Organic Chemistry: Chapter 7, 8, and 9 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
is the pi bond in an alkene an electrophile or nucleophile?
answer
nucleophile
question
can the alkene be a branch?
answer
no
question
what gets the lowest number when naming an alkene?
answer
the alkene
question
what does the parent chain name end with for an alkene?
answer
ene
question
if the alkene number is a tie, look at ___________ to decide
answer
branches (lowest number)
question
alkene is always number ____, the _____ position is always on the other side of the alkene
answer
1, 2
question
branches are only there to settle _____ ____________
answer
tie breakers
question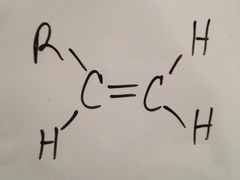
one non-H

answer
monosubstituted
question
do monosubstituted alkenes have stereoisomers?
answer
no
question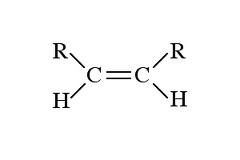
two non-H

answer
disubstituted
question
how do you differentiate between the stereoisomers of a disubstituted alkene?
answer
cis and trans
question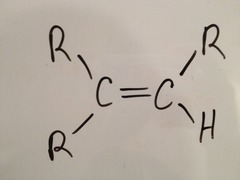
three non-H

answer
trisubstituted
question
how do you differentiate between the stereoisomers of a trisubstitued alkene?
answer
E or Z
question
rank the branches of a trisubstitued alkene by ________ __________ to determine hight or low
answer
atomic weight
question
highs on opposite sides
answer
E
question
highs on the same side
answer
Z
question
do you rank all 4 branches of a trisubstituted alkene? if no, how many do you rank?
answer
no, 2 (on each side)
question
assume all R groups are (the same or different) on a trisubstituted alkene
answer
different
question
do you put the stereoisomer (E or Z) of cyclo-alkenes in the name? if not, why?
answer
no, because it may be E or Z but it can not flip to become the other isomer
question
are alkenes nucleophiles or electrophiles?
answer
nucleophiles
question
a carbocation is most stable when more carbons (or non-hydrogens) are bound to it -carbocations pull e- closer and carbons have more e- than hydrogens
answer
Markovnikov's Rule
question
carbon bound to one other carbon
answer
primary
question
carbon bound to two other carbons
answer
secondary
question
carbon bound to three other carbons
answer
tertiary
question
is secondary or tertiary more stable?
answer
tertiary
question
is primary or secondary more stable?
answer
secondary
question
is primary or tertiary more stable?
answer
tertiary
question
movement of a hydrogen atom with a pair of electrons from one atom to another -a rearrangement that converts carbocations into more stable molecules
answer
hydride shift
question
the stereochemisty of a Br2 addition to a cycloalkene is always ________ (cis/trans)
answer
trans
question
if there is no carbocation, how many rearrangements are there?
answer
none
question
ignore ______ when naming a molecule cis or trans
answer
hydrogens
question
when cleaving an alkene with KMNO4, a monosubstituted half (of the alkene) yields what functional group?
answer
carboxylic acid
question
when cleaving an alkene with KMNO4, a disubstituted half (of the alkene) yields what functional group?
answer
ketone
question
when cleaving an alkene with KMNO4, a no substituted half (of the alkene) yields what?
answer
CO2
question
when cleaving an alkene with O3 and Zn, a monosubstituted half (of the alkene) yields what functional group?
answer
aldehyde
question
when cleaving an alkene with O3 and Zn, a disubstituted half (of the alkene) yields what functional group?
answer
ketone
question
when cleaving an alkene with O3 and Zn, a no substituted half (of the alkene) yields what functional group?
answer
formaldehyde
question
when an alkyne reacts with 1 equivalent, is there a mechanism/intermediate?
answer
no
question
a triple bond is ____ sigma bond(s) and ____ pi bond(s)
answer
1, 2
question
when an alkyne reacts with Br2, what is the stereochemistry?
answer
trans (or E)
question
when an alkyne reacts with H2 and Pt, can you stop it at 1 equivalent (alkene)?
answer
no
question
what is used in conjunction with H2 to stop an alkyne reaction at the alkene step?
answer
Lindlar's catalyst
question
when reacting an alkyne in 1 equivalent instead of excess, the reaction stops at the ________ step
answer
alkene
question
when reacting an alkyne in excess, the reaction fully reacts to the _______ step
answer
alkane
question
what reacts with the alkene during an electrophilic addition
answer
HBr
question
what is the only reaction with a hydride shift?
answer
electrophilic addition
question
what reacts with the alkene during a halohydrin reaction?
answer
Br2 and H2O (or any halogen X and water)
question
what is added to the final product during a halohydrin reaction?
answer
OH and Br (or X)
question
what reacts with the alkene during halogenation?
answer
Br2 (or any halogen X)
question
what reacts with the alkene during oxymercuration?
answer
Hg(OAc)2, H2O and NaBH4
question
what is added to the final product during oxymercuration?
answer
OH and H
question
what reacts with the alkene during hydroboration (NonMarkovnikov)?
answer
BH3 and H2O2
question
what is added to the final product during hydroboration (NonMarkovnikov)?
answer
H and OH
question
during cleavage with KMnO4, Hs turn into _____
answer
OH
question
what is added to the product during hydrogenation?
answer
Hs (on the same side)
question
what reacts with the alkene during hydrogenation?
answer
H2 and Pt
question
which is the only mechanism yields a product that is not trans?
answer
hydrogenation
question
does the reaction of an alkyne with H2 and Lindlar's catalyst yield a cis or trans product?
answer
cis
question
what do you react with an alkyne to yield trans Hs (hydration)on an alkene?
answer
Li, NH3
question
what are the reagents in a hydration (oxymercuration) reaction with an alkyne?
answer
HgSO4, H2SO4, H2O
question
when cleaving an alkyne, what are the only two functional groups that can result?
answer
carboxylic acid and CO2 (no ketone because no disubstituted alkynes)
question
what functional group is in the final product when an alkyne reacts with BH3 and H2O2 (hydroboration)?
answer
aldehyde
question
what functional group is in the final product when an alkyne reacts with HgSO4, H2SO4 and H2O (hydration)?
answer
ketone
question
can the hydration of an alkyne stop at the alkene intermediate?
answer
no (tautamerizes to ketone)
question
can the hydroboration of a alkyne stop at the alkene intermediate?
answer
no (tautamerizes to aldehyde)
question
what reagents can yield a ketone?
answer
KMnO4, O3 and Zn, or HgSO4, H2SO4 and H2O
question
what reagents can yield an aldehyde?
answer
O3 and Zn, or BH3 and H2O2
question
when naming a molecule that has an alkene and an alkyne with the same number, which wins?
answer
alkene
question
what is in the intermediate of a halohydrin reaction?
answer
brominium ion



