Medical Terminology 7th Ed Chapter 19 Terms – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
adenocarcinoma (Adeno-CA)
answer
Malignant tumor arising in a glandular organ
question
adjuvant therapy
answer
In breast cancer, adjuvant therapy includes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or hormone therapy.
question
anaplasia
answer
Characteristic of most cancerous cells in which there is a loss of differentiation and an irreversible alteration in adult cells toward more embryonic cell types.
question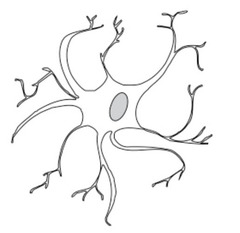
astrocytoma

answer
Tumor composed of star-shaped neuroglial cells.
question
betatron
answer
Megavoltage machine used in administering external radiation therapy.
question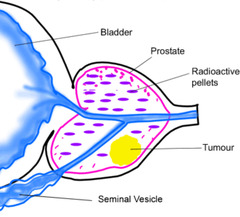
brachytherapy

answer
Radiation therapy in which the radioactive substance is inserted into a body cavity or organ. The source of radiation is located a short distance from the body area being treated. (http://www.tricountyurology.com/procedures)
question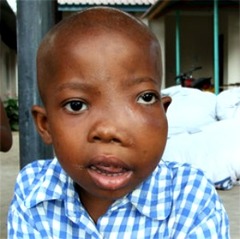
Burkitt's lymphoma

answer
Malignant tumor, most commonly found in Africa, that affects children; the characteristic symptom is a massive, swollen jaw. (http://www.medical-terms-glossary.com/Images)
question
carcinogen
answer
Agent or substance that incites or produces cancer.
question
carcinoid
answer
Tumor derived from the agentaffin cells in the intestinal tract, bile duct, pancreas, bronchus, or ovary.
question
carcinoma
answer
Malignant tumor arising in epithelial tissue.
question
chondrosarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor derived from cartilage cells
question
choriocarcinoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of the uterus or at the site of an ectopic pregnancy.
question
cyclotron
answer
Megavoltage machine used in administering external radiation therapy.
question
dedifferentiation
answer
Process by which normal cells lose their specialization (differentiation) and become malignant.
question
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
answer
Complex protein of high molecular weight found in the nucleus of every cell; controls all of the cell's activities and the genetic material necessary for the organism's heredity.
question
differentiation
answer
Process by which normal cells have a distinct appearance and specialized function.
question
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
answer
Abnormal cells that involve only the lining of a duct and have not spread outside the duct to other tissues in the breast; also called intraductal carcinoma.
question
encapsulated
answer
Enclosed within a site, sheath or capsule
question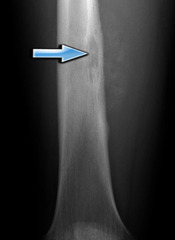
Ewing's sarcoma

answer
Primary bone cancer occurring in the pelvic area or in one of the long bones; occurs mostly in children and adolescents. (http://www.radiologyassistant.nl/data/bin/a50979791b26e5_OS-cortical-destruction2.jpg)
question
exacerbation
answer
Process of increasing the severity of symptoms; a time when the symptoms of a disease are most prevalent.
question
external radiation
answer
Process of administering radiation to the patient via a radiation machine located outside the body.
question
fibrosarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor arising in collagen-producing fibroblasts.
question
fungating
answer
Process of growing rapidly, like a fungus.
question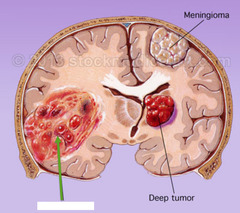
glioblastoma

answer
A rapidly growing cancerous tumor of the brain. (http://www.medicalartlibrary.com/images/brain-tumor.jpg)
question
glioma
answer
Cancerous tumor of the brain.
question
hemangiosarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor originating in blood vessels.
question
Hodgkin's disease (HD)
answer
Form of lymphoma that occurs in children and young adults. The 2 kinds of lymphoma are Hodgkin's disease (named after Dr. Thomas Hodgkin, who first recognized it in 1832) and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma).
question
human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus (HTLV)
answer
First virus known to cause cancer in humans.
question
hyperplasia
answer
Excessive formation and growth of normal cells.
question
immunosuppression
answer
Process of preventing formation of the immune response.
question
immunotherapy
answer
Treatment of disease by active, passive, or adoptive immunity.
question
infiltrative
answer
Pertaining to the process of extending or growing into normal tissue; invasive.
question
in situ
answer
Enclosed within a site; refers to tumor cells that remain at a site and have not invaded adjacent tissue.
question
invasive
answer
Pertaining to the spreading process of a malignant tumor into normal tissue.
question
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS)
answer
Malignant neoplasm that causes violaceous (purplish discoloration) vascular lesions and general lymphadenopathy; often seen in patient who have AIDS.
question
leiomyosarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of smooth muscle tissue
question
lesion
answer
Wound; an injury, altered tissue, or a single infected patch of skin.
question
leukemia
answer
Cancer of the blood characterized by overproduction of leukocytes; cancer of the blood-forming tissues.
question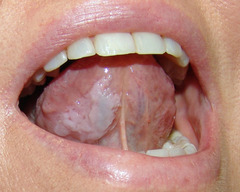
leukoplakia

answer
White, thickened patches formed on the mucous membranes of the inner cheeks, gums or tongue that tend to become cancerous. (http://www.ghorayeb.com)
question
linear accelerator
answer
Megavoltage machine used in administering external radiation therapy.
question
liposarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of fat cells.
question
lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
answer
Abnormal cells found in the lobules of the breast. This condition seldom becomes invasive cancer. However, having lobular carcinoma in situ increases the risk of developing cancer in either breast.
question
lymphangiosarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of lymphatic vessels.
question
lymphoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of lymphoid tissue.
question
lymphomosarcoma
answer
Cancerous disease of lymphatic tissue; also called lymphoblastoma.
question
malignant
answer
Pertaining to a bad wandering; refers to the spreading process of cancer from one area of the body to another.
question
medulloblastoma

answer
Cancerous tumor of the brain, the fourth ventricle, and the cerebellum. (http://weillcornellbrainandspine.org/sites/default/files)
question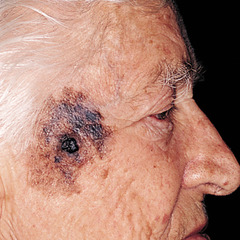
melanoma

answer
"A cancerous black mole or tumor" (https://asset.ghc.org/ghc-resources/images/public/specialties/cancer)
question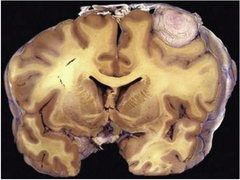
meningioma

answer
Cancerous tumor originating in the arachnoidal (meninges) membrane of the brain. ((http://www.medicalartlibrary.com/images/brain-tumor.jpg)
question
metastasis
answer
Spreading process of cancer from a primary site to a secondary site. Similarly, invasive growth is the spreading process of a malignant tumor into adjacent normal tissue.
question
mucositis
answer
Inflammation of the oral mucosa caused by exposure to high-energy beams delivered by radiation therapy.
question
mutagen
answer
Agent that causes a change in the DNA (genetic structure) of an organism.
question
mutation
answer
Process by which the DNA (genetic structure) is changed.
question
mycotoxin
answer
Substance produced by fungus growing in food or animal feed that, if ingested, can cause cancer.
question
myeloma
answer
Tumor arising in the hemopoietic portion of the bone marrow.
question
myosarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of muscle tissue.
question
neoplasm
answer
New tissue formed, such as an abnormal growth or tumor.
question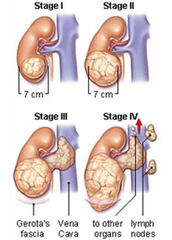
nephroblastoma

answer
Cancerous tumor of the kidney; also called Wilm's tumor; most often found in children 2-3 years of age. (http://www.physio-pedia.com/images/8/8d/)
question
neuroblastoma
answer
Cancerous tumor composed chiefly of neuroblasts; can appear anywhere but usually in the abdomen as a swelling; most often diagnosed in the first year of life.
question
oligodendroglioma
answer
Cancerous tumor composed chiefly of neuroglial cells and located in the cerebrum.
question
oncogenes
answer
Cancer-causing genes; genes in a virus that can induce tumor formation.
question
oncogenic
answer
Pertaining to the potential formation of tumors, especially cancerous ones.
question
osteogenic sarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor composed of osseous (bone) tissue
question
Paget's disease of the breast
answer
Paget's disease of the breast (also called mammary Paget's disease [MPD]) is a rare form of breast cancer. The condition was originally reported in 1874 by Sir James Paget, and English surgeon, who also described an unrelated skeletal condition known as Paget's disease of the bone. These disorders are distinct disease entities that are medically unrelated. Paget's disease of the breast is characterized by inflammatory "eczema-like" changes of the nipple that may extend to involve the areola. Initial findings often include itching, scaling and crusting of and/or discharge from the nipple. In those with Paget's disease of the breast, distinctive tumor cells (known as Paget cells) are present within the outermost layer of skin of the nipple. In addition, the condition is often associated with an underlying malignancy of the milk ducts (ductal carcinoma).
question
palliative
answer
Pertaining to a form of treatment to relieve or alleviate symptoms without curing.
question
port
answer
In radiation therapy, refers to the skin area of entry for the radiation.
question
precancerous
answer
Pertaining to changes or conditions before the onset of cancer.
question
primary site
answer
Original, initial, or principle site
question
proliferation
answer
Process of rapid production; growth by multiplying.
question
remission
answer
Process of lessening the severity of symptoms; time when symptoms of a disease are controlled.
question
reticulosarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of the lymphatic system.
question
retinoblastoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of the retina. Although relatively rare, it accounts for 5% of childhood blindness.
question
rhabdomyosarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor originating from the same embryonic cells that develop into striated muscles. It is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in children.
question
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
answer
Nucleic acid found in all living cells; responsible for protein synthesis.
question
sarcoma
answer
Cancerous tumor arising in connective tissue
question
secondary site
answer
Second site usually derived from the primary site.
question
seminoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of the testis.
question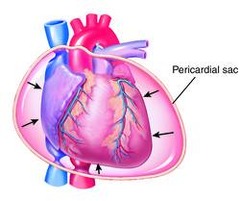
tamponade (cardiac)

answer
Excessive fluid in the pericardial sac surrounding the heart; can be caused by advanced cancer of the lung or a tumor that has metastasized to the pericardium.
question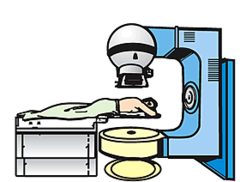
teletherapy

answer
Radiation therapy in which the radioactive substance is at a distance from the body area being treated. (http://panji1102.files.wordpress.com/2012/02/biot234photob.gif)
question
teratoma
answer
Cancerous tumor of the ovary or testis; can contain embryonic tissues of hair, teeth, bone, or muscle.
question
thymoma
answer
Tumor of the thymus gland
question
trismus
answer
Pertaining to the inability to open the mouth fully; occurs in patients with oral cancer who undergo a combination of surgery and radiation therapy.
question
tumor
answer
Abnormal growth, swelling, or enlargement.
question
viral
answer
Pertaining to a virus, which means "poison" in Latin.
question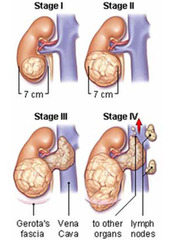
Wilm's tumor

answer
Cancerous tumor of the kidney occurring mainly in children; also called nephroblastoma; most often found in children 2-3 years of age. (http://www.physio-pedia.com/images/8/8d)
question
xerostomia
answer
Condition of dryness of the mouth; oral change caused by radiation therapy or chemotherapy.



