Hematology, RBC’s & Cell Morphology. – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Ruboblast
answer
Large Round nucleus. Thin rim of royal blue cytoplasm. Should only be seen in bone marrow.
question
Prorubicyte
answer
Round nucleus. Royal Blue Cytoplasm. Rare to see in peripheral blood.
question
rubicyte
answer
Dark purple with blue/black chromatin clumps. Seen in anemic animals. One of the youngest form of RBC
question
Metarubicyte
answer
Also know as NRBC. Increased numbers= regenerative anemia. Neoplasia. Led toxicity. Small like lymphocyte Dark blue nucleus. Seen in anemic animals. Young form of RBC
question
Polychromatophil
answer
Reticulocyte. No neclus. Basiophilic cytoplasm. Use NMB. Cats have 2 types.
question
Erythrocyte
answer
Mature celll. Pink color. Less hemoglobin in the middle.
question
Anisocytosis
answer
Varation in size of RBCs. Iorn Deficiency. Responce to anemia.
question
Macrocytes
answer
Increase number of larger than normal RBCs
question
Microcytes
answer
Smaller than normal. Iorn defiency. Decreased MCV
question
Normacyte
answer
Refers to normal mature RBCs. Pootles have increased MCV Akitas have smaller Rbcs
question
Normochromic
answer
Normal color of RBC.
question
Polychromasia
answer
variation in hemoglobin content in erythrocyte. Reticulocytes when stained with NMB
question
Hypochromasia
answer
Less staining. Decrease color. Narrow rim of hemoglobin. Iron deficiency.
question
Hyperchromasia
answer
Abnormally increased hemoglobin content. Does not occur in RBCs. Increased MCHC. Hemolysis,heinz body formation.
question
poikilocytosis
answer
Variation in cell shape. Liver, splenic, kidney and vessel problems.`
question
Acanthocyte
answer
Spur Cell. Cells with irregularly shaped margins/projections from the cell wall. Renal disease. Liver Disease.
question
Echinocyte
answer
Burr cell RBCs with evenly distributed spicules on the membrane spiculated cells with short, evenly spaced projections; artifactual result due to slow drying blood smear, renal disease, urethric animals, lymphoma or rattle snake envenomation
question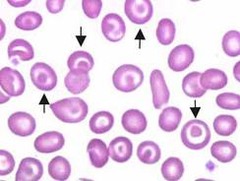
codocyte

answer
target cell liver disease
question
Leptocyte
answer
RBC with increased surface area and decreased volume. large, thin cell. associated with regenerative anemia.
question
Stomatocyte
answer
Erythrocyte with an oval-shaped central pallor. Aka mouth cell
question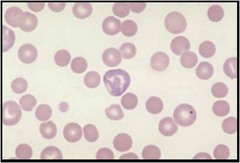
Spherocyte

answer
Herdeditary spherocytosis, Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. RBC That appears smaller than normal.Dense and dark staining.
question
Schistocytes
answer
Helmet Cell . Fractured or fragmented RBC. associated with shear injuries, seen in microangiopathy, fibrin strands in circulation, DIC, iron deficiency, liver disease, heart failure and hemangiosarcoma
question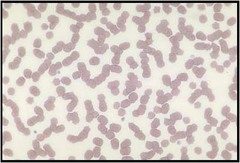
Rouleaux

answer
Cells are stacked; commonly seen in healthy horses; the result of increased fibrinogen (or other globulin). inflammatory diease. Alteration in plasma Proteins.
question
Aggluation
answer
when rbcs clump together. Reaction during or after blood transfusion.
question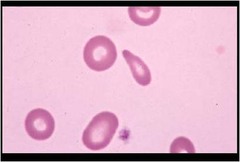
Dacryocyte

answer
tear drop cell. due to membrane damage during maturation in a crowded bone marrow. associated with extramedullary hematopoiesis, meylofibrosis, bone marrow tumors, myelomoas, leukemias.
question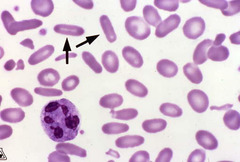
Elliptocyte

answer
non-nucleated ovalocyte. Camalids
question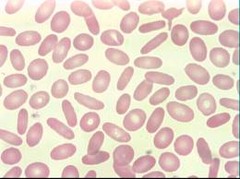
Ovalcyte

answer
another name for elliptocyte Birds, Reptiles & Frogs
question
Keratocyte
answer
spiculated RBC with two or more projections, formed due to damage to the red blood cell by intravascular trauma resulting in a pseudovacuole that may "blister" and break open
question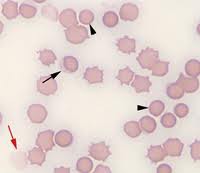
Ghost Cells

answer
associated with intravascular hemolysis
question
Eccentrocytes
answer
ragged appearance with poorly hemoglobinized fringe of cytoplasm on one side of cell. due to onion & red maple leaf toxicity
question
Drepanocytes
answer
Sickle Cell.
question
Anulocyte
answer
bowl-shaped. form as a result of loss of membrane flexibility that does not allow cells to return to normal after passing through a capillary. may be seen in any acute disease.
question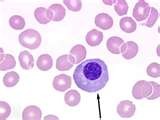
Nucleated Red blood Cell

answer
a red blood cell that contains a nucleus. It resembles a white blood cell under low-power magnification and may inflate the white blood cell count. Splenic disease. Lead poisoning.
question
Howell Jolly Body
answer
nuclear remnant remaining in the red blood cell after the nucleus is lost commonly seen in pernicious anemia and hemolytic anemias
question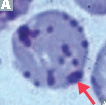
Heniz body

answer
Which red blood cell inclusion is seen as protruding from the edge of the cell. Onion. Diabetes



