Med-Surg Test #1 (Respiratory) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
A nurse is auscultating the lung sounds of a client who came to the clinic for a physical exam. There is not any history of lung disease. What should the nurse expect to hear? a. adventitious breath sounds b. bronchial breath sounds c. bronchovesicular breath sounds d. vesicular breath sounds
answer
answer: c rationale: the nurse auscultates breath sounds from side to side, moving from the upper to the lower chest. They listen anteriorly, laterally, and posteriorly. Normal breath sounds include bronchovesicular sounds.
question
A client comes to the doctor's office describing shortness of breath and strange breath sounds when inhaling deeply. Upon auscultation of the lung fields, sibilant wheezes are noted. Which of the following statements by the nurse most correct? a. "Wheezes result from air passing through narrowed passages." b. "Wheezes result from air escaping through a pneumothorax." c. "Wheezes result from air collecting in the pleural cavity." d. "Wheezes result from air between visceral and parietal pleurae."
answer
answer: a ratioanle: wheezes may be sibilant (hissing/whistling) or sonorous (full and deep). Sibilant wheezes (formerly called wheezes) are continuous musical sounds that can be heard during inspiration and expiration; and result from air passing through narrowed or partially obstructed air passages and are heard in clients with increased secretions.
question
A nurse needs to obtain a sputum specimen from an adult client. Which nursing action will best facilitate obtaining the specimen? a. ask the client to spit into the collection container b. have the client take deep breaths c. restrict the client's fluids d. wait until after the client has eaten to get the specimen.
answer
answer: b rationale: collecting a sputum specimen have the client rinse their mouth with tap water; instruct the client to take several deep breaths, cough forcefully, and expectorate into the container.
question
The nurse is giving instructions to a client having pulmonary angiography. Which of the following statements is the best evidence that the client understands the nurse's instructions about what will take place during the diagnostic procedure? Select all that apply. a. "I may feel some pressure at the site." b. "I may have bleeding at the site following the procedure." c. "I will not be allowed to cough after the procedure." d. "I will sense a warm, flushed feeling and an urge to cough when the dye is injected."
answer
answer: a,d rationale: during pulmonary angiograpy, the nurse obtains data about the client's level of anxiety and knowledge of the procedure. The nurse provides explanations and reinforces the client's understanding. The client will experience a feeling of pressure on catheter insertion. When the contrast medium is infused, the client will sense a warm, flushed feeling and an urge to cough.
question
When caring for a client having a lung scan, which of the following nursing interventions is most important during the procedure? a. reassure the client about the amount of radiation from the procedure. b. coach the client to hold his or her breath at times during the procedure c.administer sedative or narcotic as per orders before the procedure d. aid the client to rest arms and head on a pillow during the procedure.
answer
answer: a rationale: the client must receive adequate explanations before the procedure to reduce anxiety. The nurse must reassure the client that the amount of radiation from this procedure is less than that used during a chest x-ray.
question
Movement of air into and out of the lungs sufficient to maintain normal arterial oxygen and carbon dioxide tensions is termed what? a. perfusion b. ventilation c. diffusion d. inspiration
answer
answer: b rationale: ventilation is the actual movement of air in and out of the respiratory tract. This process requires a patent airway and intact and functioning respiratory muscles.
question
While conducting the physical examination during assessment of the respiratory system, which of the following would describe lung sounds produced by air movement through the trachea and are loud with long expiration? a. bronchovesicular sounds b. bronchial sounds c. sonorous wheezes d. vesicular sounds
answer
answer: b rationale: normal bronchial lung sounds are auscultated over the trachea and are loud with long expiration.
question
The physician orders arterial blood gases (ABGs) to determine various factors related to blood oxygenation on a patient who presents in respiratory distress. What site can ABGs be obtained from? a. a puncture in the raidal artery b. the trachea and bronchi c. a swab from the nasopharynx d. an intravenous catheter in the arm vein
answer
answer: a rationale: ABGs determine the blood's ph; oxygen-carrying capacity; and levels of: oxygen, carbon dioxide, and bicarbonate ion. Blood gas samples are obtained through an arterial puncture at the radial, brachial, or femoral artery.
question
Of the following instructions, which is most important for the nurse to teach the client to help loosen secretions and increase comfort during medical treatment for sinusitis? a. blow the nose frequently b. elevate the head of the bed by 45 degrees c. engage in normal activity d. increase fluid intake
answer
answer: d rationale: the nurse needs to inform the client receiving medical treatment for sinusitis that use of mouthwashes and humidification as well as increased fluid intake may loosen secretions and increase comfort; the nurse should also instruct the client to take nasal decongestants and antihistamines as ordered.
question
The nurse is providing postoperative care for a client who has undergone tonsillectomy. In which position will the nurse place the head of the bed when the client is fully awake? a. flat with the head elevated on a pillow b. slightly raised at a 15 degree angle c. raised at a 45 degree angle d. raised at a 90 degree sitting position
answer
answer: c rationale: elevate head of bed to semi-fowler's position (45 degrees) when the client is fully awake. This position decreases surgical edema and increases lung expansion.
question
A client was seen in the emergency rom with severe epistaxis. After the physician places a nasal packing, the bleeding is controlled. What should the nurse include as part of the discharge instructions? Select all that apply. a. call physician if bleeding persists or becomes worse b. continue taking baby aspirin as ordered c. do not blow the nose d. keep nasal packing in place until seen for follow-up appointment e. swallow any oozing blood to avoid coughing
answer
answer: a,c,d rationale: do not swallow blood; spit out any blood oozing from the area. Do not blow the nose. If blood has been swallowed, the client may see diarrhea and black, tarry stools for a few days; do not attempt to remove nasal packing or to cut the string anchoring the packing; do not use aspirin or ibuprofen products until bleeding is controlled; and notify the physician if bleeding persists or if any respiratory problems develop.
question
A client is seen in a clinic for possible laryngeal cancer. In reviewing the client's record, the nurse will most likely see which of the following early complaints expressed by the client? a. difficulty swallowing hot liquids b. enlarged lymph nodes in the neck c. generalized discomfort in the neck d. persistent hoarseness for the last month
answer
answer: d rationale: early signs and symptoms are persistent and progressive hoarseness (longer than 2 weeks) is usually the earliest symptom, and is usually ignored by the client.
question
A nurse identified Ineffective Airway Clearance related to a malignant mass in the client's airway. Which of the following interventions has the highest priority? a. elevate the client's head of the bed b. encourage the client to deep breathe and cough every 2 hours c. place a nasal cannula with 2L of oxygen d. provide emergency tracheostomy equipment at the bedside
answer
answer: a rationale: Maintaining the airway is the highest priority.
question
An elderly client is brought to the emergency department. Vital signs are: Temp: 102 degrees F; P: 88; R: 32; BP: 160/86. Upon physical examination, the client is having difficulty breathing. Which of the following would be most appropriate for the nurse to do next? a. Instruct the client to take slow, deep breaths b. suction the client's pharynx of secretions c. apply a pulse oximeter to the client's finger d. help the client perform postural drainage
answer
answer: b rationale: the nurse will auscultates lung sounds and monitors the client for signs of respiratory difficulty. They check oxygenation status with pulse oximetry and monitors arterial blood gases (ABGs).
question
A collection of air or gas in the pleural cavity; occurs due to traumatic or iatrogenic injury or the pleura e.g. ruptures.
answer
pneumothorax
question
S/S: onset is sudden, severe sharp pain in the side of the chest, and dyspnea; distended unilateral chest, increased resonance, decrease in or absence of breath sounds, if fluid is present-splashing sound on succussion (shaking) of the patient; chest pain r/t coughing, deep breathing, or movement; possible low BP.
answer
pneumothorax
question
Diagnostic Tests: CHEST X-RAYs confirm diagnosis of "collapsed lung"
answer
pneumothorax
question
Medical TX/MNGMNT: CHEST TUBE INSERTION is used to closed chest drainage for lung re-expansion (water-sealed) is the most likely choice for those that have suffered traumatic or iatrogenic injuries; SURGICAL REPAIR may also be needed; bed rest; a THORACOSTOMY TUBE may be required if this condition worsens or more than 15% of the lung is collapsed
answer
pneumothorax
question
Patient Care: check and monitor chest expansion, pulse ox and/or ABGs; give O2 to prevent hypoxia; give emotional support, encourage deep breathing and coughing (~hourly), administer analgesics, assist with/have ambublation; help avoid tension on the tubing until chest re-expansion is stable without suction and the tube can be taken out and covered with an occlusive dressing. Promote smoking cessation and excercise.
answer
pneumothorax rationale of picture: chest tube with suctioning; thoracostomy tube.
question
What breath sounds would you expect to hear while auscultating a client with pneumothorax?
answer
decreased breath sounds/absent breath sounds
question
Those with a hx of 2 collapsed lung; tall, thin persons; and those who smoke are high risk for what lower respiratory problem?
answer
pneumothorax
question
This lower respiratory problem involves obstruction of one the pulmonary arteries/branches.

answer
pulmonary embolism
question
S/S: when the a LARGER area is effected: more severe, severe pain, tachycardia, severe dyspnea, diaphoresis, irregular HR, wheezing, restlesness, shock, sudden death, elevated serum enzymes; if SMALLER are is effected: is less sever, pain, tachycardia, dyspnea, fever, cough, blood-streaked sputum.
answer
pulmonary embolism
question
Diagnostic Testing: chest x-rays, D-DIMER ASSAY (blood test); ECG CT scan, V-Q scan, pulmonary angiogram; ultrasonography (ultrasound); lung scan, MRI.
answer
pulmonary embolism
question
When this listening to a patient with a pulmonary embolism, the nurse knows she might hear any of these breathe sounds except... a) egophony (E sounds like A through stethoscope) b) dullness, decreased breathe sounds c) bronchovesicular sounds d) wheezing
answer
answer: c rationale: bronchovesciular sounds would be heard in person with normal breathe sounds.
question
You are caring for 3 different clients. Client A is one day postop for an emergency abdominal surgical procedure r/t getting into a car accident two nights ago and will be bedridden for several days, and you notice in his chart that he has a hx of DVT; Client B is a 30 year old woman taking estrogen replacement therapy and smokes ~pack/day. She was admitted tonight for a right leg fx-r/t an extreme hiking trip for survivors in the Alps (she proudly tells you how she had managed to go for three days without eating or drinking). Client C is found ambulating in the hall with her husband after being admitted last night for a broken wrist-she proudly tells you in passing she can't stand just lying around in bed. You know that which patient(s) at risk for having developing a pulmonary embolism, select all. a)none of them b)Client A c)Client B d)Client C
answer
answer: a,b rationale: any abdominal/leg issue/surgery raises the risk of developing a DVT, also a client needs to change positions/ambulate, dont' cross legs, keep hydrated, wear support hose, avoid constricting clothing, do leg exercises, stop smoking; history of of DVTs put you at risk, taking estrogen replacement therapy puts you at risk.
question
Medical TX/MNGMNT: IV heparin; IV injection of THROMBOLYTIC drugs with anticogulants given after the thrombolytic therapy; complete bed rest; O2; analgesics; possible pulmonary embolectomy (if lodged in main pulmonary artery); insertion of Greenfield filter (an umbrella filter device-prevents recurrent episodes from occuring);placement of Telfon clips on inferio vena cavad(keeps back large clots).
answer
pulmonary embolism
question
Nursing MNGMNT: The biggest thing for the nurse to help the patient with here is health promotion in regards to PREVENTION OF DVT; also monitor for signs of DVT (calf tenderness, swelling, increasing warmth, prominence of superficial veins in one/both lower extremeties).
answer
pulmonary embolism
question
This lower respiratory problem occurs when fluid builds up in the alveolar causing O2 not to be able to get in and get into the bloodstream.
answer
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
question
This syndrome is NOT the primary disease, there is an underlying issue, which is usually caused from a patient being critically ill (sepsis, inhalation of harmful substances, sever pneumonia)-this is the most common of causes; or with a sever injury (head, chest, or other major injury).
answer
ARDS
question
S/S: Increased resp rate; labored respirations, cyanosis, use of ACCESSORY MUSCLES; RESP DISTRESS-that can't be relieved with O2 administration; anxiety; RESTLESSNESS; mental confusion; agitation; drowsiness with cerebral anoxia (absence of O2).
answer
ARDS
question
Diagnostic Testing: To help diagnose this lower resp problem, you first have to diagnose the underlying cause; use chest x-rays; CT scan ABGs; ECG/EKG; echocardiogram (these last two will help rule out certain heart problems that this lower resp problem can resemble)
answer
ARDS
question
Medical TX/MNGMNT: #1 here is to get back a patent airway, in order for O2 TO GET BACK INTO THE BLOODSTREAM: Give humidified O2 (with a mask-for mild cases/temporary measures); artificial airways-insertion of ET tube/trache tube, mechanical ventilation: PEEP(positive end-expiratory pressure)-this will give a continuous positive pressure through all aspects of ventilation; give IV fluids, most likely Colloids (albumin) to pull fluids and put them back into the capillaries; and give adequate nutrition-enteral feedings prefered but if need be, TPN.
answer
ARDS
question
Keep in mind with the ARDS patient that is using what mechanical ventilation system, that many complications can occur while on this system, such as: pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum (air in mediastinal space); and HOTN caused by isystemic hypovolemia (loss of blood).
answer
PEEP (positive end-expiratory pressure)
question
Nursing MNGMNT: with this patient the nurse needs to promote a patent airway #1! Administer O2, ventilation; prevent complications of breathing; provide alternate methods of communication if on mechanical ventilation; assess and monitor respiratory status, O2, and ventilation.
answer
ARDS
question
What breathe sounds would the nursing student expect to hear with a patient with ARDS. Select all the apply. a)egophony b)dullness, and decreased breathe sounds c)crackles d)wheezing
answer
answer: c,d
question
what sound is this you hear of the two sounds are these that the nurse will expect to hear with an ARDS patient. crackling/wheezing
answer
wheezing
question
what sound is this you hear of the two sounds the nurse will expect to hear with an ARDS patient? crackling/wheezing
answer
crackles
question
This lower respiratory issue is split into 2 categories: NSCLCs (non-small cell lung carcinomas) and SCLCs (small cell lung carninomas; these tumors grow and either partially obstruct the lumen of an airway/completely obstruct it; resulting in airway collapse distal to tumor; tumor can hemorrhage too, causing hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
answer
lung cancer
question
S/S: #1 cardinal sign: COUGH productive of MUCOPURULENT (blood-streaked sputum); dyspnea, fatigue, anorexia; weight loss; chest pain-later stages; recurring fever.
answer
lung cancer
question
Diagnostic Tests: sputum specimens; chest x-ray-but if x-rays fail: CT scan, PET scan (positron emission tomography), or MRI; lung scan (to locate tumor); bone scan; lumph node biospy; mediastinoscopy; bronchoscopy; bronchoscopy; fine needle aspiration under fluoroscopy/CT guidance.
answer
lung cancer
question
Medical TX/MNGMNT: * IN ORDER TO TX, CLASSIFICATION&STAGING OF TUMOR MUST OCCUR FIRST: lung resection:LOBECTOMY (surgical removal of tumor-is really the only cure for this-and must occur in early stage); radiation therapy; chemo therapy; there are also new TXs: new chemos; targeted therapies; photodynamic therapy (chemical&light); vaccinations; and gene therapy.
answer
Lung Cancer
question
Nursing MNGMNT: the nurse's most important role(and really the only thing she can do) is give emotional/palliative/post-op support and care.
answer
lung cancer
question
The prognosis of this 2nd rated death in the US for both men and women is poor unless caught in its early stages; but very few people catch this during the early stage due to "blowing off" the S/S for those of other, nonthreatening reasons.
answer
lung cancer
question
The nurse would expect which sound while listening to a lung cancer patient? a)wheezing b)fine crackles c)absent breathe sounds d)stridor
answer
answer: stridor
question
The nurse would expect which sound while listening to a acute bronchitis patient? a) fine crackles b) moist crackles upon inspiratory and wheezing c) wheezing d) rales
answer
answer: b,c
question
This is a quick onset; inflammation of mucous membranes; is usually self-limiting and last for SEVERAL DAYS; if inflammatory process involves the trachea, is referred to as tracheobroncitis; and usually begins as URI (VIRAL) and turns into acute bronchitis; but can also be BACTERIAL and usually r/t H.influenza, strep, pneumonia.
answer
acute bronchitis
question
S/S: fever, chills, malaise, HA, DRY, IRRITATING, AND NONPRODUCTIVE COUGH; mucopurulent sputum r/t irritation from tracheobronchitis and coughing; paroxysmal cough attacks (those that grow in frequency); WHEEZING; MOIST CRACKLES UPON INSPIRATION.
answer
acute bronchitis
question
Diagnostic Testing: sputum cultures and chest x-ray
answer
acute bronchitis
question
Medical TX/MNGMNT: bed rest; antipyretics; expectorants; antitussives; increased fluids; humifiers; if secondary infection evident-broad spectrum antibiotic.
answer
acute bronchitis
question
Nursing MNGMNT: The nurse should auscultate for breathe sounds and monitor V/S every 4hr; have client deep breath and cough ~every 2hr; look over expectorate sputum results, and PROMOTE HANDWASHING!!; and change linens if needed r/t perspirations r/t frequent coughing spells.
answer
acute bronchitis
question
What sounds would the nurse expect to hear upon listening to a patient with pneumonia? Select all that apply. a)crackles b)rhonchi c)wheezing d) diminished breath sounds
answer
answer: a, c, d
question
This respiratory issue has SEVERAL different subtypes: typical(bacterial), atypical(viral, parasite, fungi...), HAP(getting in hosp after 48 hr of admission); CAP(getting it in community within 48hr after admission); aspiration type(inhaling foreign body/gastric content during vomit/regurgitation); chemical type(injest of kerosene/inhaling of other chemicals); broncho type(patchy, diffuse, scattered throught both lungs); radiation type; lobar type(in one/more lobes of lungs)
answer
pneumonia
question
S/S: (with bacterial version): suden onset; fever; chills; productive cough; discomfrot in chest r/t coughing; sputum with RUST COLORING; painful breathing and attempts to breath with shallow breathes; (with viral): copious sputum (abundant); slow respiration rate; slow pulse; they are WEAKER for LONGER than with bacterial version.
answer
pneumonia
question
Diagnostic Tests: auscultation; sputum clulture and sensitivity; chest x-ray; CBC (will have increased WBC count); and blood cultures( to detect microorganisms)
answer
pneumonia
question
Medical TX/MNGMNT: prompt initiation of antibiotics; supplemental O2; bed rest; CHEST PHYSICAL THERAPY& POSTURAL DRAINAGE; bronchodilators; analgesics; antipyrectics; cough expectorants/suppressants; fluid and electrolyte replacement; and intabation with mechanical vent if needed.
answer
pneumonia
question
Nursing MNGMNT: auscultate lung sounds; monitor for signs of RESPIRATORY DIFFICULTY; check O2 and and monitor ABGs; keep in semi-Fowler's position; increase fluid intake; encourage at risk clients and elderly to get VACCINATION; promote prevention
answer
pneumonia
question
Thsi is an abnormal collection of fluid between the visceral and parietal pleurae; may be a complication of pneumonia, lung cancer, TB, PE, and CHF.
answer
pleural effusion
question
The nurse expects to hear what lung sounds from a patient with pleural effusion? Select all that apply. a)friction rubs b)crackling c)wheezing d)diminished/absent breathe sounds
answer
answer: a, d
question
S/S: fever; pain; dyspnea; dullness with chest percussions over involved area; diminshed/absent breath sounds, friction rub.
answer
pleural effusion
question
Diagnostic Test: chest percussions; auscultating lungs; chest radiography; CT scan; thoracentesis (to remove pleural fluid and examine it)
answer
pleural effusion
question
Medical MNGMNT: eliminate the cause and relieve discomfort; antibiotics, analgesics; cardiotonic drugs (control CHF); THORACENTESIS; insertion of CHEST TUBE (for drainage); surgery (if cancer present)
answer
pleural effusion
question
Nursing MNGMNT: The nurse must provide comfort and support; if with chest tube: monitor the function of the drainage system and amount and nature of drainage; have patient lye on UNAFFECTED side post-op for 1hr; and have patient be on bed rest for several hours after; during thoracentesis, you will assist patient into sitting position with arms and head on pillow or in side-lying position on unaffected side& monitor for increased resp rate, asymmetry in resp movement, syncope/vertigo, chest tightness, uncontrolled cough/cough that produces blood-tinged/frothy mucus/or both, tachycardia, andhypoxemia.
answer
pleural effusion
question
This is an acute resp disease of relatively short duration; pregnant women, elderly or debilitated clients, young children/infants, and those that have chronic conditions such as cardiac disease and emphysema are considered at high risk for this.
answer
influenza (flu)
question
S/S: sudden; abrupt onset of fever and chills; severe HA; muscle aches; anorexia; weakness, apathy, malaise; sneezin; sore throat, laryngitis; dry cough; nasal discharge-rhinitis; conjunctival irritation; fever lasts about 3 days; other symptoms last about 7-10 days.
answer
influenza
question
You, the nurse, know that you performed the nasal culture correctly if your patient reacts how?
answer
their eyes water
question
True/False: Your patient comes in after suspecting she has the flu. C&S tests confirm she does. She proceeds to tell you that she had been running a fever for about 3 days but now she isn't-you confirm after taking her V/S this. She says to you, "At least no one in my household are at risk now that I'm not running a fever." You agree with her and proceed with your assessment because you know that influenza is only contagious while a person has a fever, which lasts usually 3 days.
answer
answer: False rationale: People are contagious for 1 day BEFORE they feel ill and continue to be contagious for up to 5-7 days AFTER they get sick(with or without fever).
question
The CDC recommends everyone to receive the flu vaccination and there appears to only be a small amount reasons why a person should not. What type of vaccination group is listed here? those with known or suspected immunodeficiency diseases or those receiving immunosuppressive therapy; those with underlying medical conditions (e.g. diabetes/renal dysfunciton); those with history of Guillain-Barre` syndrome; children/adolescents who regularly take aspirin; pregnant women; people with a hypersensitivity to eggs; children less than 2 years of age; those over 50 years of age.
answer
FluMist
question
Thsi is a bacterial infectious disease primarily caused by M. tuberculosis.
answer
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB)
question
S/S: asymptomatic until disease is advanced; often vague and can be overlooked; fatigue; anorexia; weight loss; and a slight, nonproductive cough; low-grade fever, particularly in late afternoon, and night sweats are comon; cough typically becomes productive of mucopurulent and blood-streaked sputum; marked weakness, wasting, hemoptysis (coughing up blood or bloody sputum); dyspnea; chest pain.
answer
TB
question
Diagnostic Test: Mantoux TST; chest radiography; CT scan, MRI; analysis of sputum and other body fluids; QFT-G test; gastric lavage; gastric aspiration; or BRONCHOSCOPY.
answer
TB
question
True/False: A positive TST result is evidence that a TB infection has existed at some time somewhere in the body and indicates active disease.
answer
answer: False rationale: a positive TST result does indicate infection existed somewhere HOWEVER DOEN NOT NECESSARILY INDICATE ACTIVE DISEASE.
question
A nurse is palpating her patients forearm, the location where she had made a pronounced wheal 48 hours ago. She finds erythema (redness) without induration. Is this significant or not significant?
answer
answer: not significant rationale: if erythema is without induration, it is not significant; if erythema IS present with induration, read the induration only,; interpret test results as follows: 0-4 mm=induration considered not significant & no follow-up needed; if greater than 5 mm=induration may be significant in clients what are considered to be at risk.
question
The nurse is caring for a client with TB. A sputum sample is ordered for the next 3 consecutive days. What time is it best for the nurse to schedule the collection of sputum? a) at bedtime b) before a meal c) following breakfast d) upon arising in the morning
answer
answer: d rationale: most clients find that it is easier to raise sputum when they first awaken; and may be necessary to collect specimens on several consecutive days.
question
Your sister says to you, "Well, I want to put Grandma in West Parks Nursing Home because they won't poke on her like those other Homes do." You ask your sister (you are a nurse), "What do you mean when you say: they won't poke on Grandma like other places will?" Your sister says, "Well, they won't make her get the flu shot and that TB shot thing, and you know-you know how she hates getting stuck by needles." What is the most appropriate thing you can say to your sister about Mantoux TST test?
answer
answer: "Grandma can refuse the flu vaccine because that is her right as the patient; however in order for Grandma to reside in any long-term care facility in the US, she would be required to receive the Mantoux TST test upon admission for TB. We should talk with Grandma about this and go from there."
question
Medical TX/MNGMNT: retarding the growth and multiplication of tubercle bacilli, thus giving the body a chance to overcome the disease; drug regimens: initial tx: INH, RIF, PZA(these are all in a combined tablet); prophylactic tx: INH and may use vitamin B6 to minimize side effects; LOBECTOMY (removal of lobe); segmental resection (removal of love segment); wedge resection (removal of a wedge of diseased tissue); and in some cases pneumonectomy (removal of entire lung).
answer
TB
question
Instruct patient with TB that the drug they will taking needs to avoid foods with tyramine and histamine(not tuna, aged cheese, red wine, soy sauce..). You know they understand which drug you have been discussing when they say, "I have a strict diet because I take..."
answer
INH
question
Because the contacts wearing,TB patient taking rifampin wants to prevent possibly destroying her her lenses she is now wearing her glasses until she gets the okay from her doctor. what side effect is causing her to make this decision?
answer
rifampin may color the contact lenses
question
Thsi is the collapse of ALVEOLI; and may involve a small portion of the lung or an entire lobe; occurs secondary to aspiration of food or vomitus, a mucous plug, fluid or air in the thoracic cavity, compression on tissue by tumors, an enlarged heart, an aneurysm, or enlarged lymph nodes in the chest.
answer
atelectasis
question
S/S: cyanosis; fever; pain; dyspnea; increased pulse and resp rates; increased pulmonary secretions; crackling; absent breath sounds; dense shadows on chest x-ray; abnormal ABG and pulse oximetry results.
answer
atelectasis
question
What type of breath sounds would the nurse expect to find in a patient with atelectasis? Select all that apply. a)wheezing without auscultation b)crackling in affected areas c)absent breath sounds d)rhonchi
answer
answer: b, c rationale: may find upon auscultaion over affected areas: crackling and usually breath sounds are absent
question
Diagnostic Test:(for the collaping of alveolar): auscultation; chest x-ray; ABG and pulse oximetry
answer
atelectasis
question
Medical MNGMNT: improving ventilation; suctioning; and deep breathing; coughing to raise secretions; bronchodilators and humidification; O2; removal of the primary cause helps correct this condition.
answer
atelectasis
question
Nursing MNGMNT: preventing atelectasis; postop deep breathing and coughing; have patient change position frequently; encourage early mobilization from bed to chair followed by early ambulation; administer prescribed opioids and sedatives judiciously to prevent resp depressin; perform postural drainage and chest percussion.
answer
atelectasis
question
this is prolonged (or extended) inflammation of the bronchi, accompanied by chronic cough and excessive production mucus for ~3 mnths each month for 2 consequtive years.
answer
chronic bronchitis
question
S/S: chronic cough productive of THICK, WHITE MUCUS; especially in the morning and the evening; bronchospasm; acute respiratory infections big time during winter months; sputum may become yellow; purulent, copious; and blood streaked after paroxysms of coughing; expiration is prolonged; cyanosis secondary to hypoxemia after coughing; dyspnea; right-sided HF; edema in extremeties.
answer
chronic bronchitis
question
Medical MNGMNT/TX: goals for this condition are to prevent recurrent irritation of bronchial mucosa by infection or chemical agents; maintain function of bronchioles; assist in removal of secretions; smoking cessation; bronchodilators; fluid intake to thin out secretions; maintain well-balanced diet; postural drainage; steroid therapy, if everything else fails; filtration of incoming air; avoid cold air and wind exposure.
answer
chronic bronchitis
question
Nursing MNGMNT: preventing infection; promote handwashing; patient educate about MDIs (metered-dose inhalers); instruct client in postural drainage techniques and measure to improve overall health.
answer
chronic bronchitis
question
When using MDIs, the client should hold their breath for how long to allow the medication to reach the airways of the lungs?
answer
~10 seconds (10 slow counts)
question
This condition is a reversible obstructive disease of the lower airway; inflammation of the airway and hyperresponsiveness of the airway to internal or external stimuli.
answer
asthma
question
There are 2 types of asthma-which are?
answer
allergic asthma and nonallergic asthma
question
Which type of asthma do many clients experience?
answer
mixed asthma rationale: a combination of both allergic and nonallergic asthma
question
This asthma type is extrinsic-occurs in response to allergens.
answer
allergic asthma
question
This asthma type is intrinsic-occurs in response to factors such as URIs, emotional upsets, and exercise
answer
nonallergic asthma
question
S/S: (acute episodes) sensation of suffocation; fear and anxiety will usually intensify the symptoms; marked prolongation of the expiratory phase; coughing; usually pale skin; thick, stringy mucus; cyanosis of lips and nail beds during an a major attack.
answer
asthma
question
When an acute asthma attack intensifies and progresses to a persistent state of asthma, it can become a life threatening emergency. What is this called?
answer
status asthmaticus
question
Diagnostic Tests: chest auscultation; PULMONARY FUNCTION STUDIES; ABGs
answer
asthma
question
Your asthma patient has been having major attacks, the nurse checks her ABGs results and notice that the PaCO2 levels appear normal, yet your patient appears in distress. What do these readings indicate?
answer
impending respiratory failure rationale: PaCO2 levels can become INCREASED if asthma gets WORSE; ~PaCO2 levels are DECREASED rt rapid resp rate; but if these levels all of a sudden appear normal in the latter part of an asthma attack they may indicate impending respiratory failure.
question
A client with moderately controlled asthma needs to use a peak flow meterl Which of the following statements by the nurse best explains the purpose of a peak flow meter? a) a peak flow meter measures the amount of forced inspiration b) a peak flow meter measures the depth of forced inhalation c)a peak flow meter measures the highest flow with forced expiration d)a peak flow meter measures the residual volume after exhalation
answer
answer: c rationale: the peak flow meter measures the peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) and is used by the client to assess the effectiveness of medication or breathing status.
question
This is an inherited multisystem disorder that affects infants, children, and young adults.
answer
CF-cystic fibrosis
question
S/S: clients with this disorder exhibit S/S in infancy or early childhood and some in late childhood, adolescence; in kids: resp symptoms, failure to thrive; and FOUL, BULKY, GREASY STOOLS; in newborns, the first sign is meconium ileus (impacted meconium in the intestines) and salty tasting skin; frequent resp infections; increased cough, purulent sputum to production of thick, tenacious(persistent) mucus; finger clubbing; hemoptysis; malabsorption of fats and fat-sol vitamins; and GI difficulties-feces show STEATORRHEA(fat in stool)
answer
cystic fibrosis
question
Diagnostic : pilocarpine iontophoresis sweat test (higher than 60 mEq/L -they got it; between 50-60 mEq/L-suggestive); PFTs; radographic studies.
answer
CF
question
Medical TX: relieving syptoms; Kalydeco given to those 6yrs and older with a specific gene mutation-this helps thin out the mucus; postural drainage; chest physical therapy with vigorous percussion, vibration; breathing exercises; fluid intake; inhalants; azithromycin(antibiotic)-preserves and improves lung function; pacreatic enzyme replacements; take multivitamins; may recive a LIVER TRANSPLANT; may receive LUNG TRANSPLANT.
answer
CF
question
Nursing: prevent complications, promote as normal a lifestyle as possible; avoid those with colds and flulike symptoms; strict adherence to a vigourous pulmonary toilet (cleansing)-chest physical therapy.
answer
CF
question
These are exposures to organic and inorganic dusts and noxious gases over a long period causing chronic lung disorders.
answer
Occupational Lung Diseases
question
This consists of pneumoconiosis; silicosis; coal dust(black lung disease, miners' disease); asbestosis.
answer
Occupational Lung Diseases
question
If a patient is expectorating black-streaked sputum, you can expect the patient to tell you that they had been exposed to what?
answer
coal dust
question
After thoracic surgery, ____ secretions, air, and blood from the thoracic cavity is necessary to allow the lungs to expand, by inserting a catheter in the pleural space, and keeping a chest tube in place until the lungs are able to expand on their own.
answer
draining rationale: this is why we use chest tubes after thoracic surgery.
question
What is coryza?
answer
"common cold"
question
Because the most common cause of coryza is the Rhinovirus; what should NOT be prescribed to treat the patient?
answer
antibiotics
question
This upper respiratory disorder, is inflammation and swelling mucus membrane lining of larynx and accompanies URIs.
answer
laryngitis
question
S/S: hoarseness (that should not persist beyond 2 weeks); inability to speak above a whisper, or aphonia (complete loss of voice); c/o throat irritation and dry, nonproductive cough.
answer
laryngitis
question
If your patient comes to you and c/o hoarseness that has persisted beyond 2 weeks the larynx needs to have what diagnostic test performed, because this complaint may indicate laryngeal cancer and merits prompt investigation.
answer
laryngoscopy
question
Medical TX: this involves voice rest and tx or removal of the cause; antibiotic therapy may be used if bacterial is the cause.
answer
laryngitis
question
Nursing: encourage patient to quit smoking and encourage them to participate in smoking-cessation programs.
answer
laryngitis
question
"nose bleed" and is a common occrrence.
answer
epistaxis
question
How long will you instruct the patient with epistaxis to hold the nares, sitting upright with head tilted forward to prevent swallowing and aspiration?
answer
hold nares 5-10 minutes
question
The LPN notes that her patient is 2 days postop from ICU for thoracic surgery; the care plan reads: Impaired Gas Exchange r/t decreased lung expansion, impaired lung function, and surgical procedure. Which interventions are of primary importance for the care of the client? Select all the apply. a) assess the client's dressings and incisions for increased drainage b)monitor client's temperature at least every 4 hours c) remind the client to deep breathe and cough at least every 2 hours d)reposition the client so that the head is elevated 30-40 degrees e) 30 minutes after giving pain meds ask client to rate pain on a scale of 1-10.
answer
answer: c, d
question
The important thing to remember about a chest tube, is that when the tube is coming from the client, it must ALWAYS be kept under what?
answer
the chest tube must always be kept under water
question
Thsi occurs during motor vehicle accidents when the neck strikes the steering wheel or other blunt trauma occurs in the NECK region, or trauma from endoscopic and ET intubations, or (uncommon) fx of thyroid cartilage.
answer
laryngeal trauma
question
Because laryngeal trauma involves a NECK INJURY, and if swelling from this injury creates a prevention of air from the upper to the lower resp airway; causing choking-it is appropriate to say that laryngeal trauma can lead to this possibly life-threatening event.
answer
laryngeal obstruction
question
This symptom can occur with laryngeal trauma if the larynx becomes greatly swollen; and is a high-pitched harsh sound during resp, indicative of airway obstruction.
answer
stridor
question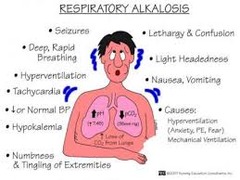
KIDNEYS EXCRETE bicarbonate to LOWER pH to compensate

answer
Respiratory Alkalosis
question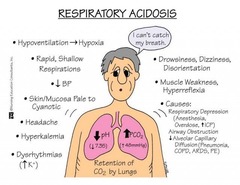
KIDNEYS RETAIN bicarbonate to RAISE pH to compensate

answer
Respiratory Acidosis
question
LUNGS "BLOW OFF' CO2 to RAISE pH to compensate

answer
Metabolic Acidosis
question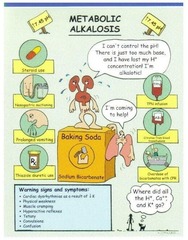
LUNGS RETAIN CO2 to LOWER pH to compensate

answer
Metabolic Alkalosis
question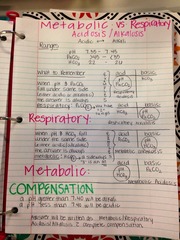
If too much bicarbonate is with pH on the acidic and PaCO2 is on the alkalitic side-(pH+bicarbonate=metabolic); so, this is referring ?

answer
metabolic ACIDOSIS
question
partial pressure carbon dioxide
answer
PaCO2
question
If PaCO2 is on the acidic side; and too much bicarbonate is on the alkalitic side-(pH+bicarbonate=metabolic); so, this is referring to?
answer
metabolic ALKALOSIS
question
if too much PaCO2 is on the acidic side and bicarbonate on the alkalitic side-(pH+PaCO2=respiratory); so, this is referring to?
answer
respiratory ACIDOSIS
question
if bicarbonate is on the acidotic side and too much PaCO2 is on the alkalitic side-(pH+PaCO2=respiratory); so, this is referring to?
answer
respiratory ALKALOSIS
question
exchanging of O2 and CO2 between the atmospheric air and the blood and between the blood and the cells is what process?
answer
respiration
question
This is the actual movement of air in and out of the resp tract.
answer
ventilation
question
when excess fluid or air accumulates in the plerual space, a procedure where the physicain inserts a needle into the chest wall to obtain a sample of pleural fluid/biopsy specimen from the pleural wall for diagnostic purposes, such as a culture and sensitivity or microscopic exam. This is what procedure?
answer
thoracentesis
question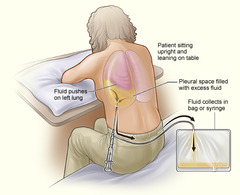
thoracentesis

answer
during procedure client sits at side of bed or exam table with head and arms on pillow; or in a side-lying postion on the unaffected side; a small needle or small tube is inserted between the ribs and into the pleural space to withdraw the fluid.
question
it is important for you, the nurse to explain that the client will experience pressure-like pain when the needle pierces the pleura and whaen fluid is withdrawn during this procedure; and that afterwards, they will need to lye down on the unaffected side for ~1hr to promote expansion of the lung to the affected side. This procedure is?
answer
thoracentesis
question
When taking ABGs sample, do you take a pulse at anytime during the procedure or not; and explain why if yes.
answer
Yes, e.g. if taking the sample at the radial site-you would palpate the radial pulse because where you feel the strongest part of the pulse; is where you will insert the needle.
question
What are the usual sites for ABGs to be drawn from?
answer
radial; brachial; or femoral; or indwelling arterial cath
question
What is, above ALL else, the MOST important thing to do for the client with an ET tube?
answer
keep a patent airway at ALL times
question
This tube is inserted through the mouth or nose into the trachea to provide a patent airway for clients who cannot maintain an adequate airway o their own.
answer
endotracheal tube (ET tube)
question
The nurse must take great considerations to not allowing accidental removal of an ET tube because this can lead to laryngeal edema or a spasm of the laryngeal muscles, resulting in narrowing of the larynx-what is this spasm called?
answer
laryngospasm
question
How long can the ET tube stay in?
answer
2 weeks
question
When the pressure in the pulmonary arteries increases, which in turn increases the workload of the right ventricle; resistance of blood flow in the pulmonary circulation causes what disorder?
answer
pulmonary HTN
question
If normal pulmonary arterial pressure is ~25/10 mm Hg then pulmonary arterial pressure is _____mm Hg in a client with pulmonary HTN?
answer
above40/15 mm Hg and can get even higher as the disorder worsens
question
How would you teach a patient to splint the chest wall, with a client who has pleurisy?
answer
splint the chest wall by turning onto the unaffected side.
question
what is the MOST common cause for acute bronchitis infections?
answer
viral
question
Besides death, what is the MOST serious complication of influenza?
answer
Staphylococchal pneumonia
question
Under normal conditions, about how many mL of fluid between the pleurae prevent friction during pleural surface movement?
answer
5-15 mL of fluid more than this indicates pleural effusion
question
With a patient being observed overnight in the hospital for broken ribs of these, what is she monitoring for? a)anxiety b)fatigue c)increased pain d)resp distress e)infection
answer
answer: c,d,e
question
During thoracic cavity surgery there are 2 types of chest tubes that can be inserted. One is placed anteriorly, the other posteriorly. What are the specifics that each "remove"?
answer
anterior chest tubes: remove AIR posterior chest tubes: remove fluid
question
This is a sign of acute respiratory failure that causes the arterial CO2 to RISE; what S/S is this?
answer
hypercapnia
question
This is a sign of acute respiratory failure that causes the FALL of arterial O2; what S/S is this?
answer
hypoxemia
question
A client dx with chronic respiratory failure will show what S/S r/t this disease building up over time?
answer
dyspnea
question
The most common causes of chronic respiratory failure are?
answer
COPD and neuromuscular disorders
question
Following surgery, what three signs would you want to monitor a patient for-that could indicate resp obstruction?
answer
cyanosis; dyspnea; restlessness
question
Acid reflux, exposure to industrial pollutants, exposure to HPV, and hx of smoking are all risk factors for what type of cancer?
answer
laryngeal cancer
question
The patient of an airway pressure release vent (APRV); experiences ventilator cycles between high to low pressure levels of CPAP. You know that this client will still be able to maintain what?
answer
This patient maintains their cough reflex
question
A 34 year old female was admitted into ICU last night as a result of MVA. MVA stands for?
answer
motor vehicle accident
question
A patient with an early glottis cancer would most likely under go what surgery because it is less invasive?
answer
laser microsurgery
question
This alaryngeal speech method requires the insertion of a prostheses into the posterior wall of the trachea followed by the insertion of a prostheses such as Blom-singer devices.
answer
tracheoesophageal puncture (TEP)
question
Following sinus surgery, during postop time, what must the nurse specifically monitor for which could indicate a possible hemorrhage?
answer
frequent swallowing
question
This URI must be closely monitored and quickly treated because it can lead to serious complications such as endocarditus and rheumatic fever (noncontagious acute fever marked by inflammation and pain in the joints)-both are cardiac issues; and harmful kidney complications such as glomerulonephritis ( acute inflammation of the kidney, typically caused by an immune response).
answer
strep throat
question
laryngeal cancer clients c/o what when drinking hot/citrus fluids?
answer
c/o of burning
question
those suspected of having laryngeal cancer will most likely c/o what symptom, besides "a hoarse throat I just can't shake" or burning when they drink hot/citrus liquids?
answer
c/o swelling in the back of the throat
question
In order for the critically ill patient to MAINTAIN, not compensate, NORMAL pH...what will they do.
answer
The LUNGS will ELIMINATE CARBONIC ACID (ca) to "BLOW OFF" more CO2.
question
serous fluid indicates what?
answer
inflammation
question
bloody fluid indicates what?
answer
trauma
question
purulent fluid indicates what?
answer
infection
question
Client at risk for Respiratory Alkalosis, how will the body attemp to restore (we are talking compensation here) acid-base balance?
answer
The KIDNEYS will EXCRETE bicarbonate to RAISE pH levels.
question
Client at risk for Respiratory Acidosis, how will the body attempt to restore (compensate) for this acid-base imbalance?
answer
The KIDNEYS will RETAIN bicarbonate to LOWER pH levels.
question
Client at risk for Metabolic Alkalosis, how will the body attempt to restore (compensate) for this acid-base imbalance?
answer
The LUNGS will RETAIN CO2 to LOWER pH levels.
question
Client at risk for Metabolic Acidosis, how will the body attempt to restore (compensate) for this acid-base imbalance?
answer
The LUNGS will "BLOW OFF" CO2 to RAISE pH levels.
question
The nurse knows that fibrosis, edema, decreased surfactant, and atelectasis can all affect lung compliance. True/False?
answer
True
question
Because alveolar walls contain less capallaries as a person ages; you now know that in the elderly this causes what to change?
answer
answer: Gas exchange. rationale: gas exchange DECREASES when there are less capillaries in the alveolar walls.
question
The sternum protrudes and ribs are sloped backward, indicates what manifistation?
answer
pectus carniatum
question
SaO2 means?
answer
arterial O2 saturation
question
If you have a client with lab readings of: PaO2 of 80-100 mm Hg; PaCO2 of 35-45 mm Hg; bicarbonate of 21-28 mmol/L; SaO2 of 95-100%...you would expect this patient's pH levels to be in what range?
answer
normal. 7.35-7.45 pH



