Physical Chemistry Chapter 7 (Thermochemistry) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
When a system goes through a change in one or more of its properties
answer
Process
question
Delta U = Q - W where Delta U is change in system's internal energy, Q is heat added to system and W is work done by the system
answer
First law of thermodynamics
question
Occur at constant temp, therefore U is constant. Therefore Delta U is 0 and Q = W
answer
Isothermal processes
question
Total internal energy of system directly related to temperature
answer
Why is isothermal imply no Delta U?
question
Hyperbola (looks like exponential decay) where area under curve = work AND ALSO the heat that entered the system
answer
Isothermal process on PV graph
question
No heat exchange. Therefore Delta U = -W Therefore Delta U equals work done ON the system Temperature not constant.
answer
Adiabatic process
question
Pressure is constant. Flat line on P-V graph
answer
Isobaric process
question
aka isochoric; no change in volume therefore no work. Delta U = Q Vertical line on P-V graph
answer
Isovolumetric process
question
Can occur without additional energy. Many of them have high Ea and therefore go slowly and may not go to completion.
answer
Spontaneous processes
question
Require energy to happen. Often coupled to spontaneous reactions so they go
answer
Nonspontaneous processes
question
...
answer
*7.2 States and State Functions*
question
Describe system in an equilibrium state. Useful for comparing one equilibrium state to another
answer
State functions
question
Describe quantitatively the pathway taken from one pathway to another
answer
Process functions
question
Pressure, density, temperature, volume, enthalpy, internal energy, Gibbs free energy, entropy
answer
Examples of state functions
question
Work and heat
answer
Examples of process functions
question
25 Celsius, 1 atm pressure, 1M For consistency in kinetics, equilibrium, and thermochem
answer
Standard conditions for Thermochemistry and why are they used?
question
Most stable form of a substance under standard conditions e.g. H2(g), H2O(l), NaCl(s)
answer
Standard state of a substance
question
Delta H naught Delta S naught Delta G naught
answer
Changes in enthalpy, entropy and free energy under standard conditions
question
Show standard and nonstandard states of matter for a given substance in an isolated system, determined by temperature and pressure.
answer
Phase diagrams
question
Reversible, and equilibrium of phases will be reached at any temp and pressure. e.g. some ice absorbs heat and melts. This heat is removed from the surrounding water, and an equal amount freezes. Similar thing happens liquid and gas phases of water in a closed container.
answer
Phase changes
question
Temperature related to average kinetic energy of the molecules that make up the substance. Therefore molecules have a range of instantaneous KE values.
answer
Temperature and KE
question
Some molecules at surface of liquids gain enough KE to escape into gas phase.
answer
Evaporation/vaporization
question
Specific type of vaporization that occurs above the BP and involves vaporization through the entire volume
answer
Boiling
question
Gas goes back into liquid phase. Occurs due to lower temp or higher pressure. In covered or closed container, escaping molecules trapped, exert a countering pressure and they go back to liquid
answer
Condensation
question
The pressure that the gas exerts over the liquid at equilibrium. Increased with temp increased because KE increases and more molecules enter gas phase
answer
Vapor pressure of the liquid
question
When vapor pressure of the liquid equals the ambient pressure
answer
Boiling point
question
The number of motions about an equilibrium position that a atom/molecule can do, which increases as temperature of solid increases.
answer
Microstates
question
Pure crystalline substances have precise MPs Amorphous solids (glass, plastic, wax, chocolate) melt or solidify over a large range of temperatures.
answer
MP of pure vs. amorphous solids
question
Device used to purify a product that is heated under reduced pressure, causing it to sublime (go to gas) Desired product usually more volatile than impurities so gas is product. Gas deposits onto cold finger, and cold water cools the gas, yielding the pure solid
answer
Cold finger
question
Indicate phase boundaries, showing the temp and pressure where equilibrium between phases happens.
answer
Phase diagrams - lines of equilibrium
question
Where the three phase boundaries meet. At this temperature and pressure, all three phases in equilibrium
answer
Triple point
question
Where the liquid-gas line ends. At and beyond this point, no distinction between liquid and gas (supercritical fluids)
answer
Critical point
question
As liquid is heated in closed system, density of liquid decreases and density of gas increases. At critical point, two densities are equal and there is no distinction between the two phases.
answer
How do supercritical fluids work?
question
Related to the average KE of the particles of a substance.
answer
Temperature (T)
question
Related to average KE of the praticles as well. Also depends on how much of the substance is present. If substance's thermal energy increases, temperature also increases
answer
Thermal energy (enthalpy)
question
Transfer of energy from one substance to another because of a difference in temperature.
answer
Heat (Q)
question
A law that if two systems are separately found to be in thermal equilibrium with a third system, the first two systems are in thermal equilibrium with each other; that is, all three systems are at the same temperature. Also known as thermodynamic equilibrium.
answer
Zeroth law of thermodynamics
question
Delta Q > 0
answer
Endothermic
question
Delta Q < 0
answer
Exothermic
question
Joule or calorie (1 cal = 4.184 J)
answer
Unit of heat
question
Constant pressure. Assume this.
answer
When is enthalpy (delta H) equivalent to heat?
question
Process of measuring transferred heat.
answer
Calorimetry
question
q = mc(delta T) where c is the specific heat and T is the change in temp (Celsius or Kelvin)
answer
Heat absorbed or released equation
question
Amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of the substance by one degree Celsius (or kelvin). c(h2o) = 1 cal/g*K
answer
Specific heat
question
mass times specific heat (= mc)
answer
Heat capacity
question
Insulated container covered with lid. Contains solution where some reaction or physical process is occurring. Atmospheric pressure stays constant and temperature can be measured as the reaction progresses.
answer
Constant-pressure calorimeter (coffee-cup)
question
Sample of matter (usually hydrocarbon) goes in steel decomposition vessel, vessel filled with O2. Vessel placed in insulated container with known mass of water. Contents of decomposition vessel ignited, and heat evolves --> heat of combustion reaction. W = P(delta V), and since isovolumetric process, no work done. System = sample + O2 + steel vessel. Surroundings = water
answer
Constant-volume calorimetry (bomb calorimeter)
question
No heat exchanged between calorimeter and rest of universe, so Q = 0 Delta Usys + Delta U surroundings = Delta U calorimeter = Qcal - Wcal = 0 Delta Usys = -DeltaUsurr No work done, so qsys = -qsurroundings (m)steel(c)steel*deltaT + m(oxygen)c(oxygen)*deltaT = -m(water)c(water)*deltaT
answer
Math for bomb calorimeter
question
No heat exchange between calorimeter and universe (therefore adiabatic process), but there is exchange between decomposition vessel and water.
answer
Heat exchange in bomb calorimeter
question
use q = mc(delta T) and the fact that qcold = -qhot. Solve for Tf
answer
Question type - two substances, equilibrium temperature?
question
Temp rises until MP or BP reached. Temp constant as compound converted to next phase. After conversion, temp begins to rise again. Temp constant during phase change because substance absorbs energy to allow particles to overcome attractive forces to go into the next phase.
answer
Heating curve
question
Solid to liquid - heat of fusion Liquid to gas - heat of vaporization
answer
Solid-liquid and liquid-gas enthalpy values for phase changes
question
q = mL L is the latent heat (enthalpy of an isothermal process - cal/g)
answer
Find heat used in a phase change
question
sum of heat for changing temp of each respective phase, and heats associated with phase changes.
answer
Total amount of heat to cross multiple phase boundaries
question
= H. A state function. delta H of a system can be calculated by comparing the enthalpy of the final state to the enthalpy of the initial
answer
Enthalpy
question
= Hproducts - Hreactants Positive delta Hrxn = endothermic Negative delta Hrxn = exothermic
answer
delta H equation
question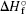
Enthalpy change accompanying rxn being carried out under standard conditions Delta H naught rxn = sum(std heat of formation, products) - sum(std heat of formation) reactants
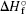
answer
Standard heat of formation (explain, and formula for rxn)
question
Enthalpy changes are additive. Note: Enthalpy change for the reverse of any reaction has same but opposite magnitude. Hess's law works for ANY STATE FUNCTION INCLUDING ENTROPY AND GIBBS FREE ENERGY
answer
Hess's law
question
Average energy required to break a particular type of bond between atoms *in the gas phase* Units of kJ/mol of bonds broken

answer
Bond enthalpy (bond dissociation energies)
question
Opposite of bond breaking, same magnitude of energy, but negative (energy released when bonds formed). delta H naught rxn = sum(deltaH bonds broken) - sum(delta H bonds formed)
answer
Bond formation
question
Add up the delta H for bonds breaking (positive) and bonds forming (negative). Multiply value for the # of bonds broken or formed. p. 224. Look at it now.
answer
Questions with finding enthalpy
question
delta H naught comb = enthalpy change associated with combustion of fuel. Measurements require reaction to be spontaneous and fast - combustion reactions are great for this.
answer
Standard heat of combustion
question
Energy is going from being localized/concentrated to being spread out or dispersed.
answer
Entropy - idea
question
Energy will spontaneously disperse from being localized to becoming spread out if it is not hindered from doing so.
answer
Second law of thermodynamics
question
Measure of spontaneous dispersal of energy at a specific temperature Where Q = Qrev (heat gained or lost in a reversible process) Units usually J/mol*K
answer
Entropy and formula
question
delta Suniverse = delta S sys + delta S surr > 0
answer
Entropy of sys and universe
question
It is a state function, therefore can calculate delta S naught reaction. delta S naught rxn = sum(delta S naught formation products) - sum(delta S naught formation reactants)
answer
Entropy as a state function
question
Measure of the change in enthalpy and the change in entropy as a system undergoes a process. Indicates if reaction is spontaneous or nonspontaneous. delta G = delta H - T delta S T is temperature in Kelvin T(delta S) represents amount of energy absorbed by system when entropy increases reversibly.

answer
Gibbs free energy
question
delta G negative = spontaneous delta G positive = nonspontaneous delta G zero = equilibrium where delta H = T(delta S)
answer
Gibbs free energy sign and spontaneity
question
For example, for equilibrium between gas and solid delta G = G(g) - G(s) = 0 *Always has to be zero*!@#*()!*@()
answer
Gibbs free energy change for phase equilibria
question
Effect on delta G = delta H - T (delta S) Spontaneous --> + deltaH + deltaS (at high T); - deltaH + deltaS (all temp); - deltaH - deltaS (at low T) Nonspontaneous --> + deltaH - deltaS (all temp)
answer
Effects of delta H and delta S on spontaneity
question
This is an endothermic process - need to put energy in. delta H and delta S will be positive. Therefore reaction will only be spontaneous (negative delta G) if T(deltaS) is larger than delta H. This only occurs at temperatures above 100 degrees. At 100 degrees, delta H - T(deltaS) = 0, and equilibrium established between liquid and gas phases - water's vapor pressure equals ambient pressure
answer
Example of water boiling.
question
delta G determines spontaneous or not. Ea determines reaction rate.
answer
Ea vs. delta G
question
Under standard state conditions. deltaG naught formation, is the free energy change occurring when 1 mole of a compound in its standard state is made from its respective elements in their standard states under standard state conditions.

answer
Standard free energy
question
= 0
answer
Standard free energy of formation for any element under standard state conditions
question
= -R T ln(Keq) R = ideal gas constant, T temperature in kelvins. Higher Keq = more positive ln = more negative standard free energy change = more spontaneous reaction
answer
Standard free energy change formula
question
They no longer apply
answer
Standard state conditions AFTER REACTION BEGINS
question
delta G (rxn) = (standard free energy change)rxn + RTlnQ = RTln(Q/Keq) If Q/Keq is less than one (Q Keq), then natural log is positive and free enegy change is positive. Reaction will go in the reverse direction until equilibrium is reached. If ratio = 1, then free energy change is 0 (ln 1 = 0)
answer
Free energy change for a reaction IN PROCESS



