Spinal Anesthesia – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is spinal anesthesia?
answer
Injection of local anesthetic into the subarachnoid space that produces a rapid response in the patient
question
What is another name for spinal anesthesia?
answer
Subarachnoid block
question
What type of procedures is spinal anesthesia used during?
answer
Can be used for surgical procedures from the chest down such as lower abdomen, perineum, and lower extremity surgeries.
question
What is the preferred anesthetics for cesarean delivery?
answer
Spinal anesthesia because it reduces morbidity and mortality because general anesthesia can cause uterine placental insufficiency and reduce blood flow to the baby
question
What are the absolute contraindications for spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Patient refusal 2. Increased intracranial pressure 3. Active coagulopathy 4. Inability to position 5. Infection at the site of injection
question
What is the number one, most important contraindication for spinal anesthesia?
answer
Patient refusal
question
What are some relative contraindications for spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Systemic infection 2. Hemodynamic profile that odes not tolerate a decrease in systemic vascular resistance such as shock or aortic stenosis
question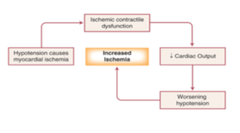
What happens to a patient with severe aortic stenosis receiving spinal anesthesia?

answer
Decrease SVR leads to decrease CO leads to worsening hypotension than MI
question
How many total spinal nerves does an adult patient have?
answer
30 spinal nerves
question
How many vertebra does an adult patient have?
answer
33
question
Where is the inferior angle of the scapula located?
answer
T6-T7
question
Where is the Superior iliac crest landmark on the vertebral column?
answer
Across the L4 body or the L4-L5 interspace
question
What is the anatomical location of the epidural insertion?
answer
The superior aspect of the iliac crest
question
How many cervical spinal nerves are there?
answer
8 spinal nerves for 7 vertbrae. All other vertebrae have one nerve per one vertebrae
question
What is another name for the end of your spinal cord?
answer
Conus medullaris
question
Where is the spinal cord normally end in the adult patient?
answer
L1
question
What is cauda equina syndrome typically secondary to?
answer
Lidocaine this is why you don't use lidocaine often in spinal anesthesia
question
What side of the spinal column is responsible for sensory?
answer
The dorsal portion carries the sensory fibers
question
What side of the spinal column is responsible for motor?
answer
The ventral portion carriers the motor signal
question
What are the neurotransmitters for the pain pathway?
answer
1. Substance P 2. Glutamate
question
Where does fast pain cross over in the body? Slow pain?
answer
Fast pain= A delta crosses over in the medulla Slow pain= C fibers crosses over at the level of spinal cord in the gray matter
question
What portions of the brain help to suppress pain?
answer
1. Raphe nucleus 2. Periadequatal grey
question
Where are the sacral cornu?
answer
The sacral cornu are bony prominences on either side of the sacral hiatus that help aid the placement of caudal anesthesia. This is common in pediatric anesthesia and sometimes in adult hemmordiectomy
question
What is the high point of the spinal vertebra when the patient is supine?
answer
C3 and L3
question
What are the low points of the spinal vertebra when the patient is supine?
answer
T6 ; S2
question
Describe the orienation of the spinous process of the vertebra?
answer
Lumbar ; cervical spinous process: relatively straight posterior and horizontal orientation Thoracic- pointing caudally or oblique orientation
question
How many total vertebrae does an adult patient have?
answer
33
question
How many total spinal nerves does a patient have?
answer
30
question
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
answer
12 (T1-T12)
question
How many cerivcal vertebrae are there?
answer
7 (C1-C7)
question
How many lumber vertebrae are there?
answer
5 vertebrae
question
How many sacral vertebrae are there?
answer
5 fused together (in adults)
question
How many coccyx vertebrae are there?
answer
4 fused together (in adults)
question
What is the name for the first cervical vertebrae?
answer
Atlas (trick to remember this: the atlas carries the weight of the world (head) on its shoulders
question
What is the name for the second cervical vertebrae?
answer
Axis
question
Why is important to understand that the blood vessels are located in the lateral aspect of the epidural space?
answer
You need to know where is the blood vessels are located in order to avoid placing your spinal needle into the blood vessel
question
What are the two different approaches for spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. median 2. paramedian
question
How does the ligamentum flavum feel?
answer
It feels grainy sort of like sand
question
How many ligaments are in the vertebral column?
answer
5
question
Where do patients spinal cords typically end?
answer
30% T12 60% L1 10% L3
question
Why do you use the superior iliac crest as the landmark for spinal anesthesia?
answer
Because it lines up with the area between L4 ; L5 where the spinal cord is not located.
question
What is tuffiers line?
answer
A line drawn across the superior iliac crest that cross the body of L4 or the interspace of L4-L5. Ideal site of spinal anesthesia
question
What are the spinal nerves in the subarachnoid space covered by?
answer
A thin layer of pia mater
question
Where do local anesthetics work for spinal anesthesia?
answer
On the spinal nerves
question
What are the common local anesthetics used for spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Bupivacaine 2. Lidocaine 3. Tetracaine 4. Procaine
question
What are some historical complications associated with lidocaine use for epidural anesthesia?
answer
1. Cauda equina syndrome 2. Transient radicular irritation ***this will manifest in leg, back, or buttock pain. Can reduce risk by using low dose, current recommendation of max dose of lidocaine is 60mg
question
What type of cases require tourinquet?
answer
Knee surgeries
question
What are the different doses for tetracaine?
answer
Lower extremity procedure = 6-10 mg Intra-abdominal procedure = 12-15 mg Pelvic procedure = 12 mg
question
What are the different bupivacaine doses: c-section, ortho, and intra abdominal?
answer
C-section= 10-12.5 mg Orthopedic cases= 12-15 mg Intra-abdominal procedures =15-18 mg
question
What is the benefit of adding a vasoconstrictor to spinal anesthesia?
answer
It prolongs the blockade by reducing blood flow preventing the local anesthetic moving away from site of action
question
What is the benefit of adding opioids to spinal anesthesia?
answer
Intensify the block
question
What kind of effect does local anesthetics and opioids have in the intrathecal space?
answer
Synergistic effects that contributes to the effectiveness of the blockade via the mu receptor
question
What is the problem with morphine administration during spinal anesthesia?
answer
It can result in delayed respiratory depression due to its hydrophillic nature. This causes a long duration of action due to low spinal cord distribution volumes and slow clearance to the plasma
question
What is the dose of morphine to adminster when giving spinal anesthesia?
answer
0.1-0.5mg
question
What happens when you increase the dose of morphine in spinal anesthesia?
answer
Increase dose= increase side effects 1. N/V 2. Pruritus 3. Respiratory depression
question
What is the benefit of using fentanyl and sufentanyl in spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Lipophillic agents 2. Rapid spread in the spinal cord 3. Due to rapid rostral spread- can possible lead to early resp depression unlike morphine's delay 4. Small dose intensifies block but does not prolong it 5. Reduce LA dose 6. Faster sensory and motor recovery
question
What is sufentanyl in spinal anesthesia most frequently used during?
answer
Labor and C-sections
question
What is the dose of spinal sufentaynl for labor?
answer
2.5-7.5mcg
question
What is the dose of spinal sufentaynl for c section?
answer
In combination with low dose bupivaine 2.5-10mcg
question
What are the most common side effects of intrathecal opioids?
answer
1. Respiratory depression 2. Pruritus 3. N/V
question
What are the two types of vasoconstrictors used in conjugation with local anesthetics in spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Epinephrine (0.2-0.3mg) or epi wash 2. Neosynphrine (2-5mg) or neo wash
question
What is the benefit of adding alpha 2 adrenergic agonist to local anesthetics for spinal anesthesia?
answer
Intensifies and prolongs sensory and motor blockade
question
What are the common side effects of adding alpha 2 adrenergic agonists to local anesthetics for spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. hypotension 2. Bradycardia 3. sedation
question
What factors can effect the uptake of local anesthetics in the neural space?
answer
1. Concentration of LA in the CSF 2. Suface area of the neural tissue 3. Lipid content of the nerve 4. Blood flow of the nerve
question
How does concentration of local anesthetics effect uptake in the neural space?
answer
The higher the concentration, the better the effect
question
How does blood flow affect the uptake of LA in the neural space?
answer
The greater the blood flow the less effective/length of block
question
How does the surface area of the neural tissue affect the uptake of LA in the neural space?
answer
Smaller the surface area= better effect
question
What are the primary nerve fibers for pain transmission?
answer
1. A delta 2. C fibers
question
What fibers are affected by anesthetic blockade first?
answer
1. C fibers (slow pain & touch) 2. A delta (fast pain) 3. A alpha (motor)
question
What functions are C fibers and A delta fibers responsible for?
answer
1. pain 2. Temperature 3. Touch
question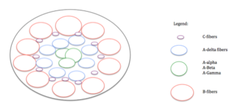
Describe the location of nerve fibers within a nerve bundle.

answer
1. B fibers 2. C fibers 3. A-delta 4. A-gamma 5. A-beta 6. A-alpha
question
What travels with pain on C fibers and A delta fibers?
answer
Temperature
question
What are B fibers responsible for?
answer
Sympathetic
question
What are A-gamma fibers responsible for?
answer
Motor tone
question
What are A-beta fibers responsible for?
answer
Touch and pressure
question
What are A-alpha fibers responsible for?
answer
Motor function & proprioception
question
Describe the zones of differential blockade?
answer
Site of injection will be T6. There will be a motor blockade two levels lower ( T8) & there will be sympathetic blockade 2-6 levels higher than the sensory level. Sensory blockade will be at level of injection.
question
What is the first fiber that recovers first after spinal anesthesia?
answer
A-alpha (motor functions)... nerve fibers return in reverse order (motor is the last to leave and first to return, etc.
question
How are neural local anesthetics injections eliminated?
answer
They are eliminate via vascular absorption not via the kidney/liver from the body
question
What changes with age effect spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Neural nerves become vulnerable to local anesthetics 2. Number of myelinated nerves decrease 3. Conduction velocity in motor nerves decrease 4. CSF volumes decreases 5. Specific gravity of CSF increases
question
Describe what you would expect to see in an elderly patient receiving spinal anesthesia.
answer
1. Faster onset 2. Higher level of blockade 3. Longer lasting anesthesia
question
Can height affect spinal anesthesia?
answer
In extreme cases, length of the spinal column may affect the spread of local anesthetic
question
Does weight of the patient affect the spread of local anesthetics during spinal anesthesia?
answer
High BMI as a result of a large abdominal mass will decrease the volume of CSF thusly spread of local anesthetic will increase
question
What conditions will decrease the amount of CSF a patient would have?
answer
1. Morbid Obesity 2. ascites 3. Anything that compresses on the spinal column
question
What is the normal CSF volume in an adult patient?
answer
150mL
question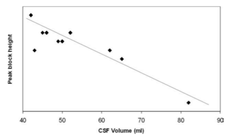
What does the graph attach reveal?

answer
The higher the volume of CSF the lower the spread of local anesthetics
question
What are the safest injection site of spinal anesthesia?
answer
L4-L5
question
Describe the spread of local anesthetics between L4-L5 & L2-L3?
answer
Spread of local anesthetic at L2-L3 is higher than L4-L5
question
Is spinal injections sites higher than L3 recommeneded?
answer
No
question
What does most studies suggestion about injecting spinal anesthesia above L3?
answer
Injections L3 and higher are at increased risk for causing neural damage
question
What happens if the opening of the whitacre needle is placed toward the cranium?
answer
It causes a higher sensory level blockade and a longer duration of action
question
What should you use in conjunction with a needle that is smaller than 22 G?
answer
Always use a transducer because they are so small you don't want to risk getting a needle stuck in their back if it breaks off
question
What is barbotage?
answer
Aspiration CSF before injecting LA, mix the LA and CSF in the syringe, ; than injecting back into the spinal column.
question
Is barbotage effective?
answer
It is found to be not effective
question
How does the dose of Local anesthetic affect the spread of the local anesthetic?
answer
Larger doses of local anesthetic increase the spread of the medication
question
What is density?
answer
Density is a physical characteristic expressed as weight in gram of 1 mL of a solution at a specified room temperature
question
What is baricity?
answer
The relationship between the density of a local anesthetic and the density of the CSF
question
What is an isobaric local anesthetic?
answer
Local anesthetic has the same density or specific gravity of CSF " stays where you put it"
question
What is an hypobaric local anesthetic?
answer
Local anesthetic that has a density or specific gravity that is less than CSF "Floats up" because its lighter than CSF
question
What is a hyperbaric local anesthetic?
answer
Local anesthetic that has a density or specific gravity that is greater than CSF "sinks" because its heavier than CSF
question
What is isobaric local anesthetics mixed with?
answer
Normal saline
question
What are hypobaric local anesthetics mixed with?
answer
Sterile water
question
What are hyberbaric local anesthetics mixed with?
answer
dextrose
question
What spinal level does sympathectomy occur at?
answer
T1-T4
question
What are cardiovascular signs of spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. hypotension 2. Sympathectomy (arterial and venous dilation) 3. Possible bradycardia
question
What do you want to do before performing spinal anesthesia?
answer
Administered crystalloids to your patient to help pretreat some of the potential cardiovascular side effects such as hypotension
question
Why do you not want glucose in IV fluids such as dextrose during spinal anesthesia?
answer
The increase in glucose will cause the patient to urinate a lot, resulting in decrease in fluid volume status
question
What is the drug of choice is a patient has severe bradycardia intraoperatively?
answer
Edephrine
question
What is the drug of choice when a patient has symptomatic bradycardia during a procedure?
answer
Mixed alpha and beta agonist
question
During spinal anesthesia, a patient experiences hypotension but has a normal or elevated heart rate, what drug would you want to administer?
answer
Phenylephrine (neo) which is an alpha agonist. This causes an increase in SVR without increasing HR
question
During spinal anesthesia, a patient experiences hypotension with bradycardia, what drug would you administer?
answer
Ephedrine because it's a mixed alpha and beta agonist that will increase PVR and HR
question
A patient becomes hypotension during subarachnoid anesthesia and received ephedrine. 10 mins past and the patient is now several hypertensive, what would you do?
answer
Manage the hypertension with vasodilators, narcotics, and anxiolytics
question
How can you tell if epedrine and phenylephrine are working?
answer
First look for heart rate increase, blood pressure increase should follow
question
Describe the respiratory complications often associated with subarachnoid anesthesia?
answer
Pulmonary alterations in healthy patients have little clinical significance. If the anesthesia is a high spinal some muscle paralyze can occur (abdominal than intercostal). If the phrenic nerves are paralyzed and loss of accessory muscle of ventilation occurs there will be an increases potential for hypoxia
question
Where are the phrenic nerves?
answer
C3-C5
question
What can happen to functional residual capacity during high spinal anesthesia?
answer
Functional residual capacity can decrease due to paralysis of abdominal muscles
question
Describe the thermoregulatory considerations for patients receiving spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Shivering due to peripheral vasodilation 2. Spinals impair central thermoregulation
question
What do you need to do before performing spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Prepare and monitor patient 2. Review history (anticoagulants and antiplatelet medications) 3. Ensure informed consent was completed 4. Prepare drugs and equipment 5. Always have general anesthesia set up
question
Dermatome level for peri-anal surgery.
answer
S2-S5 aka saddle block
question
Dermatome level for foot and ankle surgery.
answer
L2
question
Dermatome level for knee surgery
answer
L1 ***used for lower limb amputation
question
Dermatome level of thigh tourniquet procedure.
answer
T10
question
Dermatome level for vaginal delivery and uterine procedures such as TURP.
answer
T10
question
Dermatome level for urological & lower abdominal procedures.
answer
T6
question
Dermatome level for upper abdominal surgery.
answer
T4
question
What are different positions you can place patient in for spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. sitting 2. Lateral 3. jack-knife
question
Describe how to place a patient in the sitting position for spinal anesthesia.
answer
1. Hang leges over the side of the bed 2. Have patient hug a pillow 3. Put patient feet up on a stool 4. Assistant must keep patient from swaying by standing in front of them 5. Have patient curve there back in a C formation
question
What is the benefit of the C position during spinal anesthesia?
answer
It helps to palpate the spinous processes
question
How do you place a patient in the lateral position for spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Patient is placed parallel to the edge of the bed 2. Have the patients arms to the side and legs flexed up to the abdomen 3. Have patient flex forehead down toward the knees
question
What are the layers that the needle will go through when performing spinal anesthesia via median?
answer
1. Skin 2. Subcutaneous fat 3. Supraspinous ligament 4. Interspinous ligament 5. Ligamentum flavum 6. Dura Mater 7. Subdural space 8. Arachnoid Mater 9. Subarachnoid space
question
What layers does the needle travel through during spinal anesthesia utilizing a paramedian approach?
answer
Same layers as it does through the median approach except the supraspinous ligmant and interspinous ligament
question
What layers did you transverse if you hear a pop during a spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Ligamentum flavum 2. dura
question
What does hyperbaric solution look like when mixed with CSF?
answer
You will notice a swirling in the solution... isobaric and hypobaric will remain clear in apperance
question
What is the difference between paramedian and median approaches to spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Paramedian you approach it in a lateral direction 2. Paramedian does not cross the interspinous and superspinous ligament
question
What layers does the needle travel through during spinal anesthesia utilizing a paramedian approach?
answer
Same layers as it does through the median approach except the supraspinous ligmant and interspinous ligament
question
What do you do if the spinal needle is already deeply inserted and it feels like it is in the right spot but there is no CSF what will you do?
answer
1. Rotate the needle 90 degrees and wait for 10 to 15 seconds, repeat as needed 2. Inset the stylet and remove it 3. Try to aspirate at different rotating angles 4. If troubleshooting does work, withdraw needle, check patient position, and try again
question
If blood in the spinal needle/syringe a normal finding?
answer
Maybe. There may be some blood from the epidural space present in the needle. This should clear within a few drops of CSF. If blood continues to drip after this the position of the needle must be changes because it is most likely in an epidural vein
question
What do you do if the spinal needles causes pain in the patients leg?
answer
DO NOT inject anything. Withdraw the needle and redirect it more medially
question
What do you do if the needle hits the bone?
answer
1. Reposition the patient 2. Change the needle because the tip may be damaged from contact with the bone 3. Try a different interspace or paramedian technique 4. Pt with spinal stenosis are at increase risk of spinal hematoma; if you are not able to find the subarachnoid space, change the anesthesia method; do not be stubborn
question
What are you probably hitting if the needle hits the bone early in the procedure during spinal anesthesia?
answer
Spinous process; correct this by pointing the needle slight caudad
question
What bone are you probably making contact with if the needle hits bone late in the spinal anesthesia procedure?
answer
The lamina
question
What would you do if you are hitting the lamina late in the procedure during spinal anesthesia?
answer
Point the needle slightly cephalad
question
What are the reason for backaches during spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Needle trauma 2. Local anesthetic irritation 3. Ligametous strain secondary to muscle relaxation
question
What causes a postdural puncture headache?
answer
This is due to an accidental dural puncture. After the dura was punctured, the hole did not close up and CSF slowly was leaking out. When CSF continues to leak out, there is not enough CSF around the brain causing compression & cranial nerve traction, resulting in headache
question
Describe the headache associated with postdural puncture?
answer
1. Headache is worse when patient is upright 2. Pain radiates to neck "stiff neck" 3. Nausea and vomiting
question
What is a wet tap?
answer
The accidental dural puncture
question
What are some other signs and symptoms due to accidental dural puncture resulting in low CSF?
answer
1.Headache 2. Diplopia (CN 6) 3. Tinnitus (CNS 8) 4. Seizure
question
Why does diplopia occur with accidental dural punctures?
answer
Traction on cranial nerve 6 caused by low CSF result in failure of the affect eye to abduct resulting in diplopia
question
Why are seizures a possibility after accidental dural puncture?
answer
Due to cerebral vasospasm caused by cerebral hypotension from dural puncture
question
What are the two most common sign and symptoms associated with postdural headache?
answer
1. Nausea (60%) 2. Neck stiffness
question
What is the etiology of postdural headache?
answer
Loss of CSF volume exceeding CSF production ? cerebral vasodilation ? pain
question
What are some risk factors for postdural headache?
answer
1. Younger patients 2. Women 3. History of prior post dural headache 4. Multiple dural punctures 5. Needle design and size (whitarch good)
question
What is the treatment options of postdural headaches?
answer
1. Patient to remain supine 2. NSAIDS 3. Narcotics 4. Methylaxanthine derivatives (Caffeine) 5. Blood patch
question
What is a blood patch useful for treating?
answer
Postdural puncture headaches and symptoms associated with this
question
How is a blood patch performed?
answer
20ml of blood is removed from the patients arm. With the patient in the lateral position the epidural space is located with a Tuohy needle at the level of the dural puncture or a intervertbral space lower. A few mls of the patient blood is injected. The blood will then clot and hopefully occulde the perforation, preventing further CSF leak
question
Do you perform a test dose in spinal anesthesia?
answer
No only with epidural anesthesia
question
Is the risk of systemic toxicity high or low with spinal anesthesia?
answer
It is very rare with spinal anesthesia because drug doses are low. This is a more common issue among epidural anesthesia.
question
Why is a test dose performed with epidural anesthesia?
answer
To avoid systemic toxicity associated with epidural anesthesia
question
What spinal nerve innervate the lung?
answer
T2-T5
question
What is total spinal anesthesia?
answer
When sensory and motor function is lost high in the spinal cord resulting in profound hypotension, bradycardia, and possibly respiratory arrest
question
What are some complications/side effects of spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. backache 2. Post dural puncture headache 3. Total spinal anesthesia 4. Cauda equina sydrome 5. Transient neurologic symptoms 6. Spinal hematoma
question
What is transient neuologic symptoms associated with?
answer
Lidocaine use during spinal anesthesia that result in pain in the legs or buttocks after spinal anesthesia.
question
What spinal anesthesia complications are associated with lidocaine use?
answer
1. Cauda equina syndrome 2. Transient neurological symptoms
question
What is cauda equina syndrome?
answer
Caused by the pooling of toxic concentrations of undiluted lidocaine around the dependent cauda equina nerve roots. This can result in low back pain, weakness, and sensory deficits including bowel and bladder dysfunction.
question
What are some other names for spinal anesthesia?
answer
1. Intrathecal anesthesia 2. Subarachnoid anesthesia
question
Where is the end point of the spinal cord for most adults?
answer
L1
question
What is the end point of the spinal cord for children?
answer
L3



