U. S. Constitution – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Great Compromise
answer
1787; This compromise was between the large and small states of the colonies. The Great Compromise resolved that there would be representation by population in the House of Representatives, and equal representation would exist in the Senate. Each state, regardless of size, would have 2 senators. All tax bills and revenues would originate in the House. This compromise combined the needs of both large and small states and formed a fair and sensible resolution to their problems.
question
3/5 Compromise
answer
3/5th of the slaves would be counted as people in representation
question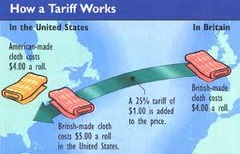
Commerce Compromise

answer
The issue over whether congress could regulate trade, Northern States said they could, The Southern States said they couldn't, The outcome was that Congress could regulate trade, No export tax, and No limit on slave trade for 20 years
question
New Jersey Plan

answer
Opposite of the Virginia Plan, it proposed a single-chamber congress in which each state had one vote. This created a conflict with representation between bigger states, who wanted control befitting their population, and smaller states, who didn't want to be bullied by larger states.
question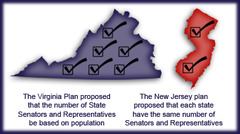
Virginia Plan

answer
"Large state" proposal for the new constitution, calling for proportional representation in both houses of a bicameral Congress. The plan favored larger states and thus prompted smaller states to come back with their own plan for apportioning representation.
question
Shay's Rebellion

answer
To pay off its Revolutionary War debt, Massachusetts imposed high taxes. Many of the farmers went into debt and lost their homes, farms, and land. Many even went to jail. The money they were paid in from the Revolutionary War was practically worthless. Daniel Shays began training farmers and led them in a rebellion. They attacked courts so that they couldn't foreclose any more property. They stormed the federal arsenal in Springfield but the state militia barely defeated them. The rebellion convinced Congress that the Articles of Confederation weren't powerful enough and that there had to be a different government.
question
Articles of Confederation

answer
Adopted in 1777 during the Revolutionary War, the Articles established the United States of America. The Articles granted limited powers to the central government, reserving most powers for the states. The result was a poorly defined national state that couldn't govern the country's finances or maintain stability. The Constitution replaced them in 1789
question
Federalist
answer
Supporters of the Constitution that were led by Alexander Hamilton and John Adams. They firmly believed the national government should be strong. They didn't want the Bill of Rights because they felt citizens' rights were already well protected by the Constitution.
question
Antifederalist

answer
They opposed the ratification of the Constitution because it gave more power to the federal government and less to the states, and because it did not ensure individual rights. Many wanted to keep the Articles of Confederation. The Antifederalists were instrumental in obtaining passage of the Bill of Rights as a prerequisite to ratification of the Constitution in several states. After the ratification of the Constitution, the Antifederalists regrouped as the Democratic-Republican (or simply Republican) party.
question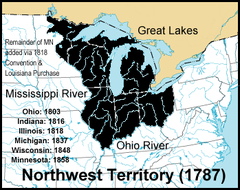
Northwest Territory

answer
Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio and Wisconsin, needed a population of 60,000 to ask the US to join the state. Slavery was banned in these areas and public schooling must be provided.
question
Northwest Ordinance of 1787

answer
Created the Northwest Territory (area north of the Ohio River and west of Pennsylvania), established conditions for self-government and statehood, included a Bill of Rights, and permanently prohibited slavery
question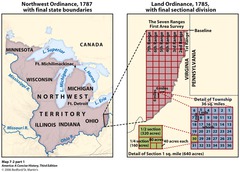
Land Ordinance of 1785

answer
A law that divided much of the United States into a system of townships to facilitate the sale of land to settlers.
question
John Locke
answer
17th century English philosopher who opposed the Divine Right of Kings and who asserted that people have a natural right to life, liberty, and property.
question
Magna Carta
answer
1215 document that listed the rights of English citizens and limited the power of the English monarch. Rights included trial by jury, no taxation without representation, protection of the law, and habeas corpus
question
English Bill of Rights
answer
King William and Queen Mary accepted this document in 1689. It guaranteed certain rights to English citizens and declared that elections for Parliament would happen frequently. By accepting this document, they supported a limited monarchy, a system in which they shared their power with Parliament and the people.
question
Mayflower Compact

answer
This document was drafted in 1620 prior to settlement by the Pilgrims at Plymouth Bay in Massachusetts. It declared that the 41 males who signed it agreed to accept majority rule and participate in a government in the best interest of all members of the colony. This agreement set the precedent for later documents outlining commonwealth rule.
question
What documents did Americans look to when creating a new government?
answer
Magna Carta, English Bill of Rights, Mayflower Compact, Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, Declaration of Independence, state constitutions, Virginia Statute of Religious Freedom
question
Describe three key ideas from these documents that influenced U.S. government
answer
rule of law, people hold the power, limited government, constitutional protection of rights, separation of powers, representative government, separation of church and state
question
Why do you think that the Committee of Thirteen did not provide for a president in the Articles of Confederation?
answer
feared a president might become as powerful as a monarch. Abuse of power by a single individual.
question
Under the Articles of Confederation, how did the power of the national government compare to that of the state governments?
answer
The state governments held most of the power, even being able to refuse requests from Congress.
question
What was the purpose of the Land Ordinance of 1785?
answer
to set up a system for surveying and dividing western public lands
question
What important rights did the Northwest Ordinance of 1787 provide?
answer
civil liberties, public education; freedom from slavery
question
How did the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation affect U.S. relations with other nations?
answer
The United States appeared weak because it had no army to enforce treaties or to give it a position of power in negotiations.
question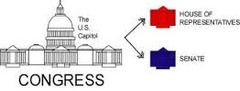
bicameral

answer
A legislature consisting of two parts, or houses
question
Bill of Rights
answer
A formal statement of the fundamental rights of the people of the United States, incorporated in the Constitution as Amendments 1-10, and in all state constitutions.
question
cabinet
answer
Advisory council for the president consisting of the heads of the executive departments, the vice president, and a few other officials selected by the president.
question
checks and balances

answer
A major principle of the American system of government. Helps maintain separation of powers so that no one branch gets too powerful. Explained in Federalist 51. Examples: President vetos laws; Senate confirms appointments & treaties; Congress impeaches president & judges...
question
Commerce Compromise

answer
Resolved differences between northern and southern states; Congress could not tax exports nor ban the slave trade for 20 yrs.
question
compromise

answer
a settlement of differences in which each side gives up something
question
Constitution

answer
A document which spells out the principles by which a government runs and the fundamental laws that govern a society
question
democracy

answer
A political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them
question
double jeopardy

answer
Trial or punishment for the same crime by the same government; forbidden by the Constitution.
question
due process

answer
Fair treatment through the judicial system: The right to a fair and speedy trial judged by an impartial jury of one's peers.
question
Elastic clause

answer
Article I, Section 8, of the Constitution, which allows Congress to make all laws that are "necessary and proper" to carry out the powers of the Constitution.
question
electoral college
answer
A certain number of electors from each state proportional to and seemingly representative of that state's population. each elector chooses a candidate believing they are representing their constituency's choice. The candidate who receives a higher proportion of electoral votes within a state receives all the electoral votes for that state.
question
eminent domain

answer
Allows the govt to take property for public use but also requires the govt to provide just compensation for that property
question
executive branch

answer
the branch of government charged with the execution and enforcement of laws and policies and the administration of public affairs
question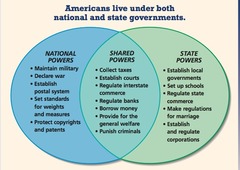
federalism

answer
A system in which power is divided between the national and state governments
question
habeas corpus

answer
Constitutional protection against unlawful imprisonment
question
impeach

answer
To accuse government officials of misconduct in office
question
indict

answer
To formally accuse of criminal activity
question
Marbury v. Madison

answer
(1803) Marbury was a midnight appointee of the Adams administration and sued Madison for commission. Chief Justice Marshall said the law that gave the courts the power to rule over this issue was unconstitutional. established judicial review
question
judicial branch

answer
Branch of government that decides if laws are carried out fairly.
question
judicial review

answer
Review by a court of law of actions of a government official or entity or of some other legally appointed person or body or the review by an appellate court of the decision of a trial court
question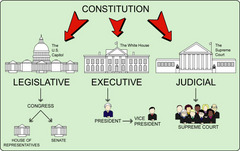
legislative branch

answer
Branch of government that passes laws
question
loose construction

answer
belief that the government can do anything that the constitution does not prohibit
question
pardon

answer
A declaration of forgiveness and freedom from punishment
question
petition

answer
A formal message requesting something that is submitted to an authority
question
popular sovereignty
answer
A government in which the people rule by their own consent.
question
preamble

answer
An introduction to a speech or piece of writing
question
precedent

answer
(n.) an example that may serve as a basis for imitation or later action
question
quartering
answer
1765 - Required the colonials to provide food, lodging, and supplies for the British troops in the colonies.
question
ratification
answer
Formal approval
question
republic
answer
A form of government in which citizens choose their leaders by voting
question
responsibilities
answer
duties owed by citizens to their government and other citizens
question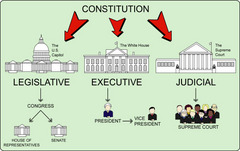
separation of powers

answer
Constitutional division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with the legislative branch making law, the executive applying and enforcing the law, and the judiciary interpreting the law
question
strict construction

answer
way of interpreting the Constitution that allows the federal government to take only those actions the Constitution specifically says it can take
question
unconstitutional
answer
Contrary to what is permitted by the constitution
question
veto
answer
Chief executive's power to reject a bill passed by a legislature
question
writs of assistance

answer
Search warrants issued by the British government. They allowed officials to search houses and ships for smuggled goods, and to enlist colonials to help them search. The writs could be used anywhere, anytime, as often as desired. The officials did not need to prove that there was reasonable cause to believe that the person subject to the search had committed a crime or might have possession of contraband before getting a writ or searching a house. The writs were protested by the colonies.
question
Concurrent powers
answer
Powers held jointly by the national and state governments.
question
Reserved powers
answer
Powers not specifically granted to the federal government or denied to the states belong to the states and the people
question
Delegated Powers
answer
Powers specifically given to the federal government by the US Constitution, for example, the authority to print money.
question
Duties and Responsibilities of citizens
answer
obey laws pay taxes attend school serve in court defend nation vote be informed volunteer respect others
question
What were some issues that divided delegates at the Constitutional Convention?
answer
how much to change the Articles and differing ideas about representation, how strong to make the government, economic concerns such as tariffs, and issues such as slavery
question
How did the Great Compromise combine elements of the Virginia and New Jersey Plans?
answer
bicameral legislature, representation in lower house based on population (Virginia Plan); representation in upper house equal (New Jersey Plan)
question
How did regional differences and the issue of slavery divide the Constitutional Convention?
answer
Southern delegates wanted slaves to be counted as part of state populations, which would give southern states more power; Northerners disagreed, because northern states had fewer slaves.
question
How did the Three-Fifths Compromise resolve the debate over slavery and population?
answer
Delegates agreed to count each slave as three-fifths of a person when determining representation.
question
Why did the delegates agree to allow the international slave trade to continue for another 20 years?
answer
to appease southern delegates and to give southern economies, which were dependent on the international slave trade, time to adjust to its end
question
What is the main responsibility of each branch of government?
answer
legislative—proposing and passing laws; executive—making sure laws are carried out; judicial—interpreting laws
question
How did the framers put into practice the idea of popular sovereignty expressed in the Declaration of Independence?
answer
established a system of federalism, in which government power is shared between the states and the federal government and in which states are required to protect the welfare of citizens
question
What were the Federalists' main arguments in favor of the Constitution?
answer
that the Constitution offered a good balance of power and was a careful compromise between various political views
question
What were the Antifederalists' main fears regarding the Constitution?
answer
that it would create a government as tyrannical as that of Britain's and fail to protect Americans' individual rights
question
Who were the main authors of the Federalist Papers?
answer
Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, John Jay
question
What fears did the Federalist Papers address?
answer
that the federal government would overpower the states; that one group would dominate the government
question
How are amendments added to the Constitution?
answer
Proposed amendments must be approved by a two-thirds majority of both houses of Congress and then ratified by threefourths of the states before taking effect.
question
What is federalism?
answer
a government system that divides powers between the states and the federal government
question
How do delegated, reserved, and concurrent powers differs?
answer
delegated—powers granted to the federal government; reserved—powers kept by the states; concurrent—powers shared by state and federal governments
question
How does the system of checks and balances make it difficult for Congress to pass a law that the president opposes?
answer
Congress must achieve a two-thirds majority vote to override a presidential veto
question
What are the requirements to serve as president?
answer
native-born U.S. citizen at least 35 years old and a U.S. resident for at least 14 years
question
Why are federal judges appointed for life?
answer
to keep them free of political party influence
question
What check does the judicial branch have over the legislative branch?
answer
It can declare a law to be unconstitutional.
question
Why is the Bill of Rights' protection of individual liberties important?
answer
to safeguard the rights of all Americans, not just the majority
question
How does the First Amendment separate church and state?
answer
It keeps the government from supporting or interfering with the practice of a religion or from favoring one religion over another
question
How does a search warrant protect Americans and their property?
answer
It prevents authorities from searching someone's home or property without permission.
question
What basic right does the Second Amendment protect?
answer
The right to bear arms.
question
How does the Sixth Amendment protect Americans in a court of law?
answer
guarantees a speedy public trial, the right to know the charges against them, the right to question witnesses, and the right to an attorney
question
In what ways has the Supreme Court influenced the way states carry out the death penalty?
answer
The Court ruled that although execution itself is not cruel and unusual, some methods of carrying out the death penalty are either cruel and unusual or unfair.
question
What are the differences between naturalized and native-born U.S. citizens?
answer
Naturalized citizens can lose their citizenship and cannot become president or vice president.
question
CHECKS & BALANCES CASE STUDY 1: President Obama appoints his cousin to the Supreme Court in order to persuade the court to support and uphold a challenge to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) (Obamacare). What ways can the Legislative Branch and the Judicial Branch check this action?
answer
The Legislative branch approves all nominations to the Supreme Court by the President per Article II Section 2.
question
CHECKS & BALANCES CASE STUDY 2: Congress passes a law restricting gun ownership so that the only weapons a citizen may own are single shot hunting rifles. What ways can the Executive Branch and the Judicial Branch check this action?
answer
Per Article I Section 7, the President may veto any bill. The Judicial Branch may declare the law unconstitutional due to it violating Amendment 2.



