Psyc121 Final – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Stress
answer
any deviation of the body from homeostasis Many of the effects of exposure to aversive stimuli are not produced by the stimuli themselves, but by our reactions to them stress activates the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
question
Hans Seyle
answer
came up with G.A.S. first to suggest in writing that stress had a causal relationship to illness
question
General Adaptation Syndrome (G.A.S.)
answer
Stage 1: alarm reaction Stage 2: adaptions Stage 3: exhaustion
question
Stage 1
answer
alarm reaction: immediate reaction to a stressor characterized by the "fight or flight" response, which prepares the body for physical activity
question
Stage 2
answer
adaptation: During this stage, if the stress continues, the body adapts to the stressors. Changes at many levels take place in order to reduce the effect of the stressor.
question
Stage 3
answer
exhaustion: The body's resistance to the stress may gradually be reduced, or may collapse altogether
question
Homeostasis
answer
tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium between interdependent elements, especially as maintained by physiological processes Deviations from homeostasis often require a vigorous response to attempt to restore homeostasis
question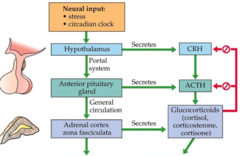
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis)

answer
H - hypothalamus (CRF) P - pituitary (ACTH) A - adrenal (Corticosterone or Cortisol) It helps regulate things such as your temperature, digestion, immune system, mood, sexuality and energy usage. It's also a major part of the system that controls your reaction to stress *helps maintain homeostasis*
question
Glucocorticoids
answer
like cortisol in your blood, they help to release stores of energy from fat They also INHIBIT the HPA axis *secreted especially in times of stress*
question
(Review) Effects of glucocorticoids
answer
Very stressed ppl may have deficits in hypothalamus or too much pumping of adrenal cortex ? *Glucocorticoids = secreted in times of stress, so they: Interfere with memory & Promotes fear/ anxiety*
question
Effects of cortisol
answer
stimulates the synthesis of glucose inhibits the uptake of glucose into fat and muscle stimulates the breakdown of fat suppresses the immune system can affect behavior like fear and learning and memory reduces plasma levels of sex steroid hormones *almost (if not all) cells have receptors for cortisol*
question
Glucocorticoids & conditioned fear
answer
Corticosterone given immediately after tone and shock pairing in rats enhances conditioned fear Corticosterone dose-dependently enhances freezing (reduces movement)
question
(Review) NBQX
answer
glutamate antagonist (GABA=glutamate agonist) blocks excitatory effects of glutamate
question
Epinephrine
answer
effects: Increased blood flow to muscles Increased heart rate Rise in blood sugar Piloerection (goosebumps) Stress activates autonomic nervous system to release epinephrine
question
Corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) & Neuropinephrine (NE)
answer
neurotransmitters that act centrally in response to stress
question
CRF
answer
*Increases anxiety* *Enhances conditioned fear* Increases arousal Decreases body weight Interferes with sexual behavior Disrupts sleep
question
Long-term stress effects
answer
*Impaired memory* *Immune suppression* Increased blood pressure Damage to muscles Susceptibility to diabetes Infertility Increased inflammatory responses Increased anxiety Susceptibility to depression
question
Long-term stress impairs memory (evidence)
answer
Rats were stressed daily for 21 days & then given training in the Y maze. Stressed rats spent less time in the baited arm at test than did control rats
question
Stress and stressor controllability
answer
Inescapable, but not escapable, shock enhances subsequent conditioned fear Following rats inescapable shock, rats show decrease in escape learning (learned helplessness)
question
The role of the dorsal raphe & serotonin in unpredictable & predictable stress
answer
After inescapable stress, the DRN (dorsal raphe nucleus) is hyper-responsive to subsequent stimuli and releases more 5-HT (serotonin receptor) in target areas, such as the amygdala
question
The role of the frontal cortex & serotonin in unpredictable & predictable stress
answer
If the frontal cortex can tell if stress is controllable, it turns off DRN (serotonin release)
question
Exercise & stress resistance
answer
Exercise prevents the escape deficit produced by inescapable shock Exercise seems to decrease 5-HTC receptors in DRN target areas (*reduces stress*)
question
Depression - prevalence
answer
Depression affects approximately 18 million Americans In any 1 year ~9.5 % of the population suffers from depression 95% of ppl w/ depression have at least 1 symptom of anxiety
question
Depression - types
answer
major depression (mood disorder consisting of unremitting depression or periods of depression that do NOT alternate w/ periods of mania) bipolar disorder (mood disorder characterized by cyclical periods of mania & depression)
question
Depression - symptoms
answer
Persistent sad, anxious, or "empty" mood Feelings of hopelessness, pessimism Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, helplessness Loss of interest or pleasure in hobbies and activities that were once enjoyed Decreased energy, fatigue, being "slowed down" Difficulty concentrating, remembering, making decisions Insomnia, early-morning awakening, or oversleeping Appetite and/or weight loss or overeating and weight gain Thoughts of death or suicide; suicide attempts Restlessness, irritability Persistent physical symptoms that do not respond to treatment
question
Depression - drug treatment
answer
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI's) Tricyclic antidepressants Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitor (SSRI)/ (SNRI) Ketamine
question
Monoamine oxidase (MAO's)
answer
5-HT (serotonin), NE (neropinephrine) & DA (dopamine) NE & DA are Catecholamine's *degrade/ break down catehcolamines & serotonin into inactive forms
question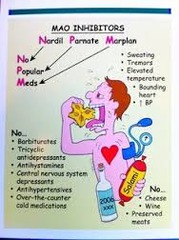
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI's)

answer
Inhibiting MAO increases synaptic levels of NE, DA and 5-HT
question
Tricyclic Antidepressants
answer
Tricyclic's block the reuptake of NE and 5-HT
question
Side effects (Tricyclic Antidepressants)
answer
sedation (histamine), blurred vision, dry mouth and constipation (Ach blockade)
question
Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRI)
answer
SSRI's block the reuptake of 5-HT
question
Side effects (SSRI)
answer
nausea, nervousness, agitation or restlessness, dizziness, reduced sexual desire, drowsiness, insomnia, weight gain or loss, headache
question
Tryptophan
answer
improves depression symptoms by increasing the level of serotonin in the brain *so, tryptophan depletion produces depressive symptoms in remitted depressed individuals*
question
Deep Brain Stimulation of the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex (subgenual ACC)
answer
disrupting focal pathological activity in limbic-cortical circuits using electrical stimulation of the subgenual cingulate white matter can effectively reverse symptoms in otherwise treatment-resistant depression.
question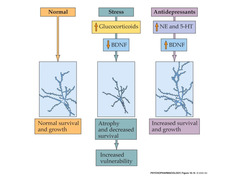
Ketamine

answer
NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist A single dose of ketamine eliminates depression within an hour and lasts up to 2 weeks. *restores synapses through BDNF (Brain Derived Neurotropihc Factor) and mTOR* In depression, BDNF lessens... w/ ketamine, BDNF goes back up
question
Acute Ketamine
answer
produces rapid reversal of depression & restores normal synaptic function
question
The role of synaptic atrophy (death) in depression
answer
depression (excessive amounts of corticosterone) results in less excitatory synaptic receptors Ketamine = excessive release of glutamate = so ketamine makes more excitatory synaptic receptors (resets back to "normal synapse" with even more excitatory receptors) b/c of BDNF
question
How do effective drug treatments suggest what the underlying biological causes of depression might be?
answer
Depression is some deficit in monoamine (including 5-HT, NE DA)
question
Anxiety - prevalence
answer
Anxiety affects approximately 25 million Americans. 19.5 % of women and 8% of men have an anxiety disorder. Up to 65% of ppl with anxiety become depressed 95% of ppl w/ depression have at least 1 symptom of anxiety
question
PTSD & amygdala activity
answer
Individuals with PTSD show exaggerated amygdala responding to fearful faces
question
Amygdala & conditioned fear
answer
Inactivation of the amygdala interferes with fear but NOT anxiety
question
Bed Nucleus of the stria terminalis & anxiety
answer
Inactivation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) interferes with anxiety but NOT fear
question
Are fear & anxiety the same?
answer
fear (Amygdala) = predictable & Short-duration stimulus anxiety (BDNF)= unpredictable & Long-duration stimulus Lesions of the BNST are the same, but not the amygdala reduce fear-like responding to: 1. bright lights 2. intracerebroventricular corticotropin-releasing factor 3. uncontrollable shock 4. exposure to predator odor
question
Benzodiazepines

answer
*effective treatments for anxiety enhance the effect of GABA (glutamate agonist), resulting in sedative properties
question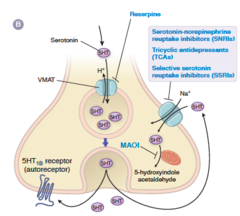
SSRI

answer
*effective treatment for anxiety Drugs that increase serotonin reduce anxiety (but the role of serotonin in anxiety is confusing)
question
(Review) acute affect of 5-HT (serotonin)/ SSRI's
answer
initial effect is anxiety (about 3 days) until the serotonin balances out
question
(Review) Choline - guest lecture
answer
*enhancement of memory* & healthy brain function most important during prenatal phase but also up until around preteen phase (when brain is still developing/ most neural plasticity)
question
The term "stress" was coined by
answer
d. Walter Cannon?--homeostasis/fight or flight a. Hans Seyle?-- stress/GAS
question
The general process by which a physiological reaction produced in the body by the perception of aversive or threatening events is referred to as
answer
e. stress
question
Secretion of glucocorticoids results in
answer
a. reduced plasma levels of sex steroid hormones. b. increased conversion of protein to glucose. c. greater availability of fatty acids as sources of energy. d. increased blood flow
question
All of the following occur during a stress response EXCEPT
answer
a. the parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system is activated
question
Hans Selye argued that ill health induced by chronic stress exposure reflects
answer
c. the prolonged secretion of glucocorticoids
question
Which of the following effects of stress would predispose an organism to develop an infectious illness?
answer
a. inhibition of the immune response
question
Episodes of depression are characterized by
answer
b. extreme sadness
question
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of depression?
answer
c. increased appetite for sex
question
A key function of monoamine oxidase is to
answer
d. degrade catecholamines and serotonin into inactive forms
question
Fluoxetine (Prozac) is an effective treatment for ________ that works by ________.
answer
depression & OCD; blocking serotonin reuptake
question
The tricyclic antidepressant drugs are monoamine agonists in that these drug
answer
a. block the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin into the terminals.
question
An effective therapy for treatment-resistant depression involves the use of
answer
e. electrical stimulation of the subgenual ACC.
question
The monoamine hypothesis states that depression is caused by
answer
a. overactivity of monoaminergic neurons.



