Psychiatry-Pharmacology (USMLE) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Drug of choice for management of chronic generalized anxiety disorder
answer
antidepressants velaxafine and SSRIs preferred over TCAs
question
What drugs can be used for acute treatment of generalized anxiety disorder or as adjuncts during initiation of antidepressant therapy?
answer
benzodiazepines
question
Name a second-line agent for generalized anxiety disorder.
answer
buspirone alternative agents: hydroxyzine and pregabalin
question
Drug of choice for panic disorder
answer
SSRIs
question
List 2 adverse effects of alprazolam that do not make it an ideal choice for treatment of panic disorder.
answer
rebound anxiety between doses withdrawal syndromes, including seizures
question
Drug of choice for social anxiety disorder
answer
SSRIs
question
List 3/5 FDA-approved drugs for the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
answer
clomipramine fluoxetine fluvoxamine paroxetine sertraline benzodiazepines or antipsychotic drugs can be added for highly anxious patients
question
Drug of choice for PTSD
answer
SSRIs
question
List 2 SSRIs approved for the ACUTE treatment of PTSD. Which is indicated for long-term management as well?
answer
sertraline: long-term management as well paroxetine
question
Drug of choice for performance anxiety
answer
propranolol and other beta-blockers
question
What amino acid precursor gives rise to dopamine?
answer
tyrosine must be transported across the blood-brain barrier into the dopamine neuron
question
What transporter allows for tyrosine uptake in the presynaptic neuron?
answer
system L Na+-independent manner
question
What is the rate-limiting enzyme in dopamine synthesis?
answer
tyrosine hydroxylase tetrahydrobiopterin cofactor required
question
What enzyme converts DOPA to dopamine?
answer
DOPA decarboxylase so rapid that DOPA levels in brain negligible
question
How do D1 and D2 receptors affect adenylyl cyclase activity?
answer
D1: ? adenylyl cyclase D2: ? adenylyl cyclase, ? K+ conductance, ? Ca2+ conductance
question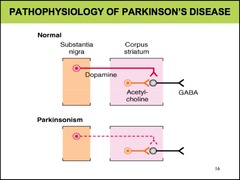
How do dopaminergic neurons from the substantia nigra affect GABAergic output from the striatum?

answer
normally inhibit the GABAergic output
question
Destruction of neurons of which dopamine pathway cause Parkinson's disease?
answer
nigrostriatal 70% of neurons destroyed at time symptoms first appear
question
In regards to dopaminergic and cholinergic neurons, what is the strategy of treatment for Parkinson's disease?
answer
restore dopamine in basal ganglia antagonize excitatory effect of cholinergic neurons
question
What enzyme converts levodopa to dopamine?
answer
DOPA decarboxylase (in CNS)
question
Why does levodopa cause nausea, vomiting, cardiac arrhythmias, and hypotension?
answer
much of the drug is decarboxylated to dopamine in the periphery
question
Name a DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor.

answer
carbidopa does not cross the blood-brain barrier
question
What drug contains carbidopa and levodopa in fixed proportions?
answer
sinemet
question
How does food intake affect the appearance of levodopa in the plasma?
answer
delays appearance of levodopa in plasma
question
Why does responsiveness to levodopa eventually decrease in Parkinson's disease patients?
answer
disappearance of dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons
question
What vitamin is contraindicated with levodopa?
answer
vitamin B6 increases peripheral metabolism of levodopa
question
What emergency can occur with concomitant administration of nonspecific MAO inhibitors and levodopa?
answer
hypertensive crisis
question
Why are antipsychotics contraindicated in Parkinson's disease?
answer
may produce a parkinsonian syndrome
question
Why is levodopa contraindicated in angle-closure glaucoma?
answer
...
question
Name an ergo dopamine agonist. Which dopamine receptor subtype is acted upon by this drug?
answer
bromocriptine D2 receptor used alongside levodopa
question
Name 2 nonergot dopamine agonists used in younger patients.
answer
pramipexole ropinirole
question
What nonergot dopamine agonist was available in a transdermal formulation?
answer
rotigotine recalled due to formation of rotigone crystals
question
What nonergot dopamine agonist is used for rescue therapy for treatment of "off" episodes of akinisia in patients on dopaminergic therapy?
answer
apomorphine pretreatment with antiemetic trimethobenzamide
question
Apomorphine adverse effects (3/6)
answer
QT prolongation dyskinesias drowsiness sweating hypotension bruising at the injection site
question
Name 2 MAOIs that selectively and IRREVERSIBLY inhibit MAO-B.
answer
deprenyl (selegiline) mainly used as adjunct to levodopa; allows dose of levodopa to be reduced rasagiline
question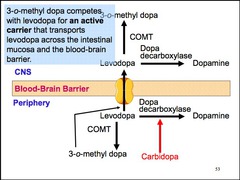
Inhibition of DOPA decarboxylase by carbidopa increases what peripheral metabolite?

answer
3-o-methylDOPA
question
What COMT inhibitor is associated with fulminating hepatic necrosis?
answer
tolcapone
question
Name 2 COMT inhibitors.
answer
entacapone tolcapone
question
Amantadine antiparkinsonian MOA
answer
increases synthesis, release or reuptake of dopamine from the surviving neurons less efficacious than levodopa and tolerance develops more readily, but fewer side effects
question
Amantadine systemic adverse effects (3/4)
answer
restlessness agitation confusion peripheral edema
question
What adverse effect is associated with high doses of amantadine?
answer
acute toxic psychosis
question
What dermatologic adverse effect is associated with amantadine?
answer
livedo reticularis
question
Drug of choice for Parkinson's disease

answer
levodopa + carbidopa
question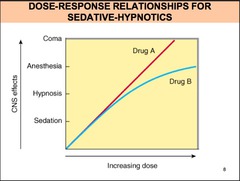
Are sedative-hypnotics with linear or non-linear dose-response relationships dangerous?

answer
linear dose-response curve increase in dose above that needed for hypnosis may lead to a state of general anesthesia higher doses, they may depress respiratory and vasomotor centers in the medulla, leading to coma and death
question
What drugs are the most widely used anxiolytic drugs?
answer
benzodiazepines
question
To what receptors do benzodiazepines bind?
answer
GABAA receptors chloride channels
question
List the subunits that make up the pentameric structure of the GABAA receptor.
;img src=;https://chmanchacentro.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/list-the-subunits-that-make-up-the-pentameric-structure-of-the-gabaa-receptor.jpg; title=;List the subunits that make up the pentameric structure of the GABAA receptor." alt="List the subunits that make up the pentameric structure of the GABAA receptor.">
answer
alpha-2-beta-2-gamma binding sites located between adjacent alpha and beta subunits
question
Between which 2 subunits of the GABAA receptor does benzodiazepine bind?
<img src="https://chmanchacentro.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/between-which-2-subunits-of-the-gabaa-receptor-does-benzodiazepine-bind.jpg" title="Between which 2 subunits of the GABAA receptor does benzodiazepine bind?" alt="Between which 2 subunits of the GABAA receptor does benzodiazepine bind?";
answer
alpha subunit gamma subunit increased in frequency of channel opening events
question
Which 2 benzodiazepine receptor subtypes are found in the CNS?
answer
BZ1 BZ2
question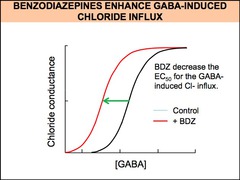
How does benzodiazepine affect the EC50 for the GABA-induced Cl- influx?

answer
decreases EC50
question
Name a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist.
answer
flumazenil
question
List 3/5 actions of benzodiazepines.
answer
reduction of anxiety sedative and hypnotic actions anticonvulsant muscle relaxant anesthesia
question
List 2 long-acting benzodiazepines.
answer
diazepam flurazepam 1-3 days
question
List 3 intermediate-acting benzodiazepines.
answer
alprazolam lorazepam temazepam 10-20 hours
question
List 2 short-acting benzodiazepines.
answer
oxazepam triazolam 3-8 hours
question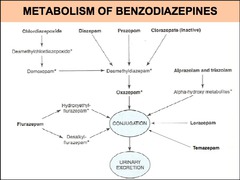
List 3 benzodiazepines that are conjugated directly and not metabolized by the CYP450 system.

answer
oxazepam lorazepam temazepam
question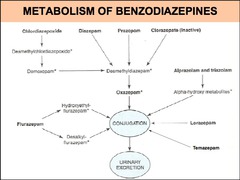
List 2 active metabolites of flurazepam that result from oxidation by liver enzymes.

answer
hydroxyethyl-flurazepam desalkyl-flurazepamx half-life: 30-100 hours
question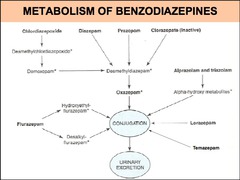
What benzodiazepine prodrug is decarboxylated to desmethyldiazepam in gastric juice?

answer
clorazepate
question
What benzodiazepine is useful in the treatment of skeletal muscle spasms and in treating spasticity from degenerative disorders like multiple sclerosis and cerebral palsy?
answer
diazepam
question
Which benzodiazepine is used for some types of epileptic seizures?
answer
clonazepam
question
List 2 benzodiazepines used in status epilepticus.
answer
lorazepam diazepam
question
List 2 benzodiazepines used in the management of withdrawal from ethanol.
answer
diazepam oxazepam
question
List a long-acting, intermediate-acting, and short-acting benzodiazepine used for sleep disorders.
answer
flurazepam temazepam triazolam
question
What are the 2 most common side effects of benzodiazepines?
answer
drowsiness confusion ataxia, cognitive impairment
question
Benzodiazepines withdrawal symptoms (3/6)
answer
confusion anxiety agitation restlessness insomnia tension
question
Benzodiazepine overdose Rx
answer
flumazenil
question
What receptors are associated with barbiturates?
answer
GABAA receptors different binding site than that of benzodiazepines increase the duration of the GABA-gated chloride channel openings
question
How do barbiturates affect CYP450 enzymes?
answer
induce CYP450 enzymes
question
Barbiturate used for anesthesia
answer
thiopental ultra short-acting
question
Barbiturate used as an anticonvulsant
answer
phenobarbital long-term management of tonic-clonic seizures, status epilepticus and eclampsia
question
What nondepressant barbiturate can be used to treat hyperbilirubinemia and kernicterus in neonates?
answer
N-phenylbarbital
question
How do barbiturates affect porphyrin synthesis?
answer
increase porphyrin synthesis
question
What emergency situation can arise with rapid IV injection of barbiturates?
answer
cardiovascular collapse
question
Which benzodiazepine receptor subtype is associated with non-benzodiazepine benzodiazepeine receptor agonists?
answer
BZ1 subtype
question
List 2 non-benzodiazepine benzodiazepine receptor agonists that are indicated for the short-term treatment of insomnia?
answer
zolpidem difficulties with sleep initiation zaleplon rapid onset and very short duration of action
question
What non-benzodiazepine benzodiazepeine receptor agonist decreases sleep latency and improves sleep maintenance?
answer
eszopiclone active enatiomer of zopiclone
question
Name a 5-HT1A partial agonist indicated for management of anxiety disorders.

answer
buspirone
question
Name a melatonin receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulty with sleep onset.
answer
ramelteon agonist at MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors
question
Which antihistamine is approved for symptomatic relief of anxiety?
answer
hydroxyzine diphenhydramine and doxylamine effective in treating MILD types of insomnia
question
What beta-blocker is widely used to control performance anxiety?
answer
propranolol
question
What alpha-blocker is used to modify autonomic expression of anxiety?
answer
clonidine
question
Positive psychotic symptoms are believed to be linked to overactivity of _____ neurons in the _____ dopamine pathway.
answer
Positive psychotic symptoms are believed to be linked to overactivity of dopamine neurons in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway.
question
Which dopamine receptors are blocked by antipsychotic drugs?
answer
D2 receptors
question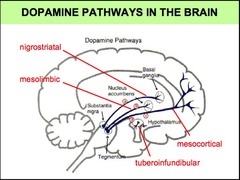
List the 4 well-defined dopamine pathways in the brain.

answer
mesolimbic pathway nigrostriatal pathway mesocortical pathway tuberoinfundibular pathway
question
Blockade of D2 receptors in which dopamine pathway is believed to mediate the antipsychotic effects of antipsychotic drugs?
answer
mesolimbic pathway
question
Describe the projection associated with the mesolimbic pathway.
answer
brainstem to limbic areas important role in emotional behaviors
question
Describe the projection associated with the nigrostriatal pathway.
answer
substantia nigra to basal ganglia controls motor movements
question
Which dopamine pathway is part of the extrapyramidal nervous system?
answer
nigrostriatal pathway
question
Describe the projection associated with the mesocortical pathway.
answer
brainstem to the limbic cortex
question
Negative symptoms seen in psychosis may be due to deficit of dopamine in which pathway?
answer
mesocortical pathway
question
Describe the projection associated with the tuberoinfundibular pathway.
answer
hypothalamus anterior pituitary
question
Dopamine released from the neurons in the tuberoinfundibular pathway inhibits secretion of which hormone?
answer
prolactin may cause galactorrhea
question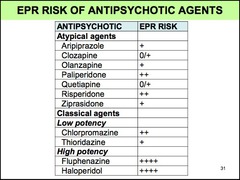
Name 5 classical antipsychotic drugs. Which 3 are high-potency drugs? Which 2 are low-potency drugs?

answer
fluphenazine haloperidol thiothixene more likely to produce extrapyramidal reactions ----- chlorpromazine thioridazine more likely to produce sedation and postural hypotension
question
Name 4/7 atypical antipsychotic drugs.
answer
clozapine risperidone olanzapine quetiapine ziprasidone aripiprazole paliperidone
question
What makes atypical antipsychotic drugs "atypical?"

answer
higher affinities for other receptors than for the D2 receptor
question
Typical vs. Atypical Antipsychotics exert part of their action by blocking 5-HT receptors more likely to cause extrapyramidal reactions less likely to cause tardive dyskinesia less likely to cause increases in prolactin more effective at treating negative symptoms less effective in refractory populations
answer
exert part of their action by blocking 5-Ht receptors: *atypical* more likely to cause extrapyramidal reactions: *typical* less likely to cause tardive dyskinesia: *atypical* less likely to cause increases in prolactin: *atypical* more effective at treating negative symptoms: *atypical* less effective in refractory populations: *typical*
question
How do antipsychotic drugs affect intellectual function and motor coordination?
answer
do not depress intellectual function minimal motor incoordination
question
List 2 antipsychotics that do not have antiemetic effects.
answer
aripiprazole thioridazine antiemetic effects mediated by blockade of D2 receptors of the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the medulla
question
List 3 CYP450 enzymes that metabolize antipsychotic drugs.
answer
1A2 2D6 3A4 do not interfere with the metabolism of other drugs
question
What drug is contraindicated in patients with extrapyramidal reactions due to antipsychotics?
answer
levodopa
question
List 2 antimuscarinic drugs that can be used to treat Parkinsonism.
answer
benztropine trihexyphenidyl addition of diphenydramine OR amantadine
question
List 2 drugs most commonly used to manage akathisia caused by antipsychotic medications.
answer
clonazepam propranolol
question
Name the most important unwanted effect of antipsychotics that may be due to dopamine receptor upregulation.
answer
tardive dyskinesia
question
Which antipsychotic is recommended for patients with tardive dyskinesia who require antipsychotics?

answer
clozapine
question
A patient using antipsychotic medication presents with muscle rigidity, fever, altered mental status, stupor, unstable blood pressure, and myoglobinemia.
answer
neuroleptic malignant syndrome dantrolene or bromocriptine may be helpful
question
List 2 antipsychotics that are commonly associated with seizures.
answer
chlorpromazine clozapine
question
List 2 consequences of alpha-1 receptor blockade by antipsychotics.
answer
orthostatic hypotension impaired ejaculation
question
Which antipsychotic can cause agranulocytosis in 1-2% of patients?
answer
clozapine regular blood cell counts are mandatory
question
How do antipsychotics affect prolactin secretion?

answer
increase in prolactin secretion
question
Which 2 antipsychotics can cause weight gain?
answer
clozapine olanzapine
question
Which antipsychotic is least likely to cause weight gain?
answer
ziprasidone
question
Which antipsychotic causes a high incidence of QTc- and T-wave changes and may (rarely) produce ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death?
answer
thioridazine ziprasidone also can prolong QT
question
Which antipsychotic causes deposits in the cornea and lens?
answer
chlorpromazine
question
Which antipsychotic causes retinal deposits?
answer
thioridazine
question
List 3/5 psychiatric indications for antipsychotics.
answer
schizophrenia bipolar disorder (atypical) Tourette's syndrome Huntington's disease Alzheimer's dementia (control of disturbed behavior)
question
List 2 non-psychiatric indications for antipsychotics.
answer
nausea vomiting
question
What antipsychotic is used in combination with fentanyl in neurolept-anesthesia?
answer
droperidol
question
Which antipsychotic is category B?
answer
clozapine others are category C
question
Name 4 MAOIs.
answer
isocarboxazid phenelzine tranylcypromine selegiline
question
MAOIs adverse effects (3/6)
answer
drowsiness orthostatic hypotension blurred vision dry mouth dysuria constipation
question
Overstimulation of which 2 receptors are associated with serotonin syndrome?
answer
5-HT1A 5-HT2 hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, myoclonus caused by any drug that increases serotonin
question
What monoamine compound can cause drug interactions with MAOIs?

answer
tyramine
question
OTC cold preparations that contain _____ and _____ are contraindicated in patients taking MAO inhibitors.
answer
OTC cold preparations that contain pseudoephedrine and phenylpropanolamine are contraindicated in patients taking MAO inhibitors.
question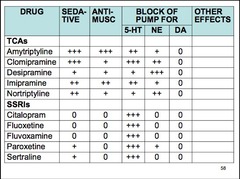
Name 3/5 tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs).

answer
amitriptyline clomipramine desipramine imipramine nortriptyline
question
What 2 transporters are blocked by TCAs (major MOA)?
answer
serotonin transporter (SERT) norepinephrine transporter (NERT) increased monoamine concentration in the cleft
question
Name a TCA that has very little affinity for NET, but potently binds SERT.
answer
clomipramine
question
Name 2 TCAs that are more selective for NET than for SERT.
answer
desipramine nortriptyline
question
List 4 additional receptors blocked by TCAs.
answer
alpha-adrenergic receptors muscarinic receptors histamine receptors 5-HT receptors
question
Blockade of which receptors by TCAs can cause the following adverse effects: blurred vision xerostomia uirinary retention constipation aggravation of narrow-angle glaucoma
answer
muscarinic receptors
question
The mechanism by which TCAs cause arrhythmias is similar to that of which antiarrhythmic drug?
answer
quinidine
question
What is the most serious adverse effect of TCAs associated with the elderly (2)?
answer
orthostatic hypotension reflex tachycardia blockade of alpha-1-adrenoceptors
question
Blockade of which receptors by TCAs causes sedation and weight gain?
answer
H1 blockade
question
Describe the sexual adverse effects of TCAs with highly serotonergic effects.
answer
...
question
What lethal complications are associated with TCA overdose?
answer
arrhythmias treatment includes cardiac monitoring, airway support and gastric lavage; sodium bicarbonate useful in reversing conduction block
question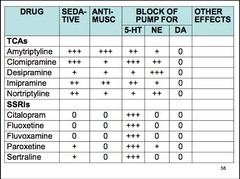
Name 3/6 SSRIs.

answer
citalopram escitalopram fluoxetine fluvoxamine paroxetine sertraline
question
Drug of choice for depression
answer
SSRIs
question
List 3/4 adverse effects associated with TCAs that are not seen with SSRI use.
answer
orthostatic hypotension sedation dry mouth blurred vision little blocking activity at muscarinic, alpha-adrenergic, and histamine H1 receptors
question
List 4/7 uses for SSRIs other than depression.
answer
obsessive-compulsive disorder PD GAD PTSD seasonal affective disorder PMDD bulimia
question
List 3 gastrointestinal adverse effects of SSRIs.
answer
nausea GI upset diarrhea
question
Which 2 SSRIs inhibit CYP2D6?
answer
fluoxetine paroxetine
question
Which SSRI inhibits CYP1A2, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4
answer
fluvoxamine
question
List 3 SSRIs that have low potential for drug interactions.
answer
citalopram escitalopram sertraline
question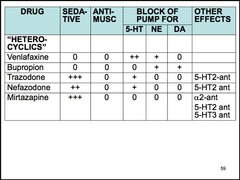
Name 2 SNRIs.

answer
venlafaxine duloxetine lack blockade of H1, muscarinic and alpha-1 receptors
question
Which SNRI is a potent inhibitor of 5-HT uptake that inhibits norepinephrine uptake at higher doses?
answer
venlafaxine
question
Which SNRI has weak inhibition of dopamine reuptake?
answer
venlafaxine
question
Do SNRIs or SSRIs have fewer CYP450 interactions?
answer
SNRIs
question
Name a norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI).
answer
buproprion not associated with sexual dysfunction problems which occur with SSRIs because it lacks the serotonergic component
question
What disorder is associated with SSRI and NDRI overdose?
answer
seizures
question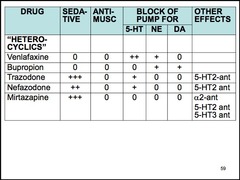
Name 2 5-HT2 antagonists/reuptake inhibitors (SARIs).

answer
nefazodone trazodone *combine 5-HT reuptake blockade with 5-HT2 antagonism
question
Stimulation of which 5-HT receptors in the raphe nuclei can help treat depression?
answer
5-HT1A Stimulation of 5-HT2 receptors in the forebrain may cause agitation or anxiety, while stimulation of 5-HT2 receptors in the spinal cord may cause sexual dysfunction.
question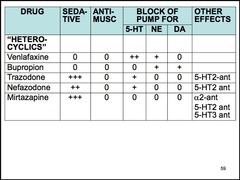
Name a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (NASSA).

answer
mirtazapine
question
NASSAs are antagonists of central presynaptic _____ receptors. They enhance the release of _____ and _____. Additionally, these drugs are antagonists at _____ and _____ receptors. Finally, _____ is a potent H1 antagonist, which is associated with sedation and weight gain.
answer
NASSAs are antagonists of central presynaptic alpha-2 receptors. They enhance the release of norepinephrine and 5-HT. Additionally, these drugs are antagonists at 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. Finally, mirtazapine is a potent H1 antagonist, which is associated with sedation and weight gain.
question
Drug of choice for anxiety disorders
answer
SSRIs
question
Drug of choice for neuropathic pain

answer
TCAs
question
Are SSRIs useful for treating anorexia or bulimia?
answer
bulimia
question
SSRI of choice for treatment of bulimia
answer
fluoxetine
question
Which antidepressants are beneficial to women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder? Which 2 specific drugs are indicated for this disorder?
answer
SSRIs fluoxetine, sertraline
question
Which antidepressant is as effective as nicotine patches in smoking cessation therapy?
answer
buproprion
question
Which antidepressants can be used for enuresis?
answer
TCAs not commonly used because of adverse effects
question
What "theory" is the most widely accepted explanation for the actions of lithium in treating bipolar disorder?

answer
inositol depletion theory
question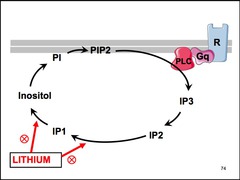
How does lithium block the regeneration of inositol?

answer
inhibition of inositol polyphosphatase and monophosphatase Free inositol is essential for the synthesis of PIP2, therefore lithium blocks the phosphatidylinositol signaling cascade in the brain
question
List the 2 mechanisms of inositol synthesis in CNS neurons.
answer
regeneration from IP3 de novo synthesis from glucose 6-phosphate both inhibited by lithium, which leads to inhibition of central adrenergic, muscarinic, and serotonergic neurotransmission
question
What type of antagonism is associated with lithium use?
answer
uncompetitive antagonism only neurons with active receptors will be affected by lithium
question
Lithium adverse effects (3/4)
answer
tremor sedation ataxia aphasia
question
Lithium contraindications (2)
answer
pregnancy: category D increased incidence of congenital cardiac anomalies nursing mothers
question
List 2 types of indirect-acting adrenergic agonists.
answer
releasing agents uptake inhibitors
question
List 3 releasing agents (indirect-acting adrenergic agonist).
answer
amphetamine methylphenydate tyramine
question
Tyramine mechanism
answer
causes norepinephrine release from presynaptic terminals - potentiates effects of NE produced endogenously
question
List 2 ways by which amphetamines increase blood pressure.
answer
increases blood pressure by alpha-agonist action on vasculature increases blood pressure by beta-stimulatory effects on heart - has central stimulatory action
question
Name a structural analogue of amphetamine widely used to treat ADHD in children.
answer
methylphenidate
question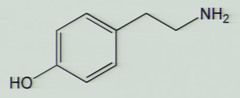
Releasing agent (indirect-acting adrenergic agonist) found in fermented food such as ripe cheese and Chianti wine

answer
tyramine
question
Tyramine drug interaction
answer
tyramine is normally oxidized by MAO patients taking MAO inhibitors can manifest serious vasopressor episodes
question
Ephedrine actions on blood pressure and respiratory system
answer
increases systolic and diastolic blood pressures bronchodilation
question
Ephedrine mechanism and uses (2)
answer
stimulates alpha and beta receptors and releases NE from nerve endings - poor substrate for COMT and MAO since it is not a catecholamine - excellent absorption orally and penetrates the CNS sometimes used prophylactically in chronic treatment of asthma to prevent attacks mild stimulation of CNS: increases alertness, decreases fatigue and prevents sleep
question
Pseudoephedrine uses
answer
available over the counter as a component of many decongestant mixtures
question
Phenoxybenzamine mechanism and uses (2)
answer
irreversible non-selective alpha antagonist prior to surgical removal of pheochromocytoma chronic management of inoperable tumors - non-selective alpha antagonists usually not successful for hypertension
question
How does blockade of alpha1-adrenergic receptors affect sympathetic tone of blood vessels and peripheral vascular resistance?
answer
reduces sympathetic tone of blood vessels and decreases PVR
question
Phentolamine mechanism and uses (4)
answer
reversible non-selective alpha antagonist ----- short term control of hypertension diagnosis of pheochromocytoma by phentolamine blocking test hypertensive crisis associated with stimulant drug overdose (cocaine) hypertensive crisis due to sudden withdrawal of sympatholytic anti-hypertensive drugs, e.g. clonidine
question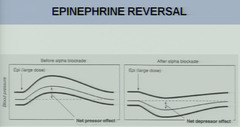
The systemic blood pressure decreases in response to epinephrine given with pretreatment of phenoxybenzamine. What is this phenomenon called?

answer
epinephrine reversal - the vasoconstrictive alpha1 action of epinephrine is blocked, but the vasodilation caused by activation of beta2-receptors is not
question
Alpha1-selective adrenergic blockers use
answer
treatment of hypertension
question
Alpha1-blockers CV effects
answer
lower arterial blood pressure by relaxing both arterial and venous smooth muscle
question
Why must the first dose of alpha1-blockers be 1/3 or 1/4 of the normal dose?
answer
the first dose produces an exaggerated hypotensive response that can result in syncope
question
Are alpha1-blockers the drugs of choice for hypertension?
answer
no
question
Drug class of choice for benign prostatic hyperplasia symptom relief
answer
alpha1-blockers - relaxes smooth muscle in the bladder neck, prostate capsule and prostatic urethra, improving urinary flow
question
Terazosin mechanism and use (2)
answer
alpha1-blocker with longer half-life than prazosin - used for hypertension and BPH
question
Doxazosin mechanism and use (2)
answer
alpha1-blocker with longer half-life - used for hypertension and BPH
question
Tamsulosin mechanism and use
answer
alpha1-blocker - used for BPH - little effect on bp, so less likely to cause orthostatic hypotension
question
Yohimbine mechanism and use
answer
alpha2-selective adrenergic blocker - used in the past to treat erectile dysfunction <-- phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors have replaced it
question
Propranolol mechanism
answer
non-selective beta-blocker
question
How do beta-blockers affect heart rate and myocardial contractility?
answer
slow heart rate decrease myocardial contractility
question
Why are non-selective beta-blockers contraindicated in patients with asthma?
answer
blocking beta2 receptors in the lungs can precipitate a respiratory crisis in patients with COPD or asthma
question
How do non-selective beta-blockers affect glycogenolysis and glucagon secretion?
answer
decreases both
question
Non-selective beta-blockers uses (3/9)
answer
hypertension - beta-blockers lower blood pressure in hypertension by decreasing CO glaucoma - diminish intraocular pressure migraine - effective prophylaxis - mechanism may depend on blockade of catecholamine-induced vasodilation of brain vasculature hyperthyroidism - beta-blockers blunt sympathetic stimulation angina pectoris - decrease O2 requirement of heart muscle - not for acute management atrial fibrillation - control ventricular rate MI - protective effect on the myocardium performance anxiety - preferred Rx essential tremor - most commonly used drugs for treatment
question
List 2 reasons that diabetics should be careful while taking non-selective beta-blockers.
answer
non-selective beta-blockers may impair recovery from hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetics mask the tachycardia that is typically seen with hypoglycemia, denying the patient an important warning sign
question
List 2 ways in which non-selective beta-blockers adversely affect one's serum lipid profile.
answer
inhibit TAG breakdown in adipose tissue reduce HDL, increase LDL, increase TAGs - beta1-blockers improve serum lipid profile of dyslipidemic patients
question
Why is it important to not withdraw beta-blocker therapy abruptly?
answer
up-regulation of beta-receptors due to long-term therapy can cause acute tachycardia, hypertension, and/or ischemia upon abrupt withdrawal
question
Nadolol mechanism and uses (2)
answer
non-selective beta-blocker - management of angina pectoris - management of hypertension
question
Timolol mechanism and uses (3)
answer
non-selective beta-blocker - treatment of hypertension - prophylaxis of migraine headache - treatment of intraocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma
question
What 2 patient populations (with specific disorders) benefit from beta1-selective adrenergic antagonists?
answer
hypertensive patients with impaired pulmonary function diabetic hypertensive patients who are receiving insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents
question
Atenolol mechanism and uses (3)
answer
beta1-selective adrenergic antagonist - management of hypertension - long-term management of angina pectoris - management of MI to reduce CV mortality
question
Metoprolol mechanism and uses (3)
answer
beta1-selective adrenergic antagonist - management of hypertension - long-term management of angina pectoris - management of MI to reduce CV mortality
question
Esmolol mechanism and uses
answer
ultra-short acting beta1-selective adrenergic antagonist (half-life = ~10 minutes) - supraventricular arrhythmias - arrhythmias associated with thyrotoxicosis - perioperative hypertension - myocardial ischemia in acutely ill patients
question
Labetalol mechanism and use
answer
competitive antagonist at beta and alpha1 receptors - management of hypertension * substantially more potent as a beta-antagonist than as an alpha-antagonist
question
Carvedilol mechanism and uses (2)
answer
competitive antagonist at beta- and alpha1-receptors - used in hypertension and congestive heart failure * substantially more potent as a beta-antagonist than as an alpha-antagonist
question
Pindolol mechanism and uses
answer
partial beta-agonist - antihypertensive in individuals with diminished cardiac reserve or a propensity to bradycardia * not demonstrated in controlled trials, but may be important in individual patients
question
Alpha-methyltyrosine (metyrosine) mechanism and uses (2)
answer
competitive inhibitor of tyrosine hydroxylase (inhibits NE synthesis) - management of malignant pheochromocytoma - preoperative preparation of patients for resection of pheochromocytoma
question
Reserpine mechanism and uses
answer
irreversibly damages VMAT (vesicles cannot store NE and dopamine); MAO free to degrade NE in the cytoplasm - gradual decrease in blood pressure and slowing of cardiac rate
question
Guanethidine mechanism and use
answer
displaces NE from transmitter vesicles leading to depletion of NE - antihypertensive (causes a gradual decrease in bp and heart rate) * additionally, the drug inhibits release of NE ;-- primarily responsible for its antihypertensive action
question
Trazodone side effects (3)
answer
priapism in men sedation postural hypotension
question
Excessive self-administration of any substance for nonmedical purposes
answer
abuse
question
List 3 actions that can cause withdrawal syndromes.
answer
abrupt cessation rapid dose reduction administration of an antagonist
question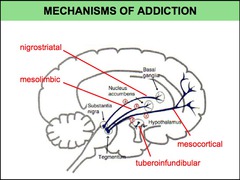
What neurological system is the prime target of addictive drugs?

answer
mesolimbic dopamine system all addictive drugs activate the mesolimbic dopamine system
question
CNS depressants (3)
answer
ethanol benzodiazepines barbiturates
question
Receptors affected by ethanol (3/6)
answer
GABA(A) receptors Kir3/GIRK channels adenosine reuptake glycine receptors NMDA receptors 5-HT3 receptors
question
Tremor, nausea, vomiting, sweating, agitation, anxiety
answer
ethanol withdrawal may be followed by hallucinations
question
Ethanol Withdrawal Syndrome 24-48 hours 48-72 hours
answer
24-48 hours: generalized seizures 48-72 hours: delirium tremens delirium tremens associated with 5-15% mortality
question
Alcohol withdrawal Rx (2)
answer
diazepam chlordiazepoxide long half-life benzodiazepines ? smoother withdrawal and rebound withdrawal symptoms less likely to occur
question
Alcohol withdrawal Rx in elderly and those with liver failure (2)
answer
lorazepam oxazepam intermediate-acting drugs not as dependent on hepatic metabolism
question
Alcoholism Rx (3)
answer
disulfiram naltrexone acamprosate
question
Enzyme inhibited by disulfiram
answer
aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitor used to create aversion to drinking
question
Receptor antagonized by naltrexone
answer
opioid receptor reduces craving for alcohol
question
Receptor antagonized by acamprosate
answer
NMDA receptor prevents relapse
question
Name a GABA agonist that may reduce cravings for alcohol.
answer
topiramate: antagonizes glutamate receptors not FDA-approved
question
Benzodiazepines physical dependence addiction
answer
physical dependence: yes addiction: rare
question
Nausea, vomiting, tremor, incoordination, restlessness, blurred vision, sweating, anorexia
answer
low-dose benzodiazepine withdrawal
question
Seizures, psychosis, depression
answer
high-dose benzodiazepine withdrawal includes symptoms of low-dose withdrawal
question
Low-dose benzodiazepine withdrawal Rx
answer
diazepam switched to a long-acting drug
question
Is low-dose or high-dose benzodiazepine withdrawal associated with illicit drug and/or alcohol use?
answer
high-dose withdrawal
question
Psychostimulants (3)
answer
methylxanthines cocaine amphetamines
question
Methylxanthines (3)
answer
caffeine theophylline theobromine
question
Receptors blocked by methylxanthines
answer
presynaptic adenosine receptors blockade of adenosine receptors increases norepinephrine release
question
Caffeine amount decrease in fatigue and increased mental alertness anxiety and tremors spinal cord stimulation
answer
decrease in fatigue and increased mental alertness: 100-200 mg anxiety and tremors: 1.5 g spinal cord stimulation: 2-5 g
question
Methylxanthines actions cardiac inotropy and chronotropy gastric mucosa HCl secretion
answer
positive inotropic and chronotropic effects on the heart stimulates secretion of HCl individuals with peptic ulcers should avoid
question
Methylxanthines high dose adverse effects (2)
answer
emesis convulsions
question
Lethal dose of caffeine
answer
10 g (about 100 cups of coffee) ? cardiac arrhythmias
question
Is caffeine listed in the category of addicting stimulants?
answer
NO! classified as schedule 2 drug by DEA
question
Reuptake inhibited by cocaine (3)
answer
dopamine prolongation of dopaminergic effects in brain's limbic system produces intense euphoria norepinephrine serotonin
question
Parts of the brain stimulated by cocaine (2)
answer
cortex brainstem
question
High doses of cocaine adverse effects (4)
answer
tremors convulsions respiratory depression vasomotor depression
question
Cocaine Actions heart rate blood pressure pupils peripheral vascular tone
answer
tachycardia hypertension pupillary dilation peripheral vasoconstriction
question
Dysphoria, depression, sleepiness, fatigue, bradycardia
answer
cocaine withdrawal syndrome treatment usually not required
question
Amphetamines (4)
answer
amphetamine methamphetamine phenmetrazine methylphenidate
question
Amphetamines actions (3)
answer
increase release of catecholamines similar to cocaine due to release of dopamine weak inhibitors of MAO direct catecholaminergic agonists in the brain
question
High dose amphetamines adverse effects (2)
answer
psychosis convulsions
question
Amphetamine and methylphenidate uses (2)
answer
attention deficit syndrome narcolepsy
question
Increased appetite, sleepiness, exhaustion, mental depression
answer
amphetamines withdrawal syndrome antidepressants may be indicated
question
What part of the brain comprises of dopamine neurons with nicotinic receptors?
answer
ventral tegmental area nicotine action excites these neurons, releasing dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex
question
How does nicotine affect attention, learning, problem solving, and reaction time?
answer
improves all
question
How does nicotine affect appetite?
answer
appetite suppressant
question
List 2 complications of high doses of nicotine.
answer
central respiratory paralysis severe hypotension caused by medullary paralysis
question
Nicotine withdrawal syndrome (2)
answer
irritability sleeplessness
question
Nicotine addiction Rx (3)
answer
nicotine replacement therapy sustained-release buproprion mechanism unclear varenicline partial agonist at nicotinic receptors in the CNS
question
Most commonly abused opioids (4)
answer
heroin morphine codeine oxycodone
question
Most commonly abused opioids among health professionals (2)
answer
meperidine fentanyl
question
Dysphoria, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, yawning
answer
opioid withdrawal syndrome
question
Opioid detoxification Rx (2 opioids)
answer
methadone buprenorphine long-acting opioids
question
Opioid detoxification Rx (2 adrenergic agonists)
answer
clonidine lofexidine presynaptic alpha-2 agonists many withdrawal symptoms due to noradrenergic storm that results from rebound firing due to tolerance to the effects of opioids on the ANS
question
What cannabinoid produces most of the effects of smoking marijuana?
answer
delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol
question
What type of receptor is associated with the 2 cannabinoid receptor subtypes (CB1 and CB2)?
answer
G protein-linked receptors inhibition of adenylyl cyclase opens potassium channels and closes calcium channels
question
CB1 receptor location
answer
brain mediate the psychological effects of THC
question
CB2 receptor location
answer
immune cells
question
Name the 2 cannabinoid ligands.
answer
anandamide 2-arachidonylglycerol
question
Marijuana adverse effects (3/4)

answer
increased heart rate decreased blood pressure reddening of the conjunctiva toxic psychosis at high doses
question
Dronabinol uses (2)
answer
anorexia associated with weight loss in patients with AIDS nausea and vomiting associated with cancer chemotherapy (second line)
question
Psychedelic agents (5)
answer
LSD mescaline psilocybin phencyclidine MDMA
question
Drugs that affect thought, perception and mood without causing marked psychomotor stimulation or depression
answer
psychedelic agents
question
List 2 LSD-like drugs.
answer
mescaline psilocybin
question
What receptors are acted upon by LSD?
answer
5-HT2 receptors in the CNS
question
Does LSD cause addiction and/or a withdrawal syndrome?
answer
no
question
LSD-induced agitation Rx
answer
diazepam
question
What type of receptors are antagonized by phencyclidine? What type of antagonist is phencyclidine?
answer
NMDA subtype of glutamate receptor noncompetitive
question
What 2 dissociative conditions are associated with phencyclidine use?
answer
dissociative anesthesia dissociative analgesia
question
Reuptake of what neurotransmitter is inhibited by high doses of phencyclidine?
answer
dopamine
question
Drug that fosters feelings of empathy and intimacy without impairing intellectual capacities
answer
MDMA (ecstasy)
question
What neurotransmitter is associated with MDMA use?
answer
serotonin
question
What mood disorder is associated with MDMA use?
answer
depression
question
Inhalant that produces euphoria and analgesia and then loss of consciousness

answer
nitrous oxide
question
Which group of inhalants is implicated in cancer, cardiotoxicity, neuropathies, and hepatotoxicity?
answer
volatile organic solvents
question
List 2 organic nitrites used to enhance erection.
answer
amyl nitrite butyl nitrite not addictive



