USMLE FIRST AID 2017 Biochemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Histone proteins
answer
H1 linker H2A H2B H3 H4 x2 nucleosome
question
Amino acids rich in histone
answer
Lysine and arginine
question
Phase during mitosis that DNA and histone synthesis occur
answer
S phase
question
Heterochromatin
answer
Condensed, inactive, high methylation, low acetylation
question
Barr bodies
answer
Inactive X chromosomes, heterchromatine
question
Euchromatin
answer
Less condensed, active
question
DNA methylation sites
answer
Cytosine and adenine
question
CpG islands
answer
DNA methylation at CpG islands represses transcription
question
Histone methylation
answer
Usually represses transcription, activates in some cases depending on methylation location
question
Histone acetylation
answer
Activates transcription
question
Purine
answer
A, G 2 rings
question
Pyrimidines
answer
C, U, T 1 ring
question
Deamination of cytosine
answer
Uracil
question
Deamination of adenine
answer
Guanine
question
Methylation of uracil
answer
Thymine
question
Amino acids necessary for purine synthesis
answer
Glycine Aspartate Glutamine
question
Leflunomide
answer
Inhibits dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
question
Methotrexate Trimethoprim Pyrimethamine
answer
Inhibit dihydrofolate reductase in humans, bacteria, and Protozoa, respectively Decrease dTMP
question
5-flurouracil
answer
Forms 5-F-dUMP inhibits thymidylate synthase Decrease dTMP
question
6-mercaptopurine
answer
Inhibits de novo purine synthesis Prodrug is azathioprine
question
Mycophenolate Ribavirin
answer
Inhibit inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase Decrease GMP
question
Hydroxyurea
answer
Inhibits ribonucleotide reductase
question
Adenosine deaminase deficiency
answer
ADA is required for degradation of adenosine and deoxyadenosine Increase dATP -> toxicity in lymphocytes Autosomal recessive SCID
question
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
answer
Absent HGPRT, which converts hypoxanthine to IMP and guanine to GMP Excess uric acid Increased de novo purine synthesis X-linked recessive Hyperuricemia Gout Pissed off (agreesion, self-mutilation) Retardation (intellectual disability) Dystonia Orange "sand" [sodium urate crystals] in diaper Tx: allopurinol, febuxostat (2nd line)
question
RNA codon for tryptophan
answer
UGG
question
RNA codon for methionine
answer
AUG
question
Eukaryotic topoisomerse I inhibitor
answer
Irinotecan Topotecan
question
Eukaryotic topoisomerase II inhibitor
answer
Etoposide Teniposide
question
Fluoroquinolones
answer
Inhibit prokaryotic topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV
question
DNA polymerase III
answer
Prokaryotes only 5'-;3' synthesis and proofreads with 3'-;5' exonuclease
question
DNA polymerase I
answer
Prokaryotes only 5'-;3' synthesis and proofreads with 3'-;5' exonuclease Excises RNA primer with 5'-;3' exonuclease
question
Transition mutation in DNA
answer
Purine to purine Pyrimidine to pyrimidine
question
Transversion mutation in DNA
answer
Purine to pyrimidine Pyrimidine to purine
question
Example of missense mutation
answer
Sickle cell disease (glutamic acid to valine)
question
Examples of frameshift mutation
answer
Duchenne muscular dystrophy Tay-Sachs disease
question
Examples of splice site mutation
answer
Rare cause of cancers, dementia, epilepsy, some types of b-thalassemia
question
Nucleotide excision repair
answer
Occurs in G1 Xeroderma pigmentosum
question
Base excision repair
answer
Glycosylase AP site AP-endonuclease Lyase DNA polymerase-b DNA ligase Occurs throughout cell cycle Repair spontaneous/toxic deamination
question
Mismatch repair
answer
Occurs predominantly in G2 Lynch syndrome (HNPCC)
question
Nonhomologous end joining
answer
Some DNA may be lost Ataxia telangiectasia Breast/ovarian cancers with BRCA1 mutation Fanconi anemia
question
mRNA start codons
answer
AUG rarely GUG methionine in eukaryotics, may be removed before translation is completed N-formylmethionine (fMet) in prokaryotes
question
mRNA stop codons
answer
UAG UAA UGA
question
a-amanitin
answer
Found in Amanita phalloides (death cap mushrooms Inhibits RNA polymerase II severe hepatotoxicity
question
Actinomycin D
answer
Inhibits RNA polymerase in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
question
Rifampin
answer
Inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in prokaryotes
question
Capping of 5' end of hnRNA
answer
Addition of 7-methylguanosine cap
question
P-bodies
answer
Cytoplasmic processing bodies for mRNA quality control Exonuclease Decapping enzymes MicroRNAs mRNA may be stored for future translation
question
Anti-smith antibodies
answer
Antibodies to spliceosomal snRNPs Highly specific for SLE
question
Anti-U1 RNP antibodies
answer
Highly associated with mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD)
question
microRNAs
answer
Targeting 3' UTR of specific mRNAs for degradation or translational repression
question
tRNA 3' end
answer
Covalently binds to amino acid CCA
question
tRNA T-arm
answer
T¥C ribothymidine, pseudouridine, cytidine tRNA-ribosome binding
question
tRNA D-arm
answer
Dihydrouridine residues necessary for tRNA recognition by the correct aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
question
p53
answer
Induced p21, which inhibits CDKs Hypophosphorylation of Rb (activation) Inhibition of G1-S progression Mutations result in unrestrained cell division (Li-Fraumeni syndrome)
question
Permanent cell type
answer
Remain in G0, regenerate from stem cells Neurons, skeletal and cardiac muscle, RBCs
question
Stable (quiescent) cell type
answer
Enter G1 from G0 when stimulated Hepatocytes, lymphocytes
question
Labile cell type
answer
Never go to G0 Divide rapidly with a short G1 Most affected by chemotherapy Bone marrow, gut epithelium, skin, hair follicles, germ cells
question
RER
answer
Synthesis of secretory proteins N-linked oligosaccharide addition Nissl bodies (neuron) synthesize peptide neurotransmitters Free ribosomes Mucus-secreting goblet cells of small intestine, antibody-secreting plasma cells
question
SER
answer
Steroid synthesis, detoxification of drugs and poisons Liver hepatocytes, steroid hormone-producing cells of the adrenal cortex, gonads
question
N-oligosaccharides
answer
On asparagine, in Golgi
question
O-oligosaccharides
answer
On serine and threonine, in Golgi
question
Inclusion cell disease
answer
I-cell disease Mucolipiododis type II Inherited lysosomal storage disorder Defect in N-acetylglucosoaminyl-1-phosphotransferase Failure of Golgi to phosphrylate mannose residues on glycoproteins Decreased mannose-6-phosphate Proteins are secreted extracellularly rather than delivered to lysosomes Coarse facial feature, clouded corneas, restricted joint movement, high plasma levels of lysosomal enzymes Often fatal in childhood
question
Peroxisome
answer
Catabolism of very-long-chain fatty acids, branched-chain fatty acids, amino acids, and ethanol Disorders commonly lead to neurologic diseases due to deficits in synthesis of plasmalogens, important phospholipids in myelin
question
Zellweger syndrome
answer
Peroxisomal disease Hypotonia Seizures Hepatomegaly Early death
question
Refsum
answer
Peroxisomal disease Scaly skin Ataxia Cataracts/night blindness Shortening of 4th toe Epiphyseal dysplasia
question
Defects in the ubiquitin-proteasome system have been implicated in some cases of which disease?
answer
Parkinson disease
question
Microfilaments
answer
Function: muscle contraction, cytokinesis Actin, microvilli
question
Intermediate filaments
answer
Function: maintain cell structure Vimentin, desmin, cytokeratin, lamins, glial fibrillary acid proteins, neurofilaments
question
Microtubules
answer
Function: movement, cell division Cilia, flagella, mitotic spindle, axonal trafficking, centrioles
question
Vimentin
answer
Cell type: mesenchymal tissue (fibroblasts, endothelial cells, macrophages) Identifies: mesenchymal tumors (sarcoma), many other tumors (endometrial carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, meningioma)
question
Desmin
answer
Cell type: muscle Identifies: muscle tumor (rhabdomyosarcoma)
question
Cytokeratin
answer
Cell type: epithelial cells Identifies: epithelial tumors (squamous cell carcinoma)
question
GFAP
answer
Cell type: neuroglia (astrocytes, Schwann cells, oligodendrocytes) Identifies: astrocytoma, glioblastoma
question
Neurofilaments
answer
Cell type: neurons Identifies: neuronal tumors (neuroblastoma)
question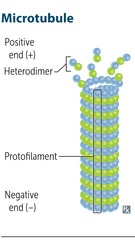
Microtubule

answer
Cylindrical outer structure composed of a helical array of polymerized heterodimers of a- and b-tubulin Each dimer has 2 GTP bound Grows slowly, collapses quickly Slow axoplasmic transport in neurons
question
Molecular motor proteins
answer
Dynein Retrograde + -; - Kinesin Anterograde - -; + Negative end near nucleus Positive end points to periphery
question
Drugs act on microtubules
answer
Mebendazole (antihelminthic) Griseofulvin (antifungal) Colchicine (antigout) Vincristine/Vvinblastine (anticancer) Paclitaxel (anticancer)
question
Cilia structure
answer
9 doublets + 2 singlet arrangement of microtubules Basal body (base of cilium below cell membrane) consists of 9 microtubules triplets with no central microtubules
question
Axonemal dynein
answer
ATPase that links peripheral 9 doublets and causes bending of cilium by differential sliding of doublets
question
Kartagener syndrome
answer
1' ciliary dyskinesia Immotile cilia due to a dynein arm defect Decreased fertility Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy Bronchiectasis Recurrent sinusitis Chronic ear infections Conductive hearing loss Situs inversus
question
Ouabain
answer
Inhibits by binding to K+ site of Na+ - K+ ATPase
question
Cardiac glycosides
answer
Digoxin Digitoxin Directly inhibit Na+ - K+ ATPase -> indirect inhibition of Na+/Ca2+ exchange -> increase [Ca2+]i -> increase cardiac contractility
question
Type I collagen
answer
Most common (90%) Bone, skin, tendon, dentin, fascia, cornea, late wound repair Decrease production in osteogenesis imperfecta type I
question
Type II collagen
answer
Cartilage (including hyaline), vitreous body, nucleus pulposus
question
Type III collagen
answer
Reticulin Skin, blood vessels, uterus, fetal tissue, granulation tissue Deficient in the uncommon, vascular type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
question
Type IV collagen
answer
Basement membrane, basal lamina, lens Defective in Alport syndrome Targeted by autoantibodies in Goodpasture syndrome
question
Collagen synthesis 1 Synthesis
answer
Translation of collagen a chains (preprocollagen) Usually Gly-X-Y (X and Y are proline or lysine) Collagen is 1/3 glycine
question
Collagen synthesis 2 Hydroxylation
answer
Hydroxylation of specific proline and lysine residues Requires vitamin C deficiency -> scurvy
question
Collagen synthesis 3 Glycosylation
answer
Glycosylation of pro-a-chain hydroxylysine residues and formation of procollagen via hydrogen and disulfide bonds (triple helix of 3 collagen a chains) Problems forming triple helix -> osteogenesis imperfecta
question
Collagen synthesis 4 Exocytosis
answer
Exocytosis of procollagen into extracellular space
question
Collagen synthesis 5 Proteolytic processing
answer
Cleavage of disulfide-rich terminal regions of procollagen -> insoluble tropocollagen Problems with cleavage -> Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
question
Collagen synthesis 6 Cross-linking
answer
Reinforcement of many staggered tropocollagen molecules by covalent lysine-hydroxylysine cross-linkage (by copper-containing lysyl oxidase) to make collagen fibrils Problems with cross-linking -> Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Menkes disease
question
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
answer
Faulty collagen synthesis hyperextensible skin, tendency to bleed (easy bruising), and hypermobile joints Multiple types. Inheritance and severity vary. Can be autosomal dominant or recessive May be associated with joint dislocation, berry and aortic aneurysm, organ rupture Hypermobility type (joint instability): most common type Classical type (joint and skin symptoms): mutation in type V collagen (COL5A1, COL5A2) Vascular type (vascular and organ rupture): deficient type III collagen
question
Menkes disease
answer
X-linked recessive connective tissue disease Caused by impaired copper absorption and transport due to defective Menkes protein (ATP7A) Decrease activity of lysyl oxidase (copper is a necessary cofactor) Brittle, "kinky" hair Growth retardation Hypotonia
question
Osteogenesis imperfecta
answer
Brittle bone disease Genetic bone disorder caused by a variety of gene defects Most commonly COL1A1 and COL1A2 Most common autosomal dominant, decrease production of otherwise normal type I collagen Multiple fractures with minimal trauma, may occur during the birth process Blue sclerae due to the translucent connective tissue over choroidal veins Some forms have tooth abnormalities, including opalescent teeth that wear easily due to lack of dentin (dentinogenesis imperfecta) Hearing loss (abnormal ossicles) May be confused with child abuse
question
Elastin
answer
Stretchy protein within skin, lungs, large arteries, elastic ligaments, vocal cords, ligmenta flava Rich in nonhydroxylated proline, glycine, lysine Tropoelastin with fibrillin scaffolding Cross-linking takes place extracellularly and gives elastin its elastic properties Broken down by elastase, which is normally inhibited by a1-antitrypsin a1-antitrypsin deficiency results in excess elastase activity, which can cause emphysema Wrinkles of aging are due to decreased collagen and elastin production
question
Marfan syndrome
answer
Autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder Affecting skeleton, heart, and eyes FBN1 gene mutation on chromosome 15 results in defective fibrillin, a glycoprotein that forms a sheath around elastin Tall with long extremities Pectus carinatum (more specific) or pectus excavatum Hypermobile joints Long, tapering fingers and toes (arachnodactyly) Cystic medial necrosis of aorta Aortic incompetence and dissecting aortic aneurysm Floppy mitral valve Subluxation of lenses, typically upward and temporally
question
Codominance example
answer
Blood groups A, B, AB a1-antitrypsin deficiency
question
Variable expressivity example
answer
2 patients with NF1 may have varying disease severity
question
Incomplete penetrance example
answer
BRCA1 gene mutations do not always result in breast or ovarian cancer
question
Pleiotropy example
answer
Untreated PKU manifests with light skin, intellectual disability, and musty body odor
question
Anticipation example
answer
Trinucleotide repeat diseases (Huntington disease)
question
Loss of heterozygosity example
answer
Retinoblastoma and the "two-hit hypothesis" Lynch syndrome (HNPCC) Li-Fraumeni syndrome
question
Dominant negative mutation example
answer
Mutation of a transcription factor in its allosteric site. Non functioning mutant can still bind DNA, preventing wild-type transcription factor from binding
question
Linkage disequilibrium
answer
Tendency for certain alleles at 2 linked loci to occur together more or less often than expected by chance. Measured in a population, not in a family, and often varies in different population
question
Mosaicism
answer
Presence of genetically distinct cell lines in the same Individual
question
Somatic mosaicism
answer
Mutation arises from mitotic errors after fertilization and propagates through multiple tissue or organs
question
Gonadal mosaicism
answer
Mutation only in egg or sperm cells. If parents and relatives do not have the disease, suspect gonadal (or germline) mosaicism
question
McCune-Albright syndrome
answer
Example of mosaicism Mutation affecting G-protein signling. Unilateral cafe-au-lait spots with ragged edges Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia At least 1 endocrinopathy (eg, precocious puberty) Lethal if mutation occurs before fertilization (affecting all cells), but survivable in patients with mosaicism
question
Locus heterogeneity
answer
Mutations at different loci can produce similar phenotype Albinism
question
Allelic heterogeneity
answer
Different mutations in the same locus produce the same phenotype b-thalassemia
question
Heteroplasmy
answer
Presence of both normal and mutated mtDNA, resulting in variable expression in mitochondrially inherited disease
question
Uniparental disomy
answer
Offspring receives 2 copies of a chromosome from 1 parent and no copies from the other parent Heterodisomy (heterozygous) indicates a meiosis I error. Isodisomy (homozygous) indicates a meiosis II error or postzygotic chromosomal duplication of one of a pair of chromosomes, and loss of the other of the original pair. Uniparental is euploid (correct number of chromosomes), not aneuploid. Most occurrences of uniparental disomy (UPD) -> normal phenotype. Consider UPD in an individual manifesting a recessive disorder when only one parent is a carrier
question
Hardy-Weinberg population genetics
answer
p2+2pq+q2=1 p+q=1 p2= frequency of homozygosity for A q2= frequency of homozygosity for a 2pq= frequency of heterozygosity (carrier frequency, if an autosomal recessive disease) The frequency of an X-linked recessive disease in males = q and in females = q2 Assumptions: No mutation occurring at the locus Natural selection is not occurring Completely random mating No net migration
question
Imprinting
answer
At some loci, only one allele is active; the other is inactive (imprinted/inactivated by methylation) With one allele inactivated, deletion of the active allele -> disease Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes are due to mutation or deletion of genes on chromosome 15
question
Prader-Willi syndrome
answer
Mutation of deletion of genes on chromosome 15 Maternal imprinting: gene from mom is normally silent and paternal gene is deleted/mutated Hyperphagia Obesity Intellectual disability Hypogonadism Hypotonia 25% of cases due to maternal uniparental disomy (two maternally imprinted genes are received; no paternal gene received)
question
Angelman syndrome
answer
Paternal imprinting: gene from dad is normally silent and maternal gene is deleted/mutated Inappropriate laughter ("happy puppet") Seizures Ataxia Severe intellectual disability 5% of cases due to paternal uniparental disomy (two paternally imprinted genes are received; no maternal gene received)
question
Autosomal dominant
answer
Often due to defects in structural genes Many generations Both males and females are affected Often pleiotropic (multiple apparently unrelated effects) and variably expressive (different between individuals) Family history crucial to diagnosis With one affected (heterozygous) parent, on average, 1/2 of children affected
question
Autosomal recessive
answer
Often due to enzyme deficiencies Usually seen in only 1 generation Commonly more severe than dominant disorders; patients often present in childhood Increased risk in consanguineous families With 2 carrier (heterozygous) parents, on average: 1/4 of children will be affected (homozygous) 1/2 of children will be carriers 1/4 of children will be neither affected nor carriers
question
X-linked recessive
answer
Sons of heterozygous mothers have a 50% chance of being affected No male-to-male transmission Skips generations Commonly more severe in males Females usually must be homozygous to be affected
question
X-linked dominant
answer
Transmitted through both parents Mothers transmit to 50% of daughters and sons Fathers transmit to all daughters but no sons Hypophosphatemic rickets (Vitamin D-resistant rickets) Fragile X syndrome Alport syndrome
question
Hypophosphatemic rickets
answer
X-linked dominant Formerly known as vitamin D-resistant rickets Inherited disorder resulting in increased phosphate wasting at proximal tubule Results in rickets-like presentation
question
Mitochondrial inheritance
answer
Transmitted only through the mother All offspring of affected females may show signs of disease Variable expression in a population or even within a family due to heteroplasmy Mitochondrial myopathies
question
Mitochondrial myopathies
answer
Mitochondrial inheritance Rare disorders Often present with myopathy, lactic acidosis, and CNS disease, eg, MELAS syndrome (mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes 2' to failure in oxidative phosphorylation Muscle biopsy often shows "ragged red fibres" (due to accumulation of diseased mitochondria)
question
List of autosomal dominant diseases
answer
Achondroplasia ADPKD FAP Familial hypercholesterolemia Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia Hereditary spherocytosis Huntington disease Li-Fraumeni syndrome Marfan syndrome Multiple endocrine neoplasias NF1, von Recklinghausen disease NF2 Tuberous sclerosis von Hippel-Lindau disease
question
List of autosomal recessive diseases
answer
Albinism ARPKD CF Glycogen storage diseases Hemochromatosis Kartagener syndrome Mucopolysaccharidoses (except Hunter syndrome) PKU Sickle cell anemia Sphingolipidoses (except Fabry disease) Thalassemias Wilson disease
question
CF genetics
answer
Autosomal recessive Defect in CFTR gene on Ch7 Commonly deletion of Phe508 Most common lethal genetic disease in Caucasian
question
CF pathophysiology
answer
CFTR encoded ATP-gated Cl- channel Secrets Cl- in lungs, GI tract Reabsorbs Cl- in sweat glands Most common mutation-; misfolded protein -; retained in RER -; decreased Cl- and H2O secretion Increased intracellular Cl- -; compensatory increased Na+ reabsorption via epithelial Na+ channels -; increased H2O reabsorption -; abnormally thick mucus secreted into lungs and GI tract Increased Na+ reabsorption also -; more negative transepithelial potential difference
question
CF diagnosis
answer
Increased Cl- concentration ;60mEq/L in sweat is Dx Can present with contraction alkalosis and hypokalemia (ECF effects analogous to a patient taking a loop diuretic) because of ECF H2O/Na+ losses and concomitant K+/H+ wasting Increased immunoreactive trypsinogen (newborn screening)
question
CF complications
answer
Recurrent pulmonary infection (S aureus [infancy], P aeruginosa [adolescence]), chronic bronchitis and bronchiectasis -; reticulonodular pattern on CXR, opacification of sinuses Pancreatic insufficiency, malabsorption with steatorrhea, fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies (A, D, E, K), biliary cirrhosis, liver disease. Meconium ileus in newborns Infertility in men (absence of vas deferens, spermatogenesis may be unaffected) and subfertility in women (amenorrhea, abnormally thick cervical mucus) Nasal polyps, clubbing of nails
question
CF treatment
answer
Multifactorial: chest physiotherapy, albuterol, aerosolized dornase alfa (DNAase), hypertonic saline facilitate mucus clearance Azithromycin used as anti-inflammatory agent Ibuprofen shows disease progression Pancreatic enzymes for insufficiency
question
List of X-linked recessive disorders
answer
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency Fabry disease Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome Ocular albinism G6PD deficiency Hunter syndrome Bruton agammaglobulinemia Hemophilia A and B Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Duchenne (and Becker) muscular dystrophy
question
Lyonization
answer
Female carriers variably affected depending on the pattern of inactivation of the X chromosome carrying the mutant vs normal gene
question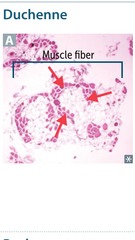
Duchenne muscular dystrophy

answer
X-linked framshift or nonsense mutations -; truncated or absent dystrophin protein -; progressive myofiber damage Weakness begins in pelvic girdle muscles and progresses superiorly Psedohypertrophy of calf muscles Waddling gait Onset before 5ya Dilated cardiomyopathy is common cause of death Dystrophin gene (DMD) is the largest protein-coding human gene -; increased chance of spontaneous mutation Dystrophin helps anchor muscle fibres, primarily in skeletal and cardiac muscle It connects intracellular cytoskeleton (actin) to transmembrane protein a- and b-dystroglycan, which are connected to ECM Loss of dystrophin -; myonecrosis Increased CK and aldolase Genetic testing confirms dx
question
Becker muscular dystrophy
answer
X-linked Non-frameshift deletions in dystrophin gene (partially functional instead of truncated) Less severe than Duchenne Onset in adolescence or early adulthood Deletion can cause both Duchenne and Backer muscular dystrophies 2/3 of cases have large deletions spanning one or more exons
question
Myotonic type 1 muscular dystrophy
answer
Autosomal dominant CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the DMPK gene -; abnormal expression of myotonin protein kinase -; myotonia, muscle wasting, cataracts, testicular atrophy, frontal balding, arrhythmia
question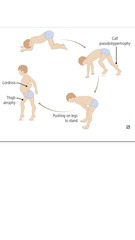
Grower sign

answer
Patient uses upper extremities to help stand up Classically seen in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, but also seen in other muscular dystrophies and inflammatory myopathies (polymyositis)
question
Fragile X syndrome
answer
X-linked dominant CGG repeat in FMR1 gene -; hypermethylation -; decreased expression Most common cause of inherited intellectual disability and autism 2nd most common cause of genetically associated mental deficiency (after Down syndrome) Post-pubertal macroorchidism Long face with large jaw Large everted ears Autism Mitral valve prolapse
question
Trinucleotide repeat expansion disease
answer
Huntington disease CAG Myotonic dystrophy CTG Fragile X syndrome CGG Friedreich ataxia GAA May show genetic anticipation (disease severity increases and age of onset decreased in successive generations)
question
Down syndrome physical findings
answer
Intellectual disability Flat facies Prominent epicanthal folds Single palmar crease Gap between 1st 2 toes Duodenal atresia Hirschsprung disease Congenital heart disease (AVSD) Brushfield spots Associated with early-onset Alzheimer disease (Ch21 codes for amyloid precursor protein) High risk of ALL and AML Most common viable chromosomal disorder and cause of genetic intellectual disability
question
Down syndrome causes
answer
95% meiotic nondisjunction (increase with advanced maternal age, from 1:1500 in 45ya) overall 1:700 4% unbalanced Robertsonian translocation, most typical between Ch14 and 21 1% mosaicism (no association with maternal nondisjunction; postfertilization mitotic error)
question
Down syndrome prenatal findings
answer
1st Tri U/S increased nuchal translucency Hypoplastic nasal bone Low serum PAPP-A High free b-hCG 2nd tri quad screen Low a-fetoprotrin High b-hCG Low estriol High inhibin A
question
Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18)
answer
Prominent occiput Rocker-bottom feet Intellectual disability Nondisjunction Clenched fists with overlapping fingers Low-set ears Micrognathia (small jaw) Congenital heart disease Death usually occurs by 1ya Incidence 1:8000 2nd most common autosomal trisomy resulting in live birth (after Down syndrome) 1st Tri: low PAPP-A and free b-hCG Quad screen: low AFP, b-hCG, estriol, low or normal inhibin A
question
Patau syndrome (trisomy 13)
answer
Severe intellectual disability Rocker-bottom feet Microphthalmia Microcephaly Cleft lip/palate Holoprosencephaly Polydactyly Cutis aplasia Congenital heart disease Death at 1ya Incidence 1:15000 1st Tri: low free b-hCG, PAPP-A
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 3
answer
von Hippel-Lindau disease Renal cell carcinoma
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 4
answer
ADPKD (PKD2) Achondroplasia Huntington disease
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 5
answer
Cri-du-chat syndrome Familial adenomatous polyposis
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 6
answer
Hemochromatosis (HFE)
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 7
answer
Williams syndrome Cystic fibrosis
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 9
answer
Friedreich ataxia
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 11
answer
Wilms tumor b-globin gene defects (sickle cell disease, b-thalassemia, MEN1)
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 13
answer
Patau syndrome Wilson disease Retinoblastoma (RB1) BRCA2
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 15
answer
Prader-Willi syndrome Angelman syndrome Marfan syndrome
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 16
answer
ADPKD (PKD1) a-globin gene defects (a-thalassemia)
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 17
answer
NF1 BRCA1 p53
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 18
answer
Edwards syndrome
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 21
answer
Down syndrome
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome 22
answer
NF2 DiGeorge syndrome (22q11)
question
Genetic disorders by chromosome X
answer
Fragile X syndrome X-linked agammaglobulinemia Klinefelter syndrome (XXY)
question
Robertsonian translocation
answer
Commonly involves chromosome pairs 13, 14, 15, 21, 22 One of the most common types of translocation Occurs when the long arms of 2 acrocentric chromosomes (chromosomes with centromeres near their ends) fuse at the centromere and the 2 short arms are lost Balanced translocations normally do not cause any abnormal phenotype Unbalanced translocations can result in miscarriage, stillbirth, chromosomal imbalance (Down syndrome, Patau syndrome)
question
Cri-du-chat syndrome
answer
Congenital microdeletion of short arm of ch5 (46, XX or XY, 5p-) Microcephaly Mod to severe intellectual disability High-pitched crying/meowing Epicanthal folds Cardiac abnormalities (VSD)
question
William syndrome
answer
Congenital microdeletion of long arm of ch7 (deleted region includes elastin gene) Distinctive "elfin" facies Intellectual disability Hypercalcemia (high sensitivity to vitamin D) Well-developed verbal skills Extreme friendliness with strangers Cardiovascular problems
question
22q11 deletion syndromes
answer
Microdeletion Due to aberrant development of 3rd and 4th branchial pouches Variable presentations Cleft palate Abnormal facies Thymic aplasia -; T-cell deficiency Cardiac defects Hypocalcemia 2' to parathyroid aplasia
question
DiGeorge syndrome
answer
Thymic Parathyroid Cardic defects
question
Velocardiofacial syndrome
answer
Palate Facial Cardiac defects
question
Vitamins: fat soluble
answer
A, D, E, K Absorption dependent on gut and pancreas Toxicity more common than for water-soluble vitamins because fat-soluble vitamins accumulate in fat Malabsorption syndromes with steatorrhea, eg. CF, celiac disease, mineral oil intake can cause fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies
question
Vitamins: water soluble
answer
B1 thiamine: TPP B2 riboflavin: FAD, FMN B3 niacin: NAD+ B5 pantothenic acid: CoA B6 pyridoxine: PLP B7 biotin B9 folate B12 cobalamin C ascorbic acid All wash out easily from body except B12 and B9 B12 stored in liver for 3-4 years B9 stored in liver for 3-4 months B-complex deficiencies often result in dermatitis, glossitis, diarrhea Can be coenzymes (ascorbic acid) or precursors to organic cofactors (FAD, NAD+)
question
Vitamin A (retinol) function
answer
Antioxidant Constituent of visual pigments (retinal) Essential for normal differentiation of epithelial cells into specialized tissue (pancreatic cells, mucus-secreting cells) Prevents squamous metaplasia Used to treat measles and acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) Found in liver and leafy vegetables Oral isotretinoin to treat severe cystic acne Use all-trans retinoic acid to treat acute promyelocytic leukemia
question
Vitamin A (retinol) deficiency
answer
Night blindness (nyctalopia) Dry, scaly skin (xerosis cutis) Corneal degeneration (keratomalacia) Bitot spots on conjunctiva Immunosuppression
question
Vitamin A (retinol) excess
answer
Acute toxicity Nausea, vomiting, vertigo, blurred vision Chronic toxicity Alopecia, dry skin (scaliness), hepatic toxicity and enlargement, arthralgias, pseudotumor cerebri Taratogenic (cleft palate, cardiac abnormalities) -ve preg test + 2 forms of contraception required before prescribing isotretinoin
question
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) function
answer
In thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), cofactors for: Pyruvate dehydrogenase a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (TCA) Transketolase (HMP shunt) Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase
question
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency
answer
Impaired glucose breakdown -> ATP depletion worsened by glucose infusion Highly aerobic tissues (brain, heart) affected first EtOH or malnourished patients, give thiamine before dextrose to decrease risk of precipitating Wernicke encephalopathy Dx made by increase in RBC transketolase activity following vitamin B1 administration Dry beriberi: polyneuritis, symmetrical muscle wasting Wet beriberi: high-output cardiac failure (dilated cardiomyopathy), edema
question
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
answer
Confusion Ophthalmoplegia Ataxia (classic triad) Confabulation Personality change Memory loss (permanent) Damage to medial dorsal nucleus of thalamus, mammillary bodies
question
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) function
answer
Component of flavins FAD and FMN Cofactors in redox reactions Succinate dehydrogenase reaction in TCA cycle
question
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) deficiency
answer
Cheilosis (inflammation of lips, scaling and fissures at the corners of the mouth) Corneal vascularization
question
Vitamin B3 (niacin) function
answer
Constituent of NAD+, NADP+ (used in redox reactions) Derived from tryptophan Synthesis requires vitamin B2 and B6 Used to treat dyslipidemia, lowers levels of VLDL and raises levels of HDL
question
Vitamin B3 (niacin) deficiency
answer
Glossitis Severe deficiency leads to pellagra, which can be caused by Hartnup disease, malignant carcinoid syndrome (high tryptophan metabolism), isoniazid (lowers vitamin B6) Symptoms of pellagra: Diarrhea Dementia (also hallucinations) Dermatitis (C3/C4 dermatome circumferential "broad collar" rash [Casal necklace], hyperpigmentation of sun-exposed limbs
question
Hartnup disease
answer
Autosomal recessive Deficiency of neutral amino acid (tryptophan) transportors in proximal renal tubular cells and on enterocytes -> neutral aminoaciduria and decreased absorption from the gut -> decreased tryptophan for conversion to niacin -> pellagra-like symptoms Tx with high-protein diet and nicotinic acid
question
Vitamin B3 (niacin) excess
answer
Facial flushing (induced by prostaglandin, not histamine; can avoid by taking aspirin with niacin) Hyperglycemia Hyperuricemia
question
Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) function
answer
Essential component of coenzyme A (CoA, a cofactor for acyl transfers) and fatty acid synthase
question
Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) deficiency
answer
Dermatitis Enteritis Alopecia Adrenal insufficiency
question
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) function
answer
Converted to pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), a cofactor used in transamination (ALT and AST), decarboxylation reactions, glycogen phosphorylase. Synthesis of cystathionine, heme, niacin, histamine, and neurotransmitters including serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine (NE), dopamine, GABA
question
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) deficiency
answer
Convulsions Hyperirritability Peripheral neuropathy (deficiency inducible by isoniazid and oral contraceptives) Sideroblastic anemias due to impaired hemoglobin synthesis and iron excess
question
Vitamin B7 (biotin) function
answer
Cofactor for carboxylation enzymes: Pyruvate carboxylase: pyruvate (3C) -> oxaloacetate (4C) Acetyl-CoA carboxylase: acetyl-CoA (2C) -> malonyl-CoA (3C) Propionyl-CoA carboxylase: propionyl-CoA (3C) -> methylmalonyl-CoA (4C)
question
Vitamin B7 (biotin) deficiency
answer
Relatively rare Dermatitis Alopecia Enteritis Caused by antibiotic use or excessive ingestion of raw egg whites
question
Vitamin B9 (folate) function
answer
Converted to THF, a coenzyme for 1-carbon transfer/methylation reactions Important for the synthesis of nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA Found in leafy green vegetables Absorbed in jejunum Small reserve pool stored primarily in the liver
question
Vitamin B9 (folate) deficiency
answer
Macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia Hypersegmented PMNs Glossitis No neurological symptoms (as opposed to vitamin B12 deficiency) High homocysteine Normal methylmalonic acid levels Most common vitamin deficiency in USA Seen in alcoholism and pregnancy Deficiency can be caused by several drugs (phenytoin, sulfonamides, methotrexate) Supplemental maternal folic acid at least 1 month prior to conception and during early pregnancy to reduce risk of neural tube defects
question
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) function
answer
Cofactor for methionine synthase (transfers CH3 groups as methylcobalamin) and methylmalonyl-CoA mutase Important for DNA synthesis
question
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency
answer
Macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia Hypersegemented PMNs Paresthesias and subacute combined degeneration (dorsal columns, lateral corticospinal tracts, spinocerebellar tracts) due to abnormal myelin High serum homocysteine and methylmalonic acid levels 2' folate deficiency Prolonged deficiency -; irreversible nerve damage
question
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency causes
answer
Found in animal products Synthesized only by microorganisms Very large reserve pool (several years) stored primarily in the liver Deficiency caused by malabsorption (sprue, enteritis, Diphyllobothrium latum), lack of intrinsic factor (pernicious anemia, gastric bypass surgery), absence of terminal ileum (surgery resection, for Crohn disease), insufficient intake (veganism) Anti-intrinsic factor antibodies diagnostic for pernicious anemia
question
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) function
answer
Antioxidant Facilitates iron absorption by reducing it to Fe2+ state Necessary for hydroxylation of proline and lysine in collagen synthesis Necessary for dopamine b-hydroxylase, converts dopamine to NE Found in fruits and vegetables Ancillary Tx for methemoglobinemia by reducing Fe3+ to Fe2+
question
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) deficiency
answer
Scurvy Swollen gums Bruising Petechiae Hemarthrosis Anemia Poor wound healing Perifollicular and subperiosteal hemorrhages Corkscrew hair Weakened immune response
question
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) excess
answer
Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea Fatigue Calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis Increased risk of iron toxicity in predisposed individuals (transfusions, hereditary hemochromatosis)
question
Vitamin D forms
answer
D2 ergocalciferol - ingested from plants D3 cholecalciferol - consumed in milk, formed in sun-exposed skin (stratum basale) 25-OH D3 storage form 1,25-(OH)2 D3 calcitriol active form
question
Vitamin D function
answer
Increases intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphate Increases bone mineralization at low Levels Increases bone resorption at higher levels
question
Vitamin D deficiency
answer
Rickets in children (deformity, genu varum) Osteomalacia in adults (bone pain and muscle weakness) Hypocalcemia tetany Breastfed infants should receive oral vitamin D Deficiency is exacerbated by low sun exposure, pigmented skin, prematurity
question
Vitamin D excess
answer
Hypercalcemia Hypercalciuria Loss of appetite Stupor Seen in granulomatous disease (high activation of vitamin D by epithelioid macrophages
question
Vitamin E (tocopherol/tocotrienol) function
answer
Antioxidant (protects RBCs and membranes from free radical damage) High-dose supplementation may alter metabolism of vitamin K -; enhanced anticoagulant effects of warfarin
question
Vitamin E (tocopherol/tocotrienol) deficiency
answer
Hemolytic anemia Acanthocytosis Muscle weakness Posterior column and spinocerebellar tract demyelination Neurologic presentation may appear similar to vitamin B12 deficiency, but without megaloblastic anemia, hypersegmented PMNs, or high serum methylmalonic acid levels
question
Vitamin K (phytomenadione, phylloquinone, phytonadione) function
answer
Activated by epoxide reductase to the reduced form Cofactor for the gamma-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues on various proteins required for blood clotting Synthesized by intestinal flora II, VII, IX, X, C, S Warfarin inhibits vitamin K-dependent synthesis of these factors and proteins
question
Vitamin K (phytomenadione, phylloquinone, phytonadione) deficiency
answer
Neonatal hemorrhage with high PT and aPTT normal bleeding time Neonates have sterile intestines and are unable to synthesize vitamin K Can also occur after prolonged use of broad-spectrum antibiotics Not in breast milk Neonates are given vitamin K injection at birth
question
Zinc function
answer
Activity of 100+ enzymes Formation of zinc fingers (transcription factor motif)
question
Zinc deficiency
answer
Delayed wound healing Hypogonadism Loss of adult hair (axillary, facial, pubic) Dysgeusia Anosmia Acrodermatitis enteropathica May predispose to alcoholic cirrhosis
question
Kwashiorkor
answer
Protein malnutrition Edema due to low plasma oncotic pressure Anemia Liver malfunction (fatty change due to low apolipoprotein synthesis) Skin lesions (hyperkeratosis/hyperpigmentation) Small child with swollen abdomen
question
Marasmus
answer
Malnutrition not causing edema Diet is deficient in calories but no nutrients are entirely absent Muscle wasting
question
Fomepizole
answer
Inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase Antidote for overdoses of methanol or ethylene glycol
question
Disulfiram
answer
Inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (acetaldhyde accumulates, contributing to hangover symptoms), discouraging drinking
question
Limiting factor in ethanol metabolism
answer
NAD+
question
Metabolic reactions only in mitochondria
answer
Fatty acid oxidation (b-oxidation) Acetyl-CoA production TCA cycle Oxidative phosphorylation Ketogenesis
question
Metabolic reactions only in cytoplasm
answer
Glycolysis HMP shunt Synthesis of steroids (SER), proteins (ribosomes, RER), fatty acids, cholesterol, nucleotides
question
Metabolic reactions in both mitochondria and cytoplasm
answer
Heme synthesis Urea cycle Gluconeogenesis
question
Rate-determining enzyme of glycolysis
answer
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) + AMP fructose-2,6-bisphosphate - ATP citrate
question
Rate-determining enzyme of gluconeogenesis
answer
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase + Citrate - AMP Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
question
Rate-determining enzyme of TCA cycle
answer
Isocitrate dehydrogenase + ADP - ATP NADH
question
Rate-determining enzyme of glycogenesis
answer
Glycogen synthase + Glucose-6-phosphate Insulin Cortisol - Epinephrine Glucagon
question
Rate-determining enzyme of glycogenolysis
answer
Glycogen phosphorylase + Epinephrine Glucagon AMP - Glucose-6-phosphate Insulin ATP
question
Rate-determining enzyme of HMP shunt
answer
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) + NADP+ - NADPH
question
Rate-determining enzyme of de novo pyrimidine synthesis
answer
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II + ATP PRPP - UTP
question
Rate-determining enzyme of de novo purine synthesis
answer
Glutamine-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) amidotransferase - AMP Inosine monophosphate (IMP) GMP
question
Rate-determining enzyme of urea cycle
answer
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I + N-acetylglutamate
question
Rate-determining enzyme of fatty acid synthesis
answer
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) + Insulin Citrate - Glucagon Palmitoyl-CoA
question
Rate-determining enzyme of fatty acid oxidation
answer
Carnitine acyltransferase I - Malonyl-CoA
question
Rate-determining enzyme of ketogenesis
answer
HMG-CoA synthase
question
Rate-determining enzyme of cholesterol synthesis
answer
HMG-CoA reductase + Insulin Thyroxine - Glucagon Cholesterol
question
ATP production number
answer
Aerobic 32 via malate-aspartate shuttle (heart and liver) 30 via glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle (muscle) Anaerobic 2 Arsenic 0
question
Carrier molecules and activated form
answer
ATP: Phosphoryl groups NADH, NADPH, FADH2: Electrons CoA, lipoamide: Acyl groups Biotin: CO2 Tetrahydrofolates: 1-carbon units S-adenosylmethionine (SAM): CH3 groups TPP: Aldehydes
question
Universal electron acceptors
answer
NAD+ NADP+ FAD+
question
NADPH
answer
Product of HMP shunt Used in Anabolic processes Respiratory burst Cytochrome P-450 system Glutathione reductase
question
Glycolysis net reaction
answer
Glucose + 2Pi + 2ADP + 2NAD+ -; 2pyruvate + 2ATP + 2NADH + 2H+ + 2H2O
question
ATP requiring reactions in glycolysis
answer
Glucose -; glucose-6-phosphate Hexokinase/glucokinase Glucose-6-P - hexokinase Fructose-6-P - glucokinase Fructose-6-P -; fructose-1,6-BP Phosphofructokinase-1
question
ATP producing reaction in glycolysis
answer
1,3-BPG 3-PG Phosphoglycerate kinase Phosphoenolpyruvate -; pyruvate Pyruvate kinase + Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate - ATP Alanine
question
Pyruvate dehydrogenase net reaction
answer
Pyruvate + NAD+ + CoA -; acetyl-CoA + CO2 + NADH + NAD+/NADH ratio ADP Ca2+ - ATP Acetyl-CoA NADH
question
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex cofactors
answer
Thiamine pyrohosphate (B1) Lipoic acid CoA (B5, pantothenic acid) FAD (B2, riboflavin) NAD+ (B3, niacin)
question
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency
answer
Build up of pyruvate shunted to lactate (LDH) and alanine (ALT) Neurologic defects Lactate acidosis High serum alanine starting in infancy Tx: increase intake of ketogenic nutrients (high fat or lysine and leucine)
question
Arsenic
answer
Inhibits lipoic acid Vomiting Rice-water stools Garlic breath QT prolongation
question
Number of ATP produced from NADH and FADH2
answer
NADH 2.5 FADH2 1.5
question
Electron transport inhibitor
answer
Decrease proton gradient Block ATP synthesis Rotenone complex1 Antimycin A complex3 Cyanide/CO complex4
question
ATP synthase inhibitor
answer
Increase proton gradient No ATP production Oligomycin
question
Uncoupling agent
answer
Increase permeability Decrease proton gradient Increase O2 consumption ATP synthesis stops Electron transport continues Produce heat 2,4-Dinitrophenol (weight loss) Aspirin Thermogenin (in brown fat)
question
Pyruvate carboxylase
answer
Pyruvate -; oxaloacetate Gluconeogenesis, irreversible enzyme In mitochondria Requires biotin, ATP Activated by acetyl-CoA
question
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
answer
Oxaloacetate -; phosphoenolpyruvate Gluconeogenesis, irreversible enzyme In cytosol Requires GTP
question
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
answer
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate -; fructose-6-phosphate Gluconeogenesis, irreversible enzyme In cytosol - Citrate + AMP Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
question
Glucose-6-phosphatase
answer
Glucose-6-phosphate -; glucose Gluconeogenesis, irreversible enzyme In ER
question
Gluconeogenesis
answer
Primarily in liver Not muscle (no glucose-6-phosphatase) Odd-chain fatty acids -; 1 propionyl-CoA, enter TCA as succinyl-CoA, gluconeogenesis Even-chain fatty acids -; acetyl-CoA equivalents, no gluconeogenesis
question
HMP shunt (pentose phosphate pathway)

answer
Source of NADPH Cytoplasm No ATP used or produced Lactating mammary glands Liver Adrenal cortex (fatty acid or steroid synthesis) RBCs
question
G6PD
answer
Hemolytic anemia Poor RBC defence against oxidizing agents (fava beans, sulfonamides, primaquine, antituberculosis drugs), infections, inflammatory response X-linked recessive Most common human enzyme deficiency More prevalent in African American Increase malarial resistance Heinz bodies (denatured hemoglobin) Bite cells
question
Essential fructosuria
answer
Defect in fructokinase Autosomal recessive Benign, asymptomatic Fructose not trapped in cells Fructose appears in blood and urine Disorders of fructose metabolism milder than galactose metabolism
question
Fructose intolerance
answer
Hereditary deficiency of aldolase B Autosomal recessive Fructose-1-phosphate accumulates -; decrease available phosphate -; inhibition of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis Follow eating fruit, juice, honey Urine dipstick -ve (glucose) Reducing sugar in urine Hypoglycemia Jaundice Cirrhosis Vomiting Tx: decrease intake of fructose and sucrose
question
Galactokinase deficiency
answer
Hereditary deficiency Galactitol accumulates (aldose reductase) Relatively mild Autosomal recessive Galactose in blood and urine Infantile cataracts Failure to track objects Develop a social smile
question
Classic galactosemia
answer
Absence of galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase Autosomal recessive Accumulation of toxic substances (galactitol in lens of eye) Symptoms develop when infant begins feeding Failure to thrive Jaundice Hepatomegaly Infantile cataracts Intellectual disability Predispose to E coli sepsis in neonates Tx: exclude galactose and lactose from diet The most serious defects lead to PO4 3- depletion
question
Sorbitol

answer
Alcohol counterpart of glucose Intracellular accumulation -; osmotic damage cataracts, retinopathy, peripheral neuropathy
question
Lactase deficiency
answer
Primary: absence of lactase-persistent allele, common in Asian, AA, Native American Secondary: loss of brush border due to gastroenteritis(rotavirus), autoimmune disease Congenital deficiency rare, due to defective gene Stool low pH, breath high hydrogen content Normal mucosa in hereditary lactose intolerance biopsy Bloating, cramps, flatulence, osmotic diarrhea Tx: avoid dairy, add lactase pills, lactose-free milk
question
Essential amino acids
answer
Glucogenic: Met, his, val Glucogenic/ketogenic: Ile, phe, thr, trp Ketogenic: Leu, Lys
question
Acidic amino acids
answer
Asp, glu
question
Basic amino acids
answer
His, lys, arg (most basic)
question
Hyperammonemia
answer
Acquired (liver disease) vs hereditary (urea cycle enzyme deficiencies) Excess NH3, deplets a-ketoglutarate -; inhibition of TCA Tx: limit protein Lactulose Abx (rifaximin) Benzoate, phenylactate, phenylbutyrate react with glycine or glutamine, forming products renally excreted Tremor(asterixis) Slurring of speech Somnolence Vomiting Cerebral edema Blurring vision
question
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency
answer
Most common urea cycle disorder X-linked recessive (other urea cycle enzyme deficiencies are autosomal recessive) First few days of life, may present later Excess carbamoyl phosphate converted to orotic acid High orotic acid in blood and urine Low BUN Hyperammonemia symptoms No megaloblastic anemia (vs orotic aciduria)
question
Phenylketonuria
answer
Low phenylalanine hydroxylase or tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) cofactor (malignant PKU) Excess phenyl ketones in urine Intellectual disability Growth retardation Seizures Fair skin Eczema Musty body odor Tx: low phenylalanine and high tyrosine diet, BH4 supplementation Autosomal recessive, 1:10,000 Screening 2-3days after birth (normal at birth from maternal enzyme) Phenyl ketones - phenylacetate, phenyllactate, phenylpyruvate Disorder of aromatic amino acid metabolism -; musty body odor Must avoid aspartame (contains phenylalanine)
question
Maternal PKU
answer
lack of dietary therapy Microcephaly Intellectual disability Growth retardation Congenital heart defects
question
Maple syrup urine disease
answer
Blocked degradation of branched amino acids: Isoleucine, leucine, valine Low branched-chain a-ketoacid dehydrogenase (B1) High a-ketoacids in blood, esp leucine Severe CNS defects Intellectual disability Death Tx: restriction isoleucine, leucine, valine Thiamine supplementation Autosomal recessive Vomiting, poor feeding, maple syrup/burnt sugar smell urine
question
Alkaptonuria
answer
Homogentisate oxidase deficiency Degradation pathway of tyrosine to fumarate Pigment-forming homogenetisic acid accumulates in tissue Autosomal recessive Usually benign Bluish-black connective tissue, ear cartilage, and sclerae (ochronosis) Urine turns black on prolonged exposure to air Debilitating arthralgias (homogentisic acid toxic to cartilage)
question
Homocystinuria
answer
All autosomal recessive Cystathionine synthase deficiency (Tx: low methionine, high cysteine, B6, B12, folate diet) Decreased affinity of cystathionine synthase for pyridoxal phosphate (Tx: high B6 and cysteine diet) Methionine synthase (homocysteine methyltransferase) deficiency (Tx: high methionine diet) All forms -; excess homocysteine High homocysteine in urine Osteoporosis Marfanoid habitus Ocular change (down and inward lens subluxation) Cardiovascular effects (thrombosis and atherosclerosis -; CVA and MI) Kyphosis Intellectual disability
question
Cystinuria
answer
Defect of renal PCT and intestinal amino acid transporter Prevents reabsorption of cystine, ornithine, lysine, arginine Excess cystine in urine Recurrent hexagonal cystine stones Tx: alkalinization (K citrate, acetazolamide), chelating agents (penicillamine) increase solubility of cystine stones, good hydration Autosomal recessive 1:7000 Dx: urinary cyanide-nitroprusside test Cystine = 2 cystines with disulfide bond
question
Glycogen storage diseases
answer
12 types PAS identifies glycogen I, II, III, V are autosomal recessive
question
Von Gierke disease
answer
Type I glycogen storage disease (AR) Glucose-6-phosphate deficiency Impaired gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis Severe fasting hypoglycemia High glycogen in liver High blood lactate High triglycerides High uric acid (gout) Hepatomegaly
question
Pompe disease
answer
Type II glycogen storage disease (AR) Lysosomal acid a-1,4-glucosidase with a-1,6-glucosidase activity (acid maltase) deficiency Cardiomegaly Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Hypotonia Exercise intolerance Systemic findings lead to early death (heart, liver, muscle)
question
Cori disease
answer
Type III glycogen storage disease (AR) Debranching enzyme (a-1,6-glucosidase) deficiency Gluconeogenesis is intact Milder form of von Gierke (type I) with normal blood lactate levels Accumulation of limit dextrin-like structures in cytosol
question
McArdle disease
answer
Type V glycogen storage disease (AR) Skeletal muscle glycogen phosphorylase (myophosphorylase) deficiency Blood glucose levels typically unaffected High glycogen in muscle, but unable to break down Painful muscle cramps Myoglobinuria (red urine) with strenuous exercise Arrhythmia from electrolyte abnormalities Second-wind phenomenon during exercise due to increased muscular blood flow
question
Lysosomal storage diseases
answer
Sphingolipidoses: Tay-Sachs disease Fabry disease Metachromatic leukodystrophy Krabbe disease Gaucher disease Niemann-Pick disease Mucopolysaccharidoses: Hurler syndrome Hunter syndrome High incidence of Tay-Sachs, Neimann-Pick, and some forms of Gaucher disease in Ashkenazi Jews
question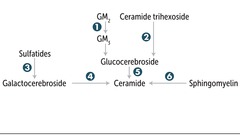
Lysosomal storage pathway

answer
1. Hexosaminidase A 2. a-galactosidase A 3. Arylsulfatase A 4. Galactocerebrosidase 5. Glucocerebrosidase (b-glucosidase) 6. Sphingomyelinase
question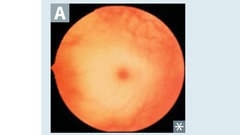
Tay-Sachs disease

answer
Lysosomal storage disease Sphingolipidoses Autosomal recessive Hexosaminidase A deficiency GM2 ganglioside accumulation Progressive neurodegeneration Developmental delay Cherry-red spot on macula Lysosomes with onion skin No hepatosplenomegaly (vs Niemann-Pick)
question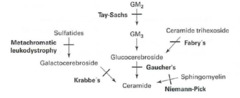
Fabry disease

answer
Lysosomal storage disease Sphingolipidoses X-linked recessive a-galactosidase A deficiency Ceramide trihexoside accumulation Early: triad of episodic peripheral neuropathy, angiokeratomas, hypohidrosis Late: progressive renal failure, cardiovascular disease
question
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
answer
Lysosomal storage disease Sphingolipidoses Autosomal recessive Arylsulfatase A deficiency Cerebroside sulfate accumulation Central and peripheral demyelination with ataxia, dementia
question
Krabbe disease
answer
Lysosomal storage disease Sphingolipidoses Autosomal recessive Galactocerebrosidase deficiency Galactocerebroside, psychosine accumulation Peripheral neuropathy Destruction of oligodendrocytes Developmental delay Optic atrophy Globoid cells
question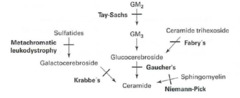
Gaucher disease

answer
Most common lysosomal storage disease Sphingolipidoses Autosomal recessive Glucocerebrosidase (b-glucosidase) deficiency Glucocerebroside accumulation Hepatosplenomegaly Pancytopenia Osteoporosis Avascular necrosis of femur Bone crises Gaucher cells (lipid-laden macrophages resembling crumpled tissue paper Tx: recombinant glucocerebrosidase
question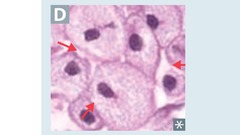
Niemann-Pick disease

answer
Lysosomal storage disease Sphingolipidoses Autosomal recessive Sphingomyelinase deficiency Sphingomyelin accumulation Progressive neurodegeneration Hepatosplenomegaly Foam cells (lipid-laden macrophages) Cherry-red spot on macula
question
Hurler syndrome
answer
Lysosomal storage disease Mucopolysaccharidoses Autosomal recessive a-L-iduronidase deficiency Heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate accumulation Developmental delay Gargoylism Airway obstruction Corneal clouding Hepatosplenomegaly
question
Hunter syndrome
answer
Lysosomal storage disease Mucopolysaccharidoses X-linked recessive Iduronate sulfatase deficiency Heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate accumulation Milder Hurler + aggressive behavior, no corneal clouding
question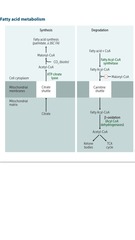
Fatty acid metabolism

answer
Synthesis predominantly occurs in liver, lactating mammary glands, and adipose tissue
question
Systemic 1' carnitine deficiency
answer
Inherited defect in transport of LCFAs into mitochondria -> toxic accumulation Weakness Hypotonia Hypoketotic hypoglycemia
question
Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
answer
Decreased ability to break down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA -> accumulation of fatty acyl carnitines in blood with hypoketotic hypoglycemia Vomiting Lethargy Seizures Coma Liver dysfunction Sudden death in infants or children Tx: avoiding fasting
question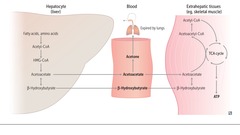
Ketone bodies

answer
Acetone, acetoacetate, b-hydroxybutyrate Urine test for ketones can detect acetoacetate, but not b-hydroxybutyrate Prolonged starvation, DKA -> oxaloacetate depleted for gluconeogenesis Alcoholism, excess NADH shunts oxaloacetate to malware Buildup of acetyl-CoA, shunts glucose and FFA to ketone bodies
question
Fed state
answer
Glycolysis and aerobic respiration Insulin stimulate storage of lipids, proteins, glycogen
question
Fasting between meals
answer
Hepatic glycogenolysis (major) Hepatic gluconeogenesis Adipose release of FFA (minor) Glucagon and epinephrine stimulate use of fuel reserves
question
Starvation 1-3 days
answer
Blood glucose levels maintained by: Hepatic glycogenolysis Adipose release of FFA Muscle and liver, shift fuel use from glucose to FFA Hepatic gluconeogenesis from peripheral tissue lactate and alanine, from adipose tissue glycerol and propionyl-CoA (odd-chain FA) Glycogen reserves depleted after day 1 RBCs lack mitochondria, cannot use ketones
question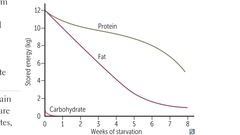
Starvation after day 3

answer
Adipose stores (ketone bodies become main source of energy for brain) After depletion, vital protein degradation accelerates -> organ failure and death Amount of excess stores determines survival time
question
Pancreatic lipase
answer
Degradation of dietary triglycerides in small intestine
question
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
answer
Degradation of triglycerides circulating in chylomicrons and VLDLs Found on vascular endothelial surface
question
Hepatic triglyceride lipase (HL)
answer
Degradation of triglycerides remaining in IDL
question
Hormone-sensitive lipase
answer
Degradation of triglycerides stored in adipocytes
question
LCAT
answer
Catalyzes esterification of 2/3 of plasma cholesterol
question
Cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP)
answer
Mediated transfer of cholesterol esters to other lipoprotein particles
question
Lipoprotein functions
answer
Lipoproteins are composed of varying proportions of cholestrol, TGs, and phospholipids LDL and HDL carry the most cholesterol LDL transports cholesterol from liver to tissues HDL transports cholesterol from periphery to liver
question
Cholesterol
answer
Needed to maintain cell membrane integrity and synthesize bile acid, steroids, and vitamin D
question
Chylomicron
answer
Delivers dietary TGs to peripheral tissues Delivers cholesterol to liver in the form of chylomicron remnants, which are mostly depleted of their TGs Secreted by intestinal epithelial cells
question
VLDL
answer
Delivers hepatic TGs to peripheral tissue Secreted by liver
question
IDL
answer
Formed in the degradation of VLDL Delivers TGs and cholesterol to liver
question
LDL
answer
Delivers hepatic cholesterol to peripheral tissues Formed by hepatic lipase modification of IDL in the liver and peripheral tissue Taken up by target cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis
question
HDL
answer
Mediates reverse cholesterol transport from periphery to liver Acts as a repository for apolipoproteins C and E (which are needed for chylomicron and VLDL metabolism Secreted from both liver and intestine Alcohol increases synthesis
question
Abetalipoproteinemia
answer
Autosomal recessive Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL absent Deficiency in ApoB48, ApoB100 Affected infants present with severe fat malabsorption, steatorrhea, failure to thrive Later manifestations include retinitis pigmentosa, spinocerebellar degeneration due to vitamin E deficiency, progressive ataxia, acanthocytosis Tx: restriction of long-chain fatty acids, large doses of oral vitamin E
question
Type I hyperchylomicronemia
answer
Autosomal recessive Lipoprotein lipase or apolipoprotein C-II deficiency High blood levels of chylomicrons, TG, cholesterol Pancreatitis Hepatosplenomegaly Eruptive/pruritic xanthomas (no increased risk for atherosclerosis) Creamy layer in supernatant
question
Type II familial hypercholesterolemia
answer
Autosomal dominant Absent or defective LDL receptors High blood levels of LDL, cholesterol (IIa) or LDL, cholesterol, VLDL (IIb) Heterozygotes (1:500) have cholesterol 300mg/dL Homozygotes (very rare) have cholesterol 700+ mg/dL Accelerated atherosclerosis (may have MI before 20ya) Tendon (Achilles) xanthomas Corneal arcus
question
Type III dysbetalipoproteinemia
answer
Autosomal recessive Defective ApoE High blood level of chylomicrons, VLDL Premature atherosclerosis Tuberoeruptive xanthomas Xanthoma striatum palmare
question
Type IV hypertriglyceridemia
answer
Autosomal dominant Hepatic overproduction of VLDL High blood levels of VLDL, TG Hypertriglyceridemia >1000 mg/dL can cause pancreatitis



