Pre-Intra-Post-Op Nursing Care – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Reasons for surgery
answer
Diagnostic: determines origin and cause of disorder Curative: resolves health problem by repairing or removing cause Restorative: improves patient's functional ability Palliative: relieves sx of disease process, but does not cure Cosmetic: alters/enhances personal appearance
question
Urgency and degree of risk
answer
Urgency: Elective, Urgent, Emergent Degree of Risk: Minor, Major Surgical home? - may help enhance outcomes in pts if there was a surgical home that coordinated care throughout entire surgical process (pre, intra, post)
question
Extent of surgery/procedures
answer
Simple: localized approach Radical: involves surrounding musculature / area Minimally invasive (MIS): laparoscopy or robotic techniques Bedside, VASC (outpt surgery center @ UVA), Main
question
Collaborative management: Assessment
answer
*History ; data collection*: Age; Drugs, Substance use; Medical hx (including cardiac and pulmonary); Complementary/alternative practices; Previous surgeries, anesthesia; Blood donations; Discharge planning *OSA (Obstructive Sleep Apnea) Score*: how likely is that the person has sleep apnea ; helps inform airway problems patient may have
question
System assessment
answer
*Cardiovascular*: CAD, MI w/i 6 mos of surgery, angina, HTN, dysrhythmias *BLOOD THINNERS*: HOLD 1 WK b/fore surgery ; Xarelto - blood thinner can be used *Respiratory*: Chronic respiratory problems; Smoking decr O2 delivery, diminishes ability to wound heal, skin integrity *Renal/Urinary*: Kidney impairment inhibits drugs/anesthetic agent excretion * Endocrine*: DM, importance of insulin control
question
System Assessment Cont
answer
*Neurologic*: Determine baseline - need to know whether any change in consciousness is typical or not ; Assess LOC ; ability to follow commands *Musculoskeletal* *Nutritional status*: Malnutrition ; obesity increase surgical risk *Psychological*: consent, self care? ; is patient able to provide their own informed consent? *Psychosocial*
question
Lab Assessments
answer
Blood type ; crossmatch CBC or H/H Clotting studies (PT/INR ; PTT) Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP): electrolytes, Creat Pregnancy test: may be contraindication in surgery ; weigh risks/benefits Also: CXR, EKG
question
Information
answer
*Preoperative teaching* *Informed consent*: is a process ; begins w/ surgeon, ask pt several times what they're having & where; Surgeon obtains signed consent b/fore sedation and/or surgery; Nurse clarifies facts & dispels myths about surgery: not responsible for providing detailed info about procedure! Pt may sign with "X"; In emergency, telephone authorization is acceptable *Ensure correct site is selected & wrong site is avoided* *Licensed independent practitioner marks site, involving pt if possible*
question
Skin preparation
answer
Break in the skin increases risk for infection Pt may be asked to shower using antiseptic solution Hair removal by electric clippers, depilatories > Shaving creates risk for infection!
question
Dietary restrictions
answer
NPO: Pt not to ingest anything PO for 6-8 hrs before surgery Decreases risk for aspiration Give pts written/oral directions to stress adherence Surgery can be canceled if instructions not followed
question
Administering regular medications
answer
Consult w/ physician and anesthesia provider for instructions Drugs for certain conditions often allowed w/ sip of water: will be person dependent > pt may or may not need to take meds for: Cardiac disease, Respiratory disease, Seizures, HTN
question
Bowel/GI prep?
answer
Performed to prevent injury to colon; reduces number of intestinal bacteria Enema or laxative
question
Patient preparation
answer
Remove most clothing; provide gown Leave valuables with family member or lock up Tape rings in place if cannot be removed Ensure patient is wearing ID band Remove: Dentures, Prosthetic devices, Hearing aids, Contact lenses, Fingernail polish, Artificial nails, Pierced jewelry
question
Members of surgical team
answer
Surgeon & surgical assistant, Anesthesia providers Holding area nurse (SAS), Circulating nurse, Scrub nurse, Specialty nurses Surgical technologist *Safety*: Time-out, Surgical count, Surgical checklist
question
Minimally invasive & robotic surgery
answer
Now common practice Preferred technique for many surgery types, including: Cholecystectomy, Joint surgery, Cardiac surgery (some), Splenectomy, Spinal surgery Ex) Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery
question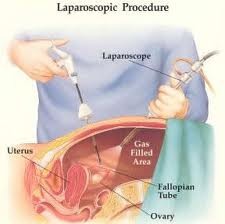
Laparoscopy

answer
Can cause referred shoulder pain d/t gas filled area
question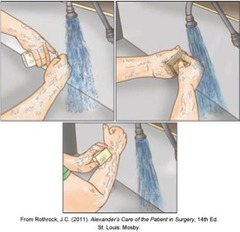
Surgical scrubbing

answer
Broad-spectrum, surgical antimicrobial solution Vigorous rubbing creates friction Used from fingertips to elbow Scrub continues for 3-5 min
question
General anesthesia
answer
*Reversible* loss of consciousness induced by inhibiting neuronal impulses in several areas of CNS Involves single or combination of agents *Depresses CNS*: results in analgesia, amnesia, unconsciousness w/ loss of muscle tone & reflexes Risk for?
question
General Anesthesia (GA) Cont.
answer
Inhalation IV injection *Adjuncts to general anesthetic agents*: Hypnotics, Opioid analgesics, Neuromuscular blocking agents *Balanced anesthesia*: e.g., nitrous oxide for amnesia, morphine for analgesia, pancuronium for muscle relaxation May need to use a hypnotic, a paralytic, and an analgesic
question
Complications from GA
answer
*Malignant hyperthermia* Overdose Unrecognized hypoventilation Problems with specific anesthetic agents Intubation problems Tachycardia, Skin mottling, Cyanosis Myoglobinuria, Rise in CO2, Elevated temperature
question
Malignant hyperthermia
answer
Acute, life-threatening complication May be genetic Begins when skeletal muscle is exposed to a specific agent Causes incr metabolism of drug > incr Ca++ levels in muscle cells > leads to acidosis, high temperature, dysrhythmias
question
Treatment of complications
answer
Establish open airway *SAFETY*: regaining consciousness Give oxygen Notify surgeon *Epinephrine* for unexplained bradycardia
question
Local anesthesia
answer
Briefly disrupts sensory nerve impulse transmission from specific body area/region Delivered topically and by local infiltration Pt remains conscious, able to follow instructions
question
Regional anesthesia
answer
Blocks multiple peripheral nerves in specific body region: Field Nerve Spinal Epidural
question
Moderate sedation
answer
IV delivery of sedative, hypnotic, opioid drugs to reduce level of consciousness Patient maintains patent airway, can respond to verbal commands Amnesia action is short i.e. colonoscopy
question
Postoperative period
answer
Begins w/ completion of surgery & transfer to PACU, ambulatory care unit, or ICU Handoff/communication > *Most critical of the transfers* N/V: many anesthesia agents can cause N/V: give Zofran or other antiemetic Airway: want to prevent vomiting if possible Abx order: know when they got the last dose & when the next one is due How cold did the pt get? Do we need warming blankets?
question
Respiratory assessment
answer
Patent airway, adequate gas exchange Note artificial airway when applicable Rate, pattern, depth of breathing Breath sounds Accessory muscle use Snoring and stridor Respiratory depression or hypoxemia
question
Cardiovascular monitoring
answer
Vital signs Heart sounds Cardiac monitoring *Peripheral vascular assessment*: Monitor for DVT, Administer prophylaxis (SCDs)
question
Post-op monitoring - Neuro
answer
Cerebral functioning Motor and sensory assessment after epidural or spinal anesthesia Know LOC before & after surgery
question
Post-op monitoring - Fluid/electrolyte
answer
Monitor I/O, Hydration status, IVF Vomit Urine Wound drainage, NG tube drainage Acid-base balance
question
Post-op monitoring - GI system
answer
Postoperative N/V common: 30% of patients experience N/V after general anesthesia Peristalsis may be delayed up to 24 hrs Monitor for bowel sounds *To reduce nausea/vomiting*: Ondansetron (Zofran), Meclizine (Antivert, Dramamine), Benadryl (I know!), Phenergan
question
If NG inserted:
answer
*May have been inserted during surgery to*: Decompress and drain stomach, Promote GI rest Allow lower GI tract to heal, Provide enteral feeding route Monitor gastric bleeding, Prevent intestinal obstruction *Assess any NG tube drainage*
question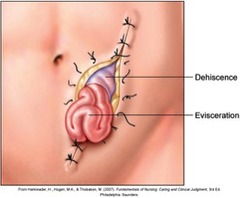
Skin assessment

answer
*Impaired wound healing*: seen most often 5 - 10 days after surgery *Dehiscence*: wound starts to break apart *Evisceration*: bulging out What impacts wound healing? Nutrition, age, glucose, mobility, tobacco use
question
Surgical drains
answer
Assess drainage q 4h, or PRN
question
Post-op Pain
answer
1) Pain/discomfort expected after surgery 2) Look for Physical & emotional signs of pain 3) Consider type, extent, length of surgery when assessing pt's pain ; need for meds *S/Sx of Pain*: Increased HR/BP/RR, Profuse sweating, Restlessness, Confusion (older adults), Wincing, moaning, crying 4) Make sure you give pt a stool softener
question
Lab assessment
answer
Analysis of electrolytes CBC "Left-shift" on differential: elevated WBCs Anemia? Blood loss? ; Check H/H ABGs Urine and renal laboratory tests Blood glucose
question
Potential for hypoxemia
answer
Highest incidence occurs on *DAY 2 postop* *Interventions*: Airway maintenance, Monitor SpO2 Semi-Fowler's position, O2 therapy, breathing exercises, Mobilization ASAP
question
Wound Infection (SSI) & delayed healing
answer
*Interventions*: Nursing assessment of surgical area *Dressings*: first change usually done by surgeon *Drains*: provide exit route for air, blood, bile; help prevent deep infections, abscess formation during healing Irrigation, debridement, surgical re-open



