Telomers, Telomase, Meiosis and Mitosis – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Has our life span or life expectancy increased?
answer
Life expectancy only (the point before we start developing fatal illnesses) If we want to increase life span, we have to find a way to rebuild telomeres
question
What are telomeres?
answer
a repeating DNA molecules sequence (for example, TTAGGG) at the end of Eukaryotic chromosomes
question
What are the main functions of telomeres?
answer
Telomeres function by preventing chromosomes from losing base pair sequences at their ends. They also stop chromosomes from fusing to each other.
question
How long can telomeres get?
answer
telomere can reach a length of 15,000 base pairs
question
Does telomeres prevent the shortening of DNA molecules?
answer
No, but they do postpone the erosion of genes near the ends of DNA molecules
question
How does a telemere lose its function?
answer
Each time a cell divides, some of the telomere is lost (usually 25-200 base pairs per division). When the telomere becomes too short, the chromosome reaches a "critical length" and can no longer replicate. This means that a cell becomes "old" and dies by a process called apoptosis.
question
What contributes to the shortening of telomeres?
answer
the shortening of telomeres is connected to aging
question
What are Telomerase?
answer
rebuilds the telomers at the end of our chromosomes so that we don't degrade the end of chromosomes Enzyme that catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in germ cells.. Also called telomere terminal transferase, is an enzyme made of protein and RNA subunits that elongates chromosomes by adding TTAGGG sequences to the end of existing chromosomes.
question
When does telomerase rebuild telomers?
answer
During embryonic developments and in germ cells
question
What is another name for germ cells?
answer
stem cells-- germ means germative.. can germinate many cells
question
What happens if chromosomes of germ cells became shorter in every cell cycle?
answer
essential genes would eventually be missing from the gametes they produce
question
As we age, the stem cells get slower in replacing cells and cell death in the existing cell starts to?
answer
increase ... for a while the stems cells will keep up with each other but they will eventually slow down
question
How does the shortening of telomeres might protect cells from cancerous growth
answer
limiting the number of cell divisions When a cell becomes cancerous, DNA has been damaged during replication process. If DNA is damaged and we don't see it become cancer, then the next time it divides and the telomeres are all shorten/gone.. it means the cell will die anyways. In this sense, it limits the cancer growth
question
If a cell is damaged
answer
then the probability of cancer is higher. If it divides again and there is no telomere to continue the dna sequence, then the cell will not have a chance to grow into cancer
question
What is apoptosis?
answer
This means that a cell becomes "old" and dies by a process called apoptosis.
question
What is cancer cell?
answer
It is an uncontrolled mitosis-uncontrolled cell division. cells keeps dividing nonstop and in the process, doesn't go through cell differentiation. they stay as embryonic cells.. thy never take on functional shape and do their job
question
How does a cell become cancerous?
answer
DNA has been damaged during replication process, through cancer causing agents, aging process, or something went wrong during the process of cell division
question
There is evidence of telomerase activity in cancer cells, which may allow cancer cells to persist .. Explain
answer
Some cancer cells can actually produce telomerease. Telomerase is the enzyme that rebuilds tolomeres at the end of our chromosomes. If it is a cancer cell and it is constantly getting rebuilt, then that means the cancer cell is immortal = bad!
question
What are immortal cells?
answer
cells that can keep rebuilding telomeres and keep reproducing .. some cancer cells are like this. If they keep reproducing then there will always be more cancer
question
Telomerase and immortal cells
answer
Telomerase is an enzyme made of protein and RNA subunits Function is to elongates chromosomes by adding TTAGGG sequences to the end of existing chromosomes. Telomerase is found in fetal tissues, adult germ cells, and also tumor cells. Telomerase activity is regulated during development and has a very low, almost undetectable activity in somatic (body) cells. Because these somatic cells do not regularly use telomerase, they age. The result of aging cells is an aging body.
question
What happens if telomerase is activated in a cell
answer
the cell will continue to grow and divide. This "immortal cell" theory is important in two areas of research: aging and cancer.
question
How to extent a human's life span, expectancy and fountain of youth
answer
If we can find a way to keep stem cells active and its telemerase
question
How does losing telomeres and producing tolemerase bad?
answer
Losing telomeres signals the end of a cell's life.. contributing to aging process Producing too much telemerase can cause a cell to become cancerous
question
Why do we need to replicate DNA? When do we do it?
answer
We replicate DNA in order to repair and grow in humans, we do two types of cell reproduction 1. growth of the individual 2. for repair of damaged cells 3. production of a new individual/offspring
question
3 reasons we do dna replication
answer
grown, repair and production of offspring
question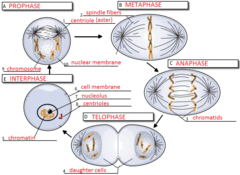
What is mitosis?

answer
-Cell division that takes place in somatic cells ( somatic cells are not involved in sexual reproduction. -Results in daughter cells with identical genetic information, DNA
question
What reasons has to do with mitosis?
answer
Growth and repair
question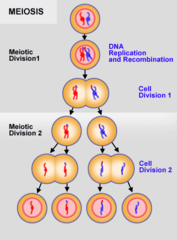
What is meiosis?

answer
A special type of division produces nonidentical daughter cells (gametes, or sperm and egg cells)
question
What type of genetic do we produce in mitosis?
answer
identical daughter cells
question
The asexual reproduction of mitosis occurs where?
answer
in the somatic of the body
question
What are somatic cells?
answer
general cells .. skin cells. any cells that do not produce egg or sperms is somatic
question
Where are somatic cells found?
answer
heart, lungs, liver, brain, kidneys, etc.
question
What reasons has to do with meiosis?
answer
production of offspring
question
What type of reproduction is mitosis?
answer
Asexual reproduction .. prefix "a" always means without (sex)
question
What type of reproduction is meiosis?
answer
Sexual reproduction
question
What type of genetic do we produce in meiosis?
answer
Different/ non identical daughter cells
question
The sexual reproduction of meiosis occurs where?
answer
in the gamete producing cells. in humans, it happens in ovaries and testies .. eggs and sperms
question
What are the gammete producing cells?
answer
ovaries and testies are gammete producing cells.. meiosis occurs to produce egg cells or sperm cells
question
Where are gammete cells produced?
answer
ovaries and testies.. all infants start out as a female btw.. in them meiosis occurs to produce egg cells or sperm cells
question
Our bodies does how many different types of DNA replication
answer
2 different types 1. copying of the DNA 2. depending on what cell of the body, they will separate differently
question
How many chromosomes do somatic cells have?
answer
have 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs 1 chromosomes from mom, 1 from dad to make a pair - have similar lengths and carry the same genetic information as the pair does
question
The 23rd pair is called the sex chromosomes.. it determines
answer
gender
question
When the expression of a chromosome is different, it is called
answer
recessive and dominant
question
How many chromosomes does meiosis have?
answer
23 chromosomes, no pairs The chromosomes are 1/2 of each pair of the 46 chromosomes .. it is divided in half
question
When cell doesn't show chromosomes, it is
answer
chromatin. it is unwind, not condense. consist of DNA and histone (a packing protein).. chromatin is a thin strand that is barely visible
question
When does chromatin condenses?
answer
when the cell is prepared to do cell division. It condenses into a chromosome
question
When DNA is presented as an X, this means
answer
it is a replicated chromosome
question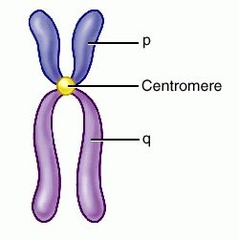
What is the centromere

answer
When DNA replication occurs, the two new strands don't immediately replicate. They are held together by centromere, or central unit holding it together.. At this time, it is still considered 1 chromosome
question
The DNA replication that is being held together by a centromere/central unit is considered?
answer
1 chromosome
question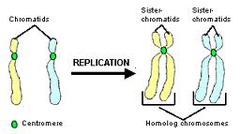
What is chromatids

answer
Each replicated side of a DNA that is being held by centromere .. One replicated chromosome consist of 2 daughter chromatids.. As long as they are attached, they're chromatids
question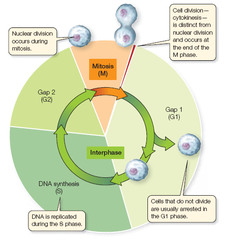
What is interphase?

answer
The very beginning when it is prior to cell division, the DNA is scattered throughout the Nucleus as Chromatin. NOT chromosomes
question
What happens after interphase?
answer
it enters meiosis where the chromosomes starts to seprate
question
What does mitosis do during this replication?
answer
It is responsible for pulling the chromosomes apart so that it can become a separate chromosomes, called chromatids. Then the chromatids will become separate chromosomes
question
In cell division, Meiosis and Mitosis does what?
answer
separates the chromosomes
question
In unicellular organisms: (Bacteria, Protozoa)
answer
division of one cell reproduces the entire organism .. can do sexual and asexual. Bacteria always does asexual, but some protozoas can do both
question
In Multicellular organisms: (Most fungi, plants and animals)
answer
division results in the production of gametes (egg & sperm in meiosis) - Growth - Repair for mitosis
question
In mitosis, are the 2 daughter cells identical in every aspect?
answer
no.. only identical in dna
question
2 types of cell divisions
answer
Types of cell division in eukaryotes 1. Mitosis: Cell division that takes place in somatic cells ( somatic cells are not involved in sexual reproduction. -Results in daughter cells with identical genetic information, DNA 2. Meiosis -A special type of division produces nonidentical daughter cells (gametes, or sperm and egg cells)



