Nursing 203 Ovarian Cancer Exam 2 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion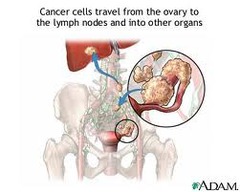
ovarian cancer facts

answer
Malignant tumor of the ovaries 22,280 new cases yearly, 15,000 deaths annually(?) 5th leading cause of cancer deaths in US -Most have advanced disease at time of diagnosis -Difficult to detect, deep in the pelvis. -No early screening mechanisms exists at this time Women between 55 and 65, Caucasian women> African American
question
risk factors for ovarian cancer

answer
Genetics: gene mutation BRCA1/BRCA2 genes -1st degree relative: hx of ovarian, breast/colon cancer. Age: > 50 yrs, more common after menopause Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): (estrogen without progesterone for at least 5-10yrs) Obesity (higher death rates) Infertility(nullparity), endometriosis, Early menarche and late menopause Ethnicity: Caucasian >African-American women
question
decrease risk for ovarian cancer
answer
Pregnancy: younger age with first birth, multiple pregnancies Breast feeding Oral contraceptives: BCP> than 5 years. -recent Harvard study:10-12% decrease after 1 year of use, approximately 50 % decrease after 5 years of use. (Cancer and Steroid Hormone Study or CASH): OC formulations with high levels of progestin reduced ovarian cancer risk more than preparations with low progestin levels. Prophylactic oophorectomy in women with genetic mutation BMI<30
question
patho of ovarian cancer
answer
90% :epithelial. (outer surface of ovary) 10% : germ cell tumors (cells that produce eggs) Histological grading:Grade I- III (according to cell differentiation) - Grade I: well differentiated, good prognosis. -Grade II: moderately well differentiated - Grade III, poorly differentiated, poor prognosis. Metastasis: Uterus, bladder, bowel ,omentum. Advanced spread to stomach, colon, liver and other parts.... Symptoms?
question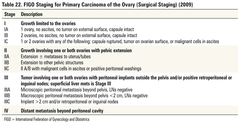
ovarian cancer grading

answer
Histological grading:Grade I- III (according to cell differentiation) - Grade I: well differentiated, good prognosis. -Grade II: moderately well differentiated - Grade III, poorly differentiated, poor prognosis. Metastasis: Uterus, bladder, bowel ,omentum. Advanced spread to stomach, colon, liver and other parts.... Symptoms?
question
why is ovarian cancer difficult to diagnose
answer
diff to diagnose until it has spread to lymph system or by direct extension to other organs or tissues
question
clinical manifestations of ovarian cancer
answer
Non specific, vague symptoms in early stages in abdominal/pelvic region: Easily ignored -abdominal pain, bloating, urinary urgency or frequency and difficulty eating or feeling full quickly. Need to educate that if women have one or more of these symptoms, especially if new or persistent or worsening: need MD follow up. Early identification impacts treatment and prognosis
question
ovarian cancer diagnostics
answer
NO screening tests available Pelvic exams recommended yearly. (ID presence of ovarian mass) -Abdominal and transvaginal ultrasound, exploratory laparotomy (dx & stage) Serum OVA-1(detects biomarker levels of ovarian involvement; differentiates benign or malignant status prior to surgical removal) High Risk women: -Serum levels of protein; CA-125 (tumor marker, can be + with other malignancies or fibroids, endometriosis) -Ultrasound of the ovaries Clinical trial results: Neither resulted in fewer deaths
question
serum OVA1
answer
Serum OVA-1(detects biomarker levels of ovarian involvement; differentiates benign or malignant status prior to surgical removal)
question
high risk women ovarian cancer diagnostics
answer
High Risk women: -Serum levels of protein; CA-125 (tumor marker, can be + with other malignancies or fibroids, endometriosis) -Ultrasound of the ovaries Clinical trial results: Neither resulted in fewer deaths
question
american cancer society ovarian recommendations
answer
ACS recommends that if any of these symptoms occur almost daily or last a few weeks and are new, the woman should seek the attention of her physician. In many cases, symptoms do not occur until the ovarian cancer is in an advanced stage. The symptoms of ovarian cancer may resemble other medical conditions or problems. Always consult your physician for a diagnosis
question
nurses educate on ovarian cancer
answer
Identify high risk females -family and health history Counseling: for high risk population. Options include: - prophylactic oophorectomy (reduces risk of ovarian cancer but does not eliminate possibility) -use of oral contraceptives
question
stage 1 ovarian cancer
answer
limited to ovaries
question
stage 1 ovarian cancer treatment
answer
TX: surgery:total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy May do tumor debulking. Chemo: Intra-peritoneal radiation if poorly differentiated 90% survival
question
stage 2 ovarian cancer
answer
disease limited to pelvis
question
stage 2 ovarian cancer treatment
answer
TX: surgery hysterectomy AND external abdominal/ pelvic radiation, intraperitoneal radiation OR systemic combined chemo.after tumor debulking surgery monitor for recurrent disease
question
stage 3 ovarian cancer
answer
disease limited to abdominal cavity
question
stage 3 ovarian cancer treatment
answer
Surgery: Debulking and chemotherapy: cisplatin(Platinol), Carboplatin (parplatin) survival rate 36%
question
stage 4 ovarian cancer
answer
distant metastic disease
question
stage 4 ovarian cancer treatment
answer
Surgery: Debulking and chemotherapy; cisplatin(Platinol), Carboplatin (parplatin) Paclitaxel(Taxol) Topotecan (Hycamtin) survival rate 20%
question
ovarian cancer treatment and Nursing responsibility
answer
Most patients with ovarian cancer have widespread disease at time of diagnosis Surgery: total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, with omentectomy with tumor debulking (removal of as much of the tumor as possible) Patient problems? Complications of surgery? Nursing interventions?
question
ovarian cancer radiation
answer
Radiation: Nursing interventions? intra peritoneal instillation of radioisotopes (intracavity):placing an isotope into the area of the cancer or in the area where micrometastasis (unseen cancer) is suspected(abdominal, small and large bowel lining) -allows uniform spread throughout abdominal cavity Side effects: N/V/D, fleeting abdominal pain, low grade fever(22%) External abdominal radiation Pelvic radiation therapy
question
side effects of ovarian cancer radiation
answer
Side effects: N/V/D, fleeting abdominal pain, low grade fever(22%) External abdominal radiation Pelvic radiation therapy
question
internal radiation therapy
answer
sealed radiation: intracavity, interstitial clients excretion is not radioactive. bodily fluids not contaminated private room properly labeled no kids under 18 no pregnant women wear film badge prevent dislodgemnt monitor VS q4hrs accurate I/O's Time, distance, shield Dosimeter Hospital policy
question
ovarian cancer chemo nursing responsibilities
answer
Type and amount of chemotherapy dictated by cell differentiation and stage of ovarian cancer Intra-peritoneal chemotherapy Systemic chemotherapy:Combination medications Platinum compound (Cisplatin,Carboplatin) combined with taxane (paclitaxel,or docetaxel:taxotere) 3-6 cycles Monitor and treat side effects of chemotherapy Chemo: treat recurrent disease or palliation
question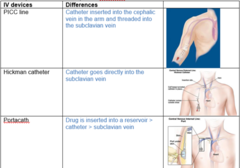
purpose of chemotherapy

answer
Chemo: treat recurrent disease or palliation Monitor and treat side effects of chemotherapy
question
nursing diagnosis: patient problems with ovarian cancer
answer
Anticipated grieving, anxiety, fear of cancer, loss of child bearing capacity : active listening Tissue integrity(radiation): Fatigue, weakness, lack of appetite (chemotherapy): gentile exercise program Early menopause: risk of osteoporosis Body image, sexuality(surgical hysterectomy, hair loss) Knowledge deficit(treatment side effects, complications )
question
after ovarian cancer treatment
answer
If patient is clinically clear after completing treatment: -repeat exploratory laporoscopy.. "second look" for evidence of disease...if no evidence Monitor for recurrent disease -recommendation: pelvic exam every 2-4 months x 2 years following treatment, every 6 months for next 3 years -Other tests may include: CXR, CT scan, urinalysis, serum CA-125. Fear of recurrence is common
question
ovarian cancer after treatment tests
answer
-Other tests may include: CXR, CT scan, urinalysis, serum CA-125. Fear of recurrence is common
question
how to monitor for recurrent pelvic disease
answer
Monitor for recurrent disease -recommendation: pelvic exam every 2-4 months x 2 years following treatment, every 6 months for next 3 years
question
how nurses can help with ovarian cancer
answer
Educate women not to ignore any symptoms Awareness Active listening Good history Support Coping Hope



