Pain – Flashcard
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Nerve fiber types and sensory/motor function: 1) A alpha 2) A beta 3) A gamma 4) A delta 5) B 6) C
answer
1) Proprioception, motor 2) Touch, pressure 3) Muscle spindle (muscle tone) 4) Pain, cold temperature, touch 5) Preganglionic autonomic 6) Dull pain, warm temperature, touch
question
Nerve fiber types from largest to smallest
answer
A alpha A beta A gamma A delta B C
question
Nerve fiber types from fastest to slowest
answer
A alpha A beta A gamma A delta B C
question
What kind of pain do different nerve fibers convey?
answer
1) A delta: sharp, stabbing, well localized pain (somatic) 2) C: dull, aching, poorly localized pain (visceral)
question
3 types of pain
answer
1) Somatic 2) Visceral 3) Neuropathic
question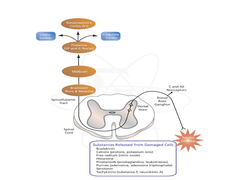
Pain pathway (excitatory)

answer
A delta and C nerve fibers ---> sustantia gelatinosa (dorsal horn) ---> release subtance P, somatostatin, VP, endophin ---> spinothalamic tract ---> thalamus ---> cortex
question
Definition of pain terms: 1) Allodynia 2) Hyperalgesia 3) Hyperesthesia 4) Hyperpathia 5) Anesthesia dolorosa 6) Dysesthesia 7) Hypoalgesia 8) Neuralgia 9) Paresthesia
answer
1) Pain to a stimulus that is not normally painful 2) Inreased pain to a normally painful stimulus 3) Increased sensitivity to stimulation 4) Syndrome of abnormally painful reacion to stimulus 5) Pain in an area that is numb to touch (trigeminal neuralgia) 6) Unpleasant abnormal sensation 7) Decreased pain to a normally painful stimulus 8) Pain in a nerve distribution 9) Abnormal (not unpleasant) sensation
question
Diffrence between CRPS I and CRPS II
answer
CRPS I: no major nerve damage (reflex sympathetic dystrophy) CRPS II: major nerve damage (causalgia)
question
Diagnostic criteria for CRPS I
answer
1) Presence of initiating noxious event or a cause of immobilzation (actual nerve injury for CRPS II) 2) Pain, allodyina, hyperalgesia disproportionate to inciting event 3) Edema, change in skin blood flow, decreased motor activity 4) No other cause
question
Hallmark symptoms of CRPS by stage
answer
1) Acute (weeks): wam, swollen, red, dry skin 2) Dystrophic (months): edematous, discolored, cold, clammy skin 3) Atrophic (> 4 months): atrophic, tight/shiny skin with decreased range of motion
question
CRPS treatment
answer
1) Physical therapy 2) Drugs: TCA (amytirptaline), gabapentin, mild opioid, steroids, NSAID 3) Sympathetic block: stellate ganglion block, lumbar sympathetic block 4) Somatic block (if sympathetic fails): brachial plexus, epidural, spinal) 5) Spinal cord stimulator 6) TENS 7) Biofeedback
question
Sympathetic supply to upper extremity
answer
T2-T9: synapse with stellate ganglion
question
Anatomic landmarks for stellate ganglion block
answer
1) Transverse process of C7 2) Neck of 1st rib 3) C6 tubercle at level of cricoid (Chassaignac's tubercle) when using the anterior paratracheal technique
question
Indications for stellate ganglion block
answer
1) CRPS 2) Refractory angina 3) Phantom limb pain 4) Vascular insufficiency 5) Hyperhydrosis
question
Side effects/risks of stellate ganglion block
answer
1) Vertebral artery injection 2) Horner's synrome (ptosis, miosis, anhydrosis) 3) Phrenic nerve paralysis 4) Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis (hoarseness, lump in throat) 5) Hematoma 6) Brachial plexus injury 7) Pneumothorax 8) Epidural/spinal injection 9) Esophageal perforation
question
Position of lumbar plexus for block
answer
Anterior lateral aspect of L2 vertebral body
question
Test to determine success of sympathetic block
answer
Incrased skin temperature 2C
question
Nerve distribution of trigeminal neuralgia
answer
Maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve (V2)
question
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
answer
1) Drugs: carbamazepine, phenytoin, baclofen, gabapentin 2) Surgical: microvascular decompression, nerve lesion (glycerol, radiofrequency) 3) Gasserion ganglion (trigeminal ganglion) block
question
Treatment of phantom limb pain
answer
1) Drugs: opioids, anticonvulsants, antidepressants, pregabalin, memantine, calcitonin 2) TENS 3) Deep brain stimulator 4) Spinal cord stimulator 5) Sympathetic block (stellate ganglion, lumbar) 6) Acupuncture
question
Anatomic location of celiac plexus
answer
L1 vertebral body, lateral to aorta
question
Celiac plexus is formed by which nerves?
answer
Greater and lesser splanchnic nerves
question
Celiac plexus block anatomic landmarks
answer
L1 vertebral body
question
Celiac plexus block: 1) Distribution 2) Indications
answer
1) Stomach to mid transverse colon 2) Cancer (visceral pain)
question
Complication of celiac plexus block
answer
1) Diarrhea 2) Hypotension 3) Paraplegia 4) Local anesthetic toxicity 5) Organ puncture 6) Pneumothorax
question
Superior hypogastric plexus block: 1) Distribution 2) Indications
answer
1) Descending colon, rectum, testes, penis, prostate, perineum, vulva, vagina, uterus, urethra and bladder 2) Chronic pelvic pain, cancer
question
Anatomic landmarks for superior hypogastric plexus block
answer
Anterior to L4-5
question
Hallmark of myofascial pain syndrome
answer
1) Muscle trigger points 2) Widespread aching
question
Hallmark of fibromyalgia
answer
1) Pain in 11 of 19 trigger points 2) Widespread pain 3) Fatigue/waking unrefreshed 4) Cognitive symptoms 4) Somatic symptoms in general (headache, weakness, bowel problems, nausea, dizziness, numbness/tingling, hair loss) 5) Other causes ruled out 6) Symptoms for at least 3 months
question
Treatment of fibromyalgia
answer
Amytriptyline (TCA) Duloxetine (SNRI) (NOT NSAIDS)
question
Order in which nerve fibers are blocked with local anesthetics
answer
Small myelinated (B) > small unmyelinated (C, A delta) > large myelinated (A gamma, beta, alpha) > large unmyelinated Pain, temperature, touch, proprioception, skeletal muscle tone.
question
Site of action of intrathecal opioids
answer
Substantia gelatinosa in dorsal horn spinal cord
question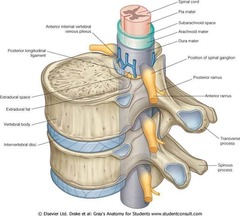
Primary barrier to opioid transfer from epidural space to spinal cord

answer
Arachnoid mater
question
Epidurally administered opioid penetration into the spinal tissue depends on what?
answer
Lipid solubility (highly lipid soluble = high uptake by epidural fat and veins and poor arachnoid penetration)
question
What is meralgia paresthetica
answer
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve numbness
question
Most common distribution for post-herpatic neuralgia
answer
Thoracic Trigeminal
question
Treatment of postherpetic neuralgia
answer
Capsaicin (poorly tolerated for acute zoster) Lidoderm patch TCAs (amitriptyline), SSRI, duloxetine Gabapentin Opioids Sympathetic block (only useful in acute attack of zoster) Antiviral (only if given within 72 hours of onset of zoster)
question
Phenol versus ethanol for neurolytic block
answer
1) Phenol: painless, shorter acting, hyperbaric 2) Ethanol: painful, longer acting, hypobaric
question
Causes for increased risk of post dural puncture headache
answer
1) Age < 40 2) Female 3) H/o post dural puncture headache 4) Low BMI 5) Cutting/beveled needle (vs. pencil point) 6) Needle bevel perpendicular to spine
question
How does TENS therapy work
answer
Activates larger neurons to override C fiber activation (gate-control theory)
question
Indications for spinal cord stimulator
answer
1) Failed Back Syndrome 2) Radicular pain syndrome or radiculopathies resulting in pain secondary to FBSS or herniated disk 3) Postlaminectomy pain 4) Multiple back operations 5) Unsuccessful disk surgery 6) Degenerative Disk Disease (DDD)/herniated disk pain refractory to conservative and surgical therapies 7) Peripheral causalgia 8) Epidural fibrosis 9) Arachnoiditis or lumbar adhesive arachnoiditis 10) Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) I or II
question
Indications for TENS therapy
answer
1) Neurogenic pain: phantom limb pain, sympathetically mediated pain (CRPS), postherpetic neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, pain after spinal cord injury 2) Musculoskeletal pain: Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, acute postoperative pain, acute posttraumatic pain. 3) Visceral pain and dysmenorrhea 4) Diabetic neuropathy 5) Angina pectoris 6) Urge incontinence 7) Control nausea in patients undergoing chemotherapy
question
Indications for intrathecal pain pump
answer
1) Chronic intractable pain (morphine) 2) Severe chronic pain (zicinotide - CCB) 3) Spasticity (baclofen)
question
When length of time is diagnostic of chronic pain
answer
6 months of ongoing pain
question
How to obtain history evaluation of pain
answer
1) Nature of pain (sharp, stabbing, dull, throbbing) 2) Intensity 3) Location/radiation 4) Duration 5) Aggravating/alleviating factos "NILDA"



