Visual Anatomy And Physiology Answers – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Structure specialized to receive a specific stimulus Sometimes part of a "full sense" organ, which combines nervous tissue and other tissue to enhance the reception
answer
Receptor
question
Organ that combines nervous tissue and other tissue to enhance the reception ofa stimulus Ex: eyes and inner-ear Not somatosensation (touch, pain, pressure)
answer
Sense organ
question
Conversion of energy from one form to another, typically conversion of the stimulus into an electrical signal for the nervous system to interpret
answer
Transduction
question
Small local electrical change, the initial effect of a stimulus as it contacts the receptor When sensory cells are nerve cells, these can build up to trigger an A.P. When sensory cells are NOT nerve cells, there are synaptic vesicles and their release is triggered by ________ _________.
answer
Receptor potential
question
Subjective awareness of stimulus When sensory input reaches the brain
answer
Sensation
question
The type of stimulus received or sensation produced by the receptor
answer
Modality
question
Modality - what? Location - where? Intensity - how much? Duration - how long?
answer
Information transmitted by receptors
question
Some receptors have large _______ _________, this allows you to use fewer receptors to cover an area. Some receptors have small _______ __________, this allows densely packed receptors to provide more detail. The area over which a single receptor can receive sensory stimuli.
answer
Receptive fields
question
Different that habituation. Habituation is top down regulation. ________ __________ is bottom up regulation. The process of slowing the firing of the receptor as a repeated stimulus continues over time.
answer
Sensory adaptation
question
Generate burst of signals when first stimulated, then adapt quickly and send few or no signals during a continued stimulus. Ex: Smell, hair movement, and cutaneous pressure
answer
Phasic receptors
question
Generate signals steadily during a stimulus and adapt slowly Ex: proprioceptors and pain receptors
answer
Tonic receptors
question
Wavelength of human vision
answer
400-700nm
question
Name for eyelids. Cover the eye and prevent foreign matter from damaging the eye.
answer
Palpebrae
question
Covers the inside of the eyelids and part of the anterior side of the eye. Transparent mucous membrane, produces mucus to keep the eye from drying Highly vascularized
answer
Conjunctiva
question
Produces and drains tears: -Lacrimal gland -Lacrimal punctum -Lacrimal canal -Lacrimal sac -Nasolacrimal duct
answer
Lacrimal apparatus
question
Produces tears, located in the frontal bone at the superolateral corner of the eyes
answer
Lacrimal gland
question
Drain for tears
answer
Lacrimal punctum
question
Drains from lacrimal punctum to lacrimal sac
answer
Lacrimal canal
question
empties lacrimal fluid into the nasal cavity
answer
Nasolacrimal duct
question
connect to the eye and allow it to move within the orbit
answer
Extrinsic eye muscles
question
Muscle that moves the eye up
answer
Superior rectus
question
Muscle that moves the eye down
answer
Inferior rectus
question
Muscle that moves the eye laterally
answer
Lateral rectus
question
Muscle that moves the eye medially
answer
Medial rectus
question
Muscle that passes through trochlea (pulley) at superomedial corner of the eye
answer
Superior oblique
question
Muscle that attaches at inferolateral region of the eye
answer
Inferior oblique
question
the sclera (posterior eye wall, opaque) and cornea (anterior eye wall, transparent) made of collagenous CT with blood vessels and nerves
answer
Fibrous tunic
question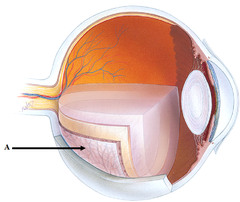
Choroid layer, ciliary body and iris

answer
Vascular tunic
question
The retina and the optic nerve AKA the "inner tunic"
answer
Nervous tunic
question
Protects the eye and attaches extrinsic eye muscles
answer
Sclera
question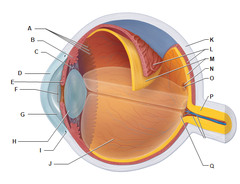
Allows the passage of light into the eye, very compact, nourished by fluids inside the eye

answer
Cornea
question
Highly vascularized and pigmented, and absorbs excess light Dark layer that absorbs light and contains many blood vessels to nourish the cells of the eye
answer
Choroid layer
question
Forms muscular ring around lens and helps to change the shape of the lens
answer
Ciliary body
question
An adjustable ring around the pupil
answer
Iris
question
An open space in the middle of the iris
answer
Pupil
question
Contains chromatophores (pigmented cells) that give the eye its color
answer
Anterior border layer
question
Blocks stray light
answer
Posterior pigment epithelium
question
Receives light from the environment A sheet of photoreceptors and their nervous associates
answer
Retina
question
Space behind the iris until the lens
answer
Posterior chamber
question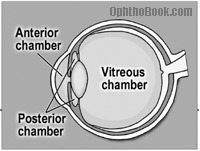
Space between the iris and cornea

answer
Anterior chamber
question
Chamber that contains vitreous humor Largest chamber of the eye
answer
Vitreous chamber
question
A watery fluid that nourishes the lens, iris, and cornea Produced by the ciliary body Flows from posterior chamber to anterior chamber, through the pupil and then out of the eye through venous sinus
answer
Aqueous humor
question
Most of the eye is filled with ________ ________. Gelatinous substance that keeps the eye in shape Not recycled much, problems hard to manage
answer
Vitreous humor
question
Transparent mass composed of flattened transparent cells (lens fibers) Attached to ciliary body by suspensory ligaments and sits posterior to the pupil Acts as a prism to focus light on the retina
answer
Lens
question
Patch of cells lateral to the optic disc A yellowish central area of the retina that is rich in cones and that mediates clear detailed vision
answer
Macula lutea
question
Pit at the center of macula Receives finest detail in images
answer
Fovea centralis
question
Process in which the brain uses surrounding signals to predict what should be in the blind spot
answer
Visual filling
question
The visual axis of both eyes orients to the same object

answer
Convergence of eyes
question
Pupil constricts to keep light from passing through the edges of the lens, where refraction is not as great
answer
Constriction of pupils
question
Ciliary body contracts and lens relaxes, making lens more round and refracting light more, focusing light from closer object onto retina
answer
Accommodation
question
Receptors which capture photons of light and transduce the signal for interpretation by the brain
answer
Photoreceptor cells
question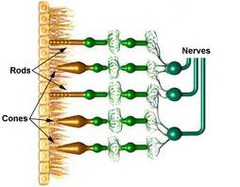
Non-neuron receptor cell with a cylindrical outer segment containing RHODOPSIN, senses contrast but not color

answer
Rod
question
Non-neuron receptor cell with a conical outer segment containing PHOTOPSIN, senses color but not contrast
answer
Cone
question
420 nm wavelength Blue-ish
answer
S cone
question
531 nm wavelength Green-ish
answer
M cone
question
558 nm wavelength Red-ish
answer
L cone
question
Contains photopigments while inner segments contain mitochondria and organelles Cell body contains nucleus and processes taht synapse with neurons
answer
Outer segment
question
Contain mitochondria and organelles. Situated between photopigments and cell body
answer
Inner segment
question
Visual purple The pigment of rods a visual pigment consisting of RETINAL and OPSIN.
answer
Rhodopsin
question
A class of protein that, together with retinal, constitutes the photopigments
answer
Opsin
question
A chemical synthesized from vitamin A; joins with an opsin to form a photopigment
answer
Retinal
question
Only in cones. Responsible for color. Based on different wavelengths. -Red -Blue -Green
answer
Photopsin
question
Day vision Daytime lighting, cones do the bulk of the work
answer
Photopic
question
Night vision Cannot resolve finely detailed images; extensive neuronal convergence. Rods do the work.
answer
Scotopic
question
default bend shape of retinal rods (In Dark)
answer
cis-retinal
question
Light converts cis-retinal to ___-_________ position
answer
trans-retinal
question
Adjustment in vision when you move from dark to light.
answer
Light adaptation
question
Adjustment in vision when you move from light to dark.
answer
Dark adaptation
question
One receptor cannot have both high sensitivity and high resolution.
answer
Duplicity theory
question
Inability to see some or all color
answer
Colorblindness
question
The most common form of color blindness. Sex linked to X chromosome. More common in men.
answer
Red-green colorblindness
question
Perception of space and depth caused chiefly by the fact that the eyes receive different images
answer
Stereoscopic vision
question
fibers coming from the medial regions of the eyes decussate, and will go to the contralateral visual cortex of the brain, while fibers coming from the lateral regions do not decussate and will go to the ipsilateral visual cortex
answer
Hemidecussation
question
Nearsightedness caused by an elongated eyeball
answer
Myopia
question
Farsightedness caused by eyeball being shortened
answer
Hyperopia
question
Eyes cannot focus light rays entering from different planes at the same time resulting from a misshapen lens
answer
Astigmatism
question
impaired vision as a result of aging poor near vision due to reduced accommodation of the lens from reduced flexibility•Corrected with bifocals
answer
Presbyopia
question
Increased pressure in the eye puts pressure on and causes damage to the optic nerve
answer
Glaucoma
question
lens becomes opaque, so light cannot pass through, resulting in blurred vision
answer
Cataracts
question
retina separates from the back of the eye due to trauma, diabetes, or decreased vitreous fluid volume, causing blurred vision, "floaters," and shadows in the visual field
answer
Detached retina
question
incomplete maturation of visual system due to infection or vitamin A deficiency causes monocular vision loss
answer
Amblyopia
question
damage to the occipital lobe renders individual unable to perceive visual input, though the eyes are undamaged
answer
Cortical blindness



