NUR 106 (UNIT 5) Cardiovascular Therapy: Non-Diuretic Cardiac Drugs – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
chronotropic
answer
+ chronotropic = increase in heart rate - chronotropic = decrease heart rate
question
inotropic
answer
+ inotropic = increase force of contraction - inotropic = decrease force of contraction
question
dromotropic
answer
+ dromotropic = increase in heart rhythm (conduction) - dromotropic = decrease in heart rhythm (conduction)
question
Preload
answer
amount of blood coming into the heart from superior and inferior vena cava
question
Afterload
answer
the resistance that the ventricles have to overcome to pump out the blood through the aorta.
question
ACE-Inhibitors (memory)

answer
A-pril A for ACE inhibitor and the names contain "-pril"
question
ACE Inhibitor method of action
answer
Decrease in blood flow (kidneys) signals --> release of renin --> angiotension --> enzyme --> angiotensen II --> increase in peripheral resistance --> increase in BP ACE Inhibitors block the enzyme and stops the process which leads to a reduction in BP
question
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE) Actions
answer
Blocks ACE from converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II, leading to a decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in aldosterone production, and a small increase in serum potassium levels along with sodium and fluid loss
question
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE) Contras
answer
Allergies Impaired renal function Pregnancy (birth defects) and lactation
question
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE) Caution
answer
HF (don't want to slow down the heart too much)
question
ACE Inhibitor Prototype: Captopril: Indications
answer
Treatment of hypertension, CHF, diabetic nephropathy, left ventricular dysfunction after an MI
question
ACE Inhibitor Prototype: Captopril: Actions
answer
Blocks ACE from converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II, leading to a decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in aldosterone production, and a small increase in serum potassium levels along with sodium and fluid loss
question
ACE Inhibitor Prototype: Captopril: PK:
answer
Oral, onset 15 min, peak 30-90 min HL: 2 hours; excreted in urine
question
ACE Inhibitor Prototype: Captopril: AE/SE
answer
Tachycardia, MI, rash, pruritus, gastric irritation, aphthous ulcers, peptic ulcers, dysgeusia, proteinuria, bone marrow suppression, cough
question
ACE Inhibitors Nursing Considerations
answer
Assess blood pressure prior to administration Hold for BP 90-100/60 (Have to have BP before giving drug) Administer on an empty stomach 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals Watch for "first dose phenomenon" Prevent dehydration Decrease dose for renal failure Dry, hacking cough is a common adverse effect
question
The mechanism of action of an ACE inhibitor is the blocking of ACE from converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II. What does this cause? a. Decrease in serum potassium levels b. Decrease in aldosterone production c. Sodium and fluid loss d. Increase in blood pressure
answer
b. Decrease in aldosterone production Rationale: Blocks ACE from converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II, leading to a decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in aldosterone production, and a small increase in serum potassium levels along with sodium and fluid loss
question
The nurse is caring for a 27-year-old African American woman who was just prescribed an ACE inhibitor for management of her hypertension. What should you advise this patient about contraception? a. The use of spermicidal jellies is recommended. b. The minipill is the contraception method of choice. c. Use barrier contraceptives to prevent pregnancy while taking these drugs. d. No special precautions need to be taken.
answer
c. Use barrier contraceptives to prevent pregnancy while taking these drugs. Rationale: The safety for the use of these drugs during pregnancy has not been established. ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and renin inhibitors should not be used during pregnancy, and women of child-bearing age should be advised to use barrier contraceptives to prevent pregnancy while taking these drugs.
question
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers: Prototype: Losartan: Indications
answer
Alone or as part of combination therapy for the treatment of hypertension; treatment of diabetic nephropathy with an elevated serum creatinine and proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension
question
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers: Prototype: Losartan: Actions
answer
Selectively blocks the binding of angiotensin II to specific tissue receptors found in the vascular smooth muscle and adrenal glands; blocks the vasoconstriction and release of aldosterone associated with the renin-angiotensin system
question
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers: Prototype: Losartan: PK:
answer
Oral, Varies, 1-3 h, 24 h HL: 2 hours, then 6-9 hours; metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine and feces
question
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers: Prototype: Losartan: AE/SE
answer
Dizziness, headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection, cough, back pain, fever, muscle weakness, hypotension (Liver and kidneys must be in good working order)
question
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Nursing Considerations
answer
Can take with food (irritating to GI tract) Prevent dehydration Do not use if pregnant or breastfeeding Use barrier contraceptives Discontinue immediately if pregnant Watch for syncope, cough, alopecia (hair loss)
question
Beta Blockers Mnemonic
answer
B = Bronchospasms - do NOT give to patients with bronchoconstrictive diseases E = Elicits decrease in cardiac output ; contractility T = Treat hypertension A = AV conduction decreases - treats arrhythmias Do NOT discontinue abruptly - causes rebound angina, confusion in elderly, psychosis
question
Beta Blockers Prototype: Propranolol: Indications
answer
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, especially supraventricular tachycardia; treatment of ventricular tachycardia induced by digitalis or catecholamines
question
Beta Blockers Prototype: Propranolol: Action
answer
Competitively blocks beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart and kidney; has a membrane-stabilizing effect and decreases the influence of the sympathetic nervous system
question
Beta Blockers Prototype: Propranolol: PK:
answer
Oral, 20-30 min, 60-90 min, 6-12 h IV, Immediate, 1 min, 4-6 h HL: 3-5 hours; metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine
question
Beta Blockers Prototype: Propranolol: AE/SE
answer
Bradycardia, CHF, cardiac arrhythmias, heart blocks, cerebrovascular accident (CVA), pulmonary edema, gastric pain, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, impotence, decreased exercise tolerance, antinuclear antibody (ANA) development
question
Beta Blockers Nursing Considerations
answer
Monitor BP, Pulse, and Respiratory status (you will want to know if the lings are filling up c fluid) Obtain medical history * asthma, COPD smoking - drugs cause loss of bronchodilation diabetics - monitor blood glucose frequently (due to the tendency of B blockers to increase blood glucose levels) Wean off drug over 2 weeks Teach to change positions slowly Explain change in sexual function Review laboratory tests: kidney, liver, electrolytes
question
Calcium Channel Blockers Actions
answer
Inhibits the movement of calcium ions across the membranes of cardiac and arterial muscle cells, depressing the impulse and leading to slowed conduction, decreased myocardial contractility, and dilation of arterioles, which lowers blood pressure and decreases myocardial oxygen consumption
question
Calcium Channel Blockers
answer
Allergy, heart block or sick sinus syndrome (don't want to decrease it if it is already too slow), renal or hepatic dysfunction, pregnancy, and lactation
question
Calcium Channel Blockers Prototype: Diltiazem: Indications
answer
Treatment of essential hypertension in the extended-release form
question
Calcium Channel Blockers Prototype: Diltiazem: Actions
answer
Inhibits the movement of calcium ions across the membranes of cardiac and arterial muscle cells, depressing the impulse and leading to slowed conduction, decreased myocardial contractility, and dilation of arterioles, which lowers blood pressure and decreases myocardial oxygen consumption
question
Calcium Channel Blockers Prototype: Diltiazem: PK:
answer
Oral/ER, 30-60 min, 6-11 h, 12 h HL: 5-7 hours; metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine
question
Calcium Channel Blockers Prototype: Diltiazem: AE/SE
answer
Dizziness, light-headedness, headache, peripheral edema, bradycardia, atrioventricular block, flushing, nausea
question
Calcium Channel Blockers Nursing Considerations
answer
Monitor BP, Pulse, cardiac status (are there any arrhythmias? listen to the apical and feel the radial pulse at the same time) Grapefruit juice increases drug to toxic level (interferes c P-450 enzyme system which is the livers system to detoxify drugs) Take 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals Prevent dehydration Wean off drug Do not use in pregnancy or breastfeeding African Americans respond better to CCBs
question
Vasodilators and Hypertensive Crisis:
answer
Diastolic BP > 120mmHg Relax vascular smooth muscle Monitor closely as sudden decrease in BP can cause cerebral ischemia & stroke (can cause not enough O2 to get to the heart/brain) Do NOT block reflex tachycardia when BP decreases and renin release = Na+ and H20 retention Contraindicated with pregnancy
question
Vasodilators: diazoxide (Hyperstat):
answer
IV for hospitalized patients with severe hypertension; increases blood glucose levels (not ideal for diabetics)
question
Vasodilators: hydralazine (Apresoline):
answer
Maintains increased renal blood flow, decreases peripheral vascular resistance (smooth muscle relaxant)
question
Vasodilators: minoxidil (Loniten):
answer
Used only for severe and unresponsive hypertension
question
Vasodilators: nitroprusside (Nitropress):
answer
Used for hypertensive crisis; maintain hypertension during surgery
question
Vasodilators: Prototype: Nitroprusside: Indications
answer
Hypertensive crisis, maintenance of controlled hypotension during anesthesia, acute CHF
question
Vasodilators: Prototype: Nitroprusside: Actions
answer
Acts directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause vasodilation and drop of blood pressure; does not inhibit cardiovascular reflexes and tachycardia; renin release will occur
question
Vasodilators: Prototype: Nitroprusside: PK:
answer
IV, 1-2 min, rapid, 1-10 min HL: 2 min; metabolized in the liver and excretion in urine
question
Vasodilators: Prototype: Nitroprusside: AE/SE
answer
Apprehension, headache, retrosternal pressure, palpitations, cyanide toxicity, diaphoresis, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, irritation at the injection site
question
Vasodilators Nursing Considerations
answer
nitroprusside sodium (Nitropress) - Light sensitive - Monitor for cyanide toxicity - see page 687 Suppresses iodine uptake - hypothyroidism Monitor BP closely during administration Prevent dehydration
question
Hypotension Causes
answer
Heart muscle is damaged and unable to pump effectively Severe blood loss, volume drops dramatically Extreme stress when body's levels of norepinephrine are depleted (Body is unable to respond to stimuli to raise blood pressure)
question
Antihypotensive Agents: Prototype: Midodrine: Indications
answer
Symptomatic treatment of orthostatic hypotension
question
Antihypotensive Agents: Prototype: Midodrine: Actions
answer
Activates alpha-adrenergic agonist receptors in arteries and veins to produce an increase in vascular tone and an increase in blood pressure Vasopressor Drug
question
Antihypotensive Agents: Prototype: Midodrine: PK:
answer
Absorbed from GI tract, metabolized in the liver, and excreted in the urine
question
Antihypotensive Agents: Prototype: Midodrine: Contras
answer
Supine hypertension, coronary artery disease (CAD), pheochromocytoma, and with urinary retention
question
Antihypotensive Agents: Prototype: Midodrine: Cautions
answer
Pregnancy and lactation Visual problems
question
Antihypotensive Agents: Prototype: Midodrine: AE/SE
answer
Related to stimulation of alpha-receptors
question
Antihypotensive Agents: Prototype: Midodrine: Drug-Drug
answer
Cardiac glycosides, beta blockers, alpha-adrenergic agents, and corticosteroids
question
Cardiac Glycosides
answer
Slows heart rate (- chronotropic) Increases force of myocardial contraction (+ inotropic) Decreases conduction velocity through the AV node (- dromotropic) Increases cardiac output and renal perfusion Increases urine output and decreased blood volume
question
Cardiac Glycosides Prototype: Digoxin:
answer
Treatment of CHF, atrial fibrillation
question
Cardiac Glycosides Prototype: Digoxin:
answer
Increases intracellular calcium and allows more calcium to enter the myocardial cell during depolarization; this causes a positive inotropic effect (increased force of contraction), increased renal perfusion with a diuretic effect and decrease in renin release, a negative chronotropic effect (slower heart rate), and slowed conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node
question
Cardiac Glycosides Prototype: Digoxin:
answer
Oral, 30-120 min, 2-6 h, 6-8 days IV, 5-30 min, 1-5 h, 4-5 days HL: 30-40 hours; largely excreted unchanged in the urine
question
Cardiac Glycosides Prototype: Digoxin:
answer
Headache, weakness, drowsiness, visual disturbances, arrhythmias, GI upset
question
digoxin (Lanoxin, Lanoxicaps) Nursing Considerations
answer
Take apical pulse for 1 minute before administration. Withhold medication if apical pulse below parameters (Adult = 60, Child = 70, Infant = 90, newborn = 100) Administer loading or "digitalizing" dose Narrow therapeutic index (0.5 - 2.0 ng/ml - toxic ; 2.0 ng/ml)(must follow c labs to monitor) Monitor lab values - K+ Monitor I ; O, daily weight No IM injection, administer IV slowly over 5 minutes Antidote: Digoxin Immune Fab, Digibind, Digifab
question
Cardiac Glycosides Patient/Family Teaching
answer
Take radial pulse daily report 110 (at ;110 drug levels are either getting too toxic or not working) Immediately report adverse effects Check weight daily, report gain 2 lb in 2 days Administer before or after meals - not with food Diet - eat high K+ foods (wastes K+) Take as prescribed Do not take any OTC medications, esp. antacids (antacids interfere with absorption) Do not switch brands Do not breastfeed
question
Cardiac Glycosides (memory)

answer
Lizzy Diggy
question
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors (Cardiotonic (inotropic) agents): inamrinone (Inocor):
answer
Approved only for use in patients with HF that has not responded to digoxin, diuretics, or vasodilators Contraindicated if allergy to bisulfites Precipitates if given with furosemide
question
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors (Cardiotonic (inotropic) agents): milrinone (Primacor):
answer
Short-term management of HF in patients who are receiving digoxin and diuretics Contraindicated if allergy to bisulfites Precipitates if given with furosemide
question
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor Prototype: Inamrinone:
answer
Short-term treatment of CHF in patients who have not responded to digitalis, diuretics, or vasodilators
question
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor Prototype: Inamrinone:
answer
Blocks the enzyme phosphodiesterase, which leads to an increase in myocardial cell cAMP, which increases calcium levels in the cell, causing a stronger contraction and prolonged response to sympathetic stimulation; directly relaxes vascular smooth muscle
question
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor Prototype: Inamrinone:
answer
IV, Immediate, 10 min, 2 h HL: 3.6-5.8 hours; metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine and feces
question
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor Prototype: Inamrinone:
answer
Arrhythmias, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, thrombocytopenia (watch out for bruising and bleeding), pericarditis, pleuritis, fever, chest pain, burning at injection site
question
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors Nursing Considerations
answer
Assess BP, Pulse, cardiac status Monitor for ventricular arrhythmias Protect from light Obtain daily weight, I ; O Monitor IV site Monitor platelet count (Watch for bruising, petechiae)
question
The nurse is caring for a patient who has presented at the emergency department with signs and symptoms of an acute MI. While making an initial assessment of this patient the nurse notes the patient has had adverse reactions to digoxin and a history of heart failure. What drug would the nurse be concerned about if it is ordered? a. furosemide (Lasix) b. milrinone (Primacor) c. propranolol (Inderal) d. aspirin
answer
b. milrinone (Primacor) Rationale: They are contraindicated in the following conditions: severe aortic or pulmonic valvular disease, which could be exacerbated by increased contraction; acute MI, which could be exacerbated by increased oxygen consumption and increased force of contraction; fluid volume deficit, which could be made worse by increased renal perfusion; and ventricular arrhythmias, which could be exacerbated by these drugs.
question
Angina:
answer
chest pain caused by decrease O2 to heart muscle
question
Antianginal Drugs
answer
Improve blood delivery to the heart muscle by dilating blood vessels Increasing the supply of oxygen Improve blood delivery to the heart muscle by decreasing the work of the heart Decreasing the demand for oxygen Nitrates Beta-Adrenergic Blockers Calcium Channel Blockers
question
Antianginal: Nitrates: Actions
answer
Act directly on smooth muscle to cause relaxation and depress muscle tone
question
Antianginal: Nitrates: PK:
answer
IV Sublingual Translingual Spray Transmucosal Tablet Oral, SR Tablet Topical Ointment Transdermal
question
Antianginal: Nitrates: Contras
answer
Allergy Severe anemia Head trauma or cerebral hemorrhage Pregnancy and lactation
question
Antianginal: Nitrates: Cautions
answer
Hepatic or renal disease Hypotension, hypovolemia, and conditions that limit cardiac output
question
Antianginal: Nitrates: Drug-Drug
answer
Do NOT administer with erectile dysfunction drugs (can cause fatal drop in blood pressure)
question
Anti-Anginals Prototype: Nitroglycerin: Indications
answer
Treatment of acute angina, prophylaxis of angina, intravenous treatment of angina unresponsive to beta-blockers or organic nitrates, perioperative hypertension, congestive heart failure (CHF) associated with acute MI; to produce controlled hypotension during surgery
question
Anti-Anginals Prototype: Nitroglycerin: Actions
answer
Relaxes vascular smooth muscle with a resultant decrease in venous return and decrease in arterial blood pressure, reducing the left ventricular workload and decreasing myocardial oxygen consumption
question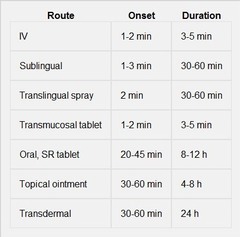
Anti-Anginals Prototype: Nitroglycerin: PK

answer
1-4 min; metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine (Very fast acting)
question
Anti-Anginals Prototype: Nitroglycerin: AE/SE
answer
Hypotension, headache, dizziness, tachycardia, rash, flushing, nausea, vomiting, sweating, chest pain
question
Nitrates Nursing Considerations
answer
Administer 1 tab SL every 5 min x 15 min No relief call health care provider Store dark vial Tablet should burn or "fizzle" Instruct not to swallow tablets Instruct not to chew/crush sustained-release Wear gloves for transdermal patch (can cause headache die to vasodilation) Spray translingual spray under tongue, not inhaled Wean off over 4-6 weeks
question
Nitrates Patient/Family Teaching
answer
Take at earliest sign of anginal pain Slow position changes Call 911 if pain unrelieved by 3 tablets - 5 minutes apart - over 15 minutes Take 5 -10 minutes prior to exercise Remove patches at bedtime, apply in AM Report blurred vision, dry mouth, chest pain, fainting Avoid alcohol, coffee, cigarettes Wear medic-alert bracelet Store in dark container, replace every 3 months (lose potency really quickly) Dress appropriately in cold weather - wear mask (cold gives chest pains - teach to stay in when very cold)



