MCAT Physics: Atomic and Nuclear Phenomena – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
- When light of a sufficiently high frequency is incident on a metal in a vacuum, the metal ions emit electrons - liberated electrons produce a current
answer
Photoelectric Effect
question
- The minimum frequency of light that causes ejection of electrons (ft) - photoelectric effect is an all or nothing response
answer
Threshold Frequency
question
- light quanta in a light beam
answer
Photon
question
E=hf - energy of each photon is proportional to light h= 6.626 x 10^-34 - energy of a photon increases with increasing frequency
answer
Energy of each photon
question
where W is the work function of the metal in question - energy can be anywhere from 0 to Kmax
answer
Maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electron
question
- The minimum energy required to emit an electron - W=h ft (ft = threshold frequency) - activation energy in a sense
answer
Work Function
question
- when an electron falls from a higher energy level to a lower energy level, a photon of light is emitted with an energy equal to the energy difference between the two orbitals
answer
Absorption and Emission
question
- looks at the absorption of light in the visible and ultraviolet range
answer
UV- Vis Spectroscopy
question
- if you excite a fluorescent substance with UV radiation it will begin to glow with visible light
answer
Fluorescence
question
- mass of the nucleus is NOT the sum of the masses of all the protons and neutrons inside of it - The actual mass is slightly smaller due to matter being converted to energy E=mc^2 - because c is squared, a small amount of mass will yield a huge amount of energy
answer
Mass Defect
question
- When protons and neutrons come together to form the nucleus they are attracted to each other by this force - binding energy allows the nucleons to bind together
answer
Strong Nuclear Force
question
- much less strong than strong nuclear force
answer
Weak Nuclear Force
question
- small nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus
answer
Fusion
question
- large nucleus splits into smaller nuclei - chain reaction - powers most commercial power plants
answer
Fission
question
- naturally occurring spontaneous decay accompanied by the emission of specific particles Know these types of problems 1) the integer arithmetic of particle and isotope species 2) Radioactive half life problems 3) The use of exponential decay curves and decay constants
answer
Radioactive Decay
question
- the sum of the atomic numbers must be the same on both sides of the equation and the sum of the mass numbers must be the same on both sides as well
answer
Isotope Decay Arithmetic and Nucleon Conversion
question
- Emission of an alpha particle - alpha particle consists of two protons, two neutrons and zero electrons - atomic number is 2 less and mass number is 4 less
answer
Alpha Decay
question
- emission of a beta particle which is an electron - emitted when a neutron decays into a proton, a beta particle and an antineutrino
answer
Beta Decay
question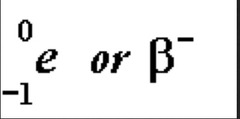
- neutron converted to a proton and a beta - particle - atomic number is one higher and mass number does not change
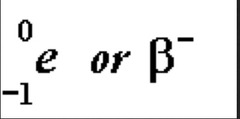
answer
Beta - Decay
question
- a proton is converted into a neutron and a beta + particle - the atomic number will be one lower and the mass number will not change
answer
Beta + Decay
question
- The emission of gamma rays which are high energy photons - carry now charge and simply lower the energy of the parent nucleus without changing the mass or atomic number
answer
Gamma Decay
question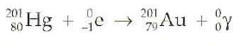
- capture an inner electron that combines with a proton to form a neutron - atomic number is one less but the mass number stays the same
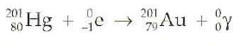
answer
Electron Capture
question
- the time it takes for half of the sample to decay
answer
Half Life
question
- the rate at which nuclei decay is proportional to the number that remain - gamma is decay constant
answer
Exponential Decay
question
- n(o) is the number of undecayed nuclei at t=0
answer
Exponential Decay
question
ln 2=0.693
answer
Decay constant and half life



