P3 – Ch 2 – Risk Management – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
1 - Risk management models
answer
Risk management models provide a coherent framework for orgs to deal with risk, based on the following components: - Risk appetite - Risk identification - Risk assessment - Risk profiling - Risk quantification - Risk management - Review and feedback * RM models are designed to show that RM is continuous and that it is a logical process.
question
1 - Risk management models ERM definition
answer
* ERM is a process, effected by an entity's board of directors, management and other personnel, applied in strategy setting and across the enterprise, designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity and manage risks to be within its risk appetite, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives.
question
1 - Risk management models COSO's RM model
answer
* The Committee of Sponsoring Organisations of the Treadway Commission furthers the ERM definition, identifying ERM to have the following: - Process - Operated at every level - Applied in strategy setting - Applied across the enterprise - Identifies key events and manage their risks - Provides reasonable reassurance - Geared to achievement of objectives
question
1 - Risk management models Benefits of ERM [p28]
answer
* Alignment of risk appetite and strategy * Link growth, risk and return * Choose best risk response * Minimise surprises ans losses * Identify and manage risks across the org * Provide responses to multiple risks * Seize opportunities * Rationalise capital
question
1 - Risk management models IFAC's Risk architecture
answer
* 8 components or the architecture - Acceptance of a risk management framework - Commitment from executives - Establishment of a risk response strategy - Assignment of a responsibility for RM process - Resourcing - Communication and training - Reinforcing risk cultures through human resources mechanisms - Monitoring the RM process * 4 components of RM - Structure to facilitate the identification and communication of risk - Resources - sufficient to support implementation - Culture - reinforcing decision-making processes - Tools and techniques - developed to enable org-wide management of risk
question
1 - Risk management models
answer
provide a coherent framework for orgs to deal with risk, based on the following components: - Risk appetite - Risk identification - Risk assessment - Risk profiling - Risk quantification - Risk management - Review and feedback
question
2 - Risk appetite and culture
answer
Even if orgs manage risk systematically, that does not remove the human element from decision-making on dealing with risks. How orgs respond to risk will be determined by the views of the directors or managers, and also the stakeholders to whom they are accountable. * Factors influencing risk appetites - mgnmt perceptions or appetite to take risk. Also influences risk culture, the values and practices that influence how an org deals with risk in it's ops * Personal views; emotional satisfactions * Response to s'holder demand
question
2 - Risk appetite and culture
answer
* Organisational influences - influenced by history, significant losses, changes in regulation and best practice, changing views * National influences * Cultural influences - Fatalists - Hierarchists - Individualists - Egalitarians
question
2 - Risk appetite and culture Aversion, seeking, conformance and performance
answer
* Risk aversion and risk tolerance - aversion focuses on the risk level: seeking focuses on the return level * Conformance and performance - conformance focuses on controlling pure (only downside) strategic risks: performance focuses on taking advantage of opportunities to increase overall returns within a business. IFAC states that RM should seek to reconcile performance and conformance - the two enhance eachother.
question
3 - Risk assessment
answer
* Framework - Identification - Analysis - Mapping - Consolidation
question
3 - Risk assessment Risk and event identification
answer
- External events - Internal events - Leading event indicators - Trends and root cacuses - Escalation triggers - Event interdependencies
question
3 - Risk assessment Analysis
answer
means obtaining an idea of the severity of the consequences of the risk materialising and how frequently (or likely) it is that the risk will materialise. * Risk quantification - risk that require more analysis can be quantified, where possible results or losses and probabilities are calculated and distributions or confidence limits added on. From this exercise is derived the following key data: - Average or expected result or loss - Frequency of losses - Chances of losses - Largest predictable loss
question
3 - Risk assessment Consolidation
answer
Now risk needs to be aggregated to corp leveel and grouped into categories. A good way to approach exam questions on risk is to analyse: - what do we know or what can we infer from the scenario about the risks and their causes (consider events that result in risk and conditions that result in risk) - what is the likelihood of the risk materialising and how severe will the consequences be * A risk register lists and prioritises the main risks an org faces and can be used for decisions. Monetary value sh/be added, interdependencies, who is responsible, actions taken, levels before and after control has been taken for a CBA.
question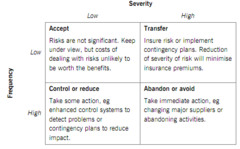
4 - Risk response

answer
Methods of dealing with risk include abandonment, control, acceptance and transfer
question
4 - Risk response
answer
* Abandonment - Take immediate action, eg changing major suppliers or abandoning activities * Control of risk - Take some action, eg enhanced control systems to detect problems or reduce impact (hedging, diversification, procedures, physical devices, education) * Acceptance - Risks are not significant. Keep under view, but costs of dealing with risks unlikely to be worth the benefits * Transfer - Insure risk or implement contingency plans. Reduction of severitiy of risk will minimise insurance premiums
question
5 - Risk responsibilities
answer
Orgs need to approach RM in a systematic way. A risk policy statement sets out general guidelines, incl responsibilities for RM. Everyone in the org has some responsibility for RM, but the org may employ specialists to oversee the RM processes. - the board (resp determining RM strategy) - RM group - Internal and external audit - line managers - staff
question
6 - Risk monitoring
answer
* Board review is an essential part of the RM process * Board review should be based on information collected from various sources * Factors influencing the extent of external reporting of risk include regulations, governance codes, and attitudes of stakeholders, particularly shareholders
question
Round up
answer
* RM models provide a coherent framework for ogs to deal with risk, based on the following components: Risk: - Appetite - Identification - Assessment - Profiling - Quantification - Management - Review and feedback * Mgt responses to risk are not automatic, but will be determined by their own attitudes to risk, which in turn will be influenced by shareholder attitudes and cultural factors * Risk analysis involves identifying, assessing, profiling and quantifying risks * Methods of dealing with risk include abandonment, acceptance, transfer or control
question
Round up
answer
* General steps orgs can take to manage risks include issuing a risk policy statement, appointing a risk manager or risk specialists and communicating risks to staff and shareholders * Board review is an essential part of the RM process * Board review should be based on info collected from various sources * Factors influencing the extent of external reporting of risk include regulations, governance codes and attitudes of stakeholders, particularly shareholders
question
Formal RM process
answer
1) Risk appetite 2) Establishment of RM process 3) Responsibilities for RM process 4) Risk identification 5) Risk assessment 6) Risk profiling 7) RM measures 8) Risk reporting



