Synaptic transmission and neurochemistry 1 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
neurocrine
answer
an electrical signal that travels along a nerve cell until it reaches the very end of the cell, where it is translated into a chemical signal secreted by the neuron
question
neurotransmitter
answer
diffuse across a small gap to the target cell rapid
question
neuromodulator
answer
acts more slowly as an autocrine/paracrine signal
question
neurohormone
answer
chemicals released by neurons into the blood for distribution
question
electrical synapses
answer
electrical current flowing from one neuron to the other
question
chemical synapses
answer
chemical transmitters transfer info from one neuron to the other
question
loewi vagustoff
answer
electrical stimulation of axons innervating frog heart released chemical that mimicked effects of neuron stimulation on hearbeat vagustoff released, acetylcholine
question
gap junctions
answer
where direct transfer of ionic current from one cell to the next occurs formed with 2 connexons- one from each cell aplyasia tail and ink firing
question
mammalian brain and gap junctions
answer
formed between glial cells astrocytes are interconnected through gap junctions - glial network
question
gap junctions between neurons
answer
generation of AP in one neuron causes small amount of current to flow through gap junctions into a second neuron
question
chemical synapses presynaptic element
answer
usually axon mitochondria secretory granules synaptic vesicles active zones
question
chemical synapses postsynaptic element
answer
usually dendrite postsynaptic density: receptors and enzymes accumulate just under membrane
question
types of synapsese in CNS
answer
axodendritic axosomatic axoaxonic dendrodendritic
question
neurotransmission process
answer
neurotransmitter synthesis load into synaptic vesicle vesicles fuse to presynaptic membrane neurotransmitter released binds to postsynaptic receptors neurotransmitter removal from the synaptic cleft
question
5 types of neurotransmitter chemicals
answer
amines acetylcholine peptides amino acids purines, gases, lipids
question
amines made with three amino acids...
answer
tyrosine, trytophan, histidine dopamine, serotonin, histamine
question
glutamate gaba ^amino acids
answer
excitatory, depolarization inhibitory (entry of Na, Ca), hyperpolarization (entry of Cl-)
question
neurotransmitter release
answer
arrival of AP in axon terminal depolarization voltage gated Ca channels open Ca enters exocytosis of vesicles and release of content in synaptic cleft vesicle membrane recovered by endocytosis
question
release of peptide transmitters
answer
by secretory granules, Ca dependent requires high frequency firing release of peptides takes longer
question
termination of neurotransmitter activity
answer
diffusion reuptake enzymatic degradation
question
receptors of neurotransmitters
answer
over 100 2 major classes ionotropic metabotropic
question
ionotropic receptor
answer
receptor channel ligand-gated ion flow
question
metabotropic receptor
answer
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) ion channel/enzyme activity
question
basic signal transduction
answer
signal molecule (ligand) membrane receptor intracellular signal molecules target proteins response SIGNAL AMPLIFICATION
question
second messengers
answer
cAMP, cGMP, IP3, DAG, Ca2+
question
how second messengers are formed AC GC PLC
answer
Atp>cAMP GTP>cGMP membrane phospholipids> IP3 + DAG
question
GPCRs
answer
when activated: open an ion channel in the membrane alter enzyme activity in cytoplasm through AC and PLC
question
cAMP pathway
answer
AC catalyzes cAMP from ATP decrease in cAMP, decrease of PKA
question
PLC pathway
answer
cleaves phospholipid into two messengers IP3 and DAG ligate receptors, binds and opens up then Ca released from smooth ER DAG finds PKC and activates phophorylation
question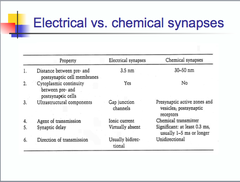
electrical vs chemical synapses

answer
ELEC=IONS CHEM=NEUROTRANS



