Gynecologic Oncology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion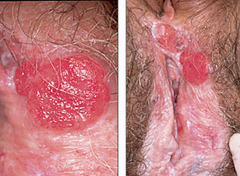
What is vulvar neoplasia?

answer
1. Starts as VIN - Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia I, II,III 2. Progesses into Invasive vulvar carcinoma
question
What are some S/S of Vulvar neoplasia?
answer
-Pruritis -pigmentations -ulceration
question
What is the Dx for vulvar neoplasia?
answer
Biopsy
question
What is the TX for vulvar neoplasia?
answer
1. For VIN you can do a local excision 2. For Invasive carcinoma - vulvuectomy
question
What is Vaginal Neoplasia?
answer
1. Starts as VAIN - Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia I,II, III 2. Progresses to Invasive vaginal cancer (rare) 3. Usually an incidental finding on colposcopy
question
How do you Tx Vaginal cancer?
answer
- Treat VAIN with local excision - Treat invasive cancer with vaginectomy
question
What is cervical cancer?
answer
Cancer of the cervix - duh • Premalignant disease very common • Screening is easy and can detect treatable premalignant disease (PAP smear)
question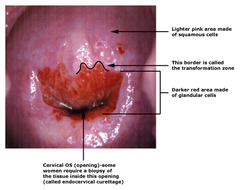
What is the cervical anatomy?

answer
1. The smooth pink is the ECTOCERVIX - Squamous epithelium 2. The deep red near the os is the start of ENDOCERVIX - Glandular epithelium - may not always be evident outside the os 3. *TRANSITION ZONE* - this is where the cells are changing -Want Pap smear here
question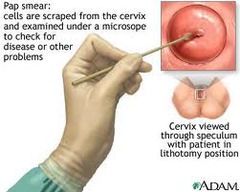
What are the current Pap screening guidelines?

answer
• Begin pap smear and annual pelvic exam at age 18 or after sexual activity begins (to monitor HPV exposure) • After 3 consecutive normal pap smears, frequency is at discretion of physician
question
What are the RISK FACTORS for cervical cancer?
answer
1. Early first coitus - immature cervix less likely to fend off HPV 2. Multiple sex partners 3. Infection with HPV (subtypes *16, 18*, 31,33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, 69) 4. Smoking 5. Low socioeconomic status 6. HIV infection or other immunodeficiency - presence of cervical cancer in HIV+ will push them into the AIDS catagory
question
What are the S/S of Cervical Cancer?
answer
** Preinvasive disease usually asymptomatic -Symptoms *occur when cancer is invasive* • Watery, blood-tinged vaginal discharge • Postcoital spotting • Painless menorrhagia
question
What is the Method for a "Good" Pap Smear?

answer
1. ot during menses 2. Tell pt. to avoid intercourse, douches, lubricants, and tampons for 24 hours prior 3. Do pap before bimanual 4. Water lubrication only (if needed) OLD SHCHOOL OF DOING IT: 1. Sample endocervix with brush 2. Sample ectocervix with spatula • Include T-zone, spread thin on slide MODERN THIN PREP: 1. Use Broom to take sample - Long bristle go in os and get endocervix - short bristles scrape ectocervix **Turn in 1 direction 2. Place head of brrom in liquid solution
question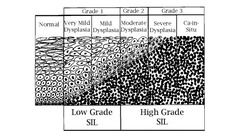
What is the Bethesda System for Pap results?

answer
How pathologists classify Pap results: 1. * Squamous cell Findings* - *ASC* - Atypical squamous cells • *ASCUS* - Of undetermined significance • *ASC-H* - Cannot exclude HSIL - *LSIL* Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion - *HSIL* High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion - Squamous cell carcinoma 2. *Glandular Cell Findings* - *AGC* - Atypical glandular cells - (endocervical or endometrial) - Atypical glandular cells, favor neoplastic - *AIS* Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ - Adenocarcinoma
question
What does ASCUS really mean?
answer
They found some weird cells in the sample but can't really pinpoint the reason
question
How do you manage benign cellular changes found on pap due to infex or atrophy?
answer
Treat the underlying cause
question
What are some things other than cancer that a pap can pick up?
answer
• *Organisms* - Trichomonas (swimmers) - Candida (yeast) - Bacterial flora shift (BV) - Actinomyces (IUD) - Cell changes consistent with herpes • *Other non-neoplastic findings* - Reactive cellular changes associated with inflammation, radiation, or IUD • *Glandular cells post hysterectomy* • *Atrophy*
question
How do you manage ASCUS?
answer
1. Repeat Pap in 4-6 months x 2 - if still ASCUS then colposcopy *OR* 2. HPV DNA test, if high risk HPV, then colpo *OR* 3. directly to colposcopy
question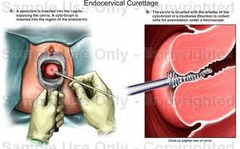
How do you manage ASC-H?

answer
- Colpo with biopsy and ECC - ECC is endocervical curettage
question
How do you manage LSIL?
answer
Colposcopy or Observe
question
How do you manage HSIL?
answer
Colposcopy
question
How do you manage AGUS?
answer
1. Colposcopy 2. possible endometrial biopsy if >35 or abnormal bleeding
question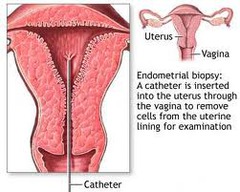
How do you manage Aytpical endometrial cells?

answer
Endometrial biospy ***remember these cells come from the uterus and not the vagina
question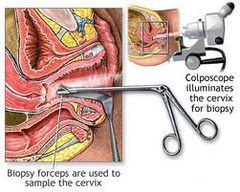
What is a colposcopy?

answer
• Inspection of cervix and vagina under magnification • Inspect for atypical vessels • 3% acetic acid (vinegar) applied to cervix for acetowhitening - turns irregular areas white • Iodine application: non-staining areas
question
What should you do if you seen something on colposcopy?
answer
• Suspicious areas are biopsied • Endocervical curettage
question
Does the pap DIAGNOSE cancer?
answer
NOPE - Tx is done by colposcopy and biopsy **Pap is SCREENING
question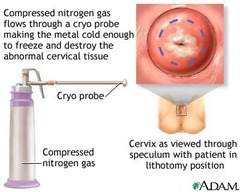
When would you use cryotsurgery?

answer
LSIL lesions
question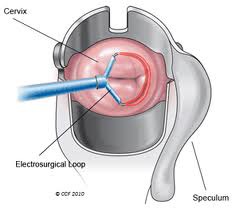
When would you use LEEP?

answer
- loop electrosurgical excision procedure - HSIL with negative ECC - Persistent LSIL or atypia
question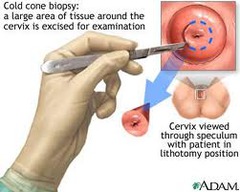
When do you do a cone biopsy?

answer
Cone biopsy: - Unsatisfactory colposcopy - Endocervical neoplasia - Cytology grade > histology - Microinvasive carcinoma (Tx) - Adenocarcinoma in situ (Tx) ** Can lead to stenosis/scarring of the cervix or incompetence of the cervix
question
When do you do a hysterectomy?
answer
- + ECC margin on cone with no desire for future fertility - Microinvasive disease - Adenocarcinoma in situ
question
What are the indications for for the HPV Vaccine?
answer
- Females age 9-26 • HPV 6, 11 benign warts • HPV 16, 18 (70% of cervical cancers) • Most effective prior to the start of sexual intercourse
question
What is endometrial hyperplasia?
answer
• Some types of endometrial proliferation may lead to carcinoma • Symptoms include irregular or postmenopausal bleeding • Diagnosed by endometrial biopsy
question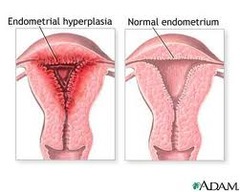
What is a simple (cystic) hyperplasia?

answer
Inactive endometrium, no malignant potential: -Cells look like Swiss cheese
question
What is Complex (adenomatous) hyperplasia?
answer
increased # of glands, gland crowding - may lead to malignancy
question
What is Hyperplasia with atypia?
answer
irregular nuclei, may progress to malignancy
question
What is the best TX for Hyperplasia in a woman who is under 40 yo?
answer
1. medical (progesterone) 2. surgical D&C 3. repeat biopsy in 3-6 months. 4. If childbearing complete, do hysterectomy
question
What is the best TX for Hyperplasia in a woman who is over 40 yo?
answer
1. either treat as for < age 40 2. offer hysterectomy. ***If atypia present, do hysterectomy - make sure she has completed childbearing
question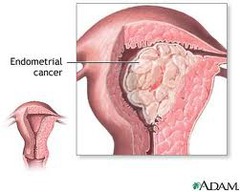
What are the risk factors for Endometrial Carcinoma (cancer or Uterine lining)?

answer
1. Any cause of increased estrogen 2. Early menarche 3. Exogenous unopposed estrogen (HRT) 4. Polycystic ovarian disease 5. Obesity 6. Nulliparity (never been knocked up) 7. HTN 8. Diabetes 9. Family history 10. Late menopause 11. Radiation exposure ***BC pills have no effect on this**
question
What are the S/S of Endometrial cancer?
answer
peri or postmenopausal bleeding
question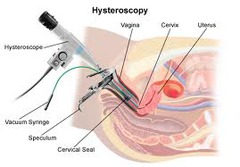
How do you Dx Endometrial Cancer?

answer
1. endometrial biopsy 2. ultrasound for endometrial thickness and consistency 3. Hysteroscopy and D&C if EMB unsuccessful or not correlated with TVS (transvaginal ultrasound), or symptoms persist
question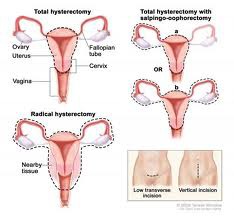
What is the Tx for Endometrial Cancer?

answer
1. surgical staging-TAH/BSO, 2.omentectomy (removal of omentum) 3. lymph node dissection 4. radiation, 5. chemotherapy
question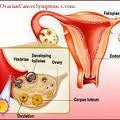
What are the S/S of Ovarian Cancer?

answer
• Few early symptoms • **Most cases stage III-IV at time of diagnosis • Abdominal enlargement • Pain • Early satiety • Menstrual irregularities - Polyuria
question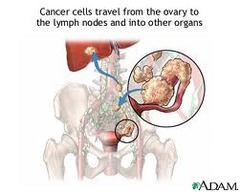
What are the risk factors for Ovarian Cancer?

answer
• Nulliparity • BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations • Family history • Advancing age - Seems to be related to # of ovulations
question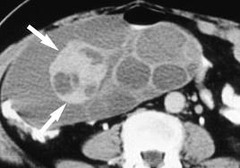
How do you Dx Ovarian Cancer?

answer
• Pelvic exam • Ultrasound • CT scan
question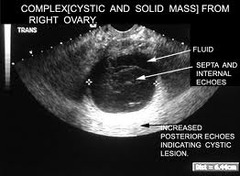
What are the signs you'd see on US for Ovarian Cancer?

answer
• Solid • Septations • Papillations • Size • Adhesions • Bilateral • **Ascites
question
What are the tumor markers for Ovarian Cancer and when would you use them?
answer
*CA-125, AFP, HCG* - Use only to follow disease after surgery - Not really used for screening in high risk patients - Not present in all tumors
question
What are the Tx for Ovarian Cancer?
answer
• TAH/BSO • Omentectomy • Lymph node dissection • Peritoneal washings • Irradiation • Chemotherapy • Tumor debulking • Second look laparoscopy later, or if tumor markers rise
question
What are peritoneal washings?
answer
a procedure used to look for malignant cells, i.e. cancer, in the peritoneum. Peritoneal washes are routinely done to stage abdominal and pelvic tumors, e.g. ovarian cancer.
question
What should you do for screening/prevention for Ovarian Cancer?
answer
• Referral for genetic counseling • CA-125 • Pelvic ultrasound • Prophylactic oophorectomy
question
What is Gestational Trophoblastic Disease?

answer
*• Only occurs in presence of a pregnancy* - Also known as *molar pregnancy* • Complete (hydatidiform) or partial moles • Invasive moles • Choriocarcinoma • Placental site trophoblastic tumor - from embryo cells • Incidence of complete or partial mole is 1/1000 pregnancies • *Asian population incidence 2-3x higher* • Complete and partial moles are clinically separate entities - Cause is completely different • Share some characteristics
question
What are the risk factors for Molar Pregnancy?
answer
• Oral contraceptive use • Previous spontaneous abortion • Increased incidence of complete mole in women > age 35 and < age 15 • increased risk if there was a previous molar pregnancy
question
What is a complete Molar pregnancy?

answer
1 sperm fertilizes an empty egg - 46 XX derived from paternal chromosomes-haploid sperm fertilizes empty egg and doubles. *No fetal tissue present* - Can become malignant - Women will be "pregnant" just no fetus
question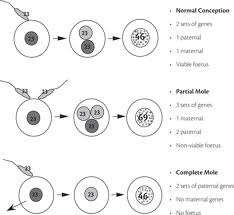
What is a partial molar pregnancy?

answer
2 Sprem fertilize one egg - Fetus develops but cannot live - 69 XXX or XXY:2 sperm fertilize one egg, fetus develops but does not survive
question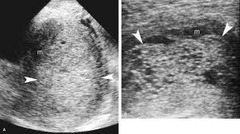
What are the FIRST TRIMESTER S/S of a complete molar pregnancy?

answer
- Vaginal bleeding/ passage of villi - Will bleed a lot - Villi are little vesicles in the blood - Excessive nausea and vomiting - Increased uterine size - *Preeclampsia* *-pre-eclampsia before 20 weeks = molar preggo* - *Greatly elevated hCG* - Hyperthyroidism (rare) - "Snowstorm pattern" on ultrasound: -complex, echogenic masses with cystic spaces in uterus; no fetus
question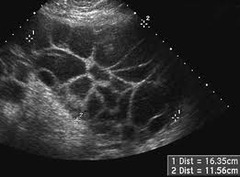
What are the SECOND TRIMESTER S/S of complete molar pregnancy?

answer
*NO FETAL HEARTBEAT* - Vaginal bleeding/ passage of villi - Excessive nausea and vomiting - Increased uterine size - Preeclampsia - Greatly elevated hCG - *Theca-lutein cysts* - 2nd tri ONLY! - *Absence of FH* - Hyperthyroidism - Snow Storm Pattern
question
What are the S/S of PARTIAL MOLAR pregnancy?
answer
• Similar to complete mole with exceptions: - Less intense, later vaginal bleeding - Uterus may be small for gestational age - Possible fetus with FH and heartbeat - hCG elevations not as dramatic - Pathological exam of POC is often only way to diagnose
question
What is the possible DDx for Molar pregnancy?
answer
• Molar pregnancy • Multiple pregnancy • Down syndrome • Germ cell tumor of ovary
question
How do you manage a molar pregnancy?
answer
1. Evacuation with dilation and curettage 2. Hysterectomy if childbearing complete 3. Baseline hCG titer - Must follow until it is ZERO 4. CXR for mets or embolized trophoblastic tissue - Mets do happen with molar pregos 5. Rh status/ Rho Gam
question
What is the Follow Up for a Molar Preggo?
answer
• hCG titers q1-2 weeks until negative • Monthly hCG titers for six negative months • Contraception x 1 year
question
What is Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia?
answer
• Most common after molar pregnancies, especially complete moles • 2 types: - Choriocarcinoma - can occur after any pregnancy, including moles - Placental site trophoblastic tumor (rare) - Persistent molar pregnancy - only occurs following molar pregnancy
question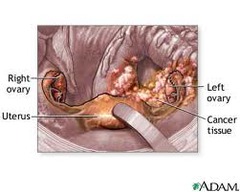
What is a Choriocarcinoma?

answer
a quick-growing form of cancer that occurs in a woman's uterus (womb). The abnormal cells start in the tissue that would normally become the placenta. • *Choriocarcinoma type is most likely to metastasize* - Lung - Vagina - Other pelvic areas
question
What is a persistent molar pregnancy?
answer
Invasive cancer that stays pretty local, like into the uterus.
question
How do you Dx choriocarcinoma or persistent molar pregnancy?
answer
• Vaginal bleeding within 1 year of any pregnancy, but especially molar pregnancy • Persistent or rising hCG titers *(exclude normal pregnancy)*



