Head and Neck Cancer Staging and NCCN Guidelines – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
T staging for lip cancer
answer
T1: less than 2 cm T2: between 2 and 4 cm T3: greater than 4 cm T4a: Invades bone, inferior alveolar nerve, floor of mouth, skin of face. T4b: Invades masticator space, pterygoid plates, skull base, or encases internal carotid.
question
T staging for oral cavity cancer
answer
T1: less than 2 cm T2: between 2 and 4 cm T3: greater than 4 cm T4a: Invades bone, into extrinsic muscles of tongue, maxillary sinus, skin of face. T4b: Invades masticator space, pterygoid plates, skull base, or encases internal carotid.
question
N staging for lip and oral cavity
answer
N1: single ipsilateral node not greater than 3 cm. N2a: single ipsilateral node between 3 and 6 cm. N2b: multiple ipsilateral nodes, none greater than 6 cm. N2c: bilateral or contralateral nodes, not greater than 6 cm. N3: any node greater than 6 cm
question
Definition of stage III for lip or oral cavity CA.
answer
T3N0 or T1 to T3 with N1, M0
question
What is the stage for T2N1M0 lip carcinoma?
answer
Stage III
question
What is the stage for T3N0M0 oral cavity CA?
answer
Stage III
question
What is the stage for T3N1M0 lip CA?
answer
Stage III
question
Definition of Stage IVa lip or oral cavity CA?
answer
T4a, any N, M0 or T1 to T3, N2, M0
question
What is the stage for T1N2M0 lip or oral cavity CA?
answer
Stage IVa
question
What is the stage for T4aN0M0 lip or oral cavity CA?
answer
Stage IVa
question
Definition of Stage IVb lip or oral cavity CA?
answer
Any T, N3, M0 or T4b, any N, M0
question
What is the stage for T1N3M0 lip or oral cavity CA?
answer
Stage IVb
question
What is the stage for T4bN1M0 lip or oral cavity CA?
answer
Stabe IVb
question
Definition of Stage IVc lip or oral cavity CA?
answer
Any T, any N, M1
question
What is the stage for T1N0M1 lip CA?
answer
Stage IVc
question
What defines Stage I and II lip carcinoma? How are they treated? Neck dissection?
answer
T1N0M0: <2cm T2N0M0: 2 to 4 cm Surgical excision preferred. External beam or brachytherapy can be used. Elective neck dissection not recommended. If margins positive, perineural/vascular/lymphatic invasion, either re-excise or treat with radiation.
question
Which sites frequently have bilateral lymphatic drainage? In addition to these sites, what other sites require bilateral neck treatment?
answer
Base of tongue, palate, supraglottic larynx, deep space pre-epiglottic involvement. Also anterior tongue or floor of mouth lesions that approximate or cross the midline.
question
According to NCCN guidelines, which tumor sites warrant selective neck dissection for N0 patients? Which levels should be addressed? What is the goal of a selective neck dissection?
answer
Oral cavity: at least levels I to III. Oropharynx: at least levels II-IV. Hypopharynx: II-IV and VI when appropriate. Larynx: II-IV and VI when appropriate. In general staging and determining the need for radiation is the goal.
question
According to the NCCN guidelines, what are the indications for selective and comprehensive neck dissections?
answer
Selective neck dissections are generally for staging and selecting candidates for adjuvant radiotherapy. Patient's with clinically positive necks should get a comprehensive neck dissection.
question
For lip or oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma, what findings would prompt post-operative adjuvant therapy according to NCCN guidelines? What therapy is recommended?
answer
For multiple positive nodes, extracapsular nodal spread, positive margins, or perineural/lymphatic/vascular invasion adjuvant chemo XRT is preferred (Category 1 high-level evidence). For a single positive node without adverse features, radiation alone is optional.
question
Which patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lip should have neck dissections according to NCCN guidelines?
answer
T1 and T2, N0 should not have an elective neck. For N1-3 neck dissection is recommended. For T3 or T4a, N0 elective neck can be considered. T4b (basically unresectable) should only have neck dissection if primary has been controlled with chemoXRT and neck disease is resectable.
question
What is the primary determinant of risk of regional metastatsis in oral cavity cancer?
answer
Thickness of the lesion.
question
Treatment of T1 or T2, N0 carcinoma of the oral cavity according to NCCN guidelines?
answer
Excision of primary lesion. Consider staging neck based on tumor thickness. If no nodes, no adverse features, then observe. If one node without adverse features, XRT optional. If positive margins or extracapsular spread, chemo/XRT preferred (Category 1 evidence). Re-excision or XRT alone are also options. If multiple nodes, perineural invasion, or nodal disease in level IV or V, XRT or chemo/XRT recommended.
question
When is neck dissection definitely recommended in oral cavity carcinoma?
answer
T1-3, N1-3 T3N0 T4a, any N (any clinical positive nodes, unless T4b, or T3, T4a regardless of nodal status)
question
Treatement of T3N0M0 carcinoma of the oral cavity according to NCCN guidelines?
answer
Excision of primary lesion and ipsilateral or bilateral neck, depending on extend of disease.. If no nodes, no adverse features, then consider optional XRT or observe. If one node without adverse features, XRT optional. If positive margins or extracapsular spread, chemo/XRT preferred (Category 1 evidence). Re-excision or XRT alone are also options. If multiple nodes, perineural invasion, or nodal disease in level IV or V, XRT or chemo/XRT recommended.
question
What's the main difference between treatment of T2N0 and T3N0 oral carcinoma according to NCCN guidelines?
answer
For T3, neck dissection is definitely recommended, for T2, it is should be considered depending on the thickness of the tumor.
question
T staging for nasopharynx.
answer
T1: confined to nasopharynx, or extends to oropharynx and/or nasal cavity without parapharyngeal extension. T2: Parapharyngeal extension. T3: Involves bony structures of skull base and/or paranasal sinuses. T4: Intracranial extension and/or involvement of cranial nerves, hypopharnx, orbit, or with extension to infratemporal fossa/masticator space.
question
What defines a T4 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Intracranial extension and/or involvement of cranial nerves, hypopharnx, orbit, or with extension to infratemporal fossa/masticator space.
question
T staging for oropharyngeal carcinoma.
answer
T1: 4 cm or extension to lingual surface of epiglottis. T4a: Invades larynx, extrinsic muscles of tongue, medial pterygoid, hard palate, or mandible. T4b: Invades lateral pterygoid, pterygoid plates, lateral nasopharynx, or skull base, or encases carotid.
question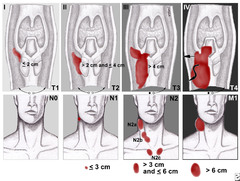
T staging for hypopharynx.

answer
T1: Limited to one subsite of hypopharynx and/or 2 cm or less. T2: Invades more than one subsite of hypopharynx or measures between 2 and 4 cm, without fixation of the hemilarynx. T3: >4cm or with fixation of hemilarynx or extension to esophagus. T4a: Invades thyroid/cricoid cartilage, hyoid bone, thyroid gland, or central compartment soft tissue. T4b: Invades prevertebral fascia, encases carotid artery, or mediastinum.
question
N staging for nasopharynx.
answer
N1: unilateral 6 cm above supraclavicular fossa or unilateral/bilateral retropharyngeal nodes 6 cm or less. N2: Bilateral, 6 cm or less, above supraclavicular fossa. N3a: >6 cm, above supraclavicular fossa. N3b: Extension to supraclavicular fossa.
question
N classification for nasopharngeal carcinoma with nodal involvement of supraclavicular fossa?
answer
N3b
question
A patient with a nasopharyngeal carcinoma has a 7 cm neck node above the supraclavicular fossa. What's the N stage?
answer
N3a
question
A patient with nasopharyngeal carcinoma has bilateral retropharyngeal nodes measuring up pto 5 cm. What's the N stage?
answer
N1.
question
A patient with nasopharyngeal carcinoma has bilateral cervical nodes, not involving the supraclavicular fossa, measuring up to 5 cm. What's the N stage?
answer
N2
question
N staging for oropharynx and hypopharynx.
answer
N1: single ipsilateral node not greater than 3 cm. N2a: single ipsilateral node between 3 and 6 cm. N2b: multiple ipsilateral nodes, none greater than 6 cm. N2c: bilateral or contralateral nodes, not greater than 6 cm. N3: any node greater than 6 cm
question
Definition of Stage III for cancer of the oropharynx or hypopharynx?
answer
T3N0 or T1 to T3 with N1, M0
question
Definition of Stage I and II for cancer of the oropharynx or hypopharynx?
answer
Stage I: T1N0M0 Stage II: T2N0M0
question
Definition of Stage IVa for cancer of the oropharynx or hypopharynx?
answer
T4a, N0-2, M0 or T1 to T3, N2, M0
question
Definition of Stage IVb for cancer of the oropharynx or hypopharynx?
answer
T4b, Any N, M0 or Any T, N3, M0
question
Definition of Stage IVc for cancer of the oropharynx or hypopharynx?
answer
Any T, Any N, M1
question
Definition of Stage I for cancer of the nasopharynx?
answer
T1N0M0
question
Definition of Stage II for cancer of the nasopharynx?
answer
T1N1M0, or T2N0M0, or T2N1M0
question
Definition of Stage III for cancer of the nasopharynx?
answer
T1 or T2, N2, M0 or T3, N0 to N2, M0
question
Definition of Stage IVa for cancer of the nasopharynx?
answer
T4, N0 to N2, M0
question
Definition of Stage IVb for cancer of the nasopharynx?
answer
Any T, N3, M0
question
Definition of Stage IVc for cancer of the nasopharynx?
answer
Any T, Any N, M1
question
Stage for T2N2M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage III
question
Stage for T3N1M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage III
question
Stage for T1N2M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage III
question
Stage for T1N1M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage II
question
Stage for T2N1M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage II
question
Stage for T4N0M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage IVa
question
Stage for T4N2M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage IVa
question
Stage for T1N3M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage IVb
question
Stage for T4N3M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage IVb
question
Stage for T4N2M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx?
answer
Stage IVa
question
Stage for T1N1M0 carcinoma of the hypopharynx?
answer
Stage III
question
Stage for T3N0M0 carcinoma of the oropharynx?
answer
Stage III
question
Stage for T1N3M0 carcinoma of the hypopharnx? What makes it N3?
answer
Stage IVb. >6 cm lymph node
question
Stage for T4aN3M0 carcinoma of the oropharynx?
answer
Stage IVb
question
Stage for T4aN2M0 carcinoma of the hypopharynx?
answer
Stage IVa
question
Recommended treatment for T2N1M0 carcinoma of the oropharynx per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Primary XRT or Excision of primary and neck dissection or Primary XRT and chemotherapy
question
Recommended treatment for T1N0M0, T1N1M0 or T2N0M0 carcinoma of the oropharynx per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Primary XRT or Excision of primary and neck dissection If residual disease after XRT, salvage surgery. If primary surgery, chemo/XRT for extracapsular spread of nodal disease with or without positive margins. Re-excision or XRT for positive margins alone. XRT or Chemo/XRT for other adverse features (perineural invasion, vascular embolism, multiple positive nodes).
question
Recommended treatment for T3 or T4a, N0 or N1 carcinoma of the oropharynx per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Primary concurrent chemo/XRT with cisplatin preferred (Category 1 evidence). Salvage therapy for residual disease.
question
Recommended treatment for N2 or N3 (Any T) carcinoma of the oropharynx per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Primary concurrent chemo/XRT with cisplatin preferred (Category 1 evidence). Salvage therapy for residual disease.
question
Recommended treatment for T1N0M0 and selected T2N0M0 (not requiring total laryngectomy) carcinoma of the hypophyarnx per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Primary XRT or partial laryngopharyngectomy (open or endoscopic) AND ipsilateral or bilateral neck dissection. If primary surgery, chemo/XRT for extracapsular spread of nodal disease with or without positive margins. Re-excision or XRT for positive margins alone. XRT or Chemo/XRT for other adverse features (perineural invasion, vascular embolism, multiple positive nodes).
question
Describe the potential role for induction chemotherapy in T1, T2, or T3 hypopharyngeal carcinoma that would normally require a layrngectomy.
answer
One potential treatment is to start with induction chemotherapy. If there is a complete response at the primary site (after 2 or 3 cycles), definitive XRT can then be performed. If residual disease persists in the neck, neck dissection is then performed. If partial response at the primary site, concurrent chemotherapy/XRT is performed, with surgery for salvage if incomplete response. If less than partial response at the primary site, surgery should be performed, with post-op adjuvant therapy for adverse features (extracapsular spread, positive margins, multiple positive nodes, perineural/vascular invasion). Note primary surgery is recommended for T4a disease (invades thyroid/cricoid cartilage, hyoid bone, thyroid gland, or central compartment soft tissue)
question
Recommended treatment per NCCN guidelines for carcinoma of the hypopharynx that invades the thryoid or cricoid cartilage, hyoid bone, thyroid gland, or central compartment soft tissue (strap muscles or superficial fat)?
answer
This is T4a disease. Primary surgery and neck dissection with post-op XRT or chemo/XRT is recommended.
question
Recommended treatment for T1N0M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Definitive XRT to nasopharynx and elective XRT to neck.
question
Recommended treatment for Stage IVc (M1) carcinoma of the nasopharynx per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Platinum-based combination chemotherapy, then XRT to primary and neck or chemo/XRT.
question
Recommended treatment for T1, N1-3, M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Primary concurrent chemo/XRT with neck dissection for any residual neck tumor after treatment.
question
Recommended treatment for T2-4, Any N, M0 carcinoma of the nasopharynx per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Primary concurrent chemo/XRT with neck dissection for any residual neck tumor after treatment.
question
T staging for supraglottic carcinoma.
answer
T1: Tumor limited to one subsite of supraglottis with normal vocal cord mobility. T2: Tumor invades mucosa of more than one adjacent subsite or region outside of supgraglottis (eg mucosa of base of tongue, vallecula, medial wall of pyriform sinus) without fixation of the larynx. T3: Limited to the larynx with vocal cord fixation and/or invades any of the following: postcricoid area, pre-epiglottic space, paraglottic space, and/or inner cortex of thyroid cartilage. T4a: Invades through the thyroid cartilage and/or invades tissues beyond the larynx (trachea, soft tissue so neck, deep extrinsic tongue muscles, strap muscles, thyroid, esophagus). T4b: Invades prevertebral space, encases carotid, invades mediastinum.
question
What is the T stage for a supraglottic carcinoma that invades the thyroid gland?
answer
T4a
question
What is the T stage for a supraglottic carcinoma that invades the pre-epiglottic space?
answer
T3
question
What is the T stage for a supraglottic carcinoma that involves the mucosa of the vallecula without fixation of the larynx?
answer
T2
question
What is the T stage for a supraglottic carcinoma that is limited to the larynx and causes vocal cord fixation?
answer
T3
question
What is the T stage for a supraglottic carcinoma that invades the inner cortex of the thyroid cartilage?
answer
T3
question
What is the T stage for a supraglottic carcinoma that invades the prevertebral space?
answer
T4b
question
Describe the T staging for glottic carcinoma.
answer
T1a: Limited to one vocal cord with normal mobility. T1b: Involves both cords with normal mobility. T2: Extends to supraglottis and/or subglottis, and/or with impaired vocal cord mobility. T3: Limited to larynx with vocal cord fixation and/or invasion of the paraglottic space, and/or inner cortex of the thyroid cartilage. T4a: Invades through the outer cortex of the thyroid cartilage and/or invades tissues beyond the larynx (trachea, soft tissue of neck including extrinsic muscles of tongue, strap muscles, thyroid, or esophagus). T4b: Invades prevertebral space, encases carotid, invades mediastinum.
question
What is the T stage for a glottic cancer with impaired (but not fixed) vocal cord mobility and invasion of the inner cortex of the thyroid cartilage?
answer
T3
question
What is the T stage for a glottic cancer with impaired (but not fixed) vocal cord mobility and invasion of the paraglottic space?
answer
T3
question
What is the T stage for a glottic cancer with impaired (but not fixed) vocal cord mobility and invasion of the thyroid gland?
answer
T4a
question
What is the T stage for a glottic cancer with impaired (but not fixed) vocal cord mobility and invasion of the prevertebral space?
answer
T4b
question
What is the T stage for a glottic cancer with impaired (but not fixed) vocal cord mobility and extension into the subglottis?
answer
T2
question
What is the T stage for a glottic cancer with vocal cord fixation and extension into the subglottis?
answer
T3
question
What is the T stage for a glottic cancer with impaired (but not fixed) vocal cord mobility and extension through the outer cortex of the thyroid cartilage?
answer
T4a
question
Describe the T staging for subglottic carcinoma
answer
T1: limited to subglottis. T2: extends to vocal cords with normal or impaired mobility. T3: limited to larynx with vocal cord fixation. T4a: invades cricoid or thyroid cartilage and/or invades tissues beyond the larynx. T4b: invades prevertebral space, encases carotid artery, or invades mediastinum.
question
What is the T stage for a subglottic carcinoma extending to the vocal cords with normal mobility?
answer
T2
question
What is the T stage for a subglottic carcinoma extending to the vocal cords with impaired mobility?
answer
T2
question
What is the T stage for a subglottic carcinoma with vocal cord fixation and limited to the larynx?
answer
T3
question
What is the T stage for a subglottic carcinoma with invasion of the cricoid cartilage?
answer
T4a
question
What is the T stage for a subglottic carcinoma with invasion of the thyroid cartilage?
answer
T4a
question
Describe the N staging for laryngeal carcinoma.
answer
N1: single ipsilateral node not greater than 3 cm. N2a: single ipsilateral node between 3 and 6 cm. N2b: multiple ipsilateral nodes, none greater than 6 cm. N2c: bilateral or contralateral nodes, not greater than 6 cm. N3: any node greater than 6 cm
question
Stage for T1N0M0 carcinoma of the larynx.
answer
Stage I
question
Stage for T2N0M0 carcinoma of the larynx.
answer
Stage II
question
How is Stage III carcinoma of the larynx defined?
answer
T3N0M0 or T1-3, N1, M0
question
How is Stage IVa carcinoma of the larynx defined?
answer
T4a, N0-2, M0 or T1-3, N2, M0
question
How is Stage IVb carcinoma of the larynx defined?
answer
T4b, Any N, M0 or Any T, N3, M0
question
How is Stabe IVc carcinoma of the larynx defined?
answer
Any T, Any N, M1
question
What is the stage for T1N1M0 carcinoma of the larynx?
answer
Stage III
question
What is the stage for T1N2M0 carcinoma of the larynx?
answer
Stage IVa
question
What is the stage for T3N0M0 carcinoma of the larynx?
answer
Stage III
question
What is the stage for T4aN0M0 carcinoma of the larynx?
answer
Stage IVa
question
What is the stage for T3N2M0 carcinoma of the larynx?
answer
Stage IVa
question
What is the stage for T4bN1M0 carcinoma of the larynx?
answer
Stage IVb
question
What is the stage for T1N3M0 carcinoma of the larynx?
answer
Stage IVb
question
What is the stage for T4aN3M0 carcinoma of the larynx?
answer
Stage IVb
question
NCCN recommendation for carcinoma in situ of the larynx?
answer
Endoscopic removal (stripping or laser) or XRT.
question
According to NCCN guidelines, what is the preferred organ preservation treatment strategy for advanced-stage laryngeal cancer?
answer
Radiotherapy with concurrent administration of cisplatin. This is favored over inducton chemotherapy. Selected cases can be managed with conservation surgical techniques that preserve vocal function.
question
According to the NCCN guidelines, what is the standard approach to a T4a glottic carcinoma?
answer
Laryngectomy with ipsilateral thyroidectomy and neck dissection as indicated: N0: neck optional N1: ipsilateral neck, contralateral optional N2-3: ipsilateral or bilateral neck If patients decline surgery, consider concurrent chemo/XRT or clinical trials or induction chemo followed by chemo/XRT.
question
Recommended treatment for T3 glottic carcinoma per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Concurrent cisplatin chemo and XRT preferred. Surgery for residual disease. OR Primary laryngectomy. Neck dissection if clinical nodes. Post-op adjuvant treatment if adverse features (multiple positive nodes, extracapsular spread, positive margins, perineural invasion, vascular embolism).
question
Describe the Intergroup R91-11 trial.
answer
Showed that concurrent cisplatin and XRT results in improved 2-yr laryngeal preservation (local control) vs. induction chemo or XRT alone for advanced glottic carcinoma. No differences in survival. Induction chemo followed by XRT had been the standard based on the 1991 VA study. Control rates were 88%, 74%, and 69%.
question
Recommended treatment for T4aN0M0 supraglottic carcinoma per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Laryngectomy, ipsilateral thyroidectomy, and neck dissection. Post-op adjuvant therapy depending on adverse features. In patients who refuse surgery, concurrent chemo/XRT.
question
Recommended treatment for T1 or T2, N0 supraglottic carcinoma per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Endoscopic resection with or without neck dissection. OR Open partial supraglottic laryngectomy with or without neck dissection. OR Definitive XRT. If surgery, consider XRT alone for single positive node. If positive margins, XRT, re-excision, or chemo/XRT. If extracapsular spread, chemoXRT.
question
Recommended treatment for T3N0 supraglottic carcinoma per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Concurrent cisplatin chemo and XRT preferred. Surgery for residual disease. OR Primary laryngectomy, ipsilateral thyroidectomy AND ipsilateral or bilateral neck dissection. Consider post op XRT if pN0 or pN1. ChemoXRT for extracapsular spread. XRT or chemo/XRT for other adverse features (multiple positive nodes, positive margins, perineural invasion, vascular embolism).
question
Recommended treatment for N+ supraglottic carcinoma with T stage less than T4 per NCCN guidelines?
answer
Concurrent cisplatin chemo/XRT preferred with surgery for residual disease. OR Surgical excision with a neck dissection. For T1, T2, and selected T3N1 partial supraglottic laryngectomy + necks. Can avoid XRT if no adverse features. Chemo/XRT for adverse features (positive margins, extracapsulara spread, etc). Total laryngectomy and ipsilateral thyroidectomy and bilateral necks for most T3N2 or T3N3. Post-op XRT recommended. Chemo/XRT for adverse features.
question
T staging for maxillary sinus carcinoma
answer
T1: Limited to maxillar sinus mucosa with no erosion of bone. T2: Bone erosion or descruction including extension into the hard palate and/or middle meatus, except extnsion to posterior wall of maxillary sinus and pterygoid plates. T3: Invades posterior wall of sinus, subcutaneous tissues, floor or medial wall of orbit, pterygoid fossa, ethmoid sinuses. T4a: Invades anterior orbital contents, skin of cheek, pterygoid plates, infratemporal fossa, cribiform plate, sphenoid, or frontal recess. T4b: Invades orbital apex, dura, brain, middle cranial fossa, cranial nerves other than V2, nasopharynx, or clivus.
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the orbital apex?
answer
T4b
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the anterior orbital contents?
answer
T4a
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the pterygoid plates?
answer
T4a
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the skin of the cheek?
answer
T4a
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading subcutaneous tissues?
answer
T3
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the bone of the posterior wall of the sinus?
answer
T3
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the cribiform plate?
answer
T4a
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the sphenoid sinus?
answer
T4a
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the ethmoid sinuses
answer
T3
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma extending into the middle meatus?
answer
T2
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the hard palate?
answer
T2
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma invading the floor of the orbit?
answer
T3
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma limited to the maxillary sinus mucosa with no bony erosion?
answer
T1
question
T staging for a maxillary sinus carcinoma involving V1?
answer
T4b (any nerve involvement except V2 makes it T4b)
question
Which head and neck cancer sites have the same N staging?
answer
Same: Lip, oral cavity, oropharynx, larynx, nasal cavity and paranasal sinus, major salivary glands. Different: Nasopharynx (supraclavicular fossa involvement moves up to N3).
question
Which head and neck sites are likely to develop HPV related squamous cell carcinoma? Which HPV subtype is most likely to be invovled?
answer
Lingual and palatine tonsils. HPV 16.
question
AJCC T staging for mucosal melanoma?
answer
T3: mucosal disease T4a: involves deep soft tissue, cartilage, bone, or overlying skin. T4b: involves brain, dura, skull base, lower cranial nerves (IX-XII), masticator space, carotid artery, prvertebral space, or mediastinal structures.
question
T stage for mucosal melanoma involving bone or cartilage?
answer
T4a
question
T stage for mucosal melanoma involving CN IX?
answer
T4b (for lower cranial nerve involvement)
question
T stage for mucosal melanoma involving CN VII?
answer
CN VII involvement doesn't impact stage. Only lower cranial nerve involvement.
question
T stage for mucosal melanoma involving overlying skin?
answer
T4a.
question
T stage for mucosal melanoma involving the carotid artery?
answer
T4b
question
N staging for mucosal melanoma?
answer
N0: no nodes. N1: regional nodes present.
question
Stage for mucosal melanoma limited to the mucosa with no regional nodes or distant mets?
answer
T3N0M0 = Stage III
question
Stage for mucosal melanoma involving bone with no regional nodes or distant mets?
answer
T4aN0M0 = Stage IVa
question
Stage for mucosal melanoma limited to the mucosa with regional positive nodes and no distant mets?
answer
T3N1M0 = Stage IVa
question
Stage for mucosal melanoma involving cranial nerve XII with or without regional nodes, no distant mets?
answer
T4bN0M0 or T4bN1M1 = Stage IVb
question
Stage for mucosal melanoma with distant mets?
answer
Any T, Any N, M1 = Stage IVc
question
Lowest possible stage for mucosal melanoma?
answer
T3. There is no T1 or T2.
question
What's included in a supraomohyoid neck dissection? When is it usually used?
answer
Levels I-III and superior parts of level V. Good for oral cavity carcinoma.
question
When should the 1st PET scan be performed after chemo/XRT to evaluate for residual disease?
answer
About 12 weeks after treatment. This increases sensitivity and reduces the false positive rate.
question
Discuss the data for post-operative cisplatin concurrent with radiotherapy for adverse findings in head and neck squamous carcinoma.
answer
The EORTC 22931 (European) trial found an overall survival benefit for patients receiving cisplatin concurrent with postoperative radiotherapy compared to radiotherapy alone in the setting of these adverse features: 1. Extracapsular spread 2. Positive margins 3. More than one positive node 4. Vascular/lymphatic/perineural invasion 5. pT3 or pT4 6. Level 4 or 5 involvement for oral or oropharyngeal tumors. The U.S. RTOG 95-01 trial found improvement in locoregional control and disease-free survival (but not overall survival) but didn't include vascular/perineural invasion or the level 4&5 involvement of oral/oropharyngeal tumors. A combined anaylsis of the two trials found that the survival advantage was limited to patients with extracapsular spread and/or positive margins.
question
General NCCN recommendation for radiation dose for primary tumor and gross adenopathy? Low and intermediate risk nodal beds? High risk beds?
answer
Positive sites: 66-74 Gy, up to 81.6 Gy with hyperfracionation. Low or intermediate risk nodal beds: 44-64 Gy. 50-60 Gy for close margins, multiple positve nodes, perineural/lymphatic/vascular invasion. High risk nodal bed (i.e. extracapsular disease, positive margins): 60-66 Gy
question
Benefit of IMRT vs. conventional XRT in the head and neck?
answer
Primarily decreased xerostomia. Overall survival and locoregional control are similar. In-field recurrences, posterior neck hair loss, and low-grade mucositis in areas away from the target can occur.
question
General NCCN treatment recommendation for primary treatment of very advanced (i.e. unresectable) head and neck squamous cell carcinoma? What about patients with less than ideal functional status? What about recurrent or persistent disease?
answer
In general, cisplatin and concurrent radiotherapy is the treatment of choice. Cetuximab + radiotherapy can be used for patients not fit for standard chemotherapy. Surgery is recommended if resectable for recurrent or persistent disease. If unresectable or can't be radiated, enrollment in a clinical trial is recommended for chemo alone.
question
What is cetuximab?
answer
A monoclonal antibody for EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor). 90% of squamous cell carcinomas express EGFR and cetuximab therefore has been useful.
question
What percent of squamous cell carcinomas express EGFR?
answer
90%
question
One year survival for patients with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck?
answer
20%
question
What percent of head and neck cancers present with an unknown primary?
answer
5%
question
In a patient with an unknown primary, testing of the FNA specimen reveals the tumor to be HPV-positive. What is the most likely site of the primary? How is this clinically helpful?
answer
Tonsil or base of tongue. This finding alone can be used to limit radiation targets to these mucosal regions.
question
NCCN anatomic subsites in the subraglottis?
answer
False cords, arytenoids, epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds
question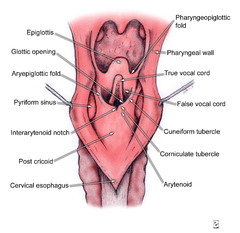
Subsites of the hypopharynx.

answer
pyriform sinus, pharyngeal wall, post-cricoid area.



