IEN Exam #2 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is crashing a project?
answer
The process of accelerating or expediting a project to reach an earlier completion date
question
Why choose an earlier completion date? (4)
answer
1. The initial schedule may be too optimistic 2. Market needs change 3. Project slipped behind schedule 4. Contractual obligations
question
How to accelerate activities (3)
answer
1. Improve the productivity of existing project resources 2. Changing the working method employed for the activity - alter technology or types of resources 3. Increasing quantity of personnel, plant, equipment
question
Time vs. Cost slope ($ per t)
answer
(Crash Cost - Normal Cost)/(Normal Time - Crash Time)
question
Why are cost estimates needed? (5)
answer
1. Support good decisions 2. Determining project cost 3. Is the project worth doing? 4. Poor estimates = failed projects 5. Cash flow needs
question
Who should be making estimates?
answer
Person(s) most familiar with task at the work package level - experts
question
Why is it good to have multiple sources of a cost estimate?
answer
Better chance of being reasonable and realistic when several people with relevant experience are used Discussion of differences can eliminate estimate errors
question
What can be considered 'Normal Conditions'
answer
Ex. working 8 hours a day, working 2 shifts, using 3 programmers Includes establishment of time units for projects
question
How should contingencies be considered?
answer
Estimates should *NOT* include contingencies Assume normal or average conditions always
question
Why add risk assessments to estimates
answer
Stakeholders can consider alternative methods and alter process decisions
question
What are top-down estimates?
answer
Cost estimates derived from using experience and/or information to determine project duration and total cost Sometimes made by top managers with very little knowledge of the processes
question
What are bottom-up estimates?
answer
Cost estimates that are pushed down to the work package level - estimates come from the people closest to the work
question
What is the Preferred Approach? (Process)
answer
Make rough top-down estimate Develop Work Breakdown Structure Make bottom-up estimates Develop schedule and budget Reconcile differences between top-down and bottom-up estimates
question
Top-Down Approaches (4)
answer
Consensus Methods Ratio Methods Apportion Methods Learning Curves Methods
question
Consensus Methods
answer
Pooled experience of senior management to estimate project duration/cost - best guess
question
Delphi Method
answer
Developed by RAND Corp. in 1969 for tech forecasting Group decision process by panel of experts about likelihood of events
question
Ratio Methods
answer
(aka parametric methods) Use of ratios to estimate Ex. Contractors using number of square feet to estimate
question
Apportion Methods
answer
Extension to ratio methods, costs are apportioned as a percentage of the total cost
question
Learning Curves Methods
answer
When projects repeat same tasks/groups of tasks, and performance improves with repetition
question
Bottom-Up Approaches (3)
answer
Template Methods Parametric Procedures Applied to Specific Tasks Range Estimating Method
question
Template Methods
answer
Estimates from past projects can be used as starting point if project is similar, and adjust to reflect the differences
question
Parametric Procedures Applied to Specific Tasks
answer
Application of parametric methods at work package level
question
Range Estimating Methods
answer
Calls for Low, Average, and High estimates when work packages have significant uncertainty
question
Types of Costs
answer
Direct costs - Labor, Material, Equipment Direct Overhead - Salaries, Space Rental, % applied to materials and labor Gen. and Admin. Overhead - Advertising, Accounting, senior management, % of total direct cost
question
Costs
answer
Labor Materials Subcontractors Equipment/Facilities Travel
question
Problems with cost estimation (6)
answer
1. Low initial estimates 2. Unexpected technical difficulties 3. Lack of definition 4. Scope creep 5. Inflation/economic factors 6. Interaction costs
question
Pitfalls of Estimating
answer
Misinterpretation of statement of work Omissions Overly optimistic schedule Inaccurate WBS Failure to account for risks No account for inflation
question
Why Monitor and Control people? (3)
answer
1. Control holds people accountable 2. Prevents small problems from developing into large problems 3. Helps to maintain focus
question
What does a project monitoring system involve?
answer
What data to collect How, when, and who will collect the data Analysis of the data Reporting current progress
question
What data is collected?
answer
Actual activity duration Resource usage and rates Actual costs (All are compared against planned times, resources, and budgets)
question
4 steps in the project control process
answer
1. Setting a baseline plan 2. Measuring progress and performance 3. Comparing plan against actual 4. Taking action
question
Setting a baseline plan
answer
Derived from the cost and duration information found in the WBS Derived from the time-sequence data from the network
question
Measuring progress and performance
answer
Quantitative measures - time and budgets Qualitative measures - meeting customer technical specs and product functions
question
Comparing plan against actual
answer
Measure deviations from plan Frequent status reports should allow for early detection of variations
question
Taking action
answer
For significant deviations, corrective action needed
question
Earned Value Management (EVM)
answer
Pioneered by Dept. of Def. in the 1960s Considers joint impact of time, cost, and performance
question
Planned value PV
answer
A cost estimate of the budgeted resources scheduled across project's life cycle Also called BCWS(cheduled)
question
Earned value EV
answer
The real budgeted cost, or "value" of the work that has actually been performed to date % complete x original budget Also called BCWP(erformed)
question
Actual Cost AC
answer
The cumulative total costs incurred in accomplishing the various project work packages Also called ACWP(erformed)
question
Cost Variance CV
answer
Difference between the Earned Value and the Actual Costs CV = EV - AC A negative value indicates a cost overrun condition
question
Schedule Variance SV
answer
Difference between the Earned Value and Planned Value SV = EV - PV A negative value indicates a behind schedule condition *always use values with a V in them
question
Schedule Performance Index
answer
EV/PV Gives the efficiency in operating the project 1/SPI x time unit length of project = time to completion
question
Cost Performance Index
answer
EV/AC Gives the efficiency with which the work has been accomplished 1/CPI x original budget = cumulative cost to completion
question
What is project risk?
answer
Any possible event that can negatively affect the viability of a project
question
What is risk management?
answer
Identifying, analyzing, and responding to risk factors throughout the life of a project
question
Types of risk management
answer
Proactive management Reactive management
question
Definition of risk (function)
answer
Risk of an event = f(Likelihood, Impact) Likelihood is the probability of occurrence Impact is the amount at stake
question
Systematic Risk Management Process (I-IV)
answer
I. Risk Identification II. Analysis of probability and consequences III. Risk mitigation strategies IV. Control and documentation
question
Financial Risk
answer
Financial exposure a firm opens itself to when developing a project Ex. a large up-front capital investment required
question
Technical Risk
answer
When new projects contain unique technical elements or unproven tech Ex. trying a new material for the first time
question
Commercial Risk
answer
For projects that have been developed for a definite commercial intent such as profitability, a constant unknown is degree of success
question
Execution Risk
answer
The specific unknowns related to the execution of the plan Ex. Weather, earthquake, poorly trained staff
question
Contractual/Legal Risk
answer
Strict terms and conditions are drawn up in advance, companies try to limit their exposure to litigation and liability
question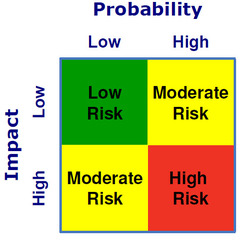
Risk Impact Matrix

answer
Consequences vs. Likelihood boxes High and Low options, produce combinations
question
Customer's Knowledge vs. Contract Type
answer
As the customer's experience level decreases, and the contract becomes more complex, there is a positive relationship on a graph for Future Risk
question
Risk Mitigation Strategies
answer
Accept Risk - Do nothing when risk is low Minimize Risk - Intervening for damage control Share Risk - Risk allocated proportionally among multiple members Transfer Risk - Client handles overruns (ex. fixed price contracts)
question
Contingency reserves
answer
Provision for unforeseen elements of a cost within the defined scope Ex. construction projects setting aside 10-15% of a project for contingency
question
A risk profile
answer
A list of questions that address traditional areas of uncertainty on a project
question
Questions in a risk profile
answer
Are the tech. requirements stable? (Technical Requirements) How reliable are the cost estimates? (Budget) Are quality considerations built into the design? (Quality) Are there any ambiguities in the contractor task definitions? (Contractor)
question
General types of risks
answer
Business risks Insurable risk - Direct property damage - Indirect consequential loss - Legal liability - Personnel
question
Types of risk (PMI Method)
answer
External - unpredictable External - predictable Internal - Non-technical Internal - Technical Legal
question
Purpose of project closeout
answer
Formalizing acceptance of the project or phase and bringing it to an orderly end
question
Closeout objectives
answer
Meet contractual obligations Transition project to next phase Analyze overall performance Close project office Pursue follow-up
question
Contract closeout
answer
Completion and settlement of the contract
question
Administrative closure
answer
Generating, gathering, and disseminating information to formalize project completion
question
Project closeout organizational structure
answer
Project closeout - Project organization: evaluate performance - Financial: conduct audits and prepare final report - Contracting: notify and pay suppliers - Site: close facilities and return equipment
question
Types of project closure
answer
Normal Premature Perpetual Failed Project Changed Priority
question
Normal closure
answer
most common, a completed project
question
Premature closure
answer
Completed early with some parts of the project having been eliminated Ex. first to market with unfinished product
question
Perpetual closure
answer
Projects that never seem to end. Constant add-ons, indicative of poorly conceived scope
question
Failed Project closure
answer
Projects fail b/c of circumstances beyond control of team
question
Changed Priority Project Closure
answer
Organizations' priorities often change and strategy shifts direction
question
How to implement closure activities (7)
answer
1. Delivery acceptance 2. Shutting down resources 3. Reassigning team members 4. Closing accounts and paid bills 5. Client sign-off 6. Post implementation audit 7. Final report
question
What goes into the final report? (5)
answer
Executive Summary Review and Analysis Recommendations Lessons Learned Appendix
question
Why document the project?
answer
Reference for future changes Historical record Training resource Input for performance evaluation and further training



