Geology test 1 BLINN MOSLEY – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
The study of rock
answer
Geology
question
minerals, stream flow, age dating
answer
Earth Geology
question
deals with physical material and the processes that act on them.
answer
Physical Geology
question
dating rocks, origin of the earth, and study of different types of plants and animals.
answer
Historical Geology
question
other topics in geology
answer
-physics -chem -biology -math
question
geologist working unit of time
answer
one million years
question
what geologists consider to be "recent"
answer
last 10,000 years
question
steps of scientific method
answer
1. make observations 2. make hypothesis 3. test hypothesis 4. theory
question
2 big ideas of geology
answer
1. catastrophism 2. uniformitarianism
question
sudden catastrophic events shape the surface of the earth. EXAMPLE: the grand canyon
answer
catastrophism
question
the processes that we see on earth today happened the same way in the past. EXAMPLE: erosion
answer
uniformitarianism
question
began in the early twentieth century as continental drift
answer
scientific revolution
question
the theory that came from scientific revolution in 1968
answer
plate tectonics
question
makes up continental crust
answer
Granite
question
makes up oceanic crust
answer
Basalt
question
four reasons why Pangea is proven to be real
answer
1. continents fit like puzzle 2.fossils match across continents 3. rock and geological features match 4. ancient climates (plants)
question
seven continental crusts
answer
1.N. America 2.S. America 3. Pacific 4. Eurasia 5. Africa 6. Australia 7. Antartica
question
what gave us a better picture of the ocean floor
answer
ocean ridge system
question
the earth's crust has individual plates that interact in various ways.
answer
theory of plate tectonics
question
the rigid outer layer of earth, includes crust and upper mantle
answer
lithosphere
question
a subdivision of the mantle situated below the lithosphere
answer
asthenosphere
question
a coherent unit of earth's rigid outer layer that includes the crust and upper unit
answer
lithosphere {plate}
question
a boundary in which two plates move apart, resulting in upwelling of material from the mantle to create new seafloor.
answer
divergent plate boundaries (spreading center)
question
process of splitting a continent into smaller pieces
answer
rifting
question
a representation of where divergent takes place
answer
rift valley
question
a hypothesis, first proposed in the 1960's by Harry Hess that suggested new oceanic crust is produced at the crests of mid- oceanic ridges, which are the sites of divergence.
answer
seafloor spreading
question
A linear zone along which continental lithosphere stretches and pulls apart. makes a new oceanic basin
answer
continental rift
question
seafloor spreading leads to the generation of new oceanic lithosphere at mid - ocean ridge systems
answer
divergent plate boundary
question
a boundary in which two plates move together, resulting in oceanic lithosphere being thrust beneath an overriding plate, eventually to be absorbed into the mantle.
answer
convergent plate boundary
question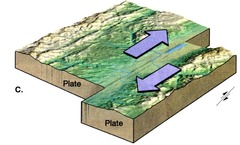
A boundary in which two plates slide past one another without creating or destroying lithosphere.

answer
transform plate boundary
question
three types of plate conversion
answer
1. oceanic - continental 2. oceanic - oceanic 3. continental - continental
question
A narrow, elongated depression of the seafloor
answer
deep - ocean trench
question
the process by which most igneous rocks melt
answer
partial melting
question
mountains formed in part by igneous activity associated with the subduction of oceanic lithosphere beneath a continent.
answer
continental volcanic arc
question
A chain of volcanic islands generally located a few hundred kilometers from a trench where there is active subduction of one ocean plate beneath another.
answer
volcanic island arc
question
A linear zone of irregular topography on the deep - ocean floor that follows transforms faults and their inactive extensions.
answer
fracture zone
question
A mass of hotter-than-typical mantle material that ascends toward the surface, where it may lead to igneous activity
answer
mantle plume
question
a concentration of heat in the mantle, capable of producing magma that, in turn, extrudes onto Earth's surface. EXAMPLE: Hawaiian islands
answer
hot spot
question
A chain of volcanic structures produced as a lithospheric plate moves over a mantle plume
answer
hot-spot track
question
the temp above which a material loses its magnetization
answer
curie point
question
the natural remnant magnetism in rock bodies
answer
paleomagnatism
question
A change in Earth's magnetic field from normal to reverse.
answer
magnetic reversal
question
A magnetic field the same as that which presently exists.
answer
normal polarity
question
A magnetic field opposite as that which currently exhists
answer
reverse polarity
question
A sensitive instrument used to measure the intensity of Earth's magnetic field at various points.
answer
magnetometer
question
composed of minerals
answer
Rock
question
minerals five components
answer
1. must be natural 2. inorganic 3. solid substance 4. definite chemical compound 5. definite crystal structure
question
90 naturally occurring elements not man made
answer
Natural Elements
question
atoms bound together
answer
compound
question
Proton + neutron 0 electron -
answer
Atom
question
number of protons, defines what element it is
answer
Atomic #
question
number of protons and neutrons
answer
Atomic mass
question
a charged atom (positive or negative)
answer
ionic bond
question
six properties of minerals
answer
1. form 2. luster 3. color 5. hardness 6. cleavage 7. specific gravity
question
name the eight mineral groups
answer
1. Oxygen 2. Silicon 3. Aluminum 4. Iron 5. Calcium 6. Sodium 7. Potassium 8. Magnetism
question
partial melting in the lower crust and upper mantle produces...
answer
magma
question
super heated, melted rock deep under ground
answer
magma (hot)
question
liquid rock at the surface
answer
lava (hot)
question
cool and harden deep under ground
answer
Intrusive igneous rocks (cold)
question
cool and harden at surface
answer
Extrusive igneous rock (cold)
question
-minerals that didn't melt -new mineral crystals
answer
solid magma
question
-liquid rock
answer
liquid magma
question
-kept in magma by pressure -happens when pressure decreases -water vapor and carbon dioxide make most of it
answer
gas magma
question
As heat and energy decreases magma starts making a ___________ structure.
answer
crystal
question
five different crystalline structures. ( tetrahedra)
answer
1. single tetrahedra 2.single chain tetrahedra 3. double chain tetrahedra 4. sheet silicate tetrahedra 5. 3D framework tetrahedra
question
igneous rocks are classified by two stuctures
answer
-texture -composition
question
size and orientation of grains
answer
texture
question
what elements are in the rock and in what amounts
answer
composition
question
three factors affecting crystal size
answer
1. rate of cooling 2. amount of silica present 3. amount of dissolved gas
question
result: large crystal size
answer
slow cooling
question
result: small crystal sizes
answer
fast cooling
question
result: no crystals or minerales
answer
instant cooling
question
6 textures
answer
1.Aphanetic 2. Phaneritic 3. Porphyritic 4. Obsidian 5. Pyroclastic 6. Pegmatetic
question
-crystals too small to be seen (need magnification) -feels like sandpaper -can be vesicular

answer
Aphanetic
question
-crystals are large enough too see and can be used to identify the rock
answer
Phaneritic
question
-has phenocrysts and ground mass -cools from slow to rapid
answer
Porphyritic
question
-no crystals/ minerals -cools rapidly

answer
Obsidian
question
-wide range of grain sizes -grain is not interlocked -comes from volcanic ash
answer
Pyroclastic
question
-very large -forms in late stage of cooling -cools fast -lots of water and silica make the atoms move quickly

answer
Pegmatic
question
igneous rocks are made of _________ minerals
answer
silicate
question
8 elements in the crust
answer
-oxygen -silicon -Aluminum -iron -calcium -sodium -potassium -magnesium
question
2 composition groups
answer
-ferromagnesium silicate -nonferromagnesium silicate
question
-has lots of iron and magnesium -less silicate -dark: black/green
answer
ferromagnesium silicate
question
-has less iron and magnesium -more silicate -light: pink, white, clear
answer
nonferromagnesium silicate
question
-felsic -low iron and magnesium -high silica
answer
granite
question
-mafic -high iron and magnesium -low silica
answer
basaltic
question
-ultramafic -very high iron and magnesium -very low silicate -makes most of mantle
answer
periodtite
question
-intermediate -middle iron and magnesium -middle silica
answer
andersetic
question
-felsic comp -quartz, feldspar, and mica -phaneritic texture -slow cooling EXAMPLE: continental crust

answer
granite
question
-felsic comp -quartz, feldspar, and mica -aphanitic texture -fast cooling EXAMPLE: Yellowstone park
answer
rhyolite
question
-felsic - mafic comp -no minerals -glassy texture -rapid cooling EXAMPLE: lava cools instantly

answer
obsidian
question
-felsic- mafic comp -no minerals -glassy and vesicular texture -rapid cooling EXAMPLE: lava cools instantly
answer
pumice
question
felsic composition (4 types)
answer
-granite -rhyolite -obsidian -pumice
question
andesitic composition (2 types)
answer
-andesite -diorite
question
-intermediate comp -plagioclase, amphibole -porphyritic to aphanitic textures PLATE TECTONICS: c-o conversions

answer
andesite
question
-intermediate comp -plagioclase, amphibole -phaneritic texture PLATE TECTONICS: c-o conversions
answer
diorite
question
mafic compositions (2 types)
answer
-basalt -gabbro
question
-mafic comp -plagioclase feldspare, pyroxene, olivine -aphanitic texture PLATE TECTONICS: o-o spread to conversions
answer
basalt
question
-mafic comp -plagioclase feldspare, pyroxene, olivine -phaneritic texture PLATE TECTONICS: oceanic crust
answer
gabbro



