Mitosis and Cancer Review Material – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
p53 does what
answer
A tumor supressor gene that triggers apoptosis in the cell
question
Prophase(2 parts) words, only
answer
Nuclear membrane starts to break down. Chromosomes are visible-
question
4 stages mitosis
answer
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase & Telophase
question
Absence and /or mutations of tumor suppressor genes
answer
can cause cancer-there is no stop signal for cell division
question
Anaphase definition-
answer
Characterized by spindle pulling apart sister chromatid pairs.
question
Genes involved in DNA repair
answer
tumor suppressor genes
question
BRCA proteins are
answer
DNA repair enzymes
question
Cancer
answer
Disease caused by to much mitosis or not enough apoptosis
question
Cancer causing mutations can occur by
answer
Chemicals, Radiation, Infectious agents, Some are inherited, Spontaneous mutations Errors in DNA replication
question
protein counters of the cell cycle.
answer
CDK's
question
Cell cycle
answer
is sequence of stages through which a cell passes; G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase ; M phase
question
Cell Cycle (cyclin cdk complexes)
answer
are important regulators of cell cycle transitions. they are counted by the cell
question
Cell cycle inhibition or cell death?
answer
As p53 can induce inhibition of cell proliferation or apoptosis in a cell, the factors that determine biological outcome depends on the following
question
Cell Growth starts in ___ phase
answer
G1
question
Characterized by the 1st appearance of the chromosomes
answer
Prophase
question
Cyclin cdk complexes
answer
Regulates the cell cycle
question
Cyclins
answer
These proteins coordinates and regulate the passage of cell through different phases of cell cycle.
question
Disruption of checkpoint leads to
answer
mutations and cancer
question
DNA replication is halted if:
answer
Genome-DNA- is damaged
question
Anaphase is blocked if:
answer
Chromosomes don't assemble properly on the mitotic spindle.
question
M phase is blocked if:
answer
DNA replication isn't completed in S stage
question
What happens after G2 phase
answer
cells enters mitosis
question
Function of tumor suppressor genes`
answer
to inhibit cell growth and/or promote cell death
question
G1 checkpoint
answer
stops of cell cycle in response to cell size problems.
question
What is the product of the cell cycle
answer
2 genetically identical body cells (somatic cell)
question
Mutated proto-oncogenes
answer
Oncogenes
question
M checkpoint
answer
arrest of chromosomal segregation -metaphase in response to misalignment on the mitotic spindle.
question
Replicated chromosomes align on a central plate.
answer
Metaphase
question
Mutations in BRCA1/BRCA2 is commonly seen
answer
in 5 10% of breast cancers
question
Mutations in cell cycle regulators
answer
can result in poor regulation of cell cycle, uncontrolled proliferation and cancer.
question
Passing on genetic material relies on what two processes:
answer
Correct replication of the DNA in S phase
question
Nuclear envelope reforms and chromosomes un-condense to chromatin
answer
in Telophase
question
The Cell Cycle and Cancer
answer
Genes encoding cell cycle regulators are frequently mutated in tumors.
question
The cell cycle implements the decisions it makes through ____ which are dependent on ____
answer
CDKs; cyclins
question
The G2 checkpoint
answer
The G2 checkpoint blocks entry into M phase in
question
The DNA is replicated in ___ phase
answer
S phase
question
Tumor suppressor gene
answer
Genes whose loss or inactivation can lead to cancer i.e. uncontrolled cell proliferation and decreased cell death
question
Prophase -picture and words

answer
DNA condenses (chromatin) into chromosome
question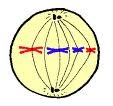
Metaphase picture and words

answer
Replicated Chromosomes align in the middle of the cell between the poles (equatorial plate)
question
Replicated chromosomes align in the center of the cell.
answer
Metaphase
question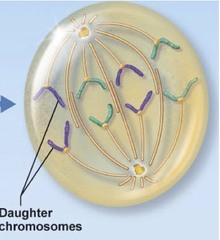
Anaphase-picture and words

answer
The microtubules contract and separate the sister chromatids from each other, pulling them toward the two poles of the cell
question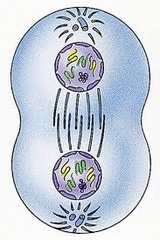
Telophase- picture and words

answer
Nuclear envelope reforms, Chromosomes decondense Spindle fibers break down
question
Plant Cell Only
answer
Cell plate forms during cytokinesis
question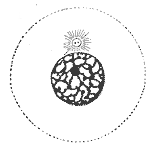
interphase-picture and words

answer
DNA has already replicated but has not yet condensed into chromosomes takes up 90% of the cell cycle
question
G1 phase
answer
Part of Interphase: Cell Growth and some organelle replication
question
G2 phase
answer
Part of Interphase: Preparation for Mitosis, organelle replication and protein formation
question
S phase
answer
Part of Interphase: DNA Replication
question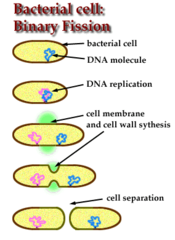
Binary fission

answer
How bacteria reproduce.
question
Contact inhibition is bad
answer
Charcteristic of a Cancer Cells
question
stop dividing when they come in contact with other cells
answer
Normal Cells
question
Cancer Cells
answer
continue to divide, piling up on top of each other
question
Normal Cells
answer
always stay anchored to other cells (or to a surface)
question
lose their anchorage dependence
answer
Characteristic of a cancer cell
question
Malignant tumor
answer
when tumor invades surrounding tissue (cancerous)
question
Metastatic tumor
answer
when individual cells break away and start a new tumor (cancerous)
question
Benign
answer
when tumor has no effect on surrounding tissue (non cancerous)
question
Normal cell division
answer
cell will stop dividing when it comes into contact with other cells.
question
Chromosome:
answer
condensed DNA. 23 pairs in humans
question
If the diploid number is 46 at the start of the cell cycle
answer
There are46 chromosomes in EACH of the 2 new cells
question
If the diploid number is eight
answer
Each new cell has 8 chromosomes
question
2n=8 diploid number
answer
n=4 . The haploid number
question
2n=46 diploid number
answer
n=23 . The haploid number of chromosomes
question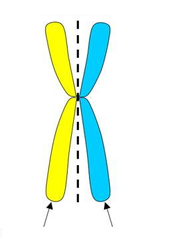
Sister chromatids

answer
One arm of a replicated chromosome
question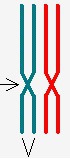
Centromere

answer
Holds sister chromatids together
question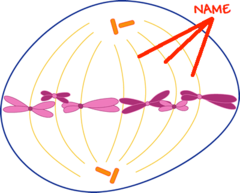
Spindle fibers

answer
Connects to chromosomes and moves chromosomes around the cell
question
Pull apart, chromosomes at the centromere
answer
Spindle fibers contract
question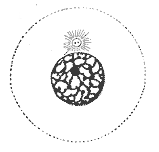
Interphase - the picture

answer
This picture is
question
P53
answer
Tumor Suppressor gene
question
Proto-oncogenes
answer
Normal genes that control cell cycle
question
Oncogenes
answer
A mutated proto-oncogene cause the cell cycle. The causes the cell cycle to move too fast
question
Tumor suppression genes - broken
answer
Do not stop the cell cycle
question
Tumor suppression genes- working
answer
Slow down the cell cycle
question
Apoptosis
answer
Cell death- cell destruction, a protective process that prevents cancer
question
Cells have two choices- at each check point
answer
Fix the problem, wait or or go to apoptosis
question
DIPLOID DEF
answer
2 sets OF CHROMOSOMES
question
CENTRIOLE
answer
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only



