Marketing: An Introduction – Chapter 1 – Notes – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion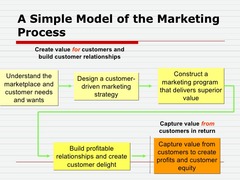
The Marketing Proccess

answer
- In the first four steps companies work to understand consumers, create customer value and build strong customer relationship. In the final step, companies reap the rewards of creating superior customer value. - By creating value for customers, they in turn capture value from consumers in the form of sales, profits, and long-term customer equity.
question
Five core customer and marketplace concepts
answer
1) needs, wants, and demands. 2) market offerings (product,services, and experiences) 3) value and satisfaction 4) exchanges and relationships 5) markets
question
Needs, Wants, and Demands
answer
- Human needs are states of felt deprivation. Physical need = food, clothing, warmth, safety Social need= belonging and affection Individual need= knowledge and self expression. - Wants are the form human needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality. Ex: A Canadian needs food but wants a breakfast sandwich fomr Tim Horton's. - Demands are wants backed by buying power.
question
Market Offerings - Products, Services, and Experiences
answer
- Consumers' needs and wants are fulfilled through market offerings. - Not limited to physical products, also include services. Ex: banking, airline, hotel, tax preparation. - Also include other entities such as: persons, places, organizations, information, and ideas. - Market myopia: paying more attention to specific products you offer than the benefits and experiences produced by these products.
question
Customer Value and Satisfaction
answer
- Customers form expectations about the value and satisfaction that various market offerings will deliver and buy accordingly. - Marketers must be careful to set the right level of expectations. Too high = buyers disappointed; Too low = fail to attract enough buyers.
question
Exchanges and Relationships
answer
- Marketing occurs when people decide to satisfy needs and wants through exchange relationships. - Marketing = actions taken to build and maintain desirable exchange relationships w/ target audiences involving a product, service, idea, or other object. - In broadest sense, marketer wants to bring about a response to some market offering. Can be more than buying or trading products. i.e. political candidate wants votes, church wants memberships, orchestra wants audience.
question
Markets
answer
- Market: set of of all actual and potential buyers of a product. - Marketers are no longer asking only "how can we reach our customers?" but also "how should our customers reach us?" and "how can our customers reach each other?"
question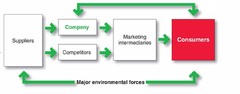
Modern Marketing System

answer
- Figure shows main elements in a marketing system - Company & Competors -> research market + interact w/ consumers. - Then they create market offerings. Send offerings & messages to consumers either directly or via intermediaries. - All parties in the system are affected by major environmental forces (demographic, economic, physical, technological, political/legal, and social/cultural). - All arrows in figure represent relationships that must be developed and managed.
question
Selecting Customers to Serve
answer
- Company must decide who it will serve. - Does this by dividing market in segments of customers (market segmentation) + selecting which segments it will go after (target marketing). - Marketing Managers must decide which clients to target based on the level, timing an, and nature of their demand.
question
Choosing a Value Proposition
answer
- Value proposition: set of benefits or values a company promises to deliver to customers to satisfy their needs. - Differentiates one brand from another. Answers question, "why should I buy your brand rather than the competitor's?"
question
Marketing Management Orientations
answer
- There are five alternative concepts under which organizations design and carry out their marketing strategy: the production, product, selling, marketing, and societal marketing concepts.
question
The Production Concept
answer
- The production concept holds that consumers will favour products that are available and highly affordable. - Management should focus on improving production and distribution efficiency. - Production concept can lead to marketing myopia. Companies run major risks of focusing too much on ops and love sight of satisfying customers + building customer relationships.
question
The Production Concept - Example
answer
Lenovo dominates the highly competitive, price-senstitive Chinese PC market through low labour costs, high production efficiency and mass distribution.
question
The Product Concept
answer
- The product concept holds that customers will favour products that offer the most in quality, performance, and innovative features. - Can also lead to marketing myopia. Focused too much on the product quality and not on customer relationships and other factors that affect customers.
question
The Selling Concept
answer
- The selling concept holds that consumers will not buy enough of the firm's products unless the company undertakes a large-scale selling and promotion effort - Typically practiced with unsought goods. - High risk. Company focused on creating sales transactions instead of building long-term, profitable customer relationships.
question
Selling Concept - Example
answer
Most firms practice the selling concept when they have overcapacity. Their aim is to sell what they make rather than make what the market wants. Examples of selling concepts are: A)Life Insurance Policies b)Nutritional Supplements c)Fundraising Meetings d)Political Parties Selling their Candidates. This group of sellers is often well equipped with various techniques or strategies aimed at finding prospects and emphasize the benefits of the products.
question
The Marketing Concept
answer
- The marketing concept holds that achieving organizational goals depends on knowing the needs and wants of target markets and delivering the desired satisfactions better than competitors do. - Customer focus and value are the paths to sales and profits. - Starts with a well-defined market, focuses on customer needs, and integrates all the marketing activities that affect customers. - In turn yields profits by creating lasting relationships with the right customers based on customer value and satisfaction.
question
Marketing Concept- Example
answer
The marketing concept states that a company's primary job is to satisfy the needs of the customer. Wal-Mart's motto of "satisfaction guaranteed" is an example of the marketing concept. The customers' needs, wants, and satisfaction should always be foremost in every manager and employees' mind. Years ago, Avis, the rental car agency, recognized that it would also be perceived as the second largest rental agency in America. So they created a marketing campaign around the idea of "Avis. We're #2, we try harder." Consumers bought into the fact that, since Avis is #2, they will try harder to win my business and create a superior car rental experience.
question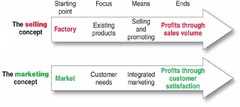
The Selling and Marketing Concepts Contrasted

answer
- Selling concept takes an inside-out perspective. starts with factory focuses on existing products calls heavily for selling and promotion to obtain sales. - Marketing concept takes an outside-in perspective. Starts with well-defined market, focuses on customer needs, and integrates all the marketing activities that affect customers.
question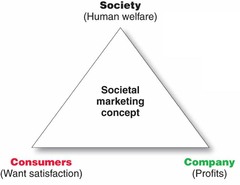
Societal Marketing Concept

answer
- The societal marketing concept questions whether the pure marketing concept overlooks possible conflicts between consumer short-run wants and consumer long-run welfare. - This concept holds that that a marketing strategy should deliver value to customers in a way that maintains or improves both the customer's and society's well-being - Calls for sustainable marketing: socially and environmental responsible marketing that meets the present needs of consumers while also preserving or enhancing the ability of future generations to to meet their needs. - More broad is "shared value": focuses on creating economic value in a way that also created value for society. Also called "Marketing 3.0".
question
Societal Marketing Concept - Example
answer
The Body Shop International plc is the original, natural and ethical beauty brand. The company uses only plant based materials for its products. It is against Animal testing, supports community trade, activate Self Esteem, Defend Human Rights, and overall protection of the planet. They have also their own charity, The Body Shop Foundation, to assist those working to achieve progress in the areas of human and civil rights, environmental and animal protection. Thus Body shop is really following the concept of Societal Marketing.
question
Preparing an Integrated Marketing Plan and Program
answer
- Company's marketing strategy -; outlines which customers this co. will serve and how it will create value for these customers. - Marketing program -; delivers the intended value to target customers. Builds customer relationships by transforming the marketing strategy into action.
question
Customer Relationship Management
answer
- The overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction. - Deals with all aspects of acquiring, keeping, and growing customers. - Most important concept of modern marketing.
question
Customer Value
answer
- Customer perceived value: the customer's evaluation of the difference between all the benefits and all the costs of a market offering relative to those of competing offers. - Customers don't often judge values and costs accurately or objectively. The act on "perceived" value.
question
Customer Satisfaction
answer
- Depends on product's perceived value relative to buyer's expectations. - If product performance expectations = customer highly satisfied/delighted. - Research shows -; Higher customer satisfaction = higher customer loyalty = better company performance. - Delighted customers become "customer evangelists" who spread the word about their good experiences.
question
Customer Relationship Levels and Tools
answer
- frequent marketing programs: reward customers who buy frequently or in large amounts. Ex: airlines offer frequent-flyer programs, hotels give room upgrades to their frequent guests. - club marketing programs: offer members special benefits and create member communities.
question
Relating with More Carefully Selected Customers
answer
- No longer target all customers. Instead target fewer, more profitable customers. - One approach - preemptively screen out potentially non-profitable customers. - Can also dismiss customers who can't be turned into profitable ones or who are too unreasonable and cost more to serve than they are worth.
question
Consumer-Generated Marketing
answer
- Consumers themselves are playing a bigger role in shaping their own brand experiences and those of others. - Increasingly companies are inviting consumers to do the above. - Harnessing consumer-generated content can be time consuming and costly.
question
Partner Relationship Management
answer
- Working closely with others inside and outside the company to jointly bring more value to customers. - Marketing channels: distributors, retailers, and others who connect the company to its buyers. - Supply chain: from raw materials to final products that are carried to final buyers. - Supply chain management: success at delivering customer value rests on how well their entire supply chain performs against competitors' supply chains.
question
Capturing Value from Customers
answer
- Outcomes of creating customer value: customer loyalty and retention, share of market and share of customer, and customer equity.
question
Creating Customer Loyalty and Retention
answer
- Recession put strong pressures on customer loyalty. Created a new spending sensibility that will last well into the future. - Research shows that it's five times cheaper to keep an old customer than acquire a new one.
question
Growing Share of Customer
answer
- Good CRM can help marketers increase their share of customer; the share they get of the customer's purchasing in their product categories. - To increase share of customer, firms can offer greater variety to current customers. Or they can create programs to cross-sell and upsell to market more products and services to existing customers.
question
Building Customer Equity
answer
- Customer equity is the total combined customer lifetime values of all the company's current and potential customers. - The more loyal the firm's profitable customers, the higher the firm's customer equity. - Whereas sales and market share reflect the past, customer equity suggests the future.
question
Building the Right Relationship with the Right Customers
answer
- The co. can classify customers according to to their potential profitability and manage its relationship with them accordingly. - Different types of customers require different relationship management strategies. The goal is to build the right relationships with the right customers.
question
The Changing Economic Environment
answer
- The recession caused many consumers to rethink their spending priorities and cut back on their buying. - More than ever marketers are emphasizing the value in their value propositions. - Marketers are focusing on value-for-the-money, practicality, and durability in their product offerings and marketing pitches. - The goal in uncertain economic ties is to build market share and strengthen customer relationships at the expense of competitors who cut back.
question
The Digital Age
answer
- The digital shift means that marketers can no longer expect consumers to always seek them out. - Digital media must be fully integrated into the marketer's customer-relationship-building efforts.
question
The Growth of Not-for-Profit Marketing
answer
- Marketing has become a major part of the strategies of not-for-profit organizations, such as universities, hospitals, museums, zoos, symphony orchestras, and even churches.
question
Rapid Globalization
answer
- Today, almost every company, large or small, is touched in some way by global competition. - Companies are now not only trying to sell more of their locally produced goods in international markets, they also are buying more supplies and components abroad.



