Psychiatric History and Assessment through the Mental Status Examination – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Overview of the Psychiatric History
answer
-ID/Chief Complaint -History of Present Illness (HPI) -Past Psychiatric History -Medical History -Family History -Personal History: May include developmental history -Social History -Mental Status Exam -Assessment/Plan
question
Psychiatric History
answer
The psychiatric history is a record of the patient's *mental health* throughout their life and includes: -Presentation of mental symptoms -History of previous symptoms -A summary of previous outpatient and inpatient treatment (Number and dates) -A discussion of previous medications, therapies, and ECT effectiveness, and the individual's compliance with these treatments -Estimate of the age of the individual at the time of INITIAL onset of symptoms -A history of PREVIOUS suicide attempts, alcohol abuse, and substance abuse -Include collateral information from others -*List any RISK factors found.* -A thorough psychiatric History is ESSENTIAL for CORRECT diagnosis and case formulation
question
Personal and Social History
answer
* Often includes a Developmental History with Prenatal and perinatal, childhood, and adolescent history with details about relationship with parents and any history of trauma.* Adulthood 1. Education 2. Occupation/Work history including military service 3. Home situation 4. Current household 5. Relationships 6. Sexual History 7. Educational history 8. Leisure activities 9. Religious or Spiritual Beliefs 10. Diet 11. Exercise 12. Sleep 13. Substance Abuse history -Smoking and other tobacco products -Caffeine -Alcohol -illicit Drugs -Unprescribed medications 14. Alternative Health Practices 15. Safety measures
question
Mental Status Exam (MSE)
answer
-Structured way of assessing the CURRENT cognitive, behavioral, emotional, and gross sensory capacity of the patient. >*Parts of MSE are observations made throughout H and P* -Rule out any potential DYSFUNCTION that may compromise the patient's self-report of symptoms. -Reveals the presence of psychiatric illness or potential symptoms of CNS disease. -Brings to light symptoms that the patient has not reported or is not aware of (ex: memory problems).
question
Mental Status Exam and Mini-Mental (status) Exam

answer
General Description -Appearance -Behavior -Attitude (cooperation) -Level of consciousness -Orientation Speech Characteristics -Speech and language Affect and Mood Thought Process/form Though Content Perception -Suicide/ homicide Insight Judgement Sensorium and cognition -Attention span -Memory -Intellectual functioning
question
Decisions that may be considered based on the results of a Mental Status Exam include:
answer
-Is the patient currently psychotic or manic? -Is the patient a danger to themselves or others? -Does the patient's medical or psychiatric treatment need to change or is it working? -Is the patient a RELIABLE source of symptom report? -Can a patient manage their own finances? -Can the patient make his or her own medical decisions? -Can the patient live INDEPENDENTLY?
question
Components of the Mental Status Examination
answer
-Appearance (observed) -Behavior (observed) -Attitude: cooperation (observed) -Level of consciousness (observed) -Orientation (inquired) -Speech and Language (observed) -Mood (inquired) -Affect (observed) -Thought process/form (inquired/observed) -Thought content (observed/inquired) -Suicide and homicide (inquired) -Insight and Judgment (observed/inquired) -Attention span (observed/inquired) -Memory (observed/inquired) -Intellectual functioning (observed/inquired)
question
Appearance
answer
Record OVERALL physical appearance/ note physical stigmata, body shape, scars, etc -How old does the patient look? Older or younger their stated age? -Grooming: are they appropriately dressed, clean? Unkempt? Immaculate? Jewelry? Makeup? -Dress -Posture -Gait -Body shape, scars, tattoos, etc -Note eye contact, facial features, and expression
question
Behavior
answer
*Overt behavior and psychomotor activity* *(Psychomotor) activity* -Gait -Gestures -Level of Activity -INVOLUNTARY or abnormal movements >Tremors, tics, hand wringing, akathisia (inner restlessness-> leg keeps shaking), echopraxia, automatisms, apraxia ("Wont unlock door when asked", etc), grimacing -The pace of movements >Psychomotor restlessness or agitation, scratching, biting fingernails, wandering around the room, unable to sit down >Psychomotor retardation (slowing of movements), flat facial expression -BE SPECIFIC!!
question
Behavior and Attitude
answer
*Cooperation: OBSERVED* -*Behavior*: Mannerisms, gestures, psychomotor activity, expression, eye contact, ability to follow requests, compulsions -*Attitude*: Cooperative, hostile, evasive, apathetic, defensive, and distracted
question
Level of consciousness
answer
-Alert -Lethargic (sluggish; appears half asleep) -Drowsy -Clouded consciousness -Obtunded: Opens eyes, responds SLOWLY, etc -Stuporous: NEAR unconsciousness -Comatose
question
Comatose
answer
NO verbal or motor responses in response to noxious stimuli -Does not respond to external stimuli
question
Coma Vigil
answer
Patient does NOT react to stimulation but appears ready to be aroused (AKA akinetic mutism-> no moving or speaking) -Eyes may be open but NON responsive
question
Stuporous
answer
Individuals require REPEATED aversive stimulation to be roused -Very close to unconsciousness
question
Obtunded
answer
Mild to moderate intensity to arouse -Can get aroused even if seems sleepy
question
Cloudiness Consciousness
answer
IN and OUT of consciousness= *Delirium* INCOMPLETE clear-mindedness with disturbances in perception and attitudes -Delirium= Restless, confused, disoriented-> associated with fear and hallucinations
question
Drowsy
answer
Individuals who are sleepy but can be roused by aversive stimuli
question
Lethargic
answer
Individuals are sleepy and indifferent. -They respond in a manner which is *incomplete and delayed*
question
Alert
answer
Wakefulness -Individuals respond promptly and appropriately.
question
Disorientation
answer
Disturbance of orientation in time, place, or person
question
Twilight State
answer
DISTURBED consciousness with hallucinations
question
Dreamlike state
answer
Often used as a synonym for *complex partial seizure or psychomotor epilepsy*
question
Somnolence
answer
ABNORMAL drowsiness
question
Confusion
answer
INVOLVED in appropriate reactions to environmental stimuli -Manifested by DISORDERED orientation
question
Sundowning
answer
Syndrome in older persons that usually occurs at night and may consist of confusion, drowsiness, ataxia (loss of muscle coordination) and falling (usually associated with overly SEDATIVE medications)
question
If consciousness is impaired what does it tell us?
answer
-Mild impairment observed in individuals with UNILATERAL cortical or thalamic lesions -SEVERE impairment in individuals with damage to the brainstem or bilateral lesions of the thalami or cerebral hemispheres -Toxic, substance, or metabolic factors also common causes of impairment->DELIRIUM
question
Orientation
answer
*A Ox3 (Inquired)* -Orientation to time: What is the full date? -Orientation to place: Where are we (floor, building, city, county, and state)? -Orientation to self (person): What is your full name? -AOx4 - to situation (How would you describe the situation we are in?) When disorientation occurs what is the most likely progression of loss? -Time, place, then self
question
Speech/Language Characteristics
answer
Here we want to describe the *manner of speech not the content* -Rate of speech: pressured, rapid, normal, slowed -Fluency and Rhythm: slurred, hesitant or halting, monotone, normal with appropriate inflections -*Volume* of speech: Loud, soft, monotone, weak, strong -*Quality*: talkative, spontaneous, expansive, paucity, poverty --- Volubility = fluency Logorrhea= pathological and excessive often incoherent speech -Important to consider medical causes for speech disturbances -Speech characteristics can be a clue to drug intoxication -Speech is a "window" to thought processes
question
Poverty of speech
answer
Amount of speech
question
Poverty of content
answer
VAGUE but of adequate amount
question
Pressured Speech
answer
RAPID and DIFFICULT to interrupt
question
Volubility
answer
copious, coherent, logical speech
question
Nonspontaneous Speech
answer
NO self initiation of speech -Only answers direct questions
question
Dysprosody
answer
LOSS of normal speech melody
question
Dysarthria
answer
ARTICULATION difficulty
question
Cluttering
answer
ERRATIC and dysrhythmic speech, consisting of RAPID and jerky spurts
question
Speech Characteristics
answer
-Important to consider medical causes for speech disturbances -Speech characteristics can be a clue to drug intoxication -Speech is a "window" to thought processes
question
Language
answer
-Language includes >Spontaneous speech ->*Paraphasic errors*: inappropriately substituted words such as pun for spun, free for tree, etc. ->Neologisms: NON-existent words -Comprehension -Naming -Repetition -Reading -Writing -Notice the patient's level of vocabulary during the interview
question
Language disorders
answer
Different kinds of language disorders are caused by lesions in the: -*Dominant* (usually left) *Frontal lobe* (Broca's area) -The left temporal and parietal lobes (Wernicke's area) -Lesions are also possible in the subcortical white matter and gray matter structures including the *thalamus and caudate nucleus* -Language disorders can also occur in the NON-dominant hemisphere --- -Right hemisphere: semantic pragmatic disorder >Prosody problems, individuals can not understand humor or metaphoric speech.
question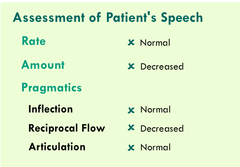
Format for write-up of Speech/Language Characteristics

answer
Describe the patient's speech with regard to rate, rhythm, volume, and quality. -Are there speech impediments, pronunciation problems, or language problems with content suggesting an aphasia, or a phonological problem, or stuttering. -Is the speech sparse or does the language contain neologisms (new words), echolalia (meaningless repetition), or other indications of possible illness. Ex.) This patient's speech is of normal rate, rhythm and volume but it is LIMITED to only direct succinct answers to the examiner's questions. -There is no spontaneous input from the patient to keep the conversation going.
question
Emotional State: Mood and Affectivity
answer
*Mood*: Patient's REPORT of his or her emotional STATUS, including frequency and duration (*subjective*) *Affect*: Observed emotional responses during the clinical interview (*objective*) -What do you see and hear when you interact with the patient?
question
Mood Questions
answer
INQUIRED/SUBJECTIVE -How are you feeling? -How are your spirits? -Have you been discouraged/depressed/low/blue lately? -Have you been energized/elated/on a high/out of control lately? -Have you been angry/irritable/edgy lately?
question
Mood Types
answer
*ELEVATED mood*: Air of confidence and enjoyment; a mood more CHEERFUL than usual. *Elation*: feelings of joy, triumph, intense self-satisfaction, or optimism *Expansive mood*: expression of feelings without restraint with an overestimation of their significance or importance *Ecstasy*: feeling of intense rapture *Euphoria*: intense elation with feelings of grandeur. *Labile Mood* (mood swings): Oscillations between euphoria and depression or anxiety -Happy then sad, then angry, then depressed *Euthymic*: normal, pleasant mood Irritable mood: EASILY annoyed and provoked to anger Depression: Pathological feeling of SADNESS *Dysphoria*: unpleasant mood-> depression (dysthymia), anxiety, irritability *Anhedonia*: LOSS of interest in and withdrawal from all regular and pleasurable activities, often associated with depression. Grief or mourning: Sadness appropriate to a real loss. Suicidal ideation: thoughts of taking one's own life. *Alexithymia*: a person's inability to or difficulty in describing or being aware of emotions or mood.
question
Affect
answer
OBSERVED/OBJECTIVE -*Appropriateness* to situation, consistency with mood, congruency with thought content -*Fluctuations*: Labile, even -*Range*: broad, restricted -*Intensity*: intense, blunted, flat, normal -*Quality*: Sad, angry, hostile, indifferent, euthymic, dysphoric, detached, elated, euphoric, anxious, animated, irritable
question
Emotional State: Affect
answer
"Normal" appropriate= a BROAD range of affect -Ex: When discussing something unhappy the individual appears sad and laughs when things are funny -Abnormal affect includes >*Inappropriate*: Disharmony between emotional feeling tone and idea, thought, or speech accompanying it >*Constricted/Restricted*: LESS severe than blunted but affect CLEARLY REDUCED ->Too depressed to act on the emotion >*Blunted*: SEVERE REDUCTION in the intensity of external tone of feeling (very narrowed range) >*Flat*: ABSENCE or near absence of any signs of affective expression (monotone, face immobile) ->Void of emotion (feature of schizophrenia) >*Labile*: RAPID and abrupt changes in emotional tone that is unrelated to external stimuli -> Happy->sad->angry->depressed
question
Biological Indicators that can alter and accompany expressed mood/affect
answer
-Ask about psychophysiological changes >Diurnal variation of mood: Changes during the day (ask when better/worse) >Changes in sleep >Changes in appetite and weight >Changes in libido -Organic Brain Difficulties can also impair affect >TBI (traumatic brain injury) or ABI (acquired brain injury) >Stroke >Multiple Sclerosis >Parkinson's Disease
question
Thought Process and Thought Content
answer
We depend on behavior and speech to EVALUATE how well mental associations are organized and expressed
question
Thought process or thought form
answer
-Linear -Goal-directed -Circumstantial -Tangential: Strays off topic and includes something unrelated/irrelevant (schizophrenics) -Looseness of associations >AKA Derailment -Flight of Ideas -Incoherent -Clang associations -Neologisms -Perseveration -Racing -Thought Blocking -Word salad
question
Thought process and Form
answer
-*Linear*: Thoughts following a step-by-step progression -*Goal-directed*: Purposeful behavior -*Circumstantial*: Disturbance in the associative though and speech processes in which a patient digresses into UNNECESSARY details and inappropriate thoughts before communicating the central idea -*Tangential*: Oblique, digressive or irrelevant manner of speech in which the central idea is not communicated. >*Ex: Doctor: "Have you had trouble sleeping lately? Patient: "I usually sleep in my bed, but now I'm sleeping on the sofa"* -*Looseness of associations*: AKA Derailment-Thinking or speech disturbance involving a disorder in the logical progression of thoughts, manifested as a failure to communicate verbally adequately; unrelated and unconnected ideas shift from one subject to another. (Schizophrenia) -*Flight of Ideas*: Rapid succession of fragmentary thoughts or speech in which content changes abruptly and speech may be incoherent (mania) -*Incoherent*: Communication that is disconnected, disorganized or incomprehensible -*Clang association*: Association or speech directed by the sound of a word rather than by its meaning; words have no logical connection; punning and rhyming may dominate the verbal behavior. (schizophrenia) -*Neologisms*: New word or phrase whose derivation cannot be understood . Also can be word approximations (e.g. headshoe to mean "hat." (Schizophrenia). -*Perseveration*: Pathological repetition of the same response to different stimuli, as in repetition of the same verbal response to different questions (2) Persistent repetition of specific words or concepts in the process of speaking (Cognitive d/o, schizophrenia, other mental illness) -*Racing thoughts*: Rapid thought patterns (Mania, anxiety, substance use, etc) -*Thought Blocking*: Abrupt interruption in train of thinking before a thought or idea is finished; after a brief pause, the person indicates no recall of what was being said or what was going to be said (Schizophrenia and anxiety) -*Word salad*: Incoherent, essentially incomprehensible mixture of words and phrases (Schizophrenia)
question
Thought content and mental process: Thought Process (Form)
answer
*Continuity of Thought* -The extent to which a person's thoughts are *goal directed.* -OR the associations between the person's ideas. -Disturbances are thought to be caused by: >Pathological disorders Ex: Schizophrenia, Bipolar disorder, Head injury >If not pathological in nature examine if they are due to LIMITED intelligence, culture factors, or a severe reaction to overwhelming negative emotional states
question
Format for write-up of Thought Processes
answer
Thought Processes: The process of the person's thoughts should be documented in terms of the flow between thoughts expressed: -Circumstantiality, flight of ideas, tangentiality, degree of tightness, or looseness of associations -Whether these thought seem to be rational, coherent, and goal directed. -There may also be evidence of evasiveness, perseveration, thought insertion, broadcasting, or blocking
question
LOA
answer
Thoughts shift from one idea to another in an UNRELATED way exhibiting a *looseness of associations* -Patient also exhibits some word finding *difficulty and neologisms*
question
Thought Content Types
answer
-Delusions -Hallucinations -Suicidal and/or Homicidal Ideation -Preoccupations: with illness or symptoms, etc -Obsessions: Repetitive, and intrusive thoughts, images, or impulses >Distressing to patients but they are UNABLE to stop the intrusion into their thinking. >Usually accompanied by a sense of ANXIETY -Phobias: excessive and irrational fears -Ideas of reference: Unfounded beliefs that objects, events, or people are personal significance. -Poverty of Content: Schizophrenic speech in which words are used correctly but communication is poor
question
Thought Content Questions
answer
-What's been on your mind lately? -Are there thoughts or pictures you just get out of your mind? -Are you worried or scared about something?
question
Delusional Thinking
answer
-Do you have personal beliefs that are not shared by others? -Do you think someone intends to harm you in some way? -Evaluate: >Severity >Fixedness >Elaborateness >Power to influence the patient >Deviation from normal: Bizarre vs. Non-Bizarre
question
Delusional Thinking (Types)
answer
*Delusions*: DEEP seated FALSE belief despite objective contradictory evidence -*Persecutory*: Others are deliberately trying to wrong, harm, or conspire against another >Believe someone trying to hurt them *Grandiose*: An EXAGGERATED sense of one's own importance, power, or significance >Believe they are Christ, president, etc. *Somatic*: Physical sensations or medical problems >Believe you have bad breath-> scared to leave home or interact with others *Reference*: Belief that otherwise innocuous events or actions refer specifically to the individual >Feel everything is about them: feel people are whispering about them, sign is referring to them, announcement on radio about them, etc *Control, influence, and passivity*: Belief that thoughts, feelings, impulses, and actions are controlled by an external agency or force >Aliens trying to invade them *Nihilistic*: Belief that self or part of self, others, or the world DOES NOT exist >Think they have no organs, are dead, do not exist, etc *Jealous*: Unreasonable belief that a partner is unfaithful >Believe spouse having an affair to point cannot take care of self, home, etc *Religious*: FALSE belief that the person has a special link with God >Act like close with God *Erotomania*: A stranger or celebrity loves the person -May think doctor loves them *Guilt*: Person believes they have committed an UNFORGIVABLE deed
question
Perceptual Disturbances
answer
Abnormal sensory functioning *Hallucinations*: Sensory impression with no external stimulus -*Auditory*: Most common in *psychosis* -*Visual*: Most common in medical disorders -*Tactile (haptic)*: Touch -*Gustatory*: Taste -*Olfactory*: Smell -*Vestibular sense*: Feels like flying -*Hallucinosis*: Associated with chronic alcohol abuse and that occur within a CLEAR sensorium >Opposed to delirium tremens (DTs), hallucinations that occur in the context of a clouded sensorium-> can occur from alcohol withdrawal (may need to go to ER) -*Illusions*: MISINTERPRETATION of real external sensory stimuli >Think you see a bug but actually is a wrapper. -Hallucinations can also occur when (these are generally NON pathological): >Falling asleep= *hypnogogic* >Awaking= *hypnopompic* -Depersonalization -Drealization
question
Thought Content: Hallucinations
answer
-Do you ever see, hear, smell, taste or feel things that other people can't? -Do you sometimes misinterpret real things around you, like shadows or muffled noises?
question
Depersonalization
answer
LOSS of reality of the SELF -The persons feels they are different -Do you ever feel detached/ removed/ changed/ different from others around you?
question
Derealization
answer
the person feels their environment has changed and that external reality is NO longer familiar -Do things seem unreal/unnatural to you?
question
Format for write-up of Perception
answer
*Perceptual Alterations*: Record hallucinations in any of the six sensory spheres (auditory, visual, olfactory, gustatory, tactile and somatosensory) being aware of possible neurologic and physical etiologies. -Document any illusions, depersonalization, or dissociation currently or in history.
question
Suicidal Thoughts/ Homicidal Thoughts
answer
In any normal patient interaction: Always ASK about suicidal thoughts especially if there is any sign of depression, anxiety, or just a sense that the patient seems hopeless or helpless. -Be DIRECT and specific: Do not beat around the bush! -Check *Homicidal* thoughts also! -In a Mental Status Exam: Always ask about any history of suicidal/ homicidal thoughts and record the response in your write-up: *"Pt denied current suicidal ideation or plan."* *"Pt. denies any history of suicidal ideation or attempt"* *DO NOT ASSUME-> ASK!*
question
Suicidal Thoughts/ Homicidal Thoughts Questions
answer
-Do you ever feel that life isn't worth living? Have you ever thought about hurting yourself? If so, how? -What would happen if you were dead? -Do you ever have thoughts about getting even with those who have wronged you? If so, how?
question
Follow-up
answer
Follow-up on all potential suicidal thoughts- learn dynamics of social support and contact-> may NEED to assume duty to warn -Assess for safety and control-> involve family members to monitor if possible -Hospitalize if the patient is unable or unwilling to follow-up or maintain contact with you. -Keep following up: Attempt to help the patient change the hopeless/helpless ideation about their life- structure and activity!
question
Insight
answer
INSIGHT: The capacity to understand that there is a problem, to think about how it came about, and how it might be solved -Internal versus External locus of control -Self-efficacy
question
Insight/ Judgment Questions
answer
-What do you think is causing your problems? -How would you describe your role in this situation? -Do you think that these thoughts, moods, perceptions are NORMAL? -How do you plan to get help for this problem? -How will you manage if ____ occurs? -If you found a stamped, addressed envelope on the street, what would you do with it? -If you were in a movie theater and smelled smoke, what would you do?
question
Levels of Insight
answer
-*Complete denial of illness* -*Slight awareness* of being sick and needing help but DENYING it at the same time. -*Awareness of being sick but blaming* it on others, on external factors, or on organic factors. -*Awareness that illness is due to something unknown* in the patient. -*Intellectual insight*: admission that the patient is ill and that symptoms or failures in social adjustment are due to the patient's own particular irrational feelings or disturbances WITHOUT applying this knowledge to future experiences. -*True emotional insight*: Emotional awareness of the motives and feelings within the patient and the important people in his or her life, which can LEAD to basic changes in behavior.
question
Format for write-up of Insight
answer
*Insight*: Document the individuals understanding of their illness, it's severity and seriousness, it's treatment and their need for therapeutic interventions, and any other special circumstances such as criminal charges, conservatorships, etc. -Use the appropriate label for the person's level of insight.
question
Judgment
answer
The ability to handle social situations (weigh consequences) and understand and adhere to reasonable social norms ("What if" questions) -Good judgement -Impaired Judgment
question
Good Judgment
answer
ABILITY to assess, discern, and choose among various options in a situation.
question
Impaired Judgment
answer
DIMINISHED ability to understand a situation correctly and to act appropriately.
question
Format for write-up of Judgment
answer
Evaluate and document the level of judgment (excellent to impaired) based on the person's responses to suggested situation and as evidenced by their DECISIONS
question
The assessment of Cognition
answer
The following areas must be also be as part of the Mental Status Exam: -Attention -Memory -Intellectual functioning: Fund of info and abstraction These areas are basic to cognitive capacity and relevant to the patient's ability to function INDEPENDENTLY
question
Attention/Concentration
answer
Ability to focus and direct cognitive processes -Digit Span: Forwards and backwards -Serial subtraction: 3's, 7's, etc -Simple subtraction/calculation -Reverse spelling -Months of the year forwards and backwards
question
Disturbance in attention
answer
-Distractibility -Selective Attention -Hypervigilance -Trance
question
Distractibility
answer
INABILITY to concentrate attention -State in which attention is drawn to UNIMPORTANT or IRRELEVANT external stimuli
question
Selective inattention
answer
BLOCKING out only those things that generate anxiety.
question
Hypervigilance
answer
EXCESSIVE attention and focus on ALL internal and external stimuli, usually secondary to delusional or paranoid states.
question
Trance
answer
FOCUSED attention and altered consciousness, usually seen in hypnosis, dissociative disorders, and ecstatic religious experiences.
question
Attention/ Concentration
answer
-Generalized impairment can occur in various focal brain lesions and diffuse abnormalities (dementia, encephalitis, etc) -Attention and concentration can also be impaired in individuals with *SEVERE mood and psychotic disorders* -Always keep in mind the relationship between level of consciousness and an individual's level of attention/concentration
question
Memory
answer
Generally, when memory fails: IMMEDIATE memory fails first and remote memory fails LAST Recent, Recent past (aka: Long-term) and Remote memory can be assessed by asking about personal information (history) and current events Watch out for confabulation (fabrication of memories)!!! Difficulty recalling information after 1-5 minutes suggests damage to the *medial temporal lobes and medial diencephalon*-> Anterograde amnesia and retrograde amnesia -Immediate Memory -Recent Memory -Recent Past Memory -Remote Memory
question
Immediate Memory
answer
*Registration* -First memory to fail Retrieving what a person has just been told 3 words
question
Recent Memory
answer
Retrieving material from the past several minutes to days: -what is my name? -what time was our appointment?
question
Recent Past Memory
answer
Retrieving data from the past few MONTHS
question
Remote Memory
answer
-Recalling events from the distant past -Last memory to fail -When did you graduate high school? -When and where did you get married?
question
Anterograde Amnesia
answer
DIFFICULTY remembering NEW facts and events occurring after the lesion occurred -Difficulty recalling information for a period of time just before a lesion occurred suggest damage to areas other than the medial temporal lobes and medial diencephalon
question
Retrograde Amnesia
answer
Difficulty remembering old facts that occurred before the lesion
question
Intelligence/ Fund of Information
answer
-A general level of intelligence can be assessed by asking patients how far they went in school *but this is not always accurate* -*Information, Vocabulary, Abstraction* -More specific measures of intelligence can also be administered (IQ tests)
question
Intelligence/ Fund of Information (to assume fund of knowledge...)
answer
To assess fund of knowledge: -Name 5 large cities in the world -Name the US president and the three before him (if culturally appropriate) -Can also use culturally appropriate questions relevant to patient's world view -Never ask a question you do not know the answer to
question
Format for write-up of Intellect/Fund of Information
answer
Consider the person's knowledge level by their vocabulary, by the general tone and content of the interview, and by their ability to perform calculations as well as their responses to information questions (name 5 large cities, the president of the US and the three before him, etc). -Consider results of previous or current psychological testing if available. EXAMPLE: Patient exhibits an extensive fund of information as evidenced by his large vocabulary, wit and ability to name the last 5 presidents. Even his paranoid ideation is complex, systemized and in great detail.
question
Abstract Reasoning
answer
Definition: Process of generalizing from concrete examples and experiences to larger, broader principles. -The ability to recognize and comprehend abstract relationships Example: How are a table and a chair alike? Example: How are a poem and a statue alike? -Also Assessed using Proverbs Ex.) What does "strike while the iron is hot" mean?
question
Abstraction Ability
answer
Record responses to the individual's interpretation of proverbs and similarities. Does the person demonstrate concrete thinking. State the proverb you used. Record the patient's words about what the proverb means.
question
A woman is seen in the emergency room. She is unable to remember where she is but knows who she is. She cannot recall what was said to her several minutes ago, but can repeat what is said to her. (Registration, recall, and orientation are...?)
answer
Registration is in tact, recall impairded, and orientation impaired
question
The same patient as before: She appears to have no emotional expression during the interview and does not report any awareness of any kind of emotional feelings. The best description for this patient is: -No affect, no mood -Inappropriate affect, dysthymic mood -Flat affect, alexithymic mood -Blunted affect, dysphoric mood OR -Restricted affect, anhedonic mood
answer
Flat affect, alexithymic



