Lecture 1 MAC, regional, GA & TIVA – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Pre-op anesthetic
answer
Interview Review of Systems Review labs EKG Old charts Discuss prior experiences with patient/family, discuss options, benefits & risks. CRNA's can order any lab test or medication that is pertinent to the anesthetic. EG: pain meds, EKG, anti-emetic, labs *Include caveat that GA may be required.
question
Intra-op anesthetic
answer
Do what you said you would. Have back-up plans, be vigilant. Expect the worst, hope for the best. Be prepared for the unexpected.
question
Post-op anesthetic
answer
PONV Pain control Morbidity (cut lips, damaged teeth, sore neck, limbs, nerve damage, sore throat, scratched eyes etc.) Exit interview a few days later.
question
Which factors affect the absorption of inhalational anesthetics?
answer
CO, respiratory rate
question
Advantages of Local Anesthetic
answer
- Don't have the risks involved with GA - If they come to OR it is monitored anesthesia care
question
Disadvantages of Local Anesthetic
answer
-Physician can do independent of CRNA, "straight local"
question
Advantages of MAC
answer
-Light to moderate to deep sedation similar to general - May need oral airway -Spinal, epidural or regional
question
Disadvantages of MAC
answer
- Sometimes people are uncomfortable so they require GA anyway.
question
Advantages of GA
answer
-A progressive depression of the CNS -Controlled passage through stage 1 and 2 to arrive in stage 3. - Patient cooperation not absolutely essential - Unconscious -Amnesia - Rapid onset of action - Titration possible
question
Disadvantages of GA
answer
-Loss of protective airway reflexes - Depression of VS - Advanced training required - Additional personnel required - Special Equipment/setting -Need recovery room - Greater risk of intra-op complications -Post-anesthetic complications -More extensive pre-op evaluation, including lab work Indications: extreme anxiety or fear, mentally/physically disabled adults or children, poor patient cooperation, infants & children, traumatic procedures Contraindications: lack of adequate training by doctor or personnel, lack of equipment, facilities or medically compromised patient
question
Mask
answer
-Oral airway or nasal airway -Nasal avoided, bleeding -Short-term case
question
LMA
answer
Most common airway manipulation -Must be spontaneously breathing - LMA at induction, ventilate until propofol wears off -Reflux not a candidate
question
ETT
answer
OETT: oral endotracheal tube NETT: nasal endotracheal tube DLT: double lumen tube (one lung ventilation- thoracic cases) Most secure airway.
question
Advantages of TIVA
answer
-Used with allergies to gas/MH history - Quick stages of anesthesia -TIVA is a general anesthetic -used for neuro cases (rapid awakening)
question
Advantages of Epidural/Neuraxial
answer
-Pain control 12-24 hours post surgery (duramorph) - no respiratory issues - Used with older or compromised patients
question
Disadvantages of Epidural/Neuraxial
answer
- Urinary retention - Immobile, pad
question
Advantages of Regional Block
answer
- Somewhat awake, will hear things - MAC cases
question
Disadvantages of Regional Block
answer
- Need to be asleep with tourniquet because it is uncomfortable - Patient can remain awake
question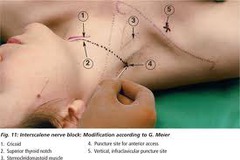
Interscalene

answer
Indications for interscalene nerve block include the following: Shoulder surgery, such as rotator cuff repair, acromioplasty, hemiarthroplasty, and total shoulder replacement Humerus fracture Other arm surgery that does not involve the medial aspect of the forearm or hand
question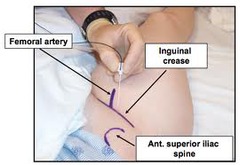
Femoral

answer
Indications: Anterior thigh and knee surgery Landmarks: Femoral (inguinal) crease, femoral artery pulse Nerve Stimulation: Twitch of the patella (quadriceps) at 0.2-0.5 mA current Local anesthetic: 20 mL Complexity level: Basic
question
Bier Block
answer
Indications: Surgery on the wrist, hand and fingers. Local anesthetic: 15 mL of 2% lidocaine (up to 40ml) Complexity level: Basic
question
Malignant Hyperthermia Cause
answer
-Open ryanodine receptor allows continuous release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. -Triggers: all anesthetic gases -Nitrous is safe.
question
MH S/S and treatment
answer
Trigger: all halogenated anesthetics and succinylcholine (nitrous is safe) Increasing CO2, hyperthermia Treat: dantrolene 2.5 mg/kg every 5 minutes up to 10mg/kg Anesthetic plan: MAC, regional, TIVA (for general) Flush machine, new absorber, new circuit
question
Stages of Anesthesia: Stage 1
answer
Stage 1: Analgesia Stage 2: Delerium Stage 3: Surgical Anesthesia Stage 4: Overdose (medullary paralysis) Stage 1: -Beginning of induction drug to loss of consciousness -dizzy, loses sense of reality -lessened sensitivity to touch and pain -hearing is increased, response to noise intensified
question
Stage 2
answer
Delirium or excitement phase: loss of consciousness to onset of rhythmicity of VS into entry of surgical anesthesia -Struggling, ? muscle tone, jaw sets, eyelids closed, may breath hold and retch , nystagmus -Reflexes are hyperactive -Respiratory pattern is irregular -"Goofy" disconjugate eyes - NEVER EXTUBATE (laryngospam)
question
Stage 3
answer
Surgical or Operative Stage: -End of stage 2 to cessation of respirations - Respirations regular, patient likely intubated or LMA There are 4 planes of anesthesia in Stage 3. -Most surgical procedures occur in plane 2.
question
Stage 4
answer
Death... cessation of respiration to death, respiratory and circulatory arrest. Circulatory collapse. -all reflexes absent - flaccid paralysis - marked hypotension - weak irregular pulse
question
IV anesthetics & pregnancy
answer
-Most are safe - Versed avoided but may be ok -Fentanyl & propofol frequently used
question
Inhalational Anesthetics & pregnancy
answer
All gas anesthetics: -depress the uterus, ? risk of miscarriage - may increase blood loss during intrauterine procedures - reduced MAC required due to higher circulating blood volume hemodilution
question
Benefit of continuous infusion of opioids
answer
-Used for maintenance of general anesthesia -Balanced technique -Morphine, fentanyl, alfentanil, sufentanil, remifentani, demerol
question
Which factors lower MAC requirements?
answer
? age Hypothermia Depressant medications ?? agonists Acute ethanol consumption Metabolic acidosis Hypoxemia Anemia Hypotension Hyponatremia Pregnancy N?O, ketamine, lidocaine, clonidine, lithium
question
Which factors raise MAC requirements?
answer
Kids (higher metabolism/RR) Hyperthermia Hyperthyroidism Hypernatremia Chronic alcohol consumption MAO Inhibitors Cocaine, levodopa
question
What is the mechanism of action of local anesthetics?
answer
- Block Na channels preventing depolarization of the cells.
question
Which medications reverses narcotics?
answer
- Narcan .04-4mg IV q 3 minutes
question
Which medications reverses benzodiazepines?
answer
- Flumazenil -Competitive agonist at receptor binding sites. Sole benzodiazepine antagonist. - 0.2 mg doses (2ml) titrated up gradually to desired LOC, up to 1mg
question
Which medications reverse paralytics?
answer
-Neostigmine .04-.07mg/kg up to 5mg (combine with robinul because neostigmine will increase salivation) - Endrophonium .5-1mg/kg (combine with atropine to block muscarinic cholinergic effects)
question
Desflurane Advantages & Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: quick, rapid uptake & elimination, minimal metabolism Disadvantages: pungent, respiratory irritant, expensive, tachycardia
question
Desflurane dosing & metabolism
answer
Dosing: 3-9% induction, 2-6% maintenance Metabolism: <0.1%
question
Isoflurane Advantages & Disadvantages
answer
Advantages:cheap, minimal metabolism Disadvantages: pungent, respiratory irritant, slow uptake & distribution, coronary steal
question
Isoflurane dosing & metabolism
answer
Dosing: 1-4% induction, .5-2% maintenance Metabolism: <1%
question
Sevoflurane Advantages & Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: not respiratory irritant, rapid uptake & distribution non-pungent Disadvantages: metabolized, compound A, expensive, ? fluoride ion concentration
question
Sevoflurane Dosing & Metabolism
answer
Dosing: 4-8% induction 1-4% maintenance Metabolism: 3-6% by liver
question
What are each anesthetic agents blood/gas solubility coeffcient? What does this number tell you?
answer
Des:0.42 Iso:1.4 Sevo: 0.6 N?O: .47 SPEED -The proportion of the anesthetic that will be soluble in the blood. -The more soluble the drug, the slower the uptake. (The gas is "tied" up and unable to get to brain.) - Poorly soluble = rapid uptake
question
What are the MAC values of each anesthetic? What does this number mean?
answer
Des: 5.8 Iso: 1.15 Sevo: 2 N?O: 105 DOSE
question
What are the oil/gas values of each anesthetic? What does this number mean?
answer
Des: 18.7 Iso: 99 Sevo: 50 N?O: 105 POTENCY
question
What is the second gas effect?
answer
Simultaneous administration of a relatively slow agent, such as iso, and a faster agent, such as N?O will speed the onset of the slower agent.
question
Nitrous Oxide Advantages & Disadvantages
answer
Advantages: moderate analgesia, rapid uptake & elimination, non pungent, does not ?BP Disadvantages: expansion of closed air spaces, ?PONV, immune supression, teratogenic, supports combustion, weak
question
Nitrous Oxide Dosing & Metabolism
answer
Dosing: 50-70% induction & maintenance Metabolism: <1%
question
Benzodiazepines
answer
-Versed- quick on and off .25 mg for elderly people, 1mg-2mg for most others
question
MAC of a Halogenated Anesthetic
answer
-The dose is expressed as minimum alveolar concentration necessary to produce anesthesia on surgical stimulation. -Faster the lung and therefore brain concentrations rise the faster the anesthesia is achieved.
question
MAC defined
answer
-MAC -MAC awake 1/3 (amnesia) -MAC bar 1.5 (block adrenergic receptors) usually goal for start of surgery -MAC intubation 2 (ETT, very stimulating)
question
Ventilation Effect
answer
The faster and more deeply a patient breathes or is ventilated the faster the patient loses consciousness and emerges. Ventilation/perfusion deficits or poor lung function hinders inhalation drug administration. Affects fast drugs the most.
question
Uptake into the Blood
answer
Vessel Rich: heart, liver, kidneys, brain, to a lesser degree muscle Vessel Poor: fat ? in CO slows uptake. Pediatric uptake is faster than adults (kids have higher alveolar ventilation per weight ratio).
question
Concentration Effect and Over-pressurizing
answer
-Concentration effect: A loading dose is given to speed initial uptake & turn up the flows ?Fi% -"Over-pressurizing" is the process of significantly increasing a volatile anesthetic delivered to a patient to increase the alveolar concentration and therefore the amount dissolved in the blood, to speed uptake. Henry's Law
question
Diffusion hypoxia
answer
-Occurs during emergence - High concentrations of nitrous have been given - Nitrous is turned off - Nitrous exits the body quickly through the lungs and is replaced by nitrogen in the air - Results in transient dilution of oxygen and carbon dioxide - Administration of 100% FIO? for several minutes will prevent
question
Placement guidelines for Epidural
answer
-Intercristal/Tuffier's line - Feel iliac crest, guide placement of epidural - mark L3/L4 space, have patient arch back - "heavy" on solutions mean hyperbaric, goes down -Isobaric same as CSF, hypobaric lower than CSF -Marcain .5-.75% in dextrose commonly used
question
Which of the following correctly describes ketamine dose for IV induction? IM
answer
- 2-3 mg/kg IV - 4-6 mg/kg IM Mixed with atropine to counteract salivation.
question
What is the longest acting local anesthetic?
answer
- Epi with tetracaine
question
What is a normal dibucaine number?
answer
-80, 80% of the PChE inhibited by dibucaine - Dibucaine Inhibition Test
question
ER, ORIF for finger reduction, ETOH
answer
- ETOH lowers MAC requirement with acute intoxication (already at .2-.3 MAC) - Chronic ETOH with raise MAC requirements (noticeable with propofol)
question
What causes bradycardia in kids?
answer
-Succinylcholine -Mix with atropine to counteract bradycardia
question
If eyes are midline which stage are they in?
answer
- Stage 1 or 3
question
During what stage do you NEVER extubate?
answer
Stage 2 -Delirium, prone to laryngospasm
question
Why are paralytics avoided in kids?
answer
- Want to maintain airway, respiratory drive - Succinylcholine causes MH, bradycardia - Use demerol and propofol for induction -Avoid reversals
question
What do narcotics do to pupils? Atropine?
answer
- Pinpoint: narcotics - Dilate: atropine
question
What medication can you use when a patient on ACE inhibitor is not responding to ephedrine or neosynephrine?
answer
- few units of vasopressin
question
Most adults use which size of MAC blade?

answer
3
question
Most adults use which size Miller blade?

answer
2 ( used ages 2+)
question
What is the size for oral airways? Colors?

answer
8- green 9- yellow, most often used 10-red
question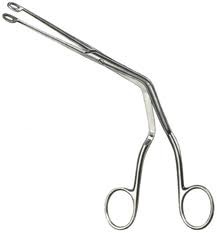
What are Mcgill forceps used for?

answer
-Nasal intubation
question
Epiglottis hangs down so which blade works better?
answer
Usually Miller blade, although Mac is easier to learn with. MAC- lifts vallecula but epiglottis hanging down (in & up motion) Miller- lifts up epiglottis tougher to see, tongue obstructs
question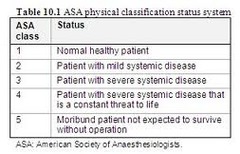
ASA Classifications

answer
ASA 6: declared brain dead, organ donor ASA E: Emergency procedure, added to ASA I-VI Used for reimbursement/ report.
question
Most outpatient surgical centers will not operate on a patient above which ASA class?
answer
ASA 3
question
Narcotics
answer
Used for maintenance of general anesthesia "Balanced technique" -Most common fentanyl - Morphine, fentanyl, alfentanil, sufentanil, remifentanil
question
Dissociative Agents
answer
Ketamine (only anesthetic/analgesic combo) 2mg/kg -Dissociates patient from environment - Minimal depression of protective reflexes - Hallucinations are common on emergence
question
Muscle Relaxants
answer
-Defasciculating dose: depolarizer before succinylcholine to prevent muscle spasm/ soreness after surgery (5-10mg zemuron/rocuronium) - Succinylcholine, atracrurium, pancuronium, rocuronium, cisatracurium- (elimination PChE in blood)
question
Barbituates
answer
-Methohexital: ECT, dental, cardioversion, lowers seizure threshold 2mg/kg -Sodium Thiopental: 2.5% solution dose 4mg
question
Non-barbituates
answer
Propofol: Induction 1-3mg/kg
question
What is the MAC of halothane?
answer
MAC = .74 Hepatitis, slow acting, good for inhalation
question
What are some tricks you can use during long cases?
answer
8 hour case, anesthetics into fat, emergence on more expensive agent, maintenance on Iso, cheaper.
question
5 Questions in the following format
answer
Laparascopic appendectomy, (regional/general/IV sedation) anesthetic. This patient (will/will not/might) recieve paralytics. This patient will be in the (supine/prone/lateral/lithotomy) position. *If it is laparascopic the patient will require paralytic.
question
How can you tell when the case is nearing completion?
answer
Suture sizing: -small 10, big 0 - know progression of case Counting sponges/supplies towards the end of case.
question
How can you tell with propofol when you can intubate or bag?
answer
- Eyelash reflex -Listen with precordial stethoscope
question
Know brand/trade names of drugs
answer
Fentanyl: sublimaze Sufenta: sufentanil Alfenta: alentanil Demerol: merperidine Marcain: bubivipcaine: sensorcaine Lidocaine:xylocaine Remifentanil:ultiva Narcan:naloxone Rocuronium: zemuron Ravlon: rapacuronium (bronchospasms) Propofol: diprivan Versed: midazolam Edrophonium:reversol:enlon:tensilon Succinylcholine:anectine:quelicin Neostigmine: prostigmin
question
List local anesthetics short acting to long acting.
answer
Lidocaine>bubivicaine>tetracaine
question
Does epinephrine work well to prolong action of bubivicaine?
answer
Not really. Epi works well to prolong duration of lidocaine and tetracaine.
question
Advantages of Continuous Opioid Infusion Box12-4
answer
Hemodynamic stability Decreased side effects Reduced need for opioid-reversal agents Reduced need for vasopressor drugs Suppression of cortisol and vasopressin response to Cardiopulmonary bypass Reduced total dosage of opioids Decreased recovery time
question
The primary factors that influence absorption of the inhalation anesthetics are:
answer
Ventilation Uptake into the blood Cardiac output Solubility of the anesthetic drug in the blood Alveolar-to-venous blood partial-pressure difference (assumed to be the same as in the brain) Concentration Second gas effect
question
ASA Examples
answer
ASA 1: normal healthy patient ASA 2: smoker, OB, thyroid, HTN, mild health issue, DM, chronic bronchitis, anemia, morbid obesity, age extremes, heart disease-slightly limits activity ASA 3: COPD, CAD-limits activity, poorly controlled HTN, DM with vascular complications, angina pectoris, previous MI ASA 4: renal or hepatic failure, CHF, persistent angina, advanced pulmonary disease ASA 5: massive trauma , AAA, uncontrolled hemorrhage "Love to give scenarios and have you pick status"



