Therapeutic Modalities: E-Stim – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion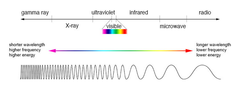
Electromagnetic Spectrum

answer
(Longwave to Shortwave) Electrical stimulating Current Commercial Radio and Television Shortwave Diathermy Microwave Diathermy Laser - Infrared Laser - Visiblie light Ultraviolet Ionizing Radiation
question
Ions
answer
Positively and negatively charged particles contained in atoms
question
Electrical Potentials
answer
Difference in concentration of electrons between two points Electrons will not move unless a potential difference exists
question
Net movement of electrons
answer
Always higher to lower
question
Electrical force is oriented in
answer
the direction of the applied force
question
Rate of electrical current measured by
answer
Ampere (amp) Coulomb Volt (V)
question
Electrons
answer
Particles of matter possessing a negative charge and a small mass Net movement of electrons is an electrical current Movement of electrons is like a domino reaction Electrons will move from higher to lower potential
question
Ampere
answer
Unit of measure which indicates rate at which electrons flow 1 amp = movement of 1 coulomb or 6.25x1018 electrons /sec Current flow is in milliamps (1/1000) or microamps (1/1,000,000)
question
Voltage
answer
Force resulting from an accumulation of electrons at one point in an electrical circuit Corresponds to a deficit of electrons at another point in the circuit Creates the potential difference Commercial current is 115 V or 220 V
question
Coulomb
answer
Indicates the NUMBER of electrons
question
Coulomb's Law
answer
Opposites attract/likes repel
question
Conductors
answer
Materials that permit free movement of electrons Composed of large numbers of free electrons Offer little resistance to current flow Good conductors - Metals (copper, gold, silver, aluminum) Electrolyte solutions
question
Insulators
answer
Materials that resist the flow of electrons Contain few free electrons Insulator materials Air, Wood, Glass
question
Electrical Impedence
answer
Resistance or opposition to flow of electrical current Measured in ohms
question
Ohm's Law
answer
Current Flow= Voltage/Resistance Current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance
question
Watt
answer
Measure of electrical power Rate at which electrical power is being used Power needed to produce a current flow of 1 A at a pressure of 1 V Watts = Volts x Amps Modalities use milliamps or microamps
question
Electrictherapeutic Currents
answer
Direct current - Galvanic or DC Alternating current - AC Pulsed Currents - Period of no current flow - Monophasic - Biphasic - Polyphasic
question
Direct (DC) or Monophasic

answer
Flow of electrons always in same direction Sometimes called galvanic Flow is always in a uniform direction Accumulation of charged ions over a period of time Creates either an acidic or alkaline environment Medical galvanism Iontophoresis
question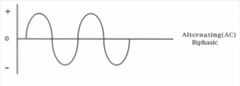
Alternating (AC) or Biphasic

answer
Flow of electrons changes direction Always flows from negative to positive pole until polarity is reversed
question
Monophasic Pulse
answer
Square Wave Twin Peaks SawTooth
question
Biphasic Pulse
answer
Sinusoidal Asymmetrical
question
Polyphasic
answer
Pulsed current waveforms Represents an electrical current in a series of pulses - Polyphasic sine - Polyphasic rectangle - Polyphasic Spiked
question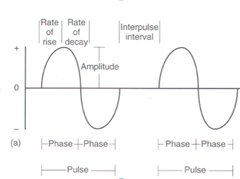
Parts of a Biphasic Waveform

answer
Pulse Phase duration Interpulse interval Direction Amplitude Rate of rise Rate of decay
question
Biphasic Pulse
answer
Individual waveform
question
Biphasic Phase duration
answer
One + or one - amplitude arch
question
Biphasic Interpulse interval
answer
Break between the pulse
question
Biphasic Direction
answer
Polarity
question
Biphasic Amplitude
answer
Height of one pulse Intensity or voltage Measured in Milliamps or microvolts Average current Determined by Interpulse interval& Current duration
question
Biphasic Rate of rise
answer
Rising part of a + pulse How quickly the pulse reaches its maximum amplitude in each phase
question
Biphasic Rate of decay
answer
Falling part of a + pulse Time to which the pulse goes from peak to 0 volt Accommodation
question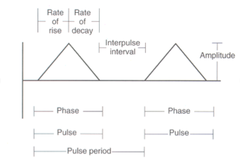
Parts of Monophasic Waveform

answer
Pulse and phase duration Interpulse interval Amplitude Rate of rise Rate of decay
question
Monophasic Pulse and phase duration
answer
Individual waveform Same base of the triangle
question
Monophasic Interpulse interval
answer
Break between the pulse and phase
question
Monophasic Amplitude
answer
Height of the triangle Intensity or voltage Measured in Milliamps or microvolts Average current Determined by Interpulse interval& Current duration
question
Monophasic Rate of rise
answer
Upward slope of the triangle How quickly the pulse reaches its maximum amplitude in each phase
question
Monophasic Rate of decay
answer
Downward slope of the triangle Time to which the pulse goes from peak to 0 volt
question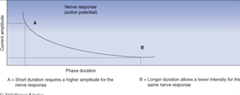
Phase Duration and Action Potentials

answer
The longer the phase duration the less energy/current needed to generate an action potential
question
Average Current
answer
Considered ½ of its complete cycle Taking into account the amount of time the current is flowing The total amount of charge delivered by a single cycle Useful when asymmetrical biphasic currents are used
question
Accommodation Phenomenon
answer
A fiber which has been subjected to constant depolarization will become more excitable at the same intensity or amplitude Rise and decay times are short Nano to milliseconds The shape of waveforms is directly related to their ability to excite nervous tissue "Body gets used to the tingling and needs to be aletered to remain effective"
question
Things that Prevent Accomodation
answer
Rate of Rise and Decay
question
Law of Dubois Reymond
answer
Stimulus must be of adequate amplitude to reach the threshold level of excitatory tissue Rate of voltage change must be enough that tissue accommodation cannot occur Length of the stimulus or phase duration must be great enough to overcome the capacitance of the tissue to allow an action potential
question
Current Modulation
answer
Any alteration in the magnitude or duration of pulses Continuous Interrupted Burst Ramped Amplitude Phase Duration
question
Continuous
answer
Amplitude remains the same for several seconds/minutes Associated with direct current Used with alternating current when trying to elicit a muscle contraction
question
Interrupted Modulation
answer
Current flow is on for a time period and off for a time period On 1-60 seconds Off 1-120 seconds Used with both monophasic and biphasic currents Sinusoidal, rectangular, and triangular waveforms Clinically used for muscle re-education and range of motion
question
Burst Modulation
answer
Occurs when pulsed current flows for a short duration and then turned off for a short duration in a repetitive cycle Milliseconds Used with monophasic and biphasic currents "Packages" of pulses to make a burst
question
Ramping Modulation
answer
Current amplitude increases or "ramps up" gradually to a preset maximum ~1/3 of the on time Clinically used in muscle re-education
question
Phase Duration Modulation
answer
Typically available in TENS units Allows the phase duration to change throughout the treatment
question
Current Density
answer
The volume of current in the tissues Highest at surface Diminishes in deeper tissue Inversely proportional to the size of the electrode 300 volts through an electrode of 10 square inches Current density = 30 V/square inch
question
Electrode Size and Current Density
answer
Larger the electrode the more the current density is spread Smaller the electrode the greater the current density High current density close to neural structure will create the greatest stimulus with less intensity/current
question
Electrode Proximity and Current Density
answer
Less intensity Farther away
question
Circuit Types
answer
Series Circuit Paralell Circuit
question
Series Circuit
answer
One path for the current to take Component placed end to end Total Resistance = Sum of Resistances Total Voltage = Sum of Voltage Decreases
question
Paralell
answer
Component resistors placed side to side with ends connected Current chooses path of least resistance Resistors have lower resistance but higher current flow than series circuit
question
Current Flow Through Tissues
answer
Higher water content, great conductivity Skin - Greatest concern for electrical impedance Blood - Best conductor of all the tissues, Comprised largely of water and ions Muscle - About 75% water, Depends on movement of ions for contraction, Tendons are poor conductors Fat - Poor conductor Peripheral nerves - 6 x better than muscle, But surrounded by fat and fibrous sheaths that are poor conductors Bone - About 5% water, Very poor conductor
question
Methods of Reducing Skin Electrode Resistance
answer
Moisten electrodes with water or conductive gel Sponge or rubber electrodes Remove dirt, oil, or flaky skin Washing with soap and water, alcohol, or acetone Warm area with a moist heat pack Gently scrub area with fine emery paper Remove excess hair Saturate sponges with commercial saline solution rather than tap water Use silver electrodes
question
Interferencial Current
answer
More comfortable than equal amplitudes delivered by other means Typical treatment goals Pain control Neuromuscular stimulation Reduction of edema The result of the interaction between the two input currents is a low frequency current
question
IFC Primary physiological effect
answer
Depolarize sensory and motor nerve fibers
question
IFC Main therapeutic effects
answer
Sensory nerve fibers Pain reduction Superficial never fibers receive lower amplitude stimulation than area of tissue Muscle fatigue Muscle spasm
question
IFC Contraindications and Precautions
answer
Whirlpools Old pads Burns Pacemakers Infections Malignancies Pregnancy Musculoskeletal problems where a muscle contraction would exacerbate conditions
question
IFC Frequency
answer
On typical interferential units Frquency = 4000-5000Hz Fixed frequency Carrier Medium-high frequency = 4000-5000Hz Variable frequency The two currents converge
question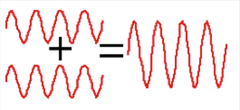
Constructive Waves

answer
When two sinusoidal waves that are exactly in phase or one, two, three or more wavelengths of phase, the waves supplement each other in constructive interference
question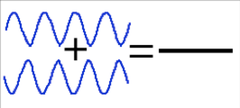
Destructive Waves

answer
When the two waves are different by 1/2 a wavelength the result is cancellation of both waves
question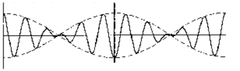
Coninuous Waves

answer
Constructive + destructive waves Slightly out of phase Collide and form a single wave with progressively increasing and decreasing amplitude
question
Beat Frequency
answer
The beat frequency is what we are delivering to the target tissue Difference in carrier frequency and variable frequency = beat frequency Example 4000Hz (carrier) -4004Hz (variable) Beat frequency = 4 Hz
question
IFC Currents
answer
When electrodes are arranged in a square interferential currents are passed through a homogeneous medium A predictable pattern of interference The body is not a homogeneous medium
question
IFC Scanning and vector
answer
Scanning/Vector Moves force around while the treatment is taking place Enlarging effective treatment area 45º angles from center of treatment area
question
IFC Pain Control Gate Control
answer
Beat frequency - 80-150 Hz Sweep Fast Sensory level Vector/Scan Based on treatment area and patient comfort
question
IFC Pain Control Opiate Release
answer
Beat frequency - 1-10 Hz Sweep Slow Sensory/Motor level Vector/Scan Based on treatment area and patient comfort
question
Pre-Mod
answer
Single alternating current Bipolar technique Mix of two channels occurring within generator instead of tissues Both output a frequency of 4,000 Hz The generator "premodulates" burst frequency within the unit Output is 1-100 bursts per second
question
Hi-Volt Distinct Specifications
answer
Two distinct specifications - Must transmit a voltage of at least 150V, Arbitrary number determining "low" and "high" volt machines Must use a twin-peaked monophasic current
question
Hi-Volt Amplitude
answer
Ranges from 0-500 V Determined by patient comfort and goal A high voltage means a lower average current Very safe modality Immediate pulse decay Second pulse begins before the first pulse reaches the isoelectric line Phase duration Varies between 50-120 ?s Depends on machine Can not be changed by the clinician
question
Twin Peak Monophasic Wave Form
answer
Allows deeper penetration of energy Short phase duration Activation of sensory and type II nerve fibers Without stimulating C and A? pain fibers Long interpulse interval
question
Why Polarity Matters?
answer
Monophasic waveform allows for choice of polarity During healing the wound emits a charge potential Depending on the stage Applying a polarity of the like charge can reinforce this physiological response Example - Leukocyte chemotaxis
question
Positive Polarity
answer
Acute injuries Increases vascular permeability
question
Negative Polarity
answer
Chronic injuries Decreases vascular permeability
question
Hi-Volt Frequency
answer
Frequency ranges from 2-120 pps
question
Hi-Volt Electrode Placement Monopolar
answer
Small active and large dispersive Goals Reduce edema Sensory pain control
question
Hi-Volt Electrode Placement Bipolar
answer
Evoke muscle contraction from specific muscle Motor level pain control
question
Hi-Volt Sensory and motor pain control
answer
Acute - Positive Chronic - Negative
question
Hi-Volt Opiate pain control
answer
Monopolar Large electrode over area and hand held probe Must stimulate A? fibers
question
Hi-Volt Sensory Level Edema Control
answer
The only current that can prevent edema If begun within 6 hours of injury Keys to success - Current flowing as long as possible - Negative electrode (cathode) over target tissue - Decreased vascular permeability - Blood cells/plasma protein repelled from cathode If setup begins too late in the healing process Can inhibit re-absorption and create further edema Combine with other treatments for best effect Post treatment care
question
Hi-Volt Motory Level Edema Control
answer
May reduce edema once formed - Positive polarity Elicit the muscle pump/contraction Increase venous and lymphatic flow Electrode placement: Motor point, Contraction from distal to proximal Use with other treatments for best effect
question
Retard Atrophy
answer
Not good for muscle re-education Short phase duration Not enough to produce a strong muscle contraction Strength of contraction is not sensitive to increases in frequency The muscle contractions elicited by high volt can be used to retard atrophy Denervated muscle
question
Hi-Volt Limitations
answer
Some units do not allow duty cycle control Strength of muscle contraction is less than NMES or Russian Lacks total current needed for maximum force production Short phase duration No time for ions attracted to each electrode to dissipate Physiochemical reaction under electrode limited No significant pH changes under skin Quick accommodation
question
Hi-Volt Precautions
answer
Stimulation of muscles: Can cause unwanted tension to be placed on muscle fibers, tendons, or bony insertion Muscle fatigue: Can rapidly develop if the duty cycle is too high Improper use: Can cause electrode burns or irritation Intense or prolonged stimulation, May result in muscle spasm and/or muscle soreness
question
T.E.N.S.
answer
Trancutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
question
TENS
answer
Primary use is control pain TENS stimulates afferent sensory fibers Gate control theory Between 0-100% can be placebo effect Elicit production of neurohumoral substances Endorphins, enkephalins and serotonin
question
TENS Indications
answer
Control chronic pain Manage post-surgical pain Reduction of post-traumatic and acute pain
question
TENS Precautions
answer
Can mask underlying pain Burns or irritate skin Prolonged use may result in muscle spasm/soreness Caffeine intake (>2000mg) may reduce effectiveness Competes with adenosine, a mediator of transmission Narcotics decrease effectiveness
question
TENS Contraindications
answer
Pacemakers Over carotid sinuses Eyes, ear, throat, mouth, etc Pregnancy Cerebral vascular disorders Stroke patients Over the chest Cardiac condition
question
High Frequency TENS
answer
Activate AB fibers
question
Low Frequency TENS
answer
Activate AB fibers Release of B-endorphins from pituitary
question
Brief-Intense TENS
answer
Noxious stimulation to active C fibers
question
High Frequency TENS
answer
Sensory TENS AB fibers are stimulated - Pure gate control theory Paresthesia is created without motor response Frequency - High Phase duration - Short Amplitude - Low to comfortable Creates the fastest relief of all techniques May stop the pain-spasms cycle
question
Low Frequency TENS
answer
Motor Tens AB fibers and B-endorphins released Longer lasting pain relief but slower to start Frequency - Low Phase duration - Long Amplitude - Low to comfortable current
question
Brief Intense TENS
answer
Stimulates C fibers Mono or biphasic current "bee sting" sensation Utilize motor, trigger or acupuncture points Frequency - High Phase duration - Long Amplitude - Max tolerable
question
Modulated Stimulation
answer
Keeps tissues reactive - No accommodation Simultaneous modulation of amplitude and pulse width As amplitude decreases, pulse width is automatically increased Deliver more consistent energy per pulse Rate can also be modulated
question
Russian Current
answer
Medium frequency - 2000Hz -10,000Hz Polyphasic, alternating current Sine wave Produced in burst mode
question
Pulse Trains (Burst)
answer
Contain individual pulses - Pulses in the train still have time-dependent characteristics, Pulse duration, interpulse interval, etc Each train is separated by "off" times - Intertrain/interburst interval To make intensity of current tolerable Generated in 50-burst-per-second trains With a 10msec interburst interval
question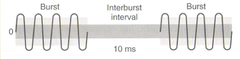
Burst and Interburst Interval Effects

answer
Dark shaded area - Total current Light shaded area -Total current without the interburst interval When generated with burst effect
question
Russian High Frequency
answer
Reduce resistance to current flow Wave form comfortable enough to tolerate Compared to the higher intensities of high volt As intensity increases more motor nerves are stimulated Increases magnitude of contraction Fast oscillating AC current As soon as nerve repolarizes it is stimulated again Produces a current that will maximally summate muscle contraction
question
Russian On-Off Time/Duty Cycle
answer
Typical should be 1:5 - Recovery, Decrease fatigue AT A MINIMUM - 1:3, Even in later stages
question
Russian Ramp Pulse
answer
Gradually increases the current Produces a more natural contraction More comfortable
question
Biofeedback
answer
Voluntary muscle contraction Body's electrical activity is amplified by the biofeedback unit Auditory or visual feedback
question
Why Biofeedback?
answer
Early stages Improper voluntary muscle contraction Example Post ACL surgery, VMO is not being contracted first
question
Biofeedback response is designed to assist in:
answer
Developing strength of the muscle contraction Facilitate muscle relaxation Control blood pressure and heart rate Also decrease physical response to stress Basis of lie detector tests
question
Electromyographic
answer
Measure electrical activity in skeletal muscle
question
Peripheral temperature
answer
Measure temperature changes Increased temperature-Relaxed muscle
question
Photoplethysmography
answer
Measure the amount of light reflected by subcutaneous tissue
question
Galvanic skin response
answer
Measure the amount of perspiration on the skin Sweaty skin contains salt
question
Not a Measure for Contraction Strength
answer
Biofeedback simply measures the conditions associated with the contraction Neurological activity - Then transfers this information into Light, sound, or meter indication
question
Biofeedback Sound Indications
answer
Turns the neurological signals into sound Buzzing, beeping, clicking, tone, etc. Advantages Allows the patient to focus on the sound and his/her own muscle contraction rather than the machine Changes pitch according to the amount of neurological activity
question
Biofeedback Electrodes
answer
Three electrodes within one pad - Two active: Measure the amount of electrical activity within the muscle - One reference: Filters out non-meaningful electrical activity Disposable versus non-disposable
question
Iontopheresis
answer
Introduction of ions into the body using direct electrical current Transports ions across a membrane or into a tissue It is a painless, sterile, noninvasive technique Demonstrated to have a positive effect on the healing process
question
Phonophoresis
answer
uses acoustic energy (ultrasound) to drive molecules into tissues
question
Iontophoresis
answer
uses electrical current to transport ions into tissues
question
Pharmacokinetics
answer
Transdermal iontophoresis delivers medication at a constant rate so that the effective plasma concentration remains within a therapeutic window for an extended period of time.
question
Iontopherisis Therapeutic window
answer
The plasma concentrations of a drug Should fall between a minimum concentration necessary for a therapeutic effect and the maximum effective concentration above which adverse effects may possibly occur
question
Advantages of taking medication via transdermal iontophoresis relative to oral medications
answer
Concentrated in a specific area Does not have to be absorbed within the GI tract Safer than administering a drug through injection
question
Ionization
answer
Soluble compounds dissolve into ions suspended in solutions that are called electrolytes
question
Electrophoresis
answer
Movement of ions in solution according to the electrically charged currents acting on them
question
Cathode
answer
Negatively charged electrode Highest concentration of electrons Repels negatively charged ions Attracts positively charged ions Accumulation of negatively charged ions in a small area creates an acidic reaction
question
Anode
answer
Positively charged electrode Lower concentration of electrons Repels positively charged ions Attracts negatively charged ions Accumulation of positively charged ions in a small area creates an alkaline reaction
question
Current density should be reduced at the
answer
cathode (negative electrode) Alkaline reaction (+ions) is more likely to produce tissue damage than acidic reaction(- ions) Thus negative electrode should be larger (2x) to reduce current density.
question
Recommended current amplitudes used for iontophoresis range between
answer
3-5 mA
question
Iontopheresis Current amplitude usually set so that current density falls between
answer
0.1-0.5 mA/cm2 of the active electrode surface
question
Iontopheresis Treatment duration ranges between
answer
10-20 minutes with 15 minutes being an average
question
Iontopheris typical treatment dose is
answer
40 mA-min but can vary depending on the medication
question
Iontophersis Indications
answer
Inflammation Analgesia Muscle spasm Ischemia Edema Calcium deposits Scar tissue Hyperhidrosis Fungi Open skin lesions Herpes Allergic rhinitis Gout Burns Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
question
Iontopheresis Contraindications
answer
Skin sensitivity reactions Sensitivity to aspirin Salicylates Gastritis or active stomach ulcer Hydrocortisone Asthma Mecholyl Sensitivity to metals Zinc, copper, magnesium Sensitivity to seafood Iodine
question
Microcurrent
answer
Can be a valuable clinical resource More may not be better For electricity to produce these effects Cells must be current sensitive Correct polarity orientation may be necessary Correct amounts of current will cause cells to be more active in healing process



