Med Surg I Quiz 2: Oncology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion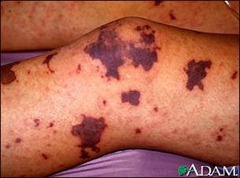
Thrombocytopenia:

answer
deficiency of platelets in the blood. This causes bleeding into the tissues, bruising, and slow blood clotting after injury.
question
Nursing intervention for Thrombocytopenia: Assess client for and report signs and symptoms of unusual bleeding:

answer
petechiae, purpura, or ecchymoses gingival bleeding prolonged bleeding from puncture sites epistaxis, hemoptysis unusual joint pain frank or occult blood in stool, urine, or vomitus increase in abdominal girth menorrhagia restlessness, confusion decreasing B/P and increased pulse rate decrease in Hct and Hb levels.
question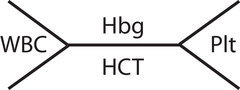
Nursing intervention for Thrombocytopenia:

answer
Monitor platelet count and coagulation test results (e.g. bleeding time). Report abnormal values. If platelet count is low, coagulation test results are abnormal, or Hct and Hb levels decrease, test all stools, urine, and vomitus for occult blood. Report positive results. Avoid aspirin & NSAIDS
question
Nursing intervention for Thrombocytopenia: Implement Measures to prevent bleeding

answer
avoid giving injections whenever possible; consult physician about prescribing an alternative route for medications ordered to be given intramuscularly or subcutaneously when giving injections or performing venous and arterial punctures, use the smallest gauge needle possible apply gentle, prolonged pressure to puncture sites after injections, venous and arterial punctures, and diagnostic tests such as bone marrow aspiration take B/P only when necessary and avoid overinflating the cuff caution client to avoid activities that increase the risk for trauma (e.g. shaving with a straight-edge razor, using stiff bristle toothbrush or dental floss) whenever possible, avoid intubations (e.g. nasogastric) and procedures that can cause injury to rectal mucosa (e.g. taking temperatures rectally, inserting a rectal suppository or tube, administering an enema) pad side rails if client is confused or restless perform actions to reduce the risk for falls (e.g. keep bed in low position with side rails up when client is in bed, avoid unnecessary clutter in room, instruct client to wear slippers/shoes with nonslip soles when ambulating) instruct client to avoid blowing nose forcefully or straining to have a bowel movement; consult physician about an order for a decongestant and/or laxative if indicated administer the following if ordered: platelet-stimulating factor (oprelvekin [Neumega]) estrogen-progestin preparations to suppress menses platelets. Avoid aspirin & NSAIDS, wear close toe shoes when ambulating, no heat (causes vasodilation) apply cold
question
Nursing intervention for Thrombocytopenia: If bleeding occurs spontaneously:

answer
apply firm, prolonged pressure to bleeding area(s) if possible if epistaxis occurs, place client in high Fowler's position and apply pressure and ice pack to nasal area maintain oxygen therapy as ordered administer whole blood or blood products (e.g. platelets) as ordered.
question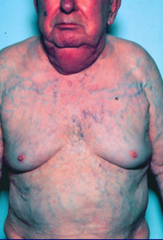
Complication of Lung Cancer:

answer
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (pressure on the superior vena cava by tumor)
question
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome is considered a:
answer
medical emergency
question
Signs ; symptoms of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome:
answer
facial edema, edema in neck, epistaxis, dyspnea, nose bleeds, purple from the nipples up
question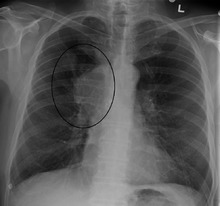
What is happening when the tumor puts pressure on the superior vena cava?

answer
Occludes blood flow to the brain (blocks flow) ; puts pressure on the airways
question
Nursing Interventions for Superior Vena Cava Syndrome:
answer
Nurses are in a key position to recognize SVCS early, allowing time for a clear histologic diagnosis prior to starting therapy. Nurses should be able to recognize those patients at high risk and be aware of the signs and symptoms of SVCS. Nursing care encompasses a variety of tasks: facilitation and coordination of diagnostic procedures, assessment of respiratory, cardiac and neurologic systems, administration of ordered therapies, emotional and psychosocial support for the patient and family, and education regarding treatment. Nurses can institute measures to help relieve dyspnea, including elevating the head of the bed, administering oxygen, and teaching energy conservation. Intravenous fluids should not be given through the upper extremities, necessitating central venous access. Additional nursing interventions should focus on the side effects caused by the treatment used (chemotherapy, radiation therapy). Through astute observation and an understanding of this complication, nurses can be instrumental in the diagnosis and treatment of SVCS.
question
Side Effects of Radiation: ( in a patient with SVCS)
answer
will vary depending on the areas included in the treatment field, and can include: skin irritation, dyspnea, cough, pneumonitis, mucositis, decrease in blood counts, appetite / taste changes, and fatigue.
question
Treatment for SVCS:
answer
Radiation Therapy Chemotherapy Medication Therapy Stent placement
question
Medications used to treat SVCS:

answer
corticosteroids, diuretics, and thrombolytic therapy.
question
thrombolytic therapy (medication therapy for SVCS) includes:
answer
heparin, warfarin, and/or tissue plasminogen activators.
question
Early signs ; symptoms of SVCS:
answer
Feeling of fullness in the head, nasal stuffiness, headache, shortness of breath, cough, chest pain, hoarseness and difficulty swallowing.
question
Late signs ; symptoms of SVCS:
answer
respiratory distress, headaches, syncope, visual changes, and mental status changes.
question
What types of lung cancer has the best prognosis?
answer
Non-small cell lung cancer
question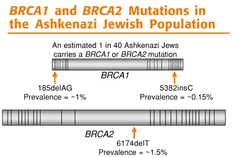
What is the inherited gene mutation the identifies families at significant risk for breast cancer ; ovarian cancer?

answer
BRCA 1 ; BRCA 2
question
1. What diseases is predominately a malignancy of of the lymphocytes?
answer
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia, Hodgkin's Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma ; B. Lymphoma KNOW THESE DISEASES. Anything with 'Lymph' in it
question
What is the difference between squamous cell carcinoma ; basal cell carcinoma?
answer
SCC is less aggressive, but faster growing and cause it invades local tissues. tends to bleed, ulcers (worse) BCC is more aggressive but does not grow as fast so SCC is the worst of the two SCC is rough, scaly lesion with central ulceration ; crusting. Bleeding possible. Localized, may metastasize. BCC: small waxy, nodule with superficial blood vessels, well defined borders. Erythema ; ulcerations. Invades local structures (nerves, bone, cartilage lymphatic ; vascular tissue) rarely metastatic but high rate of recurrence.
question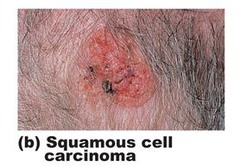
Squamous cell cancer (SCC):

answer
Squamous cell cancer (SCC) starts in the squamous cells in the upper part of the epidermis. It accounts for about 2 in 10 skin cancers. It most often starts on skin that has been exposed to the sun, like the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands. SCC is more likely than BCC to spread into deeper layers of the skin. It is also more likely to spread to other parts of the body, but this is not common
question
Basal Cell Carcinoma:
answer
About 8 of 10 skin cancers are basal cell cancers (BCCs). This is not only the most common type of skin cancer, but the most common type of cancer. BCC begins in the lowest layer of the epidermis, the basal cell layer. BCC usually begins on skin exposed to the sun, such as the head and neck.. BCC tends to grow slowly. It is very rare for BCC to spread to other parts of the body. But if it is not treated, it can grow into nearby areas and spread into the bone or other tissues under the skin. After treatment, BCC can come back (recur) in the same place on the skin. New basal cell cancers can also start in other places on the skin. As many as half of the people who have one BCC will get a new skin cancer within 5 year
question
What cancer is identified with patients having a philadelphia chromosome?
answer
chronic myelogenous leukemia and sometimes found in acute lymphocytic leukemia. KNOW THESE DISEASES
question
Complications of Hodgkin's Lymphoma:
answer
Pancytopenia pg. 1021 in ATI med surg
question
describe the cell type for multiple myeloma:
answer
formed by B cells- malignant plasma cells
question
describe the cell type for hodgkins lymphoma:
answer
formed by B cells (reed stem berg)
question
Classic signs & symptoms of pancreatic cancer:
answer
weight loss, palpable abdominal mass, enlarged gallbladder and liver, hepatomegaly, jaundice (late finding) clay or tan colored stools, dark, frothy urine, ascites (swelling, fluid in peritoneal space, pruritus (build up of bile salt), early satiety (feeling full) or anorexia Pancreatic Tumor: pain, jaundice, significant weight loss
question
Hodgkin's Lymphoma associated with:
answer
Reed stem berg from B lymphocytes
question
Difference between lymphoma ; multiple myeloma
answer
lymphoma: lymphocytes, myeloma malignant plasma cells
question
Difference between benin ; malignant:
answer
benign does not invade neighboring tissue. malignant can metastasize
question
Cervical cancer:
answer
bleeding ; pain with intercourse
question
screening for ovarian cancer:

answer
CA-125
question
Liver cancer is usually associated with:
answer
Hepatitis B or C-ATI
question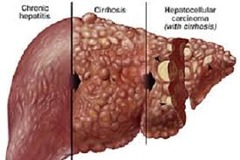
Test for Liver Cancer:

answer
alpha feta protein (can be a false positive) More definitive test:
question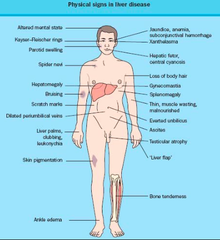
Liver signs ; symptoms

answer
right upper quadrant -weight loss -anorexia -anemia (related to iron absorption) *remember vitamins are absorbed in the liver so monitor the lab tests
question
Surgical removal of the pancreas:
answer
whipple
question
Prostate Cancer:
answer
PCA is elevated (released during a cancer) the most common type of cancer for men. Retention.
question
Treatment for Prostate Cancer:
answer
hormone therapy: estrogen
question
Bladder Cancer:
answer
hair color has a chemical carcinogen
question
Intra (bladder cancer)

answer
monitor for blood in the urine-hematuria
question
Most common cancer in women:
answer
breast cancer, colorectal
question
Growth of Tumors:
answer
initiation, promotion (enhances the development of cancer) then you have a latent period, progression
question
Hodgkin's Lymphoma you should avoid drinking....

answer
alcohol
question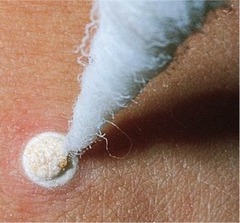
Cryotherapy/surgery:

answer
a procedure that uses extreme cold (liquid nitrogen) to destroy tissue. It is often used to treat skin lesions (skin growths or patches that do not look like the skin around them). The lesions can be benign (not cancerous) or precancerous. Cryotherapy can also be used to treat skin cancer that does not affect deep tissue.
question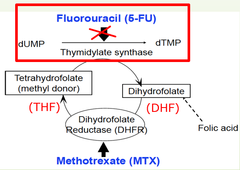
Side effects of 5 fluorouracil:

answer
Pain, itching, burning, irritation, inflammation, dryness, swelling, tenderness at the site of application. This will heal once the treatment is complete.
question
What is 5 fluorouracil?
answer
anti-cancer ("antineoplastic" or "cytotoxic") chemotherapy drug. This medication is classified as an "antimetabolite." (cream, topical)
question
This topical cancer treatment will leave a lesion will weep, crust and erode:
answer
5 fluorouracil
question
after this procedure Skin becomes edematous & tender
answer
Cryosurgery
question
Patient teaching for 5 fluorouracil:
answer
PRIOR to use: make sure you are not pregnant or breastfeeding, do not use aspirin unless permitted by your doctor. During use : Use non-metal applicator or fingertips to apply cream. Use care when applying cream or solution around the eyes, nose, and mouth. Wash your hands immediately after applying this medication. Avoid sun exposure. Wear SPF 15 (or higher) sunblock and protective clothing. If you experience symptoms or side effects, be sure to discuss them with your health care team. They can prescribe medications and/or offer other suggestions that are effective in managing such problems.
question
Description of how Antimetabolites work:
answer
are cell-cycle specific. They attack cells at very specific phases in the cycle (inhibit cancer cells from further dividing, so they die)
question
What patients should expect after cyrosurgery:
answer
The treated area will become red soon after your procedure. It also may blister and swell. If this happens, do not break open the blister. You may also see drainage on the treated area. This is normal. The treated area will heal in about 7 to 10 days with minimal scarring, but it will take longer for the discoloration (pinkness, redness, or lighter or darker skin) to go away.
question
After care teaching for cyrosurgery:

answer
Starting the day after your procedure, wash the treated area gently with fragrance-free soap and water daily. Leave the treated area uncovered unless it has ulcers or drainage. If you see any drainage, apply petroleum jelly (Vaseline®) on the treated area and cover with a bandage (Band-Aid®) if necessary. If you have any bleeding, press firmly on the area with a clean gauze pad for 15 minutes. If the bleeding doesn't stop, repeat this step. If the bleeding still hasn't stopped after repeating this step, call your doctor's office. Do not use perfumed soaps, cosmetics, or lotions on the treated area(s) until it has healed. This will usually be at least 10 days after your procedure. You may have hair loss on the treated area. This depends on how deep the freezing went. The hair loss may be permanent. Once the treated area has healed, apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to the area to protect it from scarring. You may have discoloration (pinkness, redness, or lighter or darker skin) at the treated area for up to 1 year after your procedure. Some people may have it for even longer or it may be permanent
question
Reasons to call dr. after cryosurgery:

answer
A temperature of 100.4° F (38° C) or higher Chills Any of the following symptoms at your wound or the area around it: Redness or swelling that extends to areas of untreated skin Increasing pain or discomfort in the treated area Skin in the treated area that is hot or hard to the touch Increasing oozing, or drainage (yellow or green) from the treated area Foul odor Bleeding that does not stop after applying pressure Any questions or concerns Any problems you did not expect
question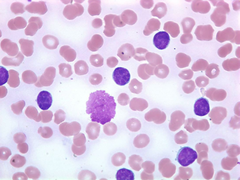
What happens to the cells in Leukemia/ Lymphoma?

answer
-nonfunctional white blood cells -Lack ability to differentiate normally -immature stage of production -Excessive proliferation
question
What are the risk factors for Leukemia ; Lymphoma
answer
-Immunosuppression -Exposure to chemotherapy causing bone marrow suppression -Genetic factors -Ionizing radiation
question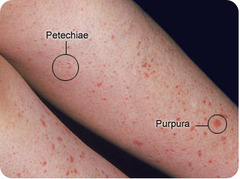
Signs ; Symptoms of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia: (ALL)

answer
-Rapid onset -Fatigue Pallor (anemia) -Infections (bone pain) -Lymphadenopathy (a disease affecting the lymph nodes) -Bruising/petechiae (Remember that the bone pain, lymphadenopathy ; brushing set ALL apart from CLL)
question
Signs ; Symptoms of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: (CLL)

answer
-Affects people over 50 -B cells do not respond to antigen activation -Low antibody count -Fatigue -Weight loss -Fever -Night Sweats -Enlarged Lymph Nodes (Remember that the flu like symptoms set CLL apart from ALL as well as the weight loss)
question
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia: (AML)
answer
-Most common among adults, unchecked proliferation of myeloblasts. Blocked differentiation.
question
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia: (AML) signs ; symptoms:

answer
-Fatigue -Pallor (anemia) -Dyspnea (difficult or labored breathing) -Bone pain -Frequent infections Remember: difficulty breathing sets this part from other leukemias
question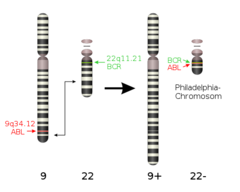
4.Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: (CML)

answer
-affects older males -chromosomal abnormality: PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME -makes a protein that allows a myeloid cell proliferation
question
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: (CML) signs ; symptoms:

answer
fatigue night sweats weight loss fever bone pain abdomen pain Enlarged spleen (causes abdomen pain?) Remember if there is weight loss, it is a chronic type of leukemia
question
Screening ; Diagnostic Tests for Leukemia:
answer
BONE marrow biopsy -Look at protein markers: this will differentiate myeloid or lymphoid (leukemia)
question
What confirms leukemia in a bone marrow biopsy?
answer
excessive blast cells
question
Treatment for leukemia:
answer
Induction Consolidation Maintenance Reinduction
question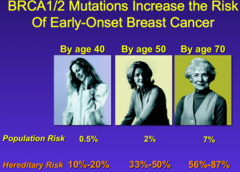
BRCA 1 gives up to a _________% risk by age ________

answer
87%, age 70
question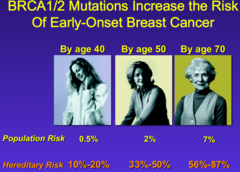
BRCA 2 gives up to a _________% risk by age ________

answer
65%, age 70
question
Non-small cell lung cancers include:

answer
Squamous cell (epidermoid) carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Large cell (undifferentiated) carcinoma: denosquamous carcinoma (less common) sarcomatoid carcinoma (less common) *remember that non-small cell has the best prognosis
question
4. What cancer is associated with patients having Philadelphia chromosome?

answer
CML-Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: makes a protein that allows myeloid cell proliferation which accumulates in bone marrow.
question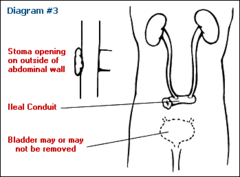
How do you eliminate after an Ileal Conduit?

answer
Continuous drainage into external pouch
question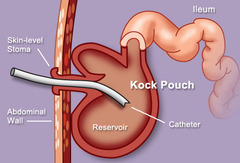
How do you eliminate after a Continent pouch?

answer
Intermittent self catheterization
question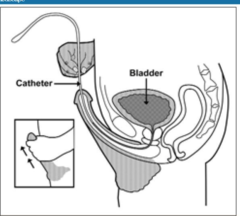
How do you eliminate after a bladder reconstruction?

answer
Intermittent Self catheterization
question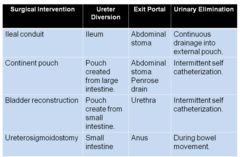
What are the surgical Interventions for Urological Cancer:

answer
Ileal conduit Continent pouch Bladder Reconstruction ureterosigmoidostomy
question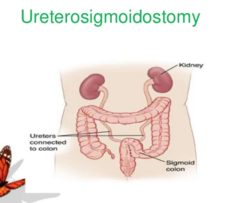
How do you eliminate after a ureterosigmoidostomy?

answer
During Bowel Movement
question
16. Describe intravesical chemotherapy and understand what the nurse would monitor a patient for?

answer
is chemotherapy that is used to treat carcinoma that has not metastasized outside of the bladder. Used for bladder cancer, TB virus must be kept in bladder for 2 hours, sit when you pee so you do not splash. Mask and half a gallon of bleach for about 15 min before they pee. No sex for 24 hours. Jac's Notes: make them sit down to pee (prevent splashing) live bacteria N95 mask, put bleach in the toilet (15 min) do not introduce TB into the sewer system), do not let families, kids, or pregnant women use the same bathroom. They can't have sex for 24 hours because they can transmit it to their partner
question
What are the differences between intravesical and systemic treatments for urological cancer?

answer
Intravesical includes the medications MED and dwells in the bladder for 2 hours. M-mytomycin E-epirubcin D-doxorubicin Systemic Chemotherapy: includes the medications CCM C-cisplatin C-cisplatin ; 5 flourouracil M-mitomycin ; 5 flourouracil http://www.healthnetworks.health.wa.gov.au/cancer/docs/Administration_Intravesical_agents.pdf
question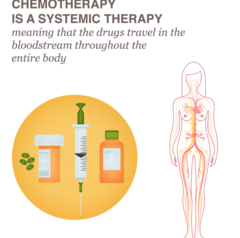
Systemic Chemotherapy:

answer
uses anti-cancer drugs that are injected into a vein or given by mouth. These drugs travel through the bloodstream to all parts of the body.
question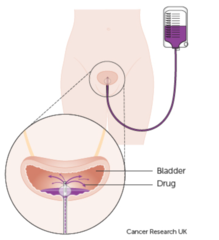
Intravesical (blank space)

answer
With ___________therapy for bladder cancer, drugs are put directly into the bladder through a catheter, instead of being injected into a vein or swallowed. Both immunotherapy and chemotherapy drugs can be given this way.
question
17. What are the complications of Hodgkin's Disease:

answer
Pancytopenia: neutropenia-anc less than 2,000/mm3 increases risk of infection Thrombocytopenia: bleeding-RISK if count is 50,000 and spontaneous bleeding at 20,000 Anemia: fatigue & hypoxemia Now think like a nurse and ask yourself what are the signs & symptoms of these complications & what are the nursing interventions?
question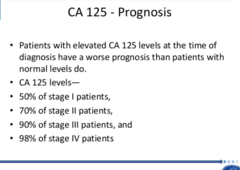
13. What is the purpose of a CA-125 test?

answer
test measures the amount of the protein CA 125 (cancer antigen 125) in your blood. A CA 125 test may be used to monitor certain cancers during and after treatment. In some cases, a CA 125 test may be used to look for early signs of ovarian cancer in women with a very high risk of the disease.
question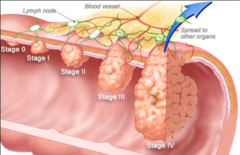
9. Describe the various phases related to the growth of tumors:

answer
a. Grade I: Cells differ slightly from normal cells and are well differentiated. b. Grade II: Cells are more abnormal and moderately differentiated. c. Grade III: Cells are very abnormal and poorly differentiated. d. Grade IV: Cells are immature and primitive and undifferentiated, cell of orgin is difficult to determine.
question
Varies Phases Related To Growth of tumors:
answer
a. Initiation: mutation of cell's genetic structure (due to chemical carcinogens, viral, radiation) b. Promotion: characterized by reversible proliferation of altered cells. Activities of promotion are reversible (obesity, smoking, alcohol, dietary fat) c. Latent period: ranges 1-40 years. Cells accumulate and reach critical mass that can be detected. d. Progression: increased growth rate of tumor, invasiveness, metastasis
question
Burkitt's Lymphoma is always associated with:
answer
Epstein Barr Virus
question
Staging of Cancer: What does the T, N, M stand for?
answer
Tumor, Node, Metastasis
question
Staging of Cancer: TX-
answer
unable to evaluate primary tumor
question
Staging of Cancer: T0-
answer
no evidence of primary tumor
question
Staging of Cancer: tis-
answer
tumor in situ
question
Staging of Cancer: T1,T2,T3,T4-
answer
size & extent of tumor
question
Staging of Cancer: NX-
answer
unable to evaluate regional lymph nodes
question
Staging of Cancer: N0-
answer
no evidence of regional node involvement
question
Staging of Cancer: N1,N2,N3-
answer
number of nodes that are involved, or & or the extent of spread
question
Staging of Cancer: MX-
answer
unable to evaluate distant metastasis
question
Staging of Cancer: M0-
answer
no evidence of distant metastasis
question
Staging of Cancer: M1-
answer
presence of distant metastasis
question
Initiation Phase:
answer
mutation of cell's genetic structure (due to chemical carcinogens, viral, radiation)
question
Promotion Phase:
answer
characterized by reversible proliferation of altered cells. Activities of promotion are reversible (obesity, smoking, alcohol, dietary fat)
question
Latent Period:
answer
ranges 1-40 years. Cells accumulate and reach critical mass that can be detected.
question
Progression:
answer
increased growth rate of tumor, invasiveness, metastasis
question
Cancer Stages 0-4:
answer
0-Cancer in situ 1-Tumor limited to tissue of origin; localized tumor growth 2-Limited local spread 3-Extensive local regional spread 4- Metastasis
question
Cancer Stage 0:
answer
This stage describes cancer in situ, which means "in place." Stage 0 cancers are still located in the place they started and have not spread to nearby tissues. This stage of cancer is often highly curable, usually by removing the entire tumor with surgery.
question
Cancer Stage 1:
answer
This stage is usually a small cancer or tumor that has not grown deeply into nearby tissues. It also has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body. It is often called early-stage cancer.
question
Cancer Stage 2:
answer
These stages indicate larger cancers or tumors that have grown more deeply into nearby tissue. They may have also spread to lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body. (2 ; 3 together)
question
Cancer Stage 3:
answer
These stages indicate larger cancers or tumors that have grown more deeply into nearby tissue. They may have also spread to lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body. (2 ; 3 together)
question
Cancer Stage 4:
answer
This stage means that the cancer has spread to other organs or parts of the body. It may also be called advanced or metastatic cancer.
question
What drug therapy may be associated with the development of gynecomastia?
answer
Hormonal Therapy • GnRH- hormone therapy • Androgen antagonists(flutamide [Euxelin]) a. estrogens and androgen b. digitalis c. isoniazid (INH) d. ranitidine (Zantac) e. spirolactone (Aldactone). The use of heroin and marijuana can also cause gynecomastia *man boobies*
question
Drug to light interval:
answer
when the drug is given to when the light is applied.
question
What type of patients are most at risk for developing multiple myelomas?
answer
The disease is twice as common in men as in women and usually develops after 40 years of age, with and average of 65 years of age. More commonly in African Americans. Also, many people with monoclonal gammopathy or exposed to radiation from an atomic bomb will eventually develop MM.
question
Alpha fetoprotein may give you a ________positive because of _________ or ___________ so the definitive test for liver cancer is the ______ test. If this test is elevated, then it indicates _________ cancer with an elevated AFP.
answer
false positive cirrhosis or hepatitis CEA test liver cancer
question
CEA test stands for
answer
Carcinoembryonic antigen (tests for cancer)
question
Elevated CEA level
answer
more than 35 units/ml
question
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia: is most common in
answer
adults (according to ATI) Lewis says CML
question
Hemoglobin Level (Hgb):
answer
Females 12-16 g/dL Males: 14 to 18 g/dL (ATI + Slides) Female: 11.7-16.0 g/dL Male: 13.2-17.3 g/dL (Lab Book)
question
Hematocrit Level: Hct
answer
Females 37-47% Males 42-52% (ATI + Slides) Female: 35%-47% Male: 39%-50% (Lab Book)
question
CBC tip:
answer
look over the lab values and rationales as they apply to leukemia and lymphomas



