mac is easier to learn with. MAC- lifts vallecula but epiglottis hanging down (in & up motion) Miller- lifts up epiglottis tougher to see, tongue obstructs
question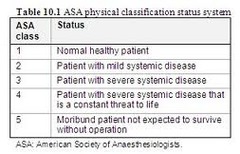
ASA Classifications

answer
ASA 6: declared brain dead, organ donor ASA E: Emergency procedure, added to ASA I-VI Used for reimbursement/ report.
question
Most outpatient surgical centers will not operate on a patient above which ASA class?
answer
ASA 3
question
Narcotics
answer
Used for maintenance of general anesthesia "Balanced technique" -Most common fentanyl - Morphine, fentanyl, alfentanil, sufentanil, remifentanil
question
Dissociative Agents
answer
Ketamine (only anesthetic/analgesic combo) 2mg/kg -Dissociates patient from environment - Minimal depression of protective reflexes - Hallucinations are common on emergence
question
Muscle Relaxants
answer
-Defasciculating dose: depolarizer before succinylcholine to prevent muscle spasm/ soreness after surgery (5-10mg zemuron/rocuronium) - Succinylcholine, atracrurium, pancuronium, rocuronium, cisatracurium- (elimination PChE in blood)
question
Barbituates
answer
-Methohexital: ECT, dental, cardioversion, lowers seizure threshold 2mg/kg -Sodium Thiopental: 2.5% solution dose 4mg
question
Non-barbituates
answer
Propofol: Induction 1-3mg/kg
question
What is the MAC of halothane?
answer
MAC = .74 Hepatitis, slow acting, good for inhalation
question
What are some tricks you can use during long cases?
answer
8 hour case, anesthetics into fat, emergence on more expensive agent, maintenance on Iso, cheaper.
question
5 Questions in the following format
answer
Laparascopic appendectomy, (regional/general/IV sedation) anesthetic. This patient (will/will not/might) recieve paralytics. This patient will be in the (supine/prone/lateral/lithotomy) position. *If it is laparascopic the patient will require paralytic.
question
How can you tell when the case is nearing completion?
answer
Suture sizing: -small 10, big 0 - know progression of case Counting sponges/supplies towards the end of case.
question
How can you tell with propofol when you can intubate or bag?
answer
- Eyelash reflex -Listen with precordial stethoscope
question
Know brand/trade names of drugs
answer
Fentanyl: sublimaze Sufenta: sufentanil Alfenta: alentanil Demerol: meperidine Marcain: bubivipcaine: sensorcaine Lidocaine:xylocaine Remifentanil:ultiva Narcan:naloxone Rocuronium: zemuron Ravlon: rapacuronium (bronchospasms) Propofol: diprivan Versed: midazolam Edrophonium:reversol:enlon:tensilon Succinylcholine:anectine:quelicin Neostigmine: prostigmin
question
List local anesthetics short acting to long acting.
answer
Lidocaine>bubivicaine>tetracaine
question
Does epinephrine work well to prolong action of bubivicaine?
answer
Not really. Epi works well to prolong duration of lidocaine and tetracaine.
question
Advantages of Continuous Opioid Infusion Box12-4
answer
Hemodynamic stability Decreased side effects Reduced need for opioid-reversal agents Reduced need for vasopressor drugs Suppression of cortisol and vasopressin response to Cardiopulmonary bypass Reduced total dosage of opioids Decreased recovery time
question
The primary factors that influence absorption of the inhalation anesthetics are:
answer
Ventilation Uptake into the blood Cardiac output Solubility of the anesthetic drug in the blood Alveolar-to-venous blood partial-pressure difference (assumed to be the same as in the brain) Concentration Second gas effect
question
ASA Examples
answer
ASA 1: normal healthy patient ASA 2: smoker, OB, thyroid, HTN, mild health issue, DM, chronic bronchitis, anemia, morbid obesity, age extremes, heart disease-slightly limits activity ASA 3: COPD, CAD-limits activity, poorly controlled HTN, DM with vascular complications, angina pectoris, previous MI ASA 4: renal or hepatic failure, CHF, persistent angina, advanced pulmonary disease ASA 5: massive trauma , AAA, uncontrolled hemorrhage "Love to give scenarios and have you pick status"
question
Benefits of thorough chart review
answer
Identify surgical risks, anesthesia history, medical conditions etc.
question
Surgical History
answer
Chart or interview, particular attention paid to any complications mentioned by patient.
question
Anesthetic History
answer
Determine reaction of patient to previous anesthetics, can modify anesthesia approach to prevent recurrence of complication. Familial history: looking for atypical cholinesterase, MH, porphyria, glycogen storage diseases
question
Drug History: Prescription
answer
Provides excellent guide for direction and depth of patient interview and assessment. Alert provider to allergies or drug interactions.
question
Drug History: Herbal
answer
Echinacea: activate cell mediated immunity Ephedra: ↑ HR, BP Garlic: inhibits platelet aggregation, fibrinolysis, BP Ginko: inhibits platelet-activating factor Ginseng: ↓ BG, inhibits platelet aggregation increased PT-PTT Kava: sedation, anxiolysis St John's Wort: inhibits NT reuptake, MAO inhibition unlikely, interacts with several drugs Valerian: sedation Discontinuation: 24 hours: ephedra, kava 36 hours: ginko 5 days: St. John's 7 days: garlic and ginseng
question
Tobacco
answer
Nicotine produces ganglionic stimulation, affects CV system. INCREASE: ↑HR, ↑BP, ↑contraction, ↑oxygen consumption, ↑PVR Carbon monoxide binds to oxygen binding sites on hemoglobin causing hypoxia. 12 hour cessation prior to surgery will decrease pulmonary complications and improve outcome.
question
ETOH
answer
Cut down alcohol use? Annoyed by people criticizing your habits? Guilty about drinking? Eye opener in the morning? More than 2 yes responses at risk for alcoholism. Signs of withdrawal: hand tremors, sweating, tachycardia, systolic HTN, anxiety, restlessness, N/V, hallucination, seizure Patient may show a resistance to other CNS depressants.
question
Illicit Drug Abuse
answer
Most abused are cocaine & marijuana. Signs & Symptoms: track marks, pupillary dilation or nystagmus, lymphadenopathy, malnourishment, poor dental care, nose perforations
question
Informed Consent
answer
Give reasonable explanation of available options for anesthesia: general, regional, local, topical or IV. Written consent recommended for medicolegal purposes. Ensure sufficient information is given about the procedures and risks that a reasonable and prudent decision can be made.
question
ECG
answer
Baseline >50 years Indications: CV disease risk Pathological murmur or palpitation Prolonged QT syndrome Moderate to severe sleep apnea (R sided strain)
question
CXR
answer
Risk usually outweighs benefit in healthy <75 year patients. Indications: abnormal CXR in past TB/ +skin test w/ no tx pulmonary infection (cough, abn.sputum) congenital heart disease, premature dysp. sleep apnea down syndrome (sublaxed atlantoaxial) malignancy that alters surgical care-mets sym/debil. COPD, asthma, Cardiovasc.
question
Pregnancy Test
answer
Routine pre-op test remains controversial. Advise of fetal risk (spont. abortion) surgery advised after 1st trimester Interview by female staff w/o family
question
Lab Draws
answer
Considered current if within 6 months and no change in patient condition. Serum potassium should be within 7 days if diuretics or digitalis is planned. BG on day of surgery. ECG within 30 days with stable disease. Chest X-ray 6 months if stable disease.
question
Fasting Considerations
answer
>6 hours for solids 4 hours breastmilk 2-3 hours for liquids no gum/ candy after midnight meds with sip 150ml-adults, 75ml-kids up to 1 hr anesthesia
question
Airway: Prediction of a Difficult Airway
answer
Mallampati: Easy in class 1-2, difficult 3-4 Thyromental distance: prominence of thyroid cartilage to bony point of mandible, <7 difficult intubation Interincisor distance: <4cm open, difficult intubation Head & neck movement: "sniff position" less tongue obscures view, inability to move neck, difficult intubation Mandibular mobility: bite upper lip, move jaw forward, easy maneuvering of laryngoscope
question
Musculoskeletal/ Obesity
answer
2/3 of US adults overweight or obese Greater risk of CV and airway issues.
question
Neurological
answer
Musculoskeletal system, sensory system, muscle reflexes, cranial nerve abnormalities, mental status & speech pattern. ECG: Q waves, deep inverted T waves, ST elevations may reflect hypothalamic ischemia & sympathetic overactivity (SAH)
question
Cardiovascular
answer
HTN is most common circulatory issue, risk factor for CAD, increases perioperative mortality. Unstable angina associated with the highest risk for perioperative MI. Patients are most at risk if MI in last 30 days. S & S: tachycardia at rest, moist rales in lungs, S3, peripheral edema *CAD main cause of death.
question
Respiratory
answer
Some form of lung disease present in 25% of adult population. The surgical site (aortic & thoracic surgeries) most important risk factor for development of post-op pulmonary complications. Most common: COPD, asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema
question
Gastrointestinal
answer
Assess: N/V/D, GI bleed, masses, dysphagia, acidity, abd/ referred pain, gastric hyperreactivity, weight loss, malnutrion Prophylactic measures in at risk patients ( EG: bicitrate to decrease stomach pH in case of aspiration)
question
Hepatobiliary
answer
Acute or chronic liver disease. Unexplained jaundice or ↑ transaminase levels should be evaluated by gastroenterologist. (post-pone surgery) Lactate dehydranase (LDH) more specific Prolonged PTT offers most rapid & reliable hallmark of liver dysfunction with acute injury.
question
Renal
answer
Evaluate fluid status, infection, retention/incontinence, hematuria Clinical signs may not be evident until >70% of nephrons are non-functional. Creatinine levels correlate more with GFR than BUN. Renal reserves: creatine clearance rate Mild renal dysfunction: < 50-80 ml/min Renal failure: <10 ml/min Monitor K 6-8 hours pre-op, HGB due to chronic anemia
question
Endocrine: Diabetes
answer
Diabetes is most common, 20.8 million people in US. DM: hyperglycemia & ketoacidosis Death is usually secondary to complications from artherosclerosis. High risk of ischemic heart disease: 12 lead EKG ↓ gastric emptying time, give reglan to reduce incidence of aspiration Goal of perioperative insulin therapy is 60
question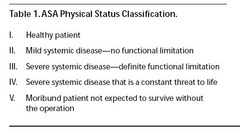
ASA Status Classification

answer
...
question
Guidelines for Preventing OR Errors
answer
Preoperative Verification Process Mark Operative Site Time-out immediately before procedure: Correct ID Correct side & site Agreement on procedure Correct patient position Availability of correct equipment
question
Valvular Heart Disease
answer
Aortic & mitral valve lesions most common. Severe aortic stenosis is greatest risk especially if cross section of aorta is < 1 cm
question
Arrythmia
answer
Dyspnea, angina or syncope suggests worsening disease. Ventricular Arrythmia Categories: 1- benign: unifocal PVC 2- potentially malignant: organic heart disease, on anti-arrythmics 3- malignant: organic heart disease, hemodynamic compromise, familial history of sudden cardiac death
question
Pacemakers
answer
Can mask the toxicity of anti-arrythmic drugs, electrolyte disorders, and myocardial ischemia & irritability
question
Diagnostic Testing for CV Disease
answer
Significant coronary disease likely if ST depression > .2 mV or if hypotension occurs. Significant stenosis: >70% narrowing of major coronary artery >50% of L main coronary artery
question
Emphysema & Chronic Bronchitis
answer
ABG: PaO2 < 60= chronic bronchitis FEV/FVC <80%= obstructive process
question
Asthma
answer
Reversible airflow obstruction, inflammation of airways. Assess frequency, severity & triggers of attacks.
question
Children & Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
answer
S/S: inflamed reddened mucosa, mucus, fever Postpone if possible, <5 years old= ↑ risk Intubation ↑ risk 11 fold
question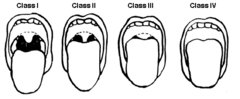
Mallampati

answer
...
question
Hyperthyroidism
answer
Excess T3 & T4 Hypermetabolic state, sympathetic overactivity. Use esmolol intraop and continue patients meds
question
length of upper incisors cautionary finding
answer
relatively long
question
relation of maxillary and mandibular incisors during normal jaw closure cautionary finding
answer
overbite (maxillary anterior to mandibular)
question
relation of maxillary and mandibular incisors during voluntary protrusion of jaw cautionary finding
answer
mandibular incisors anterior to maxillary incisors
question
Interincisor distance cautionary finding
answer
<3 cm (2 fingers)
question
visibility of uvula cautionary finding
answer
not visible when tongue is protruded in sitting position (Mallampati > II)
question
shape of palate cautionary finding
answer
highly arched or very narrow
question
compliance of mandibular space cautionary finding
answer
stiff, indurated, occupied by mass, not resilient
question
thyromental distance cautionary finding
answer
less than 3 finger-breadths (7cm)
question
length of neck cautionary finding
answer
short
question
thickness of neck cautionary finding
answer
thick
question
range of motion of head and neck cautionary finding
answer
patient cannot touch tip of chin to chest or cannot extend neck
question
most common anesthesia related medicolegal claims?
answer
dental injuries (inspect teeth and document missing, fractured, crowns, braces, ect.) inform patient of liklihood of dental damage and document on consent form to not be held liable
question
obesity
answer
20% in excess of ideal body weight
question
Ideal Body Weight calculation
answer
Men- 105lb + 6lbs for each inch > 5ft Women 100lb + 5lbs for each inch >5ft
question
Body Mass Index
answer
BMI= Weight in kg / height in meters²
question
Overweight BMI
answer
25-29.9kg/m²
question
moderate obesity
answer
30-34.9kg/m²
question
severe obesity
answer
35-39.9kg/m²
question
morbidly obese
answer
>40kg/m²
question
Asymptomatic patients should be screened for CAD if:
answer
1. abnormal baseline ECG 2. Hx of CAD/ valvular disease 3. 50 yr old and at least two: metabolic syndrome, DM, HTN, smoker, dyslipidemia, fam hx CAD
question
order pre-op sleep study if:
answer
H & P suggest obstructive sleep apnea snoring, apneic, freq. arousal during sleep, am HA, daytime sleepiness
question
anticipate difficult intubation
answer
awake intubation fiberoptic tracheal intubation drying agent upper airway anesthesia
question
Pre-op carotid endarterectomy
answer
cardiac eval by cardiologist 12- Lead ECG stress testing (at risk for MI)
question
patient with vertebral artery occlusion
answer
avoid extreme head extension, flexion, and rotation
question
Intracranial HTN avoid:
answer
sedatives, ketamine, desfluare
question
Patient is taking Phenytoin, Pre-op labs:
answer
CBC (risk for agranulocytosis) check drug level to see if therapeutic (check level with all anticonvulsants if able)
question
Signs of Cardiovascular Disease
answer
dyspnea, chest pain, fatigue, syncope, palpitation, angina obtain 12-Lead EKG
question
uncontrolled stage 3 HTN
answer
>180/110 delay surgery if organ damage is suspected heart, renal, cerebrovascular disease and condition could be improved by postponement to extent risk would be considerably decreased or care may be influenced by further pre-op exam
question
patient complains of dizziness/ syncope
answer
investigate may be cerebrovascular insufficiency or drug induced hypotension
question
Cardiovascular Physical Exam
answer
overall appearance vital signs funduscopic exam neck heart lungs abdomen extremities neuro eval
question
unstable angina elective surgery
answer
cancel until cardiovascular status can be evaluated and optimized p377
question
patient with dyspnea of unknown origin or with heart failure should undergo:
answer
pre-op eval of left ventricular function if not performed in last 12 months p.378 angiography, echocardiography, contrast ventriculography EF < 35%
question
severe aortic stenosis patient
answer
14- fold greater incidence of peri-op sudden death delay elective surgery if patient symptomatic
question
hx of symptomatic arrhythmias pre-op
answer
ECG K+/ Mag levels test level of antirhythmic drug if possible chest x-ray (if structural heart problem)
question
pacemakers can mask s/s of:
answer
MI, electrolyte abnormalities, toxicity of antirhythmic drugs, irritability
question
what function of a pacemaker is lost first
answer
sensing
question
consult cardiology for pacemaker if:
answer
pacing impulse if not associated with pulse unexpected pauses symptoms pre pacemaker have returned
question
indication for temp, transvenous pacer wire pre-op
answer
persistent bradycardia unresponsive to IV atropine/ exercise Bifascicular block with syncope hx suggesting complete heart block
question
dizziness caused by exercising the muscles adjacent to the pacemaker implies:
answer
myopotentials may be inhibiting pacemaker avoid shivering and succs which cause muscle fasciculations
question
Stress Test demonstrates
answer
how ischemia manifests itself functional hx of angina extremes of BP/HR tolerated location of ischemic leads present of arrhythmias
question
ECG s/s of significant coronary disease
answer
ST-segment depression >0.2mV ST depression early in stress test little increase in BP/HR occurs w/ ST depression hypotension occurs with ST depression (hypo prompt cardiac cath)
question
significant stenosis means
answer
narrowing of major coronary artery by 70% or narrowing of left main coronary by 50%
question
findings of poor ventricular function
answer
CI 18 mm Hg EF < 40%
question
pulmonary s/s that indicate elective surgery should be postponed
answer
severe dyspnea wheezing pulmonary congestion hypercarbia CO2>50
question
ABG Values indicating chronic bronchitis
answer
PaO2 < 60mm Hg with or w/o CO2 retention likely to develop cor pulmonale
question
Chest X-ray finding indicating COPD (emphysema)
answer
emphysema bullae pulmonary hyperlucency (vascular deficiencies in the lung periphery) Diaphragmatic flattening vertical cardiac silhouette
question
pulmonary function test
answer
determine severity of airflow obstruction and reversibility with bronchodilators FEV1/FVC less than 80% indicate obstructive process poor indicator of post-op pulm complication reserved for symptomatic pts with COPD prior to non-cardiothoracic surgery "<60% bad, FEV₁ <40% likely ventilated, <30% ventilated"
question
all patients undergoing lung resection should have what assessment pre-op
answer
spirometric assessment estimates FEV1 and suitability for resection
question
asthma
answer
reversible airway flow obstruction inflammation of the airways distal bronchoconstriction from airway hyperreactivity to stimuli
question
s/s of asthma indicating postponement of elective surgery
answer
wheezing, tachypnea, persistent cough
question
Patients at risk for per-op asthma aggravation
answer
co-existing cardiovascular disease recent hospitalization/ ER visit for asthma hx of peri-op asthma complications copious sputum production nocturnal awakening from asthma freq/cont corticosteroids
question
pre op therapy to decrease pulmonary complications
answer
stop smoking psychological preparation antibiotics for pulm infection/ bronchitis weight reduction chest PT expectorants instruction in resp maneuvers brochodilator for asthma good nutrition
question
post op therapy to decrease pulmonary complications
answer
pain control (avoid opiates) hydration IS, maximal inspiration maneuvers Chest PT mobilize secretions cough ambulation heparin (selected cases)
question
Medical History of Asthma
answer
frequency, time since last attack, last hospitalization, corticosteriod use, β-agonist use Don't want to give beta blocker- negate effect of albuterol
question
if right ventricular hypertrophy is presumed
answer
ECG implies long standing insufficient pulmonary therapy
question
when to get a chest x-ray pre op for lung issues
answer
suspect acute infiltration process like PNA or pneumothorax
question
when to get an ABG pre op for asthmatic
answer
signs of hypoxia/ hypercarbia who required emergency surgery
question
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate morning of surgery with active asthma disease
answer
compare with patient's best in recent weeks normal:80-100% moderate exacerbation: 50-80% of baseline severe episode indicating delay of surgery and more intensive therapy: <50%
question
Asthma pre-op meds
answer
β-adrenergic inhaler morning of surgery and bring to OR oral meds with sip of water 1-2 hrs preop therapeutic theophylline levels confirmed 10-20mcg/mL supplemental stress dose of corticosteroids anti-anxiety med adequate hydration
question
s/s of lower resp tract infection
answer
fever >38 pulmonary congestion rales
question
Upper Resp Tract infection- cancel surgery?
answer
uncomplicated URTI okay for elective surgery and no intubation esp if chronically has colds/ runny nose/ afebrile/ no distress CANCEL if: productive cough from lower RTI, infectious runny nose, less than 1, caution with <5, infectious nasopharyngitis: 2weeks postponement " " with Lower RTI: 4-6 weeks " "
question
Asthma Pharm Pre-op Tx for Patient on brochodilators
answer
inhaled corticosteriods, beclomethasone 320mcg per day, 1 week pre-op
question
Asthma Pharm Pre-op Tx for Patient with spirometry at or below baseline/ flare-up of symptoms
answer
predisone 0.5mg/kg for 5 days pre-op hydrocortisone 100mg IV q8hrs the morning before surgery and postop until stable
question
Asthma Pharm Pre-op Tx for Patient on Oral Steriods
answer
Increase dose for 5 days hydrocortisone 100mg IV q8hrs the morning before surgery and postop until stable
question
Cancel elective surgery for hepatic failure with what s/s
answer
grossly abnormal liver function test including coagulopathies extreme jaundice cyanosis gen tremors increased deep tendon reflexes ascites, spider nevi, hepatospenomegaly hepatorenal failure hepatic encephalopathy
question
Intra-op care of hepatic failure
answer
phytonadoine (AquaMEPHYTON) FFP/ cryoprecipitate for abnormal coags no pre-op sedative for hepatic encephal. check blood sugar ABG, CMPs, LFT
question
alkaline phosphatase enzyme
answer
may be released from bile duct in biliary obstruction/ irritation and help differentiate disease (but also from extrahepatic tissues as well) high conjugated bilirubin helps confirm cholestatic liver disease
question
hepatotoxic drugs
answer
acetaminophen NSAIDs ASA methydopa isoniazid rifampin
question
Tx and resolution of UTI esp before surgeries:
answer
prosthetic graft for mitral valve total hip replacement
question
would you expect creatinine levels to be high or low in elderly?
answer
normal even though decrease GFR, have lost of muscle mass which lowers number
question
GFR/ Creatinine Clearance
answer
UV (urinary concentration of creatinine X volume of urine) / P ( plasma concentration of creatinine)
question
Pre-op Potassium for Renal Patients obtained when
answer
6-8hrs pre- surgery regardless if dialysis or not
question
Delay elective surgery until after dialysis
answer
Potassium 5.5 and CHF is apparent
question
extreme fatigue, pallor, limited exercise tolerance, tachycardia pre-op tx
answer
RBC tranfusion
question
Cause of anemia Cause of coagulopathies in Renal Failure
answer
Anemia- Erythopoietin, fragile RBCs Coags- decreased platelet adhension bc chronic metabolic acidosis Hemodialysis can correct prolonged bleeding time
question
Pre-op Meds for Chronic Renal Failure Patient
answer
continue antihypertensive, digitalis, corticosteriods, and insulin less pre-op sedation, avoid valium GI antiacids, gastrokinetic agents (Reglan) drain peritoneal dialysate (reduce asp.)
question
Type I DM prone to what diseases
answer
organ failure diabetic retinopathy cataracts somatic/ autonomic sufficiency ( ortho hypotension, bradycardia, gastoparesis) ketoacidosis hyperglycemia
question
Extreme Hyperglycemia and Ketoacidosis Pre-op
answer
Cancel elective surgery Fluids, electrolyte, and insulin therapy
question
Consult Cardiologist for DM patient if:
answer
risk of MI- carotid endarterectomy/ ab aortic aneurysm r/sx consider: stress test, 12-Lead ECG
question
s/s of autonomic neuropathy
answer
orthostatic hypotension resting tachycardia lack of respiratory variability in cardiac rhythm
question
Diabetic Pre-op Meds
answer
Hold oral short half-life agents on day of surgery: Thiazolidinediones: "-glitazone", Glinides: Repaglinide, Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: Acarbose, Miglitol Withhold longer-acting 48hrs: Biguanides: Metformin Sulfonylureas: "-amide," "-rides," "-zides"
question
Insulin pre-op for DM 1
answer
SubQ 1/3 to 1/2 of patient's morning dose of intermediate or long acting insulin
question
pre-op med for hyperthyroid
answer
anti-thyroid drugs: methimazole or propylthiouracil for 6-8 weeks followed by iodine for 7-14 days CBC pre-op (pro. causes agranulocytosis) Beta-antagonist: Propanolol, Esmolol
question
postpone elective surgery for hyperthyroid patients until
answer
euthyroid
question
Emergency surgery for hyperthyroid
answer
Esmolol 100-300mcg/kg/min Higher doses of Benzos, Anxiolytics, sedatives avoid anticholinergics
question
Hypothyroid Meds Pre-op
answer
Levothyroxine, IV fluids, electrolytes
question
Should you delay surgery for mild/ moderate hypothyroidism
answer
No
question
Cushings syndrome
answer
excess glucocorticoids hypertension HYPOvolemia easy bruising osteoporosis
question
Hyperaldosteronism
answer
excess mineralcorticoid hypertension hypokalemia <3 sodium and water retention metabolic alkalosis
question
Addison disease
answer
glucocorticoids and often mineralocorticoids insufficiency inhibition from steroid therapy weight loss, skin hyperpigmentation, muscle wasting HYPOtension HYPOvolemia HYPOglycemia HYPOnatremia HYPERkalemia
question
Adrenocortical Dysfunction Pre-op Treatment
answer
Correct Fluid & Electrolytes, Tx Coexisting disorders (HTN, DM) Replace mineral/glucocorticoids Corticosteriods for pt tx with steriods for more than 1mo in past year and supplement daily dose if currently taking
question
Pre-op Dx Test Considerations
answer
cost-effective-cost saved from knowing results exceed expense of performing it positive benefit-risk ratio- benefits outweighs harm from false-positive available pre-surgery for intervention yield info no attainable from H&P Abnormal results in asymptomatic pt would influence care, surgery, anesthesia
question
False-positive and false- negative test results lead to....
answer
additional medical eval and potential for increased MORBIDITY 5% abnormal in normal pt if abnormal not investigated =medicolegal risk
question
Patients at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
answer
DM >40, cocaine, HTN, renal failure, circulatory disease, thyroid disease, pulmonary disease, ischemic heart disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular d
question
Preform pregnancy test if..
answer
patient is uncertain of status sexually active info last menstrual period indicates possibility birth control present/absent policies of hospital protocol mandate
question
Indications for CBC
answer
hematologic d/o vascular procedure chemotherapy unknown sickle cell status
question
Indications for HCT & HGB
answer
Age < 6mo (<1 yr if premature) hematologic malignancy radiation/ chemo renal disease anticoagulant therapy mod/high blood loss potential systemic d/o (cystic fibrosis, premature, malnutrition, renal, liver, congenital heart disease)
question
Indications for WBC Count
answer
Leukemia/ Lymphomas Radiation/ Chemo suspect infection that would cancel surgery aplastic anemia (bone marrow ↓) hypersplenism autoimmune collagen vascular disease
question
Indications for Blood Glucose
answer
DM Corticosteriods hx of hypoglycemia adrenal disease cystic fibrosis
question
Indications for Serum chemistry
answer
Renal Adrenal (K/Na) Thyroid Disease (↑ Ca w/ hyper) Chemo Pituitary (DI-Na) Hypothalamic Body Fluid Loss/Shift-dehydration/bowel Central nervous system disease
question
Indications for Potassium
answer
Digoxin therapy Diuretic therapy
question
Indications for Creatinine and Blood Urea
answer
Renal Nitrogen Cardiovascular disease (HTN) Adrenal DM Diuretic Digoxin Blood Fluid Loss or shift- dehy/bowel Radiocontrast procedure
question
Indications for Liver Function Test
answer
Hepatic disease Exposure to hepatitis Therapy with hepatotoxic agents
question
INR, Prothrombin, Partial Thromboplastin Time
answer
Leukemia Hepatic disease Bleeding disorder Anticoagulant therapy severe malnutrition/ malabsorption
question
Indications for Platelet Count/ Bleeding Time
answer
Bleeding Disorder Abnormal hemorrhage, purpura, history of easy bruising
question
Indications for Urinalysis
answer
not indicated as routine screening
question
Indications for Medication Levels
answer
Theophylline, Phenytoin, Digoxin, Carbamazepine if pt exhibits s/s of ineffective therapy, potential drug s/e, or poor drug compliance, or changed therapy w/o documented level
question
Does ASA classification system represent an estimate of anesthesia risk?
answer
No, rough correlation between physical status and post-op outcome, but does not account for other factors:surgical procedure, degree of peri-op monitoring, unfortunate circumstances (human error and equipment malfunction)
question
Guideline for Implementing Universal Protocol for preventing Wrong Site, Procedure, Person
answer
Preop Verification Process Marking the Operative Site Time-Out Immediately Before Starting Procedure
question
Universal Protocol Preop Verification Process When:
answer
surgery/procedure scheduled admission or entry in the facility anytime care is transferred to another provider with the patient involved, awake, aware before patient leaves preop area or enters surgical/procedure room
question
Preop Verification Checklist
answer
Relevant documentation (H & P, consent) Relevant images, labeled, displayed Any required implants, special equipment
question
Marking the OP Site
answer
At/ near incision Initials or "YES" (don't use an x) visible after pt prepped/ draped permanent marker (adhesive markers need 2nd marker) Method consistent throughout hospital Mark when involves laterality, multiple structures, multiple levels patient involved, awake, aware final verification during time-out defined procedure if pt refuses marking
question
Exemptions to Marking Site
answer
single-organ case catheter or instrument insertion site not predetermined (cardiac cath) teeth- but indicate op tooth on documentation or mark op tooth on dental radiographs or dental diagram premature infants (b/cm tattoo)
question
Time-Out Immediately Before Starting Procedure
answer
involves entire operative team in procedure location active communication documented Includes: Correct patient ID Correct Side and Site Agreement on Procedure to be done Correct Patient Position Available Correct Implants, special equip
question
Procedure for Non-Operating Room (ex:Bedside) Time-Out
answer
Site marking for laterality, multiple structures, multiple levels Verification, site-marking, time-out consistent throughout hospital Exception of site marking: case in which individual doing procedure is present and with patient from time decision made to do it to execution (still do time-out)
question
when should patients with a complex medical condition be evaluated?
answer
at least 1 week before scheduled surgery
question
Med Conditions that would benefit from early Pre-op Evaluation p.359
answer
inhibit normal daily activity, require monitoring/ cont. assistance at home w/i 6 months Hospital Admission for exacerbation in 2 months Meds that need modification of schedule/dosage Angina, CAD, MI, symptomatic arrhythmia, HTN > 160/110, CHF Asthma & COPD w/ chronic meds/exacerbation 6mo Hx of airway surgery, trauma, unusual anatomy, tumor Home ventilation/ monitoring DM treated with insulin/ oral hypoglycemic agents Adrenal d/o, thyroid disease hepatobiliary disease kyphosis, scoliosis, TMJ w/ restricted mobility cervical/ thoracic spine injury chemotherapy/ compromise oncologic pt Morbid obesity > 140%, hital hernia, symptomatic GERD
question
Chart Review includes
answer
Past Med Hx: previous anesthesia records/ unusual condition Patient Chart Review: verify consent with name, surgeon, procedure, date- demographics-vitals - I/O- baseline deficits- preanesthesia questionnaire
question
T/F It is acceptable to review diagnostic tests from the chart?
answer
False, must be obtained directly from original source
question
T/F It is acceptable to review medical treatment, drug dosages, and schedules from the chart?
answer
True
question
when should a patient bè tested for latex allergy?
answer
family history report of rash, swelling, or wheezing when exposed
question
when would you expect a latex allergy?
answer
chronic exposure to latex-based products spina bifida, urological reconstruction more than 9 surgeries intolèrance to latex-based products allergy to food and tropical fruits intraop ànaphlaxis of unknown cause health care worker esp w/ atopy/eczema
question
common post op complications of smokers
answer
purulent sputum, bronchospasm, secretion retention, pleural effusion, pneumothorax, pulmonary collapse, pneumonia
question
periop complications of children exposed to second-hand smoke
answer
larynospasm, coughing on induction/emergence, breath holding, post op oxyhemoglobin desat, reactive diseàse, abnormal PFTs, RTI
question
Periop complications of alcoholics? post- op complications?
answer
arrhythmias, infection, withdrawal syndrome post: poor wound healing, infection, bleeding, futher hepatic deterioation
question
abstinence syndrome s/s ( from illicit drugs)
answer
increased sym and parasympathetic HTN, tachycardia, abd cramping and diarrhea, tremors, anxiety, irritability, lacrimation, mydriasis, algid sweat, yawning
question
s/s of long term androgen use (steriods)
answer
↓ liver, hepatic adenocarcinoma, peliosis, hepatisis, MI, atherosclèrosis, hypercoagulopathy, stroke, HTN, dyslipidemia, pstchiatric/ behavior abnormal
question
anesthesia implication for chronic steriod abuser
answer
liver functioning test to determine potential hepatotoxicity with drugs given thát are metabolized by the liver
question
cannabis abuse s/s
answer
tachycardia, headache, labile BP, euphoria, dysphoria, depression, anxiety, panic reactions, psychosis, poor memory, decreased motivation
question
cocaine & amphetamine abuse s/s
answer
↑HR, labile BP, HTN, MI, arrhythmias, pulmonary edema excitement, delirium, hallucinations-psychosis euphoria, feeling of enhanced physical and mental capacity hyperreflexia, tremors, convulsions, mydriasis, sweating, hyperpyrexia, exhaustion, coma
question
hallucinogens abuse s/s (LSD, PCP)
answer
sympathomimetic, weak analgesics altered perception/ judgement- toxic psychosis dissociative anesthesia
question
opioid abuse s/s
answer
resp depression, hypotension, ↓HR, constipation, euphoria, pinpoint pupils, decreased LOC, coma
question
What is the difference between a MAC and a general?
answer
MAC: no tube GA: usually tubed
question
What is an albumin level used for?
answer
Nutritional status and protein binding of drugs.
question
What is adjusted body weight used for and how is it calculated?
answer
IBW + (real body weight - IBW)/3
question
What can you use for patient's with veneers?
answer
*1/3 of all anesthesia claims are based on dental issues. Use dental guard to protect.
question
NPO guidelines
answer
Food, milk :6 Breast Milk: 4 Clear liquid: 2 * When in a trauma situation, count NPO status from the time of injury.
question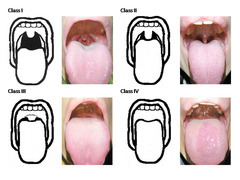
Mallampati once more...

answer
MP /Lip bite I - all structures uvula tip, soft palate, fauces, pillars II - no pillars III - no fauces IV - hard palate only Lip bite study "more sensitive indicator"
question
Mitral Stenosis
answer
- HR: keep slow to allow for filling, avoid sinus tachycardia - Rhythm: sinus, a-fib (control rate) -Preload: maintain or slightly increase to help with left ventricular filling, excess preload -Afterload: SVR maintain, avoid decreases in SVR -Contractility: maintain to provide adequate cardiac output *Epidural preferred over spinal.
question
Mitral Stenosis
answer
-Reduced LV preload - Avoid tachycardia - Full intravascular volume (normovolemia) -Avoid pulmonary HTN: hypoxia, hypercarbia, nitrous - New onset a-fib: flutter requires immediate cardioversion *NTG, milrinone, nitric oxide are pulmonary vasodilators Decrease HR beta block Epidural over SAB
question
Mitral Regurgitation
answer
-HR: maintain or ↑, avoid bradycardia which worsens regurgitation - Rhythm: sinus rhythm - Preload: maintain or ↑ (elevated= ↑ regurg/ low= inadequate CO - Contractility: maintain or ↑ to decrease LV volume
question
Aortic Stenosis
answer
- Maintain SR - Maintain normal intravascular volume - Avoid ↑ HR - Avoid hypotension - Arterial PA catheter and TEE monitoring very helpful - Early and aggressive treatment of hypotension and arrythmias is imperative 14 fold increase in peroperative death Degree mild mod severe? SAB: hypotension tachy not tolerated Treat hypotension aggressively no ephedrine, use neo Epidural slowly comes on instead of bolus
question
Aortic Insufficiency
answer
- Decrease SVR - Optimize intravascular volume - With preserved LV function, dilation, and tachycardia - Avoid bradycardia as it causes ventricular distention - PCWP underestimates true LVEDP in acute aortic insufficiency because of premature closure of MV -Antibiotics
question
Should beta blockers, cardiac meds be continued the day of surgery?
answer
Yes
question
When should ACE inhibitors be held?
answer
Day of, hypovolemia, BP can bottom out
question
When should MAOI be held?
answer
Hold for 2 weeks Ensure psych eval or provider aware during hold
question
TCA held?
answer
2 weeks
question
Lithium held?
answer
72 hours
question
Diuretics
answer
Hold, check chem profile
question
Insulin
answer
Regular: hold day of Long acting: 1/2 dose
question
Warfarin, heparin
answer
Warfarin: Hold for 5 days, may bridge with heparin Heparin: 6 hours
question
Steroids
answer
Give stress dose
question
METS Metabolic Equivalent Measures
answer
How well can this patient handle exertion. 1 flight of stairs without getting winded >4, can't <4 Putting patients under cardiac stress
question
EKG indications
answer
Male >50 Female > 60 Subtract 10 years to maximum of 20 years for each comorbitity.
question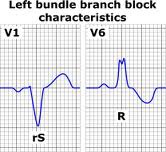
LBBB

answer
LBBB V1= broad S, V6 = broad R
question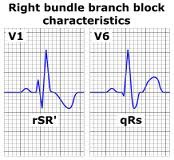
RBBB

answer
RBBB V1= rSR, V6= broad S
question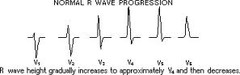
R wave progression

answer
R wave progression: flips positive to negative in leads V3-4 Poor (late)= ant MI, LBBB, WPW, L vent hypertrophy
question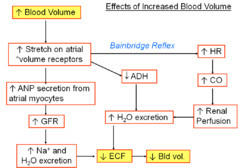
What is the Bain-Bridge reflex?

answer
Breathing pushes diaphragm down and vena cava opens up, ECG moves in a wave with respiration due to lead placement or they are hypovolemic.
question
Electrolyte Abnormality and ECG
answer
Hyper Ca+ shortens ST monitor these intra op Hypo Ca+ prolong QT blood transfusion will cause (raises K) Hyper K+ peak T waves Hypo K+ u wave inside of T wave
question
5-H-T-3
answer
Antiemetics prolong QT interval
question
Unstable Angina
answer
(1) CP w/ rest or unresponsive to meds, or >30 min duration (2) Non Q wave, non troponin, non CKMB (3) cardiac w/u and even then keep HR low normal and BP normal *Sleeping at night and wakes them up, watching TV
question
MI Mortality
answer
Peri-operative mortality > 6mos: 6% 3-6 mos: 30% < 3 mos: 50% < 30 days: do not do it unless case of life or death AHA says wait 4-6 weeks min *Q wave will indicate previous MI
question
Pacer/ Magnet
answer
-Chamber paced A,V D -Chamber sensed A,V D -Rate responsive inhibition (I), triggered (T), none(O Magnet for AICDs usually deactivates (not always) Pacer wires may dislodge New do not lift arm Dizziness w/ arm motion exercise Monitor 5 lead intraop for all serious CV conditions *Electrocautery will throw off AICD or pacer. Tech can interrogate and ID underlying rhythm. Avoid succinycholine, fasciculation....
question
How long post cessation of smoking does carboxyhemoglobin return to normal?
answer
12 hours, also ↓ HR and BP *Want them to stop >8 weeks or about 12 hours. Use sevo, less irritation, give nebulizer.
question
PFT
answer
PFT <60% bad lung function FEV1<40%, post op ventilated likely FEV1<30% for sure post op ventilated
question
Neurological
answer
Versed for seizure, continues paralyze and intubate Avoid opioids, ketamine, succinylcholine, RSI with rocuronium, brevital Which agent has least increase in ICP? Sevo or Iso (no Des)
question
LMA contraindications
answer
Intubate for case longer than 2 hours. TURP: lithotomy, ↑ gastric pressure, avoid LMA



