pathology -skin diseases/oral infection pictures – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion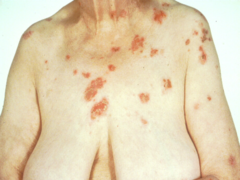
Pemphigus Vulgaris

answer
-Autoimmune disease that produces antibody-mediated -Superficial vesicles and bullae develop rapidly and rupture quickly leaving shallow erosions covered by dried serum and crust. -a lattice-like or chicken-wire pattern -can be a life-threatening disease
question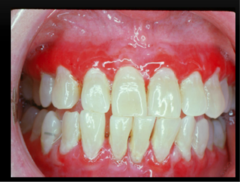
Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid

answer
-autoimmune vesiculobullous disease gets its name from its clinical similarities to pemphigus -affects attached gingiva where erosive lesions are sometimes referred to as "desquamative gingivitis." and sometimes hard palate -disease is limited to mucous membranes, it is not life-threatening
question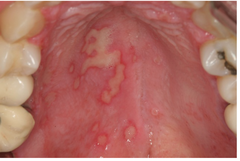
Erythema Multiforme on the palate

answer
-self-limited mucocutaneous disorder that is of acute onset -Triggers=infections, drugs, malignancies, autoimmune diseases
question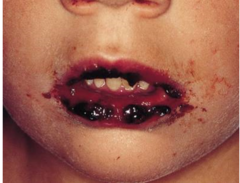
Erythema Multiforme on lips

answer
-oral involvement typically develop bloody crusty lips -self-limited 2 weeks (6 for major cases) -topical anesthetics
question
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
answer
is a rafe form of Erythema Multiforme -extensive painful skin and mucosal involvement. -Must have involvement of ocular and/or genital mucosa in addition to oral mucosa -life-threatening, may require hospitalization
question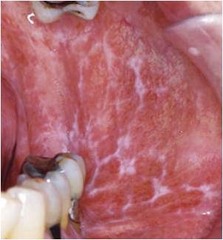
Lichen Planus=relatively common cell-mediated chronic inflammatory disease that involves the skin and mucous membranes

answer
cell-mediated cytotoxic immune response (similar to type IV hypersensitivity reaction) that targets the dermal-epidermal junction -Presenting signs on the skin are the "four Ps" - pruritic (itchy), purple/violet (when fresh and brown as they age), polygonal (abnormal shape) papules. -Striae of Wickham -looks like snowflake and is hyperkeratosis -Disease cannot be cured
question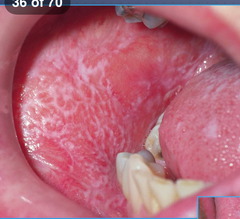
Reticular Lichen Planus

answer
most common form; characterized by white lacelike striae of Wickham, especially on buccal mucosa; often asymptomatic
question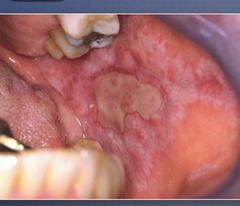
Erosive Lichen Planus

answer
-characterized by loss of surface epithelium, leaving painful red lesions; eroded areas typically have radiating white striae at edges. -associated with an increased risk for oral cancer
question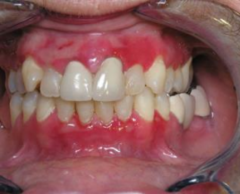
Erosive Lichen Planus on gingiva

answer
painful red lesions
question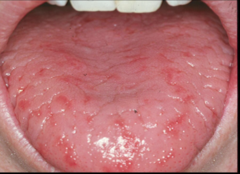
Psoriasis in the mouth

answer
autoimmune disease -characterized by salmon pink plaques on the skin with delicate silvery scales on the surface. Peeling of the scale produces pin-point bleeding spots
question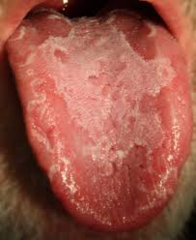
Geographic tongue

answer
-a common inflammatory oral condition -unknown etiology -multiple irregular areas devoid of filiform papillae. These areas are erythematous -No treatment is indicated for most patients
question
what is geographic tongue called when it affects oral mucosal surfaces other than the tongue?
answer
erythema migrans or stomatitis areata migrans -lesions appear as flat oval to irregular red macules
question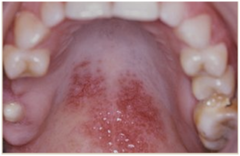
Lupus Erythematosus on palate

answer
-classic autoimmune disease -type III allergic reaction -Avoid sunlight
question
Systemic Sclerosis Oral Manifestations
answer
1) May affect oral soft tissues, including tongue and soft palate. Lips become rigid. 2) Dental radiographs may show widening of the periodontal membrane. 3) Also may have xerostomia.
question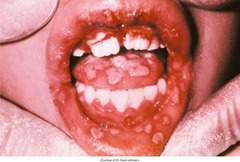
Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis

answer
b) Red swollen painful gingiva, especially interdental papillae, is characteristic. c) Vesicles rupture to leave painful ragged ulcers. d) Dorsal tongue is usually coated and there may be oral malodor. -7-10 day self-limited -topical treatment or antiviral drugs for immuno-compromised pt
question
Herpes Labialis
answer
Lesion starts with local swelling and redness, and then vesicles (1-2 mm) develop, rupture and crust over.
question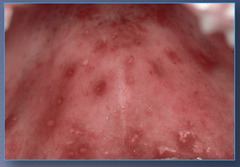
Recurrent Intraoral Herpes

answer
-hard palate and gingiva -small painful ulcers with red halos -7-10 days to heal
question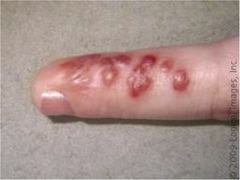
Herpetic Whitlow

answer
on skin that touched herpes infection
question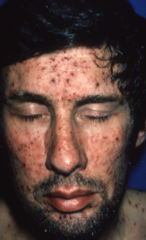
Chickenpox

answer
-It is characterized by fever, sore throat, and a blistering rash. -Like the other herpes family viruses, VZV goes into a latent phase after the acute infection is over. It most often resides in the dorsal root ganglia.
question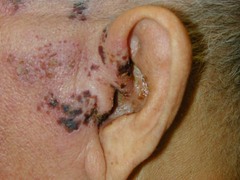
Herpes Zoster/Shingles

answer
-the recurrent form of chicken pox -Lesions are very painful. -Unilateral involvement along one or more divisions of the trigeminal nerve -may produce post-herpetic neuralgia
question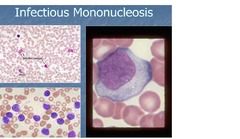
Infectious Mononucleosis

answer
-Epstein-Barr virus -Transmitted by intimate contact - petechiae on hard and soft palate
question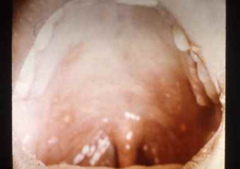
Herpangina

answer
-Caused by infection with Coxsackie group A virus -Generalized symptoms in include sore throat, fever, headache. -Small ulcers develop on the hard/soft palate (and tongue) and are preceded by vesicles. -Ulcers heal within a few days -self-limited
question
hand foot and mouth disease
answer
NO PHOTO available. photo of herpangina Resemble herpangina except: -More numerous ulcers - 1 to 30 -Not confined to the posterior areas of the mouth Most common sites affected: -Buccal mucosa -Labial mucosa -Tongue
question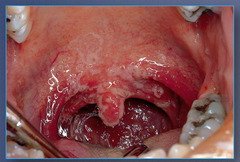
Pseudomembranous Candidiasis/Thrush

answer
erythematous mucosal surface
question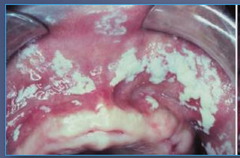
Pseudomembranous Candidiasis

answer
(classic curdled milk appearance of oral lesions)
question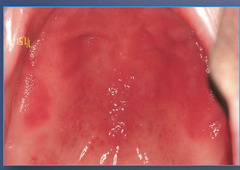
Erythematous Candidiasis

answer
under a denture -Red macules and burning sensation
question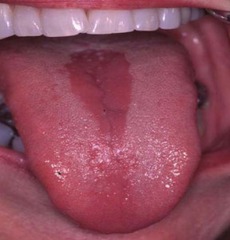
Median Rhomboid Glossitis

answer
1) Erythematous zone in posterior dorsal surface of tongue where infection is associated with loss of filiform papillae 2) Asymptomatic
question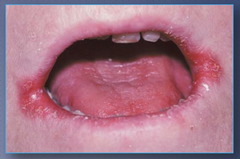
Angular Cheilitis

answer
1) Red, weeping fissure at corner of mouth 2) Often seen in denture-wearer and older persons.
question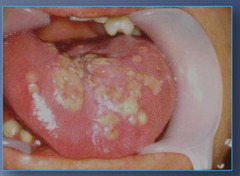
Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis

answer
1) White plaque that cannot be wiped off 2) May actually represent Candida infection superimposed on leukoplakia
question
Histoplasmosis
answer
-facultative intracellular opportunistic fungus. -ulcerated granular lesion 1) Red nodular to ulcerative mucosal lesions 2) Deep fungal infection - organism is invasive into supporting tissue. 3) May erode into/through underlying bone.
question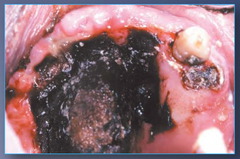
zygomycosis

answer
nectrotic lesion of palate -Opportunistic infections by organisms that normally live in decaying plants destroy host tissue as they invade
question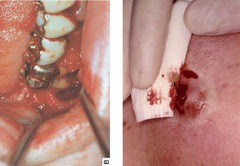
Actinomycosis

answer
-abscesses with sulfur granules in exudate -Host response to infection produces a fibrotic wall around the infection
question
Impetigo
answer
-superficial infection of the skin by group A Streptococci (S. pyogenes, etc.) or Staphylococcus aureus -facial lesion around mouth -Ruptured vesicles ooze and soon form a thick amber crust on top. Crust resembles "cornflakes glued to the surface."



