Cancer and Cell Reproduction – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
interphase
answer
cell is growing, DNA is duplicated and checked over, chromosomes are not clearly separated
question
mitosis

answer
division of DNA, duplication division
question
sister chromatid
answer
one copy of a duplicated chromosome
question
homologous

answer
being similar in characteristics
question
haploid
answer
a cell contains a single set of chromosomes in a eukaryote
question
mother cell
answer
the division starts with this one thing; the basis of where the new cells come from
question
duplication division
answer
Mitosis, growth
question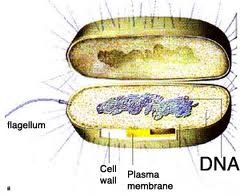
prokaryote

answer
bacteria, single-celled, no nucleus, one circular chromosome, less time for growth and less complexity
question
translocation
answer
genes from another chromosome are inserted
question
oncogenes
answer
cancer causing genes
question
telomerase
answer
enzyme that lengthens telomeres in cells
question
Hayflick Limit
answer
number of times a normal cell population will divide before it stops- cancer cells don't have one
question
Zygote
answer
a single-celled fertilized egg
question
histones

answer
supercoils in chromatin
question
synthesis
answer
stage in the cell cycle where DNA is replicated; part of Interphase
question
meiosis
answer
Production of gametes
question
centriole
answer
an aid of cell division in animals; attached to spindle fibers, at opposite ends of the cell
question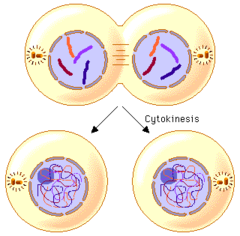
cytokinesis

answer
division of cytoplasm
question
diploid
answer
a cell containing two homologous sets of chromosomes in a eukaryote
question
daughter cell
answer
forms from a mother cell- in mitosis, an exact identical cell
question
eukaryote
answer
"me", many chromosomes, nucleus
question
cancer
answer
Uncontrollable cell growth that started from a mutation
question
proto-oncogenes
answer
normal genes that went through a mutation event and became oncogenes
question
apoptosis
answer
programmed cell death
question
gamete
answer
a sex cell; haploid egg or sperm
question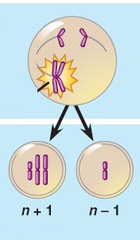
nondisjunction

answer
an accident in meiosis or mitosis where a pair of sister chromatids fail to separate at anaphase
question
Gap 1
answer
stage in cell cylce where cellular contents are duplicated
question
Gap 2
answer
stage in cell cycle where the cell double checks the duplicated chromosomes for errors; makes repairs if needed
question
Gap 0
answer
cease cell devision
question
chromosome
answer
a threadlike gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell
question
astril ray
answer
another name for spindle fibers
question
reduction division
answer
Meiosis
question
karyotype
answer
A picture or collection of all the chromosomes in an organism
question
mutation
answer
a change in DNA, caused by inherited or environmental genes
question
asexual reproduction
answer
the creation of offspring by a single parent, binary fission, cloning, prokaryotes, no nucleus, quick, doesn't require lots of energy, no mate
question
deletion
answer
the loss of one or more nucleotides from a gene by mutation
question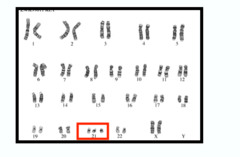
Down Syndrome

answer
a human genetic disorder resulting from the presence of an extra chromosome 21, "trisomy 21"
question
p53
answer
blocks cell cycle if DNA is damaged, s+m check
question
cell plate
answer
used in plant cell division, becomes the new cell walls
question
chromatin
answer
greatly folded ribbon-like complexes of DNA- visible as chromosomes under a light microscope
question
spindle aparatus
answer
structure involved in the movements of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis; separate chromatids
question
DNA
answer
deoxyribonucleic acid
question
binary fission
answer
a form of asexual production and cell division
question
sexual reproduction

answer
the creation of offspring through the fusion of an egg and sperm cell
question
inversion
answer
broken off chromosome reattaches in the reverse order
question
trisomy
answer
Extra chromosome in a pair
question
tumor suppressor genes
answer
causes cell growth; through a mutation even can be turned off and have uncontrollable cell growth
question
metastisis
answer
the spread of cancer from one location to a new one too
question
Chorionic Villus Sampling
answer
technique for diagnosing genetic defects while a fetus is still in an early age of the pregnancy; done between 8-10 weeks, tissue of placeta
question
angiogenic
answer
attracts blood vessels to grow
question
blastula

answer
an embryonic stage that marks the end of cleavage during animal develpment
question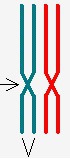
centromere

answer
wasteband of protein, goes around chromosomes
question
IPMAT
answer
interphase prophase metaphase anaphase telophase
question
clone
answer
a single organism that is genetically identical to another
question
gene
answer
a small unit of hereditary information of a sequence in DNA
question
monosomy
answer
Missing a chromosome
question
duplication
answer
repetition of part of a chromosome
question
polyploid
answer
an organism that has more than two complete sets of chromosomes as a result of an accident in cell division
question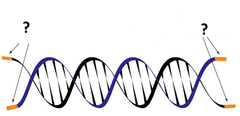
telomere

answer
a structure found at the end of a chromosome that controls how often a cell divides; get shorter and start fusing together as cells undergo division
question
malignant
answer
cancer moved out of one area, has spread
question
carcinogen
answer
a cancer causing agent such as x-rays or UV light
question
meristem
answer
plant tissue made of undifferentiated cells that divide and generate new cells and tissue
question
Walther Flemming (1879)
answer
observer of fish, first to say he saw chromosomes, identified stages of mitosis
question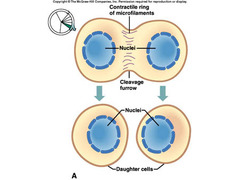
cleavage furrow

answer
pinching of cell membrane, only in animals
question
prophase
answer
Chromatin condenses and becomes visible, nuclear membrane dissolves, spindle fibers start forming, centrioles move to opposite ends
question
metaphase
answer
replicated chromosomes line up in middle, spindle aparatus attaches to centromeres
question
telophase
answer
spindle apparatus dissapears, nuclear membrane and envelope start to reform, chromosomes are just rods- no longer visible
question
anaphase
answer
sister chromatids separate, no more centromeres
question
decompose components of the cell
answer
What are the roles of proteases and enzymes in cell death?
question
they are engulfed by a neighboring cell
answer
What eventually happens to dead cells or cellular remains?
question
To receive nutrients plus get rid of wastes
answer
Why do cancer cells need a blood supply?
question
Nutrients that a cancer cell needs
answer
oxygen, glucose, amino acids
question
Waste products from a cancer cell
answer
carbon dioxide, urea, water
question
two adaptive immune system responses
answer
b cells that make antibodies and t cells that kill changed cells
question
adjuvant therapy
answer
stimulation of immune system with agents to make it hypertensive to foreign cells
question
benign
answer
localized group of cells
question
Amniocentesis
answer
14-16 weeks, needle in uterus to extract amniotic fluid, chance of getting mom's cells, could harm baby
question
Cyclin Dependent Kinase (CDk)
answer
Control switch that causes change in stages in the cell cycle, g1 to s, g2 to m
question
Maturation promoting Factor (MPF)
answer
Trigger in progresion through the cell cycle, "grow up"
question
p27
answer
Binds to cdk to block entry into synthesis



