5- thyroid cancer, diabetes – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Tall, thin teenager- abrupt onset dyspnea, left-sided chest pain. percussion on affected side reveals hyperresonance, Breath sounds diminished. Dx?
answer
spontaneous pneumothorax
question
In a population of 100 workers that cleaned an oil spill on a beach, 10 develop leukemia. In a pop of 1,000 hotel beach umbrella monitors on a clean beach, 50 develop leukemia. What is the attributable risk?
answer
AR = A/(A+B) - C/(C+D) =10/100 - 50/1000 =0.05
question
thyroid nodules- use what test?
answer
US -size -location -background thyroid tissue -abnormal neck LNs -unable to determine if a nodule is benign or malignant- Fine needle aspiration (FNA)
question
Thyroid cancer on uptake scan
answer
-cold -never hot!!
question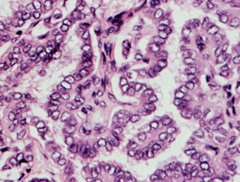
Papillary thyroid cancer

answer
-ground glass appearance of cytoplasm -*orphan annie nuclei*- white eyes (clear nucleus) -psammoma body
question
Papillary thyroid cancer- risk factors
answer
-tobacco use -radiation exposure Hereditary -RET mut -BRAF mut -act of tyrosine kinase R
question
Papillary thyroid cancer- in who
answer
good prognosis -3x F -30-50 yo
question
Papillary thyroid cancer- tx
answer
-total thyroidectomy -radioactive iodine tx
question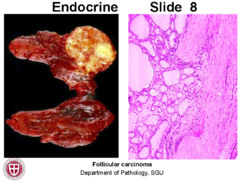
Follicular thyroid carcinoma

answer
-cuboidal cells surrounded by fibrous capsule- invasive! -can spread hematogenously Assoc w: -RAS mut -PAX8-PPAR gamma 1 rearrangement
question
Follicular adenomas
answer
-cuboidal cells surrounded by fibrous capsule- NOT invasive
question
Medullary thyroid carcinoma
answer
-prolif of parafollicular C cells which secrete calcitonin -MEN2/B- screen for pheochromocytoma!! -RET gene mut -act of tyrosine kinase R
question
Medullary thyroid carcinoma- tx
answer
-total thyroidectomy -no radioactive iodine
question
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
answer
-rock hard thyroid gland- older pt!!! (vs younger pt- riedel's thyroiditis)
question
other cancers seen in thyroid gland
answer
-metastatic -B-cell lymphoma- assoc w Hashimoto's
question
Complications of thyroid surgergy
answer
-parathyroid gland removal (back of thyroid)- hypocalcemia -damage to RLN- hoarseness
question
Which thyroid cancer? -act of R tyrosine kinases -hashimoto thyroiditis is a risk factor -arises from parafollicular C cells -RAS mut or PAX8-PPARy-1 rearrangement -rearrangements in RET -mut in BRAF
answer
-act of R tyrosine kinases- papillary and medullary carcinoma -hashimoto thyroiditis is a risk factor- B cell lymphoma -arises from parafollicular C cells- medullary carcinoma -RAS mut or PAX8-PPARy-1 rearrangement- follicular carcinoma -rearrangements in RET or NTRK1- papillary or medullary carcinoma -mut in BRAF- papillary carcinoma
question
most common thyroid cancer
answer
papillary carcinoma
question
enlarged thyroid cells w ground-glass nuclei
answer
papillary carcinoma
question
most likely electrolyte abnormality w perioral tingling, perioral paresthesias, a recent hyroidectomy
answer
-dec Ca- parathyroid gland removal
question
Number needed to harm
answer
how many have to be exposed to have 1 harmful outcome AR= A/(A+B) - C(C/D) NNH= 1/AR
question
what class of abx inhibits prokaryotic DNA topoisomerase
answer
fluoroquinolones
question
endocrine pancreas cell types
answer
-alpha- glucagon -B- insulin -delta- somatostatin
question
Glucagon
answer
-gluconeogenesis -glycogenolysis -lipolysis -insulin secretion *mobilize stored energy
question
Insulin- syn as
answer
-Preproinsulin -proinsulin -c-peptide and insulin
question
C-peptide
answer
-Type 1 vs 2 DM Causes of hypoglycemia: -exogenous insulin- no C-peptide -insulinoma- high C-peptide
question
Glucose-> into cell- triggers release of insulin how?
answer
GLUT-2 (B-cells) -inc ATP -K channels close- depolarization -Ca channel opens -exocytosis of vesicles w insulin
question
GLUT-2
answer
-B cells -liver -sm intestine -renal cells (insulin indep)
question
GLUT-4
answer
-adipose tissue -skeletal m (insulin dep)
question
GLUT-1
answer
-brain -RBCs
question
insulin R
answer
-tyrosine kinase!!
question
insulin, glucagon- fxns
answer
Insulin: -glycogen syn -TG syn -protein syn Glucagon: -glycogenolysis -lipolysis
question
DM- presentation
answer
-hyperglycemia -polyuria -polydipsia -polyphagia -wt loss
question
type 1 vs type 2 DM complications
answer
Type 1: -DKA Type 2: -hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS)
question
type 1 DM
answer
autoimmune destruction of B cells -islet cell ab against GAD -primary insulin def -onset- younger pts -non-obese
question
type 1 DM- assoc w
answer
HLA genes on chr 6 -HLA-DR3-DQ2/8
question
Type 2 DM
answer
-insulin resistance -inadequate insulin production -onset in middle age/older -overwt or obese -very hereditary -acanthosis nigricans
question
DM- dx testing
answer
-glucose-based tests- fasting serum glucose, 2-H GTT -Hemoglobin A1C
question
DM- complications caused by
answer
Nonenzymatic glycation: (BVs- leaky vessels) -retinopathy -nephropathy -vascular dz Osmotic damage: -motor, sensory, autonomic neuropathy
question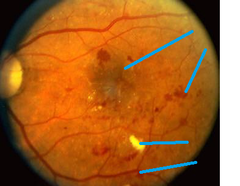
DM- retinopathy

answer
(nonenzymatic glycation) -flame hemorrhages -yellow- hard exudates -new BV formation -cotton wool spots
question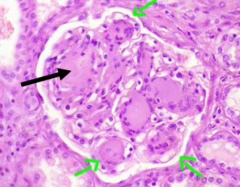
Nephropathy

answer
(nonenzymatic glycation) -proteinuria -*kimmel-stein wilson* nodules
question
Sorbitol
answer
glucose--*aldose reductase*-> sorbitol --*sorbitol dehydrogenase*-> fructose Cells don't have a sufficient supply of sorbitol dehydrogenase- sorbitol trapped in cells- osmotic P- free water in/damage -schwann cells -lens -retina -kidney
question
How is hemoglobin glycosylated in DM to form HgbA1c?
answer
-nonenzymatic glycation
question
Which type of diabetes? -assoc w obesity -may cause ketoacidosis -strong genetic predisposition -assoc w HLA-DR3/4
answer
-assoc w obesity- 2 -may cause ketoacidosis- 1 -strong genetic predisposition- 2 -assoc w HLA-DR3/4- 1
question
which tissues depend on insulin for glucose uptake?
answer
GLUT-4 -skeletal m -adipose tissue



