Disorders of Hair and Nails and Mucous Membranes plus cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
basal cell carcinoma
answer
identify
question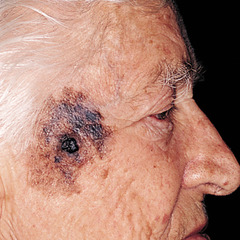
melanoma

answer
identify
question
squamous cell carcinoma
answer
identify
question
basal cell carcinoma
answer
identify the tumour.
question
basal cell carcinoma
answer
identify the tumour
question
actinic keratosis
answer
identify tumour
question
describe the appearance of androgenetic alopecia
answer
a non scarring style of hair loss in the following pattern in many men and women.
question
Describe the pathogenesis of androgenetic alopecia. what is the inheritance of this disease?
answer
in this disease, each individual follicle is genetically marked to become bald or not. Uptake, metabolism and 5 alpha reduction of testosterone is increased to DHT in balding areas. Inheritance comes from maternal and paternal sides equally.
question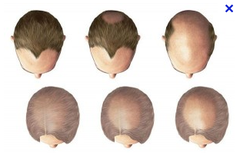
How can you treat androgenetic alopecia? How can you test for it?

answer
you treat this disorder with oral finasteride (5 alpha reductase inhibitor), topical minoxidil solution, or hair transplant surgery. you can test with the pull test and see if more than 6 hairs come out.
question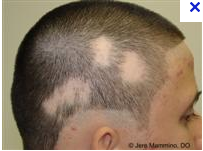
describe the appearance of alopecia areata.

answer
this disorder is marked by circumscribed circular patch(es), and the periphery may show broken hairs. Look for exclamation point hairs with taper proximally.
question
what is the course of disease in alopecia areata? what is the heritability? what are the associations with other diseases?
answer
50% of all cases resolve in 1 year without treatment. 25% of patients have a family history associated with thyroid disease, vitiligo, nail pitting
question
describe the etiology of telogen effluvium
answer
this appearance is caused by a number of stresses: parturition, febrile illness, stress, crash diets, drugs: metoprolol, anticoagulants, antithyroid drugs, sodium valproate.
question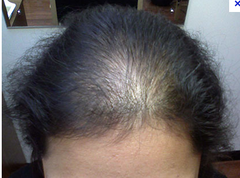
what is the common appearance of: trichotillomania telogen effluvium anagen effluvium androgenetic alopecia alopecia areata

answer
differential for this appearance of hair loss is?
question
describe the appearance and potential causes of scarring alopecia
answer
the following can be caused by discoid lupus, lichen planopilaris, or tinea capitis.
question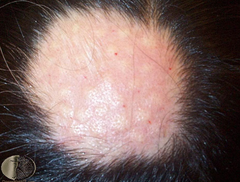
treatment for alopecia areata?

answer
you can treat this disorder with cortisone or an immunogen (like poison ivy)
question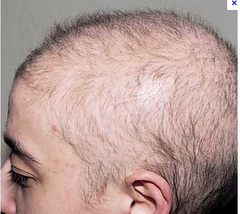
what causes anagen effluvium? pathogenesis?

answer
this pattern of hair loss is caused by chemotherapy or tadiation and involved complete discontinuance of proliferation of matrix cells of the hair shaft.
question
what are beau's grooves appearance? What causes them?
answer
these 1 mm wide depressions in the nail plate are caused commonly following dramatic illness such as MI and periods of high fever or malnutrition.
question
what nail changes occur in hypoalbuminemia accompanying chronic hepatic or renal disease. can also be benign.
answer
under what circumstances does this happen
question
what nail change happens in iron deficiency?
answer
under what circumstances does this (koilinychia) happen?
question
what nail changes are caused by staph infection of the nail?
answer
what causes parynychia?
question
what nail changes do you see with bacterial endocarditis or trichinoisis? (also with normal individuals)
answer
what causes the above splinter hemorrhages?
question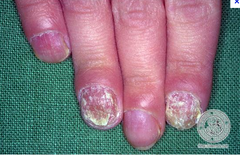
candida paronychia - who is it commonly seen in? how common is it? characterized by?

answer
commonly seen in dishwashers, bartenders and waitresses, this is the most common cause of nail inflammation. lack of pain, lack of warmth, absence of pus.
question
white lesions of the mouth include what seven things?
answer
1. lichen planus 2. candida 3. verrucae 4. SCC 5. lupus 6. syphilis 7. oral hairy leukoplakia all of these oral problems have a common sign. what is it?
question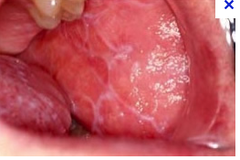
describe the appearance of lichen planus in the mouth.

answer
these white lacy lesions cannot be scraped off and are autoimmune in nature.
question
describe what squamous cell carcinoma of the mouth looks like
answer
identify this verrucous white lesion in the mouth - cancerous!
question
list the 6 different ulcerating lesions of the mouth
answer
1. herpes simplex 2. apthous stomatitis 3. Behcet's syndrome 4. lichen planus 5. pemphigus/pemphigoid 6. stevens johnson syndrome/erythema multiforme major
question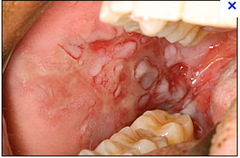
which one of the ulcerating oral lesions of the mouth is life threatening

answer
how is pemphigus/pemphigoid unique compared to the other ulcerating lesions of the mouth?



