Geology Study Guide
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What are the 2 types of IGNEOUS rocks?
answer
Intrusive & Extrusive
question
What forces form METAMORPHIC rocks?
answer
Heat & Pressure
question
What are the 2 types of Metamorphic rocks?
answer
Foliated & Non-Foliated
question
What type of metamorphism forms "FOLIATED" rocks?

answer
Regional Metamorphism
question
What type of metamorphism forms "NON-FOLIATED" rocks?

answer
Contact Metamorphism
question
Are the crystals in an INTRUSIVE igneous rock large or small?

answer
Intrusive rocks have LARGE crystals
question
Are the crystals in an EXTRUSIVE igneous rock large or small?

answer
Extrusive rocks have SMALL crystals
question
What are the 3 types of SEDIMENTARY rocks?
answer
Clastic, Chemical and Organic
question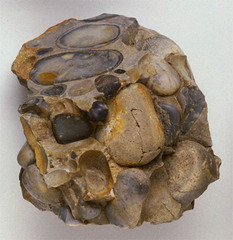
What are Clastic Sedimentary Rocks?

answer
forms from pieces of other rock (EX: Sandstone, Conglomerate)
question
What are Organic Sedimentary Rocks?

answer
forms from fossils of plants/animals (EX: Coquina, Coal)
question
What are Chemical Sedimentary Rocks?

answer
forms from chemical precipitate (EX: rock salt)
question
What forces form IGNEOUS rocks?
answer
"melting & cooling" of other rocks
question
What was the first kind of rock on Earth?
answer
Igneous Rocks
question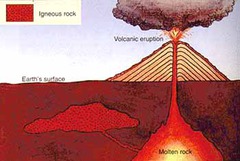
Why do INTRUSIVE igneous rocks have LARGE CRYSTALS?

answer
Because they cool slowly, so there is time for large crystals to go.
question
What is an example of an INTRUSIVE igneous rock?

answer
Granite
question
What is an example of an EXTRUSIVE igneous rock?

answer
Pumice
question
What is an example of a FOLIATED metamorphic rock?

answer
Slate
question
What is an example of a NON-FOLATED metamorphic rock?

answer
Quartzite
question
What is an example of a CLASTIC sedimentary rock?

answer
Sandstone
question
What is an example of an ORGANIC sedimentary rock?

answer
Coquina
question
What tool is required for a "FRACTURE/CLEAVAGE" test?

answer
Hammer
question
What tool is required for a "STREAK" test?

answer
Streak Plate
question
What are the characteristics of all minerals?
answer
Naturally-occurring, inorganic, solid, definite crystalline structure, same chemical formula throughout
question
What are some "properties" of minerals? (ways to tell them apart)
answer
Hardness, Streak, Color, Fracture/Cleavage, Luster
question
What is "hardness"?
answer
a mineral's resistance to scratching
question
What is "streak"?
answer
a mineral's color in powdered form
question
What is cleavage/fracture?
answer
the way a mineral breaks (smooth planes=cleavage, jagged edges=fracture)
question
What is the least reliable mineral property?
answer
color
question
What is "luster"?

answer
the way a mineral reflects light (metallic luster looks like metal, non-metallic luster is broken into "earthy" and "dull")
question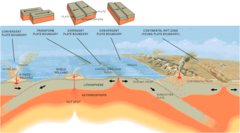
What are the 3 types of plate boundaries?

answer
Convergent, Divergent, and Transform
question
What features do continental-continental CONVERGENT plate boundaries form?

answer
mountains & earthquakes (EX: Himalyas)
question
What features do continental-oceanic CONVERGENT plate boundaries form?

answer
trenches & subduction zones, earthquakes & volcanoes (EX: Andes Mountains)
question
What features do oceanic-oceanic CONVERGENT plate boundaries form?

answer
deep trenches (EX: Marianas) & island arc systems (EX: Aleutian Islands), has earthquakes and volcanoes
question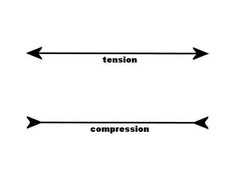
What force causes a CONVERGENT plate boundary to form?

answer
COMPRESSION
question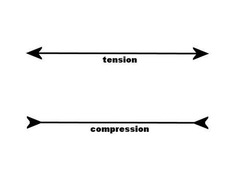
What force causes a DIVERGENT plate boundary to form?

answer
TENSION
question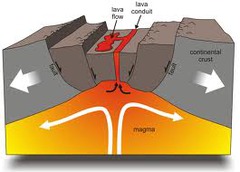
What features are found at a continental-continental DIVERGENT plate boundary?

answer
rifts, shallow earthquakes
question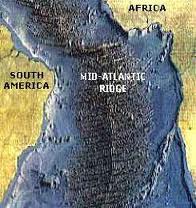
What features are found at a oceanic-oceanic DIVERGENT plate boundary?

answer
mid-ocean ridges, shallow earthquakes & volcanoes (EX: Mid-Atlantic Ocean)
question
What features are found at TRANSFORM plate boundaries?

answer
lots of earthquakes—NO volcanoes (EX: San Andreas Fault Boundary, California)
question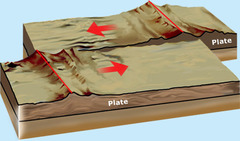
What force causes TRANSFORM plate boundaries?

answer
Torsion/Twisting
question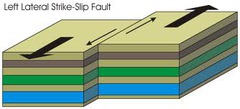
What fault is most likely to form at a TRANSFORM plate boundary?

answer
Strike-Slip Fault
question
What scale is used to measure Earthquakes?

answer
Richter Scale
question
What instrument is used to measure Earthquakes?

answer
Seismograph
question
What causes Earthquakes?
answer
pressure build-up & release
question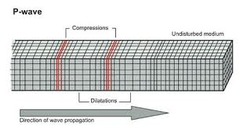
What are "P-Waves"?

answer
can travel through both solids & liquids, moves by a pushing/pulsing motion, arrives "1st" (primary waves)
question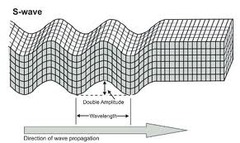
What are "S-Waves"?

answer
ONLY travels through solids, moves by a shearing motion (up & down) and causes the most damage, arrives "second"
question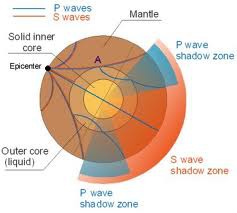
What is the "Shadow Zone"?

answer
Area of earth opposite from an earthquake where S-Waves cannot reach
question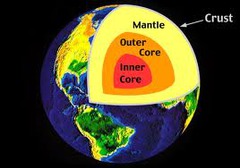
How do scientists know what the interior of Earth looks like?

answer
Scientists use data from Earthquake waves as clues--like the Mystery Box
question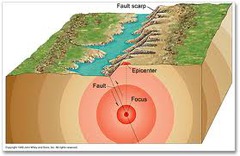
What is the "epicenter"?

answer
the location on the surface of the Earth ABOVE the earthquake's source
question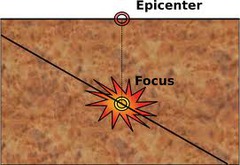
What is the "focus"?

answer
the location UNDER earth's surface where the earthquake actually happens
question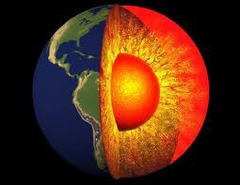
Describe the "Inner Core".

answer
Solid, mostly iron, spinning. Even though it is so hot, it is solid because the pressure at the center of the Earth makes it solid
question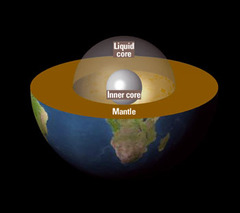
Describe the "Outer Core".

answer
liquid: S-waves cannot move through them
question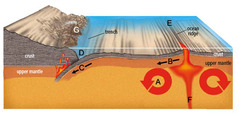
Describe the "Mantle".

answer
a liquidy-solid (plastic) where convection currents move plates
question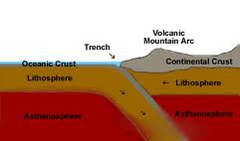
Describe the "Crust".

answer
solid, thinnest part of earth, broken into oceanic (thin but dense, basalt) and continental (thick but light, granite)
question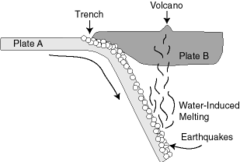
What is a "trench"?

answer
Found at subduction zones (convergent), one plate dives deep under another plate
question
What is a volcano?
answer
a vent in Earth's crust that releases steam and lava
question
What 3 locations are volcanoes found?
answer
Divergent Plate Boundaries, Convergent Plate Boundaries, Hot Spots
question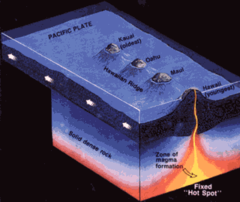
Give an example of a "Hot Spot" volcano.

answer
Hawaii



