Treatment and Therapy – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Biomedical Therapy
answer
Prescribed medications or medical procedures that act directly on the patient's nervous system
question
Counter Conditioning
answer
A behavior therapy procedure that conditions new responses to stimuli that trigger unwanted behaviors; based in classical conditioning. Includes exposure therapy and aversive conditioning
question
Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy
answer
An anxiety treatment that progressively exposes people to stimulations of their greatest fears, such as airplane flying, spiders, or public speakering
question
Meta-Analysis
answer
A procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
question
Tardive Dyskeninsia
answer
Involuntary movements of the facial muscles, tongue, and limbs; A possible neurotoxic side effect of long-term use of antipsychotic drugs that target D2 dopamine receptors
question
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)
answer
The application of repeated pulses of magnetic energy to the brain; used to stimulate or suppress brain activity.
question
Psychosurgey
answer
Surgery that removes or destorys brain tissue in an effort to change behavior
question
Extinction
answer
used in Systematic Desensitization; when the undesired behavior stops
question
Family Therapy
answer
therapy that treats the family as a system; views an individual's unwanted behaviors as influenced by or directed at other family members; attempts to guide family members toward positive relations and improved communication; seeks to change all family behaviors to benefit the entire unit
question
Flooding
answer
behavioral technique; counterconditioning; an aggressive method of desensitization; exposure to anxiety-producing stimuli is great; short-term technique; example: someone who is afraid of spiders must immediately handle a tarantula, makes me think of the show "Fear Factor"
question
Free Association
answer
Freudian technique; used in psychoanalysis; "stream of consciousness"; client talks about whatever topic comes to mind without editing, controlling, or inhibiting thoughts and fantasies; therapist acts as a "blank slate"
question
Gestalt Therapy
answer
outgrowth of Fritz Perls work; insight therapy; emphasizes the wholeness of personality and attempts to reawaken people to their emotions and sensations; works in the here-and-now; encourages face-to-face confrontations (e.g. "How is that working for you?"); therapist is active and directive; focuses on the whole person/client; uses empty chair technique
question
Group Therapy
answer
psychotherapy where multiple people meet regularly to interact and help one another to achieve insight into their feelings and behavior; allows the therapist to see how the client interacts with others, offers a social support, and shows the client that s/he is not the only person with that problem; can be less expensive; includes family, couples, and self-help groups.
question
Insight
answer
awareness of previously unconscious feelings and memories and how the this awareness influences present feelings and behaviors; working through childhood conflicts
question
Insight Therapy
answer
psychotherapy designed to help an individual come to a better awareness and understanding of his/her feelings, motivations and actions; includes psychoanalysis, Gestalt, client-centered therapy.
question
Interpretation
answer
in psychoanalysis, the analyst's noting supposed dream meanings, resistances, and other significant behaviors in order to promote insight
question
Lithium
answer
biological treatment; a chemical that provides an effective drug therapy for the mood swings of bipolar (manic-depressive) disorders; naturally occurring salt; effective in 75% of bipolar cases; needs to be monitored closely for correct dosage treatment; do not know how lithium works exactly
question
Modeling
answer
behavioral technique; process of learning a behavior by watching someone perform the behavior; helps relieve anxiety to watch someone else before the client tries (friend touches snake and lives, so can you...); very effective when combined with positive reinforcement (especially in helping people with schizophrenia); don't forget the sociocultural implications
question
Primary Prevention
answer
techniques and programs designed to improve social environment so that new cases do not develop; includes family planning, genetic counseling, sex education, effects of drugs, etc.; key word here is prevention (education)
question
Psychoanalysis
answer
Sigmund Freud's therapeutic technique; designed to bring repressed feelings and thoughts to conscious awareness so the person can deal with these issues more effectively; uses free associations, resistances, dreams, and transferences--and the therapist's interpretations of them--released previously repressed feelings, allowing the patient to gain self-insight
question
Psychopharmacology
answer
the study of the effects of drugs on mind and behavior
question
Psychostimulants
answer
biological treatment; heightens alertness and arousal; commonly used to treat AD/HD case because they increase the electrical activity of the frontal lobe and therefore cause a calming effect rather than stimulating; includes Ritalin
question
Psychosurgery
answer
biological treatment; brain surgery to change a person's behavior; includes a prefrontal lobotomy; rarely used today
question
Psychotherapy
answer
the use of psychological techniques to treat disorder; can take many forms (group, individual, family, couples, etc)
question
Rational-Emotive Therapy (RET)
answer
cognitive therapy founded by Albert Ellis; directive therapy; based on the idea that psychological distress is caused by irrational and self-defeating beliefs; therapy is designed to challenge the dysfunctional thoughts ("stinking thinking") and reinterpret the thoughts in a more positive light; therapy is challenging and confrontational; aims to lead person to more realistic and flexible ways of thinking
question
Resistance
answer
in psychoanalysis, the blocking from consciousness of anxiety-laden material
question
Revolving Door
answer
term to describe the constant entering and leaving of mental health facilities; often caused by deinstitutionalization and health insurance
question
Secondary Prevention
answer
programs to identify groups (e.g. abused children, rape victims) that are at high risk of disorders and to detect maladaptive behavior before the behavior disrupts life; includes crisis intervention, suicide hot lines
question
Self-Talk
answer
cognitive technique; suppression of negative, anxiety-provoking throughts and replaced with positive, "coping" statements
question
Short-Term Psychodynamic Therapy
answer
psychodynamic therapies that are limited in the number of sessions, for example 25 sessions; sessions are weekly for a fixed period of time unlike most psychodynamic therapies which meet 3x/week for years
question
Stress-Inoculation Therapy
answer
cognitive technique; designed to train people to deal with stressful situations by using a pattern of self-talk; replace bad statements with positive statements when in stressful situations
question
Tertiary Prevention
answer
programs to help individuals adjust to community life after institutionalization; includes day or weekend passes from hospital, day programs (spend night at home but return to hospital each day), halfway houses, or supportive therapy
question
Token Economy
answer
behavioral technique; an operant conditioning procedure that rewards desired behavior; a patient exchanges a token of some sort, earned for exhibiting the desired behavior, for various privileges or treats; often seen in elementary schools and reading programs to promote desirable behaviors, weekend passes, etc.
question
Transference
answer
in psychoanalysis, the patient's transfer to the analyst of emotions linked with other relationships; Freud thinks the client is carrying over feelings from childhood authority figures and putting them onto the therapist; can be positive or negative
question
Insight Therapies
answer
a type of psychotherapy in which the therapist helps their patient understand how their feelings, beliefs, actions, and events from the past are influencing their current mindset.
question
Behavioral Therapies
answer
A type of psychotherapy that focuses on changing or reducing the occurrence of some maladaptive behavior
question
Bio-medical Therapies
answer
Use a prescribed medication or medical procedure that acts directly on the patient's nervous system
question
Eclectic Approach
answer
The type treatment used will depend on the client's problems
question
Psychoanalytic Therapy
answer
Assumption: Problems stem from unconscious conflicts that usually date back to childhood experiences Aim: help patients gain insight into unconscious conflicts Evaluation: old, outdated, and lacks empirical evidence People: Freud
question
Dream Analysis
answer
Patient describes the "manifest content" of the dream Therapist uncovers the "latent content" of the dream
question
Psychodynamic Therapy
answer
Similarity to Psychoanalysis because they try to enhance self-insight by focusing on "unconscious forces" that and childhood experiences Differs from Psychoanalysis because they talk face to face and don't meet as much
question
Humanistic Therapies
answer
Assumption: Problems stem from obstacles that block personal growth and potential Aim: Focus on the present time (here and now) Evaluation: Unstructured, vague and subjective leaving it with little empirical proof People: Rogers
question
Client Centered Therapy
answer
Refer to people as "clients" and not patients Non-directive Approach where therapist listens without judgment and refrains from directing the client
question
Unconditional Positive Regard
answer
Important element of client centered therapy developed by Carl Rogers Blanket acceptance and support of a person regardless of what ether person says or does.
question
Active Listening
answer
involves echoing, restating and seeking clarification of what the client says and does, and acknowledging feelings
question
Empathy
answer
recognizing the clients feelings and reflecting it back to the client
question
Behavioral Therapies (aka Behavior Modification)
answer
Assumption: Problems stem from destructive behaviors Aim: Use learning principles to replace problem behaviors with constructive behaviors Evaluation: Effective but minimizes emotions People: Wolpe, Cover-Jones
question
Counterconditioning
answer
Using classical conditioning principles to create a new conditioned stimulus Includes exposure and aversive therapies
question
Bell and Pad Treatment
answer
A behavior therapy technique used to treat nighttime bedwetting by conditioning arousal from sleep in response to bodily signals of a full bladder
question
Aversive Conditioning
answer
use of something unpleasant, or a punishment, to stop an unwanted behavior
question
Cognitive Therapies
answer
Assumption:Faulty thoughts, such as negative self-talk and irrational beliefs, cause psychological problems Aims: change the faulty thoughts and replace with better ones Evaluation: Effective but minimizes emotions People: Ellis & Beck
question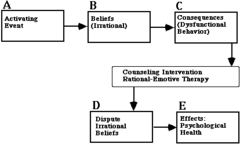
Rational Emotive therapy (RET) or Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT)

answer
Albert Ellis's cognitive therapy to eliminate emotional problems through the rational examination of irrational beliefs.
question
Negative Cognitive Bias
answer
Aaron Beck found depressed people consistently distort their experiences in a negative cognitive way
question
Cognitive Behavioral Therpay
answer
a popular integrative therapy that combines cognitive therapy with behavior therapy
question
Placebo Effect
answer
Defined: you believe it works due to the power of the mind Clients' and therapists' believe the treatment will work and therefore it does
question
Regression towards the mean
answer
Defined: the tendency for unusual events (including emotions) to return to their average state Example: When things hit bottom, going to a therapist is more likely to be followed by improvement than by further descent.
question
Meta Analysis
answer
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
question
Effective Therapies
answer
No one therapy has been shown to be best in all cases but some therapies are better suited for particular disorders Most _________ __________ are when the problem is clear cut
question
Evidence Based Practice
answer
involves clinical decision making that integrates the best available research with clinical expertise and patient characteristics and preferences. In short, available therapies are rigorously evaluated and then applied by clinicians who are mindful of their skills and of each patient's unique situation.
question
Shared Elements of Therapy
answer
Hope, New perspective, and an empathetic, caring relationship
question
EMDR
answer
therapist waves a finger inferno of the eyes of the client to unlock and reprocess previously frozen traumatic memories
question
Light Exposure Therapy
answer
a client is exposed to daily doses of light that mimics outdoor light used to fight against seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
question
Neuroleptics
answer
prescription drugs used to reduce symptoms
question
Tardive Dyskinesia
answer
involuntary movements of the facial muscles, tongue, and limbs; a possible neurotoxic side effect of long-term use of antipsychotic drugs that target certain dopamine receptors
question
Anti-Anxiety Drugs
answer
How it works: treats anxiety by increasing the level of GABA and therefore depress the activity in the central nervous system Popular Drugs: Xanax, and Valium Negative Side Effects: addictive and only reduces symptoms in the short term
question
Typical Anti-Psychotic Drugs
answer
How it works: treat schizophrenic hallucinations and paranoia by reducing dopamine activity Popular Drugs: Thorazine Negative Side Effects: tardive dyskinesia
question
Atypical Anti-Psychotic Drugs
answer
How it works: treat all schizophrenic symptoms by blocking dopamine & serotonin Popular Drugs: Abilify Negative Side Effects: less harmful than typical ones
question
Mood Stabilizing Drugs
answer
How it works: used to treat bipolar disorder by stabilizing Glutamate levels in order to stabilize current and future moods Popular Drugs: Lithium & Depakote Negative Side Effects: small difference between appropriate and toxic dosage level
question
SSRI
answer
How it works: Treats depression by preventing the reuptake of serotonin Popular Drugs: Prozac, Zoloft, and Paxil Advantages: milder side effects making it the most popular anti-depressant
question
Lobotomy

answer
A now-rare psychosurgical procedure once used to calm uncontrollably emotional or violent patients. The procedure cut the nerves that connect the frontal lobes to the emotion-controlling centers of the inner brain.
question
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)

answer
a biomedical therapy for severely depressed patients in which a brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient
question
repetitive Trans-cranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)
answer
performed on wide-awake patients where magnetic energy penetrates only to the brain's surface does not have the side effects of ECT
question
BioPsychoSocial Approach to Treating Disorders
answer
Using aerobic exercise, adequate sleep, light exposure, social connection, anti-rumination, and nutritional supplements to fight and prevent psychological problems
question
Preventing Mental Health Issues
answer
1. Build Resilience: an ability to cope with stress and recover from adversity. 2. Build a loving, nuturing environment
question
psychoanalysis
answer
cause of behavior: unconscious internal conflict, possibly stemming from early childhood trauma
question
behavioral
answer
cause of behavior: learned maladaptive behavior through faulty contingencies of reinforcement
question
humanistic
answer
cause of behavior: poor self-concept as a result of conditions of worth
question
cognitive
answer
key terms: rational emotive therapy cognitive behavior therapy cognitive triad
question
biological
answer
key terms: antianxiety drugs antidepressants antipsychotics ECT psychosurgery corpus callous transection prefrontal lobotomy
question
lobotomy
answer
(aka leucotomy) a neurosurgical operation that involves severing connections in the brain's prefrontal lobe
question
client perceptions
answer
a way to assess if therapy is working; you see therapist--> they ask how you are-->you tell them
question
clinician perceptions
answer
a way to assess if therapy is working; each therapist=good but longterm not helping and patient is getting more frustrated
question
treatment outcome research
answer
a way to assess if therapy is working; systematically measuring which therapies work best for which problem (ex: randomized clinical trial-RCT)
question
meta analysis
answer
a way to assess if therapy is working through treatment outcome research; gathers data of RCT and measures effectiveness(if treatment works and how well) and efficacy(if works better than others/comparing)
question
biomedical therapies
answer
aim to physiologically change the brain's electrochemical state with psychotropic drugs, magnetic impulses, or electrical currents and surgery
question
pharmacotherapy
answer
treatment of just taking drugs//4 types: antipsychotics, anxiolytics, antidepressants, mood stabilizers
question
antipsychotics
answer
type of pharmacotherapy; treat schizophrenia and other severe thought disorders; alter dopamine by blocking receptors with clozaril
question
anxiolytics
answer
type of pharmacotherapy; anti anxiety; depresses activity in CNS--> mellow nerves (easy to get addicted)
question
antidepressants
answer
type of pharmacotherapy; treat depression and some anxiety disorders by altering availability of serotonin and norepinephrine which helps with mood and anxiety; most effective (combined with psychotherapy)
question
mood stabilizers
answer
type of pharmacotherapy; smooths out highs and lows of bipolar disorder (ex. Lithium)
question
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
answer
sends brief electrical current through brain which excites the neurons, causing them to fire rapidly until the patient has a seizure which relieves the patient of negative symptoms
question
repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulus (rTMS)
answer
painless application of repeated electromagnetic pulses
question
Trepanning
answer
The act of drilling a hole in one's head to treat disorders/possessions
question
Psychoanalytic, Humanistic, and Cognitive Therapies
answer
Are all psychological perspectives that used insight therapy
question
Psychoanalytical Therapy
answer
The patient's free associations, resistances, dreams, transferences, and the therapist's interpretations of them-released previously repressed feelings, allowing the patient to gain self-insight
question
Manifest Content
answer
The actual content (narration) of one's dream
question
Latent Content
answer
The underlying meaning of a dream
question
Symptom Substitution
answer
Where the therapist may rid the patient of a symptom only to have another take its place without curing the problem.
question
Humanist Therapy
answer
Emphasizes personal growth, resilience, the achievement of human potential, and the clients ability to change rather than being destined to repeat past conflicts
question
Client-Centered Therapy
answer
A humanistic therapy based on Carl Roger's beliefs where the therapist creates a comfortable, non-judgmental environment by demonstrating empathy and unconditional positive regard (Non-Directive Therapy)
question
Congruence
answer
A genuine and authentic reflection where the therapist serves as the psychological mirror
question
Cognitive Therapy
answer
Therapy that teaches people new, more adaptive ways of thinking and acting; based on the assumption that negative thoughts cause psychological problems
question
Aaron Beck's Cognitive Triad
answer
The more negative thoughts you think of, the more depressed you will be
question
Albert Ellis
answer
Developed the Rational-Emotive Therapy (RET), focuses on altering client's patterns of irrational thinking to reduce maladaptive behavior and emotions
question
Rational-Emotive Therapy (RET) Model
answer
1. Adversity: Identify activating events 2. Belief: Identify belief systems 3. Consequence: Examine emotional consequences 4. Dispute: Dispute erroneous beliefs
question
Behavioral Therapy
answer
Based on classical and operant conditioning as well as observational learning; focuses on the problem behavior itself, not on insights into the behavior's underlying causes
question
Mary Cover Jones Counterconditioning
answer
Behavioral therapist, who associated something (treat, music, praise, etc.) positive with the feared object or situation.
question
Joseph Wolpe's Systematic Desensitization
answer
A type of exposure therapy that associates a pleasant relaxed state with gradually increasing anxiety-triggering stimuli. Commonly used to treat phobias.
question
In-Vivo Desensitization
answer
The actual presence of the object or situation
question
Covert Desensitization
answer
Imagined presence of object or situation
question
Aversion Therapy
answer
The therapist deliberately pairs an aversive or unpleasant stimulus with a maladaptive behavior
question
Group, Family, Self-help and Marital Therapies
answer
Other therapies (mostly using cognitive techniques) include...
question
Biomedical Therapies (Somatic Treatments)
answer
The use of drugs and electroconvulsive therapy to treat psychological disorders
question
Antipsychotic Drugs
answer
(Ex. Thorazine) work to decrease dopamine synapses in the brain to eliminate hallucinations, delusions and other symptoms of schizophrenia. Long-term use can produce dyskinesia
question
Dyskinesia
answer
A condition with involuntary muscle movements
question
Antianxiety Drugs
answer
(Ex. Xanax or Valium) are barbiturates that depress activity in the CNS to help a person relax
question
Mood-Stabilizing Drugs
answer
(Ex. Lithium) are used to treat bipolar disorder
question
Active listening
answer
empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies; a feature of Roger's client-centered therapy
question
Behavior Contracting
answer
behavioral technique; therapist and client both agree on goals and reinforcement when goals are reached; written contract; reinforces new behaviors and ignores/punishes undesirable behaviors; often used with adolescents and children
question
Behavior Therapy
answer
Approach that is based on the belief that all behavior (normal and abnormal) is learned; therapy that applies learning principles to the elimination of unwanted behaviors and to teach new, appropriate ways of behaving; includes systematic desensitization, flooding, modeling extinction, token economy, and behavior contracting; is often combined with Cognitive therapies and is known as CBT
question
Biological Treatments
answer
treatment that focuses on organic or biological aspects; includes medication, ECT, psychosurgery; best used in conjunction with other forms of therapy because when the biological treatment ceases, typically the symptoms return
question
Client-Centered Therapy (Person-Centered)
answer
a humanistic therapy, developed by Carl Rogers; therapist uses non-directive techniques such as active listening with a genuine, accepting, empathic environment to facilitate clients' growth; uses bits and pieces of neo-Freudian views; calls for unconditional positive regard; goal is to help client become a fully-functioning person
question
Beck's Cognitive Therapy
answer
cognitive technique; designed by Aaron Beck; designed to identify and change inappropriate negative and self-critical patterns of thought; primarily used to treat depression and anxiety; therapy is not as challenging and confrontational as REBT; aims to lead person to more realistic and flexible ways of thinking
question
Cognitive-Behavior Therapy
answer
a popular integrated therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior)
question
Couples Therapy
answer
therapy that is designed to treat partners who are having difficulties in their relationship; often concentrates in improving communication and expectations between the partners or misinterpretation
question
Deinstitutionalization
answer
policy of treating individuals with severe disorders in the larger community or in a small residential center (halfway house) rather than large wards in a public hospital; Problems include poorly funded community centers or no centers, poor preparation due to understaffing and lack of funding, social stigma
question
Eclecticism
answer
movement is psychotherapy that recognizes the value of a broad treatment package that best suits the client and the client's reason for seeking therapy rather than sticking to one type of approach; Example: if you are a psychoanalyst and your client comes to you for a phobia, an eclectic psychoanalyst would utilize desensitization rather than focus on childhood events
question
Exposure Therapies
answer
behavioral techniques, such as systematic desensitization, that treat anxieties by exposing people (in imagination or actuality) to the things they fear and avoid
question
Antidepressant Drugs
answer
biological treatment; typically used for depression but is often used for anxiety, OCD, GAD, panic disorder, social phobias, PTSD, and sometimes ADHD; 3 categories: tricyclics, MAO inhibitors, and SSRIs; SSRIs are more popular (Prozac, Zoloft, Effexor, Paxil) because they tend to have less side effects , SSRIs block the reuptake of serotonin in the nervous system; MAOIs and trycyclics both concentrate on serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain but have a number of side effects and limitations (food reactions), MAOIs and trycyclics are now used in serious cases and not so much after the invention of Prozac
question
Systematic Desensitization
answer
behavioral technique; a type of counterconditioning; designed to reduce a person's fear and anxiety by gradually associating a pleasant relaxed state with anxiety-triggering stimuli; commonly used to treat phobias, OCD; includes developing a hierarchy of fears
question
Biomedical
answer
Use a prescribed medication or procedures that act directly on the patient's nervous system
question
Eclectic
answer
variety of methods
question
Psychoanalytic
answer
Assumption: Problems stem from unconscious conflicts that usually date back to childhood experiences Aim: help patients gain insight into unconscious conflicts Evaluation: old, outdated, and lacks empirical evidence People: Freud
question
Humanism
answer
Assumption: Problems stem from obstacles that block personal growth and potential Aim: Focus on the present time (here and now) Evaluation: Unstructured, vague and subjective leaving it with little empirical proof People: Rogers
question
Behavioral
answer
Assumption: Problems stem from destructive actions Aim: Use learning principles to replace problem behaviors with constructive behaviors Evaluation: Effective but minimizes emotions People: Wolpe, Cover-Jones
question
Cognitive
answer
Assumption:Faulty thoughts, such as negative self-talk and irrational beliefs, cause psychological problems Aims: change the faulty thoughts and replace with better ones Evaluation: Effective but minimizes emotions People: Ellis & Beck
question
Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT)
answer
Albert Ellis's cognitive therapy to eliminate emotional problems through the rational examination of irrational beliefs.
question
Cognitive Behavioral
answer
attack thoughts and actions
question
Light Exposure
answer
used to fight against seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
question
pharmacology
answer
Assumption: biological causes exists for the disorders or behaviors Aims: provide the right medication Evaluation: helpful but medicine cannot solve all problems
question
Benzodiazepines
answer
How it works: treats anxiety by increasing the level of GABA and therefore depress the activity in the central nervous system Popular Drugs: Xanax, and Valium Negative Side Effects: addictive and only reduces symptoms in the short term
question
AntiPsychotic Drugs
answer
How it works: treat schizophrenic hallucinations and paranoia by reducing dopamine activity Popular Drugs: Thorazine Negative Side Effects: tardive dyskinesia
question
lithium
answer
How it works: used to treat bipolar disorder by stabilizing Glutamate and/or norepinephrine Negative Side Effects: small difference between appropriate and toxic dosage level



