Unit 5 – Hydrology and Oceanography – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Biotic Index

answer
A (1-10) scale that gives a measure of the quality of an ecosystem by the presence and abundance of species living in it; Involves levels of tolerance, diversity and abundance of organisms
question
River Basin
answer
The entire geographical area drained by a river and its tributaries
question
Headwaters
answer
The source of a river (A)
question
Tributary
answer
A stream or river that flows into a larger river
question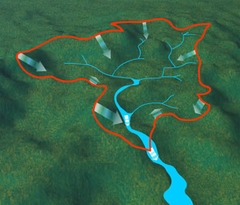
Drainage Basin

answer
the area from which a single stream or river and its tributaries drains all of the water
question
Channal
answer
The bed of a stream or river
question
Gradient

answer
a rate of inclination; a slope
question
Sediment

answer
Small particles of dirt, rock, and sand suspended in water
question
Streams

answer
any body of flowing water confined within a channel, regardless of size
question
Alluvial Fan

answer
A fan-shaped deposit of sediment formed when a stream's slope is abruptly reduced
question
Floodplain
answer
A low plain adjacent to a river that is formed chiefly of river sediment and is subject to flooding
question
Levee
answer
A wall built along a river bank to prevent flooding
question
Meander

answer
A looplike bend in the course of a river
question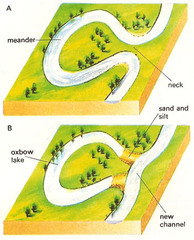
Oxbow Lake

answer
A crescent-shaped lake (often temporary) that is formed when a meander of a river is cut off from the main channel
question
Fall line
answer
An area along which rivers form waterfalls or rapids as the rivers drop to lower land.
question
Wetland
answer
A land area that is covered with a shallow layer of water during some or all of the year
question
Marsh
answer
Sea of reeds
question
Swamp
answer
An area of low, spongy land too wet to farm but usually supporting an abundance of coarse grasses, trees, or other vegetation.
question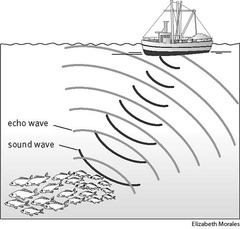
Sonar

answer
A device that determines the distance of an object under water by recording echoes of sound waves
question
Oceanography
answer
Study of the Ocean
question
Continental Margin
answer
boundary between continental land deep ocean basins
question
Ocean Basin
answer
The deepest part of the ocean floor; made up of rolling hills and flat plains.
question
Ocean Shelf
answer
this gently sloping plain forms an apron of shallow water along the edge of most continents
question
Continental Slope
answer
a steep incline of the ocean floor leading down from the edge of the continental shelf
question
Continental Rise
answer
the gently sloping surface at the base of the continental slope
question
Mid- Ocean Ridge
answer
An underwater mountain chain where new ocean floor is formed
question
Abyssal Plain
answer
A large, flat, almost level area of the deep-ocean basin
question
Ocean Trench
answer
Deep valley in the ocean floor that forms along a subduction zone
question
Rift Valley
answer
A deep valley that forms where two plates move apart
question
Seamount
answer
A mountain on the ocean floor that is completely underwater
question
Guyot
answer
A large, flat-topped seamount resulting from erosion of an island volcano when it was above sea level.
question
Traditional Aquaculture
answer
Rapid development and expansion of intensive aquaculture for species such as salmon and shrimp has, for example, resulted in widespread degradation of the environment and the displacement of coastal fishing and farming communities.
question
Sustainable Aquaculture
answer
Dynamic concept and the sustainability of an aquaculture system depends on environmental impacts, economic impacts, and community practices.
question
Thermocline
answer
In water, a distinctive temperature transition zone that separates an upper layer that is mixed by wind and a colder, deep layer that is not mixed
question
pH scale
answer
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14
question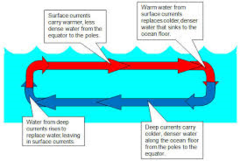
Surface Current

answer
A horizontal movement of ocean water that is caused by wind and that occurs at or near the ocean's surface
question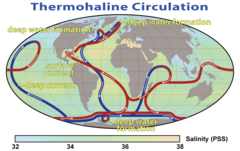
Thermohaline

answer
an oceanic circulation pattern that drives the mixing of surface water and deep water
question
Coriolis Effect

answer
The apparent curving of the path of a moving object from an otherwise straight path due to the earth's rotation
question
Crest
answer
Highest point of a wave
question
Trough
answer
Lowest point of a wave
question
Fetch
answer
The distance that the wind has traveled across open water
question
Refraction
answer
Change in direction of a wave when it changes speed as in travels from one material to another.
question
Undertow

answer
a subsurface current that is near shore and that pulls objects out to sea
question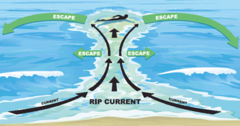
Rip Current

answer
A rush of water that flows rapidly back to sea through a narrow opening
question
Shoreline Stabilization
answer
Shorelines are dynamic interfaces, constantly undergoing erosion and sediment deposition
question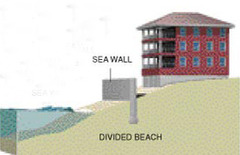
Artificial Stabilization

answer
implementing man made methods or structures to stop or slow the erosion of beaches
question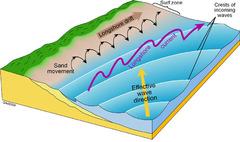
Longshore Current

answer
A water current that travels near and parallel to the shoreline
question
Turbulence

answer
A type of movement of water in which, rather than moving downstream, the water moves every which way.
question
Sea Arch
answer
an arch formed by wave erosion when caves on opposite sides of a headland unite
question
Tombolo
answer
A ridge of sand that connects an island to the mainland or to another island
question
Sandbar

answer
A ridge of sand deposited by waves as they slow down near shore.
question
Groin

answer
A wall made of rocks or concrete that is built outward from a beach to reduce erosion
question
Jetty

answer
A structure that projects into the water and protects the shore
question
Seawall

answer
a barrier constructed to prevent waves from reaching the area behind the wall. Its purpose is to defend property from the force of breaking waves.
question
Artesian Well
answer
A pressurized groundwater system, including an impermeable base layer, and a cap rock.
question
Divide

answer
A high land area that separates one watershed from another.
question
Eutrophication
answer
Process by which lakes becomes rich in nutrients from the surrounding watershed, resulting in a change in the kinds of organisms in the lake.
question
Rejuvenation
answer
When a stream actively resumes the process of down-cutting toward its base level.
question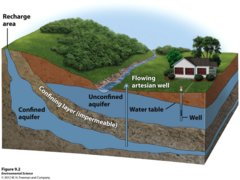
Aquifer

answer
Permeable underground layer through which groundwater flows relatively easily.
question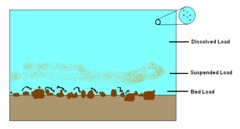
Bed Load

answer
Describes sediments that are too heavy or large to be kept in suspension or solution and are pushed or rolled along the bottom of a stream bed.
question
Delta
answer
Triangular deposit, usually made up of silt and clay particles, that forms where a stream enters a large body of water.
question
Discharge
answer
Measure of a volume of stream water that flows over a specific location in a particular amount of time.
question
Flood Plain
answer
Broad, flat, fertile area extending out from a stream's bank that is covered with water during floods.
question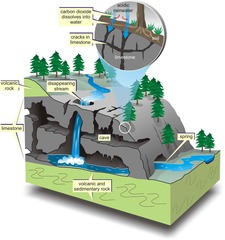
Karst Topography

answer
Irregular topography with sinkholes, sinks, and sinking streams caused by groundwater dissolution of limestone.
question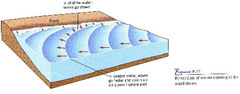
Wave Refraction

answer
A difference in wave speed causes initially straight wave crests to bend when part of the crest moves into shallow water
question
Barrier Island

answer
Long ridge of sand or other sediment deposited or shaped by longshore currents that is separated from the mainland and can be up to tens of kilometers long.
question
Density Current
answer
Movement of ocean water that occurs in depths too great to be affected by surface winds and is generated by differences in water temperature and salinity.
question
Estuary
answer
Coastal area of brackish water formed where the lower end of a freshwater river or stream enters the ocean; provides an excellent source of food and shelter to commercially important marine organisms.
question
Salinity

answer
Measure of the amount salts dissolved in seawater, which is 35 ppt on average.
question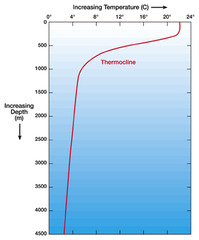
Temperature Profile

answer
Plots changing ocean water temperatures with depth, which varies, depending on location and season.
question
Tide
answer
Rapidly flowing ocean current that can cut deep-sea canyons in continental slopes and deposit the sediments in the form of continental rise.
question
Hydrologic Cycle
answer
The continuous circulation of water among the atmosphere, the oceans, and the earth.
question
Evaporation
answer
Liquid to gas
question
Transpiration
answer
the emission of water vapor from the leaves of plants
question
Condensation
answer
Gas to Liquid
question
Precipitation

answer
Condensed droplets of water that fall to the Earth as snow, rain, sleet or hail.
question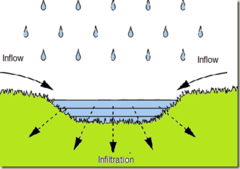
Infiltration

answer
Flow of water from the land surface into the subsurface.
question
Groundwater

answer
water that fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers
question
Lithosphere
answer
A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust.
question
Aquifer Depletion
answer
removal of groundwater more rapidly than it can be recharged by precipitation or melting snow
question
Watershed
answer
An area of land that drains into a river or lake.
question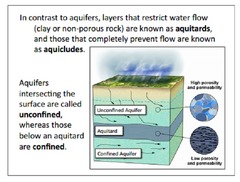
Aquitard

answer
A slab of impervious surface at the bottom of an aquifer that does not allow water to go through
question
Porosity
answer
The percentage of the total volume of a rock or sediment that consists of open spaces.
question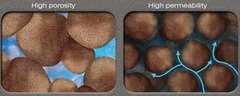
Permeability

answer
Ability of rock or soil to allow water to flow through it
question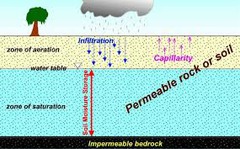
Zone of Aeration

answer
Region above the water table where materials are moist, but pores contain mostly air.
question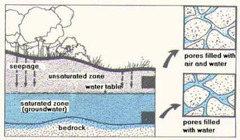
Zone of Saturation

answer
Region below Earth's surface where all the pores of a material are completely filled with groundwater.
question
Capillary Fringe
answer
region above the water table with water drawn up by capillary action
question
Water Table
answer
The upper level of the saturated zone of groundwater
question
Springs
answer
A natural source of water formed when water from an aquifer percolates up to the ground surface.
question
Geyser

answer
A fountain of water and steam that builds up pressure underground and erupts at regular intervals.
question
Water Treatment
answer
The process of purifying water to make it suitable for consumption and utilization
question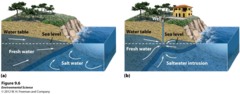
Saltwater Intrusion

answer
Movement of salt water into freshwater aquifers in coastal and inland areas as groundwater is withdrawn faster than it is recharged by precipitation.
question
Subsidence

answer
A depression of the land surface as a result of groundwater being pumped. Cracks and fissures can appear in the land. Subsidence is virtually an irreversible process.
question
Breakwater

answer
A structure protecting a nearshore area from breaking waves.
question
Beach Nourishment

answer
The process by which large quantities of sand are added to the beach system to offset losses caused by wave erosion.
question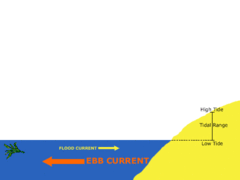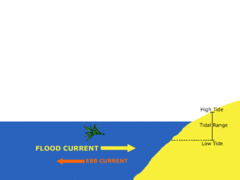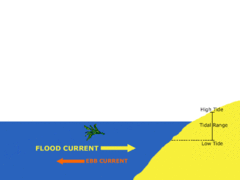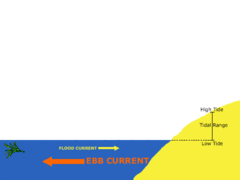
Ebb

answer
Movement of water out at sea (or tide)
question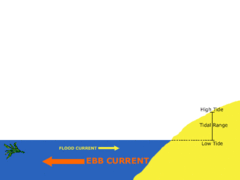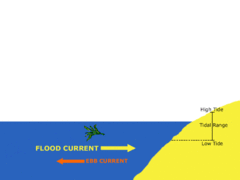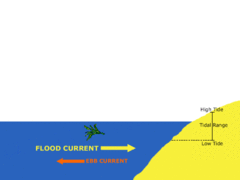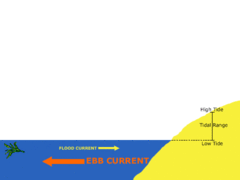
Flow

answer
Movement of water in (rising tide)
question
Tidal Range
answer
The difference in levels of ocean water at high tide and low tide
question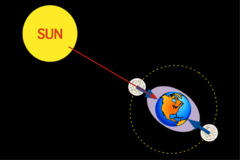
Spring Tide

answer
When the tidal range is greatest. (full moon and new moon)
question
Neap Tide
answer
A tide with the least difference between consecutive low and high tides.
question
Waning
answer
(of the moon) pertaining to the period during which the visible surface of the moon decreases
question
Waxing

answer
(of the moon) pertaining to the period during which the visible surface of the moon increases
question
Gibbous
answer
Moon phase in which more than half of the Moon appears to be illuminated.
question
Crescent
answer
Moon phase in which less than half of the Moon appears to be illuminated.



