Types of Dressings – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Hydrocolloid Dressings

answer
Consist of gel-forming polymers (gelatin, pectic) with strong film or foam adhesive backing. The dressings vary in permeability, thickness, and transparency. Hydrocolloids absordb exudate by swelling into a gel-like mass and vary from being occlusive to semipermeable. The dressing does not attach to the actual wound itself and is instead anchored to intact skin surrounding the wound
question
Hydrocolloids - Indications
answer
Useful for partial and full-thickness wounds. The dressings can be effective with granular or necrotic wounds
question
Hydrocolloids - Advantages/Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: 1. Provide moist environment for wound healing, 2. Enables autolytic debribement, 3. Offers protection from microbial contamination, 4. Provides moderate absorption, 5. Does not require secondary bandage, 6. Provides a waterproof surface Disadvantages: 1. May traumatize surrounds intact skin upon removal, 2. May tend to roll in areas of excessive friction, 3. Cannot be used on infected wounds
question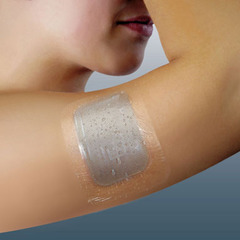
Hydrogel Dressings

answer
Consist of varying amounts of water/gel-forming materials (such as gylcerin) The dressings are available in sheet or amorphous form
question
Hydrogel Indications
answer
Commonly used on superficial and partial-thickness wounds (e.g., abrasions, blisters, pressure ulcers) that have minimal drainage. Rather than absorb drainage, hydrogels are moisture retentive
question
Hydrogel Advantages/Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: 1. Provide a moist environment for wound healing, 2. Enables autolytic debridement, 3. May reduce pressure and diminish pain, 4. Can be used as a coupling agent for ultrasound, 5. Minimally adheres to wound Disadvantages: 1. Potential for dressings to dehydrate, 2. Cannot be used on wounds with significant drainage 3. Typically requires secondary dressing
question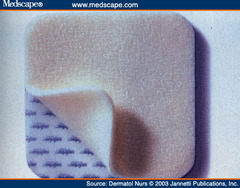
Foam Dressings

answer
Allow for exudates to be absorbed into the foam. The dressings are most commonly available in sheets or pains with varying degrees of thickness. Semipermeable foam dressings are produced in adhesive and non-adhesive forms. Non-adhesive forms require a secondary dressing
question
Foam Dressings - Indications
answer
Used to provide protection over partial and full-thickness wounds with varying levels of exudate. They can also be used as secondary dressing over amorphous hydrogels
question
Foam Dressings - Advantages/Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: 1. Provide a moist environment for wound healing, 2. Available in adhesive and non-adhesive forms, 3. Provides prophylactic protection/cushioning, 4. Encourages autolytic debridement, 5. Provides moderate absorption Disadvantages: 1. May tend to roll in areas of excessive friction, 2. Adhesive form may traumatize periwound area upon removal, 3. Lack of transparency makes inspection of wound difficult
question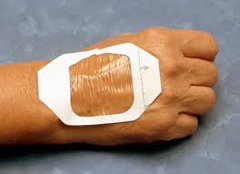
Transparent Film

answer
Thin membranes made from polyurethane with water resistant adhesives. The dressings are permeable to vapor and oxygen, but are mostly impermeable to bacteria and water. They are highly elastic, conform to a variety of body contours, and allow easy visual inspection of wound
question
Transparent Film - Indications
answer
Useful for superficial wounds (scalds, abrasions, lacerations) or partial thickness wounds with minimal drainage
question
Transparent Film - Advantages/Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: 1. Provides a moist environment for wound healing, 2. Enables autolytic debridement, 3. Allows visualization of wound, 4. Resistant to shearing/frictional forces, 5. Cost effective over time Disadvantages: 1. Excessive accumulation of exudates can result in periwound maceration, 2. Adhesive may traumatize periwound upon removal, 3. Cannot be used on infected wounds
question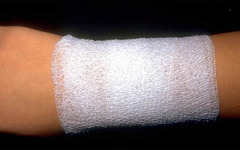
Gauze Dressings

answer
Are the most readily available dressings used in an inpatient environment. They come in many shapes and sizes (sheets, squares, rolls, packing strips). Inpregnated gauze is a variation in which materials such as petrolatum, zinc, or antimicrobials have been added
question
Gauze - Indications
answer
Commonly used on infected and non-infected wounds of any size. The dressings can used for wet-to-wet, wet-to-moist, or wet-to-dry debridement
question
Gauze - Advantages/Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: 1. Readily available, cost effective, 2. Can be used alone or in combination with other dressings/topical agents, 3. Can modify number of layers for changing wound status, 4. Can be used on infected or uninfected wounds Disadvantages: 1. Has tendency to adhere to wound bed, 2. Highly permeable and therefore requires frequent dressing changes (prolonged use decreases cost effectiveness, 3. Increased infection rate compared to occlusive dressings
question
Alginate Dressings

answer
Consist of calcium salt of alganic aci that is extracted from seaweed. Alginates are highly permeable and non-occlusive. As a result, they require a secondary dressing. These dressings are based on the interaction of calcium ions in the dressing and the sodium ions in the wound exudate
question
Alginate Dressings - Indications
answer
Typically used on partial and full-thickness draining wounds such as pressure wounds or venous insufficiency ulcers. Alginates are often used on infected wounds due to the likelihood of excessive drainage
question
Alginate Dressings - Advantages/Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: 1. High absorption capacity, 2. Enables autolytic debridement, 3. Offers protection from microbial contamination, 4. Can be used on infected or uninfected wounds, 5. Non-adhering to wound Disadvantages: 1. May require frequent dressing changes based on level of exudate. 2. Requires secondary dressing, 3. Cannot be used on wounds with an exposed tendon, joint capsule, or bone
question
Occlusion and Moisture
answer
Occlusion refers to the ability of a dressing to transmit moisture, vapor, or gases from the wound bed to the atmosphere. A truly occlusive substance would be completely impermeable, while a truly non-occulsive substance would be completely permeable
question
Dressings arranged from Most Occlusive to Least
answer
(Most) 1. Hydrocolloids, 2. Hydrogels, 3. Semipermeable foam, 4. Semipermeable film, 5. Impregnated gauze, 6. Alginates, 7. Traditional gauze (Least)
question
Dressings arranged from Most Moisture Retentive to Least
answer
(Most) 1. Alginates, 2. Semipermeable foam, 3. Hydrocolloids, 4. Hydrogels, 5. Semipermeable films
question
Primary vs. Secondary Dressings
answer
Primary Dressing - comes into direct contact with wound Secondary Dressing - placed directly over the primary dressing to provide protection, absorption, and/or occlusion



