Pulm – Flashcard
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
muscles of normal breathing
answer
inspiration: internal/external intercostals elevate ribs; diaphragm descends to create vacuum expiration: passive recoil
question
muscles of forced breathing
answer
inspiration: sternocleidomastoid elevates the sternum; scalenes elevates the ribs; pec minor elevates the ribs expiration: internal intercostals pull ribs down; abdominals pulls ribs down and diaphram up; quadratus lumborum pulls last rib down
question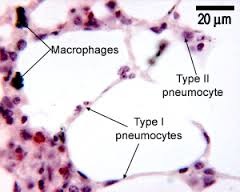
type I pneumocytes

answer
97% of alveolar surface squamous THIN for gas exchange
question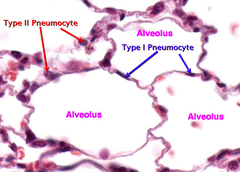
type II pneumocytes

answer
secrete surfactant via calcium channel dependent fusion of lamellar body membranes with cell membrane --exocytosis stem cells for type I and II pneymocytes; proliferate during damage
question
trachibronchial tree: conducting zone
answer
trachea is covered in C-shaped hyaline cartilage and smooth muscle; pseudostratified ciliated columnar cells with goblet, basal, and club/ clara cells; divides into two mainstem bonchi at the level of the sternal angle, T4/5 right branch is more vertical, and wider --thus aspiration almost always goes to the right right branch --three lobar bronchi left branch --two lobar bronchi; bronchi have circular shaped hyalin cartilage and smooth muscle cartilage ceases at the bronchioles and terminal bronchioles, which still have smooth muscle but simple ciliated columnar epithelium
question
where does the trachea divide ?
answer
T4/T5; level of the sternal angle right mainstem bronchi is more vertical and wider
question
where along the respiratory tree does hyalin cartilage cease?
answer
at the level of the bronchioles, which still have smooth muscle
question
respiratory zone
answer
made of the respiratory and terminal bronchioles: cuboidal ciliated cells, club cells, and smooth muscle alveolar sacs: simple squamous layer of pneumocytes, alveolar macrophages and capillaries
question
particle passage through lung:
answer
large particles stuck in mucus at the trachea, bronchi, or bronchioles are swept up and out by cilia small particles wi the respiratory bronchioles and alveoli are eaten by macrophages
question
structures passing through diaphragm
answer
IVC: T8 esophagus and vagus: T10 aorta: T12 i ate ten eggs at twelve
question
aspiration from standing
answer
base of the R lower lobe
question
aspiration from supine
answer
posterior R upper lobe or R lower lobe
question
tracheal histo
answer
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium 16-20 C shaped hyaline cartilage rings with the opening facing posteriorly smooth muscle clara cells secrete surfactant-like lecethin goblet cells and basal cells
question
bronchial histo
answer
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium O shaped hyaline cartilage rings smooth muscle clara cells secrete surfactant-like lecethin goblet cells and basal cells
question
goblet cells
answer
mucus producing cells found at the trachea and bronchi but not bronchioles
question
clara club cells
answer
secrete a surfactant like substance w high IgA which protects the lining most abundant at the terminal bronchioles
question
bronchioles and terminal bronchioles histo
answer
conducting zone: simple ciliated columnar epithelium with club/clara cells and smooth muscle no hyalin cartilage
question
respiratory bronchioles histo
answer
cuboidal ciliated cells with club/clara cells epithelium some smooth muscles but no cartilage
question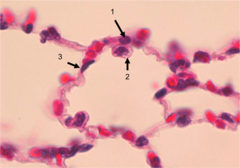
alveolar sacs

answer
NON CILIATED respiratory epithelium of pneumocytes and alveolar macrophages capillaries some smooth muscles but no cartilage
question
tidal volume

answer
tidal volume inspiratory reserve volume expiratory reserve volume residual volume
question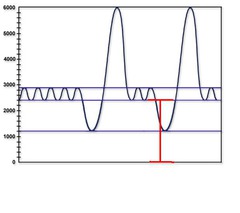
functional residual capacity

answer
residual vol+ expiratory reserve vol
question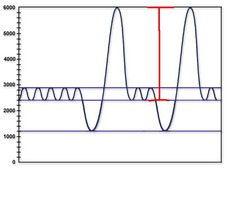
inspiratory capacity

answer
tidal vol + inspiratory reserve vol
question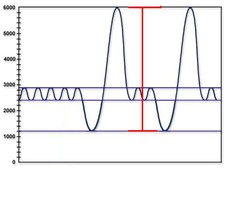
vital capacity

answer
inspiratory capacity + expiratory reserve vol (inspiratory reserve vol+tidal vol+expiratory reserve vol)
question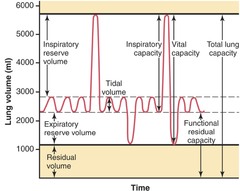
total lung capacity

answer
vital capacity + residual vol inspiratory capacity + functional residual capacity inspiratory reserve vol + tidal vol + expiratory reserve vol + residual vol
question
high altitude
answer
hypoxemia due to reduction in partial pressure of oxygen hyperventilation --respiratory alkalosis (blowing off acid) renal compensation --mild metabolic acidosis increased excretion of HCO3
question
prolonged altitude stats
answer
1. hypoxemia pO2 lower than 76 2. respiratory alkalosis LOW pCO2 below 33 3. ALKALOTIC pH above 7.45 4. compensatory metabolic acidosis, loss of HCO3 below 22
question
ventilation V
answer
air through the alveoli
question
perfusion Q
answer
blood coursing by the alveoli
question
the four major causes of hypoxemia
answer
alveolar hypoventilation VQ mismatch diffusion impairment right-left shunting
question
MCC VQ mismatch
answer
PE --where ventilation continues but there is no perfusion V>Q thus HIGH V/Q
question
VQ zones
answer
zone I apex: V>Q high V/Q (like a PE) zone II midd: V~Q zone III base: V<Q low V/Q (airway obstruction, atelectasis)
question
VQ zone I
answer
apex: V>Q more ventilation than perfusion bc gravity high V/Q (like PE)
question
VQ zone III
answer
base: V<Q more perfusion than ventilation bc gravity low V/Q (like airway obstruction, atelectasis)
question
Hg dissociation curve: right shift
answer
increased metabolic demand: decreased pH, BPG increase, temp increase MCC: lactic acidosis
question
Aa gradient
answer
A: alveolar a: arteriolar normally around 10-12 mmHg wide Aa suggests hypoxemia be O2 not getting from Alveoli to arteriorles
question
MCC wide Aa
answer
PE pt. w tachypnea, history of DVT or risk factors
question
Alveolar gas equation
answer
[150mmHg/pO2 in air] - [paCO2/.8]
question
hyperventilation
answer
blowing off CO2 causes respiratory alkalosis
question
hypoventilation
answer
retaining CO2 causes respiratory acidosis
question
cerebral blood flow is mostly determined via
answer
pCO2: high CO2 causes higher cerebral blood flow once pO2 drops below 50mmHg, cerebral blood flow determined by pO2
question
hypercapnia
answer
high CO2 levels ie patients w COPD, will tend to have higher cerebral plasma flow
question
carotid bodies
answer
chemoreceptor and baroreceptor measures pO2, pCO2, H+, and stretch transmission via glossopharyngial (IX) and solitary nucleus of medulla
question
aortic bodies
answer
chemoreceptor measures pCO2 and H+ transmission via vagus (X) and solitary nucleus of medulla
question
chemoreceptors
answer
peripheral: carotid and aortic bodies; stimulated by drop on PO2 (below 60), increase in PCO2, and decrease of pH central: stimulated by drop on pCO2 wi brain interstitial fluid
question
baroreceptors
answer
carotid bodies: stimulated with drop in arteriolar pressure or decreased stretch to increase efferent sympathetic firing, and decrease efferent parasympathetic firing thus increasing vasoconstriction, HR, and contractility via glossy (IX) which synapses at the solitary nucleus of medulla
question
chronic COPD pt and oxygen supplementation
answer
the chronic COPD pt. is perpetually hypercapnic, due to air trapping thus their peripheral chemoreceptors have been desensitized to high CO2 and low O2 thus when given extra O2, the chemoreceptors think there is plenty of oxygen, and thus the pt. might stop breathing
question
breathing centers of the brain
answer
apneustic center detects hypoxia (low O2) pneumotactic center detects hypercapnia (high CO2) both at the pons, blood from superior cerebellar, AICA, and basilar
question
apneustic breathing
answer
lesion to the pneumotactic center of the pons leads to long inhalations and short exhalations assoc. w chronic COPD bc pneumotactic is desensitized to pCO2
question
medullary breathing
answer
the medulla has a respiratory rate of about 16 --faster than usual
question
Cheyne Stokes breathing

answer
faster faster faster drop. increased speed in breathing followed by apnea MCC brain stem leasion or increased ICP
question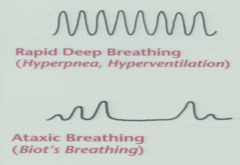
Biots breathing

answer
gasps and short pauses, characteristic of severe meningitis, head trauma, or active dying
question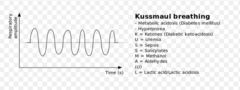
Kussmaul's breathing

answer
compensatory tachypnea and hyperpnea --fast deep breaths compensatory with metabolic acidosis, DKA, renal failure
question
Juxtacapillary J receptors
answer
within the lung interstitum increase respiratory rate in response to pulm edema, PE, or consolidation
question
slow adapting lung receptors
answer
found at the sternocostal junction stimulated w stretch and inflation responsible for exhalation
question
pulsus paradoxus
answer
exaggerated drop in BP or pulse of more than 10 on inspiration MCC: pericardial tamponade, pneumothorax
question
Kussmaul sign
answer
increased jvd on inspiration MCC pneumothorax
question
retinopathy of prematurity
answer
premies are on 100% O2, when taken off, the body things its hypoxic and increases VEGF leading to increased neovascularization creating friable wee arteries
question
hyalin membranes
answer
RDS: respiratory distress syndrome
question
ARDS
answer
widespread pulmonary microvascular endothelum damage causes leaky capillaries, increased cytokine damage, and alveolar edema compensatory goblet cell hyperplasia leads to increased REID index, exacerbating hypoxia intra-alveolar edema, inflammation, hyalin membranes with normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (bc not a cardiogenic prob)
question
Obstructive pulmonary disease findings
answer
air trapping !! increased compliance and increased stretch normal to increased lung capacity normal forced vital capacity DECREASED FEV1 DECREASED FEV1/FVC
question
decreased FEV1
answer
obstructive
question
decreased FEV1/FVC
answer
obstructive
question
Restrictive pulmonary disease findings
answer
reduced expansion/elasticity decreased lung capacity decreased forced vital capacity normal to low FEV1 normal FEV1/FVC (bc both are lowered together)
question
normal FEV1/FVC
answer
restrictive -both are lowered together
question
chronic bronchitis dx details
answer
obstructive lung volumes productive cough for more than three mos (not necessarily consecutive) per year for more than two years cyanotic due to shunting dyspnea due to hypercapnia wheezing and crackles
question
chronic complications of chronic bronchitis
answer
recurrent bacterial infections, increased PMS and inflammation secondary polycythemia pulmonary htn and cor pulmonale
question
chronic bronchitis pathophys
answer
hyperplasia of mucus secreting glands of the bronchi (goblet cells) with patchy squamous metaplasia thickened walls w Reid index ;50%
question
asthma pathology
answer
eosinophilic mediated: Il5 released recruits eosinophils curshmann spirals: shed epithelum leading to whorled mucus plugs charcot-leyden crystals: eosinophil bkdwn product increased sensitivity leads to muscle hypertrophy
question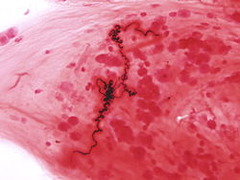
Curshmann spirals

answer
epithelial slophing into whorled mucus plugs seen with asthma
question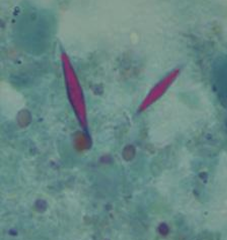
Charcot-Leyden crystals

answer
eosinophilic hexagonal double pointed needle like crystals from excessive breakdown of eosinophils in sputum
question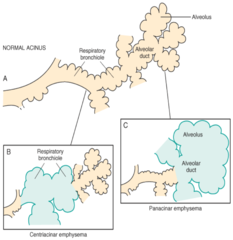
Panacinar emphysema

answer
assoc w a1 antitrypsin deficiency
question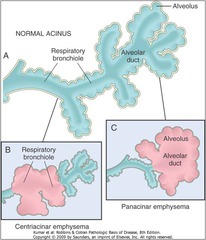
Centriacinar emphysema

answer
assoc. w smokers
question
PAS staining
answer
periodic acid schiff stains for glycoproteins positive stain assoc. a1 antitrypsin deficiency (RE ALL also PAS +)
question
expiratory wheeze
answer
caused by constriction assoc. w asthma bronchoconstriction
question
inspiratory wheeze
answer
stridor caused by obstruction assoc. w croup (paramyxoid virus)
question
bronchiolitis
answer
RSV
question
epiglottitis
answer
H. flu drooling, leaning forward, w stridor
question
croup, laryngotracheitis
answer
paramyxovirus, cornybacterium diptheria inspiratory seal like stridor
question
rust colored sputum
answer
strep pneumo due to extravasation of RBC
question
green sputum
answer
CAP: from myeloperoxidase released from PMN teen CF: pseudamona pyocyanin (re babe CF s.aureus)
question
currant jelly sputum
answer
klebsiella due to extravasation of RBC
question
pneumonia after flu
answer
staph aureus
question
foul smelling sputum
answer
anarobes -pseudamona esp assoc. w alcoholics and homeless tx w clindamycin
question
legionellosis
answer
pontiac fever: acute self-limiting flu like symptoms pneumonia GI upset, diarrhea bradycardia, confusion, headache hyponatremia sputum gram stain w high PMNs but no bacteria (doesnt gram stain)
question
hyponatremia w flu-like symptoms, GI upset, pneumonia
answer
legionarres also assoc: bradycardia, headache, confusion
question
anthracosis
answer
coal miners lung coal laden macrophages and pleural thickening with calcifications NO increase in cancer risk restrictive lung pattern and exertional dyspnea
question
asbestosis
answer
shipyard, old buildings restrictive lung pattern w increased risk of cancer calcified pleural plaques and ferruginous bodies
question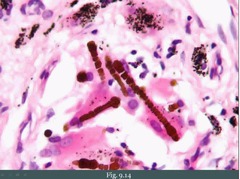
ferruginous bodies

answer
asbestosis restrictive lung disease
question
silicosis
answer
sand and glass impairs macrophages, thus increased susceptibility to Tb egg shell calcifications and restrictive lung pattern
question
egg shell calcifications

answer
silicosis
question
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
answer
restrictive lung pattern with honeycombing of the lungs repeated cycles of lung injury and wound healing with increased collagen deposition assoc. digital clubbing
question
honey combing of the lungs
answer
diffuse small reticulonodular opacities more pronounced at the lower lobes on CXR IDIOPATHIC pulmonary fibrosis
question
interstitial pneumonia bugs
answer
mycoplasma, chlamydia, legionella RSV, CMV
question
stages of a lobar pneumonia
answer
day 1. congestion w vascular dilation; alveolar exudate of bacteria day 2-3: red hepatization: alveolar exudate of PMNs, fibrin, erythrocytes with a red liver like consistency day 4-6: grey hepatization: RBC disintegrate, alveolar exudate of PMNs and fibrin; lobe grey and brown resolution: enzymatic digestion of infiltrate; restored architecture
question
red hepatization of the lungs
answer
day 2-3 of lobar pneumonia alveolar exudate of PMNs, fibrin, erythrocytes
question
grey hepatization of the lungs
answer
days 4-6 of lobar pneumonia RBC disintegrate, alveolar exudate of PMNs and fibrin
question
resolution of lobar pneumonia
answer
enzymatic digestion of intiltrate w restored architecture
question
Mesothelioma histopath
answer
malignancy of pleura assoc. w asbestosis psammoma bodies and epitheliod papillary projections lined with mesothelial cells cytokeratin+ and calretinin +
question
psammoma bodies
answer
mesolemioma meningioma papillary carcinoma of the thyroid serous papillary cystadenocarcinoma of ovary
question
Pancoast superior sulcus tumor
answer
at the apex of the lung compression syndromes recurrent laryngeal: hoarseness superior cervical ganglia: horners ipsi ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis shoulder pain due to brachial plexus irritation SVC syndrome possible but rare assoc. w non small cell
question
SVC syndrome
answer
impaired venous return from the upper part of the body, manifesting as persistent cough, dyspnea, facial edema, elevated ICP, elevated JVP assoc. w mediastinum mass
question
Small cell lung cancer
answer
aggressive and widely metastatic centrally located syndromes: cushings due to increased ACTH, SIADH, labert eaton presynaptic Ca channel abs
question
Small cell lung cancer histopath
answer
Kulchitsky cells: undifferentiated small blue cells cytokeratin+ synaptophysin+ chromogranin+ neuroenolase+
question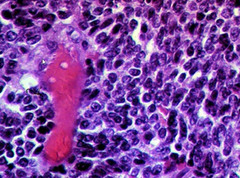
Kulchitsky cells

answer
poorly differentiated, dark blue cells with salt and pepper nucleus neuroendocrine origin cytokeratin+ synaptophysin+ chromogranin+ neuroenolase+
question
Adenocarcinoma of the lung
answer
located peripherally most common lung cancer in nonsmokers and womyn assoc. w finger clubbing, KRAS, EGFR, ALK activating mutations hazy infiltrates on CXR resemble pneumonia thickening of alveolar walls
question
Adenocarcinoma of the lung histopath
answer
glandular pattern w mucin+ stain thickening of alveolar walls
question
Squamous cell carc lung
answer
hilar mass arising from bronchus w central necrosis or cavitation high assoc. smoking: squamous metaplasia of respiratory epithelium secondary to chronic irritation (re similar to barrets) produces PTH causing hypercalcemia --Keratin pearls on histo
question
Squamous cell carc lung histopath
answer
keratin pearls (re hypercalcemia) due to squamous metaplasia secondary to smoking (similar to barrets)
question
Large cell carcinoma of lung
answer
peripherally located highly anaplastic undifferentiated tumor secrete BhCG causing gynecomastia and galactorrea
question
Bronchial carcinoid tumor
answer
low grade, epithelial origin secrete seretonin causing flushing, diarrhea, wheezing nests of neuroendocrine cells, chromogranin A+
question
Large cell carcinoma of the lung histopath
answer
pleomorphic giant cells +BhCG
question
digital clubbing
answer
assoc w large cell lung cancer, adenocarcinoma of the lung, ideopathic pulmonary fibrosis, bronchiectasis, end stage COPD, CF re anemia is spooning
question
Ghon complex
answer
caseating granulomas at hilar nodes, and the ghon focus ie lower lobe classic assoc. primary TB infection
question
primary vs reactive tb
answer
primary lesions at lower of middle lobes of lungs reactive lesions at apex of lungs primary tb is asymptomatic
question
hilar node lesions
answer
silicosis: egg shell primary Tb: granulomas sarcoidosis: lymphadenopathy squamous cell carcinoma: mass
question
coin lesion
answer
on CXR primary lung cancer re: mets have multiple lesions
question
highest fetal oxygenated blood
answer
ductus venosum which bypasses the liver from the umbilical vein to the IVC
question
where does a fish bone get stuck ?
answer
piriform recess by the vocal cords close proximity to laryngeal nerve of X (cough reflex)
question
asbestosis cancer assoc.
answer
malignant mesothelioma vv rare bronchogenic carcinoma



