Foundations and Adults Health Health Nursing Final Review – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
The nurse is caring for a patient who has had a kidney transplant. What should be included in the care of a patient with a suppressed immune system? 1.Prophylactic antibiotic therapy 2.Meticulous aseptic technique 3.Restriction of all visitors 4.Antineoplastic medication administration
answer
2.Meticulous aseptic technique
question
Which statement describes innate, or natural, immunity? 1.The body's first line of defense against disease, which protects locally against the external environment 2.The body's second line of defense against disease, which protects the internal environment 3.Mediated by B cells to produce antibodies in response to antigenic challenge 4.An immunity that is specific
answer
1.The body's first line of defense against
question
The nurse is caring for a patient with a history of numerous allergies. What is the most important teaching concept? 1.Immunotherapy regimen 2.Avoidance of the allergen 3.Antihistamine administration 4.Adrenaline administration
answer
2.Avoidance of the allergen
question
Humoral immunity is mediated by which type of cells? 1.T cells 2.B cells 3.Macrophages 4.Myeloblasts
answer
2.B cells
question
After a bee sting, the patient's face becomes edematous and she begins to wheeze. Based on this assessment, the nurse would be prepared to administer which medication? 1.Aminophylline 2.Diphenhydramine 3.Epinephrine 4.Diazepam
answer
3.Epinephrine
question
The nurse gave an intramuscular penicillin injection to a patient. What assessment finding would be most indicative of a systemic anaphylactic response? 1.Increased blood pressure 2.Bradycardia 3.Urticaria 4.Wheezing
answer
4.Wheezing
question
A 38-year-old patient is receiving 2 units of packed red blood cells at 125 mL/hour. Fifteen minutes after the start of the blood transfusion, the nurse notes the following vital signs: pulse 110 beats/minute, respirations 28 breaths/minute, blood pressure 98/58 mm Hg, and temperature 101° F. The patient is shivering. What is the nurse's initial action? 1.Slow the infusion rate. 2.Stop the infusion. 3.Administer aspirin as ordered for elevated temperature. 4.Report the findings to the nurse manager.
answer
2.Stop the infusion.
question
A 72-year-old patient is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of immunodeficiency disease. What is the primary nursing goal? 1.Reduce the risk of the patient developing an infection. 2.Encourage the patient to provide self-care. 3.Plan nutritious meals to provide adequate intake. 4.Encourage the patient to interact with other patients.
answer
1.Reduce the risk of the patient developing an infection.
question
A patient experienced an anaphylactic reaction to an antibiotic. What are the correct nursing interventions for anaphylaxis? (Select all that apply.) 1.Assess vital signs every 4 hours. 2.Assess respiratory status frequently. 3.Maintain patent airway. 4.Administer epinephrine as ordered. 5.Monitor vital signs frequently.
answer
2.Assess respiratory status frequently. 3.Maintain patent airway. 4.Administer epinephrine as ordered. 5.Monitor vital signs frequently.
question
A patient comes to the clinic for his weekly allergy injection. He missed his appointment the week before because of a family emergency. Which action is appropriate in administering the patient's injection? 1.Administer the usual dose of the allergen. 2.Double the dose to account for the missed injection the previous week. 3.Consult with the health care provider about decreasing the dose for this injection. 4.Reevaluate the patient's sensitivity to the allergen with a skin test.
answer
3.Consult with the health care provider about decreasing the dose for this injection.
question
Type I allergic reaction to latex is a response to the_______________?
answer
Rubber latex proteins
question
The most common allergens that cause an anaphylactic reaction include: (Select all that apply.) 1.Leafy green vegetables 2.Bees, wasps 3.Shellfish 4.Peanuts 5.Oranges
answer
2.Bees, wasps 3.Shellfish 4.Peanuts
question
Which illness is believed to be an autoimmune disorder? (Select all that apply.) 1.Rheumatoid arthritis 2.Lung cancer 3.Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.Guillain-Barré syndrome 5.Cardiovascular disease
answer
1.Rheumatoid arthritis 3.Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.Guillain-Barré syndrome
question
What are the two major forms of immunity?
answer
innate (natural) and acquired (adaptive).
question
What are the three major cell types active in acquired immunity?
answer
T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, and Macrophages.
question
What is the difference between T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes?
answer
B lymphocytes produce antibodies. T lymphocytes do not produce antibodies, but assist the B cells. T lymphocytes release lymphokines.
question
What is the function of macrophages?
answer
Macrophages trap, process, and present antigen to T lymphocytes.
question
What is an autoimmune disorder?
answer
Autoimmune disorders are failures of the body's tolerance to "self."
question
Plasmapheresis is used for the treatment of what?
answer
Plasmapheresis is used to treat autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, glomerulonephritis, myasthenia gravis, thrombocytopenic purpura, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
question
A primary threat to the immunosuppressed patient is what?
answer
Infection, aseptic technique is required when caring for these patients. Good skin care is necessary.
question
Why is type and cross selection of blood donors important?
answer
Careful selection of blood donors and careful typing and crossmatching of blood are important to prevent transfusion reaction.
question
What are the five factors influencing the hypersensitivity response?
answer
Host response to allergen, exposure amount, nature of the allergen, route of allergen entry, and repeated exposure.
question
What are the two types of latex allergies?
answer
Two types of latex allergies are type IV allergic contact dermatitis and type I allergic reactions. Type IV is caused by the chemicals used in the manufacturing of latex gloves, whereas the type I allergic reaction is a response to natural rubber latex proteins.
question
A 58-year-old patient with colon cancer is receiving combined radiation therapy and chemotherapy. He has developed diarrhea. The patient asks the nurse why he is now having diarrhea. What nursing response is most accurate? 1."Your diagnosis of colon cancer has caused diarrhea." 2."Because you are unable to eat or drink much during treatment, you are having loose stools." 3."Radiation is very irritating to the lining of your GI track, which has caused diarrhea." 4."You most likely have an imbalance in your fluid and electrolyte levels."
answer
3."Radiation is very irritating to the lining of your GI track, which has caused diarrhea."
question
A patient has terminal lung cancer. To maintain optimal pain control, when should analgesics be administered? 1.At scheduled intervals 2.Every 2 hours 3.As required 4.In relation to the patient's activity level
answer
1.At scheduled intervals
question
What is true regarding cancer prevention and health care promotion behaviors for patients with a diagnosis of cancer? 1.They will not decrease the risk of developing a second malignancy. 2.They will not be affected by personal choices related to diet and smoking. 3.They are increasingly important with the growing population of cancer survivors. 4.They would include only routine physical examinations.
answer
3.They are increasingly important with the growing population of cancer survivors.
question
A patient has received a diagnosis of stage I breast cancer. She is receiving adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy after a lumpectomy. What teaching point should be included in this patient's plan of care? 1.Chemotherapy-related hair loss is reversible and temporary. 2.All chemotherapeutic agents result in alopecia. 3.Hair that grows back may have a different texture and color. 4.Hair loss may result from the medication therapy.
answer
2.All chemotherapeutic agents result in alopecia.
question
A 61-year-old patient is receiving chemotherapy. The patient becomes anemic and has petechiae and ecchymoses scattered over her upper trunk, especially her arms. What side effect is the patient experiencing? 1.Bone marrow suppression 2.Cardiac suppression 3.Liver toxicity 4.Pulmonary toxicity
answer
1.Bone marrow suppression
question
Before the insertion of a cervical implant, the nurse tells the patient what to expect while it is in place. Which statement is accurate? 1."Nurses will always be available, but they will spend only a short time at your bedside." 2."Personal cleanliness is essential, so you will be given a complete bed bath each day." 3."Pain or discomfort is a common side effect of this type of radiation." 4."Your bed linens will be completely changed each day to minimize radioactive contamination."
answer
1."Nurses will always be available, but they will spend only a short time at your bedside."
question
A 24-year-old patient has been receiving chemotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Which patient statement indicates that he understands discharge teaching concerning leukopenia? 1."I am cured and have no limitations." 2."My family can catch leukopenia, so I need to be careful to not get too close to any of them." 3."I should avoid close contact with people who might give me an infection." 4."I need to be careful not to cut myself when shaving because I may not be able to stop the bleeding."
answer
3."I should avoid close contact with people who might give me an infection."
question
A 42-year-old patient has palpated a small lump on her left breast during her monthly BSE. She has scheduled an appointment with her health care provider. Which test will be used to make a definite diagnosis of a benign or malignant tumor of her breast? 1.Biopsy 2.Mammography 3.Tomography 4.Ultrasonography
answer
1.Biopsy
question
The nurse educator is discussing the importance of the reduction of carcinogens in primary prevention of cancer. Which risk factor is considered significant in many types of cancer? 1.Diet low in fat 2.Occasional moderate use of alcohol 3.High pollen count in the environment 4.Smoking
answer
4.Smoking
question
What is a therapeutic approach by the nurse to assist a patient with terminal cancer in the management of his pain? 1.Anti-inflammatory agents are effective analgesics for severe pain. 2.Opioids should be withheld because they are addictive. 3.Pain is what the patient says it is. 4.One can increase one's tolerance for pain.
answer
3.Pain is what the patient says it is.
question
A patient is receiving chemotherapy and has a low WBC count. What patient statement indicates the need for further teaching? 1."I check my mouth and teeth after each meal." 2."I've been very constipated and need an enema." 3."My husband and I have been using a vaginal lubrication before intercourse." 4."My lips are dry and cracking. I need some lubricant."
answer
2."I've been very constipated and need an enema."
question
According to the American Cancer Society, what would have the greatest influence in reducing the risk of lung cancer? 1.Five fruits and vegetables a day 2.Yearly chest radiograph for people age 50 years and older 3.Cessation of smoking 4.Reduction of environmental and chemical carcinogens
answer
3.Cessation of smoking
question
The patient is receiving chemotherapy and has the nursing diagnosis of Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements. What are likely reasons for this imbalance in nutrition? (Select all that apply.) 1.Impaired tissue integrity, related to damage to integumentary tissue 2.Alopecia and leukopenia 3.Stomatitis and anorexia 4.Myelosuppression and infection 5.Vomiting and diarrhea
answer
3.Stomatitis and anorexia 5.Vomiting and diarrhea
question
A patient has a vaginal radiation implant in place. What nursing intervention should be added to the patient's plan of care? 1.Instruct her to turn from side to side for comfort. 2.Restrict fluid intake to prevent bladder distention. 3.Promote intake of a high-residue diet to prevent constipation. 4.Monitor vital signs every 4 hours and report temperature higher than 100° F.
answer
4.Monitor vital signs every 4 hours and report temperature higher than 100° F.
question
A patient has a history of oat cell carcinoma of the lung and is being treated with chemotherapy. His WBC count is 2.5/mm3. What is the nurse's greatest concern to prevent complications? 1.Prevention of hemorrhage 2.Prevention of infection 3.Prevention of dehydration 4.Prevention of electrolyte imbalance
answer
2.Prevention of infection
question
A 63-year-old patient has a diagnosis of cancer of the prostate gland with metastasis and is experiencing cachexia. How is cachexia best described? 1.Poor health, malnutrition, weakness, and emaciation 2.Increased appetite and nervousness 3.Irritability and anger 4.Depression, fear, and anxiety
answer
1.Poor health, malnutrition, and emaciation.
question
What is the second leading cause of death in the U.S.?
answer
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States (after heart disease).
question
What kind of factors show evidence in the development of cancer?
answer
There is strong evidence that what people eat or drink and their lifestyle choices may predispose them to the development of cancer.
question
What is a common reason for a delay in diagnosing cancer?
answer
A common reason for a delay in diagnosing cancer is that early malignant changes are not accompanied by pain. Seeking medical attention when warning signs occur is also frequently delayed because people fear the possible diagnosis of cancer and hope the signs and symptoms will just go away.
question
The diagnosis of cancer has what profound effect on family members, as well as on the patient?
answer
They may experience denial, anger, fear, and depression.
question
Side effects from chemotherapeutic agents result from what?

answer
Most of the side effects from chemotherapeutic agents result from the destruction of normal cells of the hematopoietic system, hair follicles, and the GI system.
question
What is TLS?
answer
TLS is an oncologic emergency that occurs in patients with cancer who have heavy tumor cell burdens after they receive chemotherapy or irradiation, which causes rapid lysis of malignant cells.
question
What concept should be applied n the planning of care for the patient with cancer?
answer
The concept of rehabilitation should be applied in the planning of care for the patient with cancer to promote the highest level of functioning possible.
question
What is cancer?
answer
Cancer is a group of diseases: uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells.
question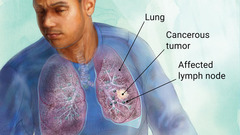
What type of cancer cause is the leading death?

answer
Lung cancer.
question
The term "carcinogenesis" refers to?
answer
The process by which normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. Various factors are possible origins of cancer.
question
The term "carcinogens" refers to ?
answer
Substances known to increase the risk for the development of cancer.
question
Risk factors for cancer include:
answer
1. Smoking: 87% of people who develop lung cancer are smokers. 2. Dietary habits: Play a role in development of colon, rectum, and breast cancer. 3. Exposure to radiation: Ultraviolet rays are a factor in the development of basal and squamous cell skin cancers and melanoma. 4. Exposure to environmental carcinogens: Fumes from rubber or dust from chloride are examples. 5. Smokeless tobacco: Increases the risk of cancer of the mouth, larynx, pharynx, and esophagus. 6. Frequent, heavy consumption of alcohol: May result in oral cancer and cancer of the larynx, throat, esophagus, and liver.
question
The odds of not inheriting cancers is?
answer
About 90% of cancers are NOT inherited.
question
Genetic susceptibility for cancer includes:
answer
1. Incidence of breast cancer is higher in women with a family history of this disease. 2. Incidence of lung cancer is high in smokers with a family history of this disease. 3. Incidence of leukemia is greater in an identical twin. 4. Colon cancer is more likely to occur in women who have a history of breast cancer.
question
Cancer risk assessment and cancer genetic counseling provides?
answer
First step toward identifying hereditary cancer predisposition and education, health promotion, informed consent, and support.
question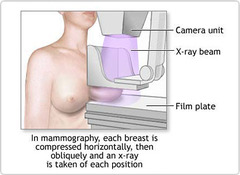
Yearly mammograms are to be initiated when?

answer
starting at age 40 Clinical breast exam (CBE) about every 3 years for women in their 20s and 30s and every year for women 40 and over.
question
The American Cancer Society guidelines for the early detection of cancer are?
answer
1. Colorectal cancer and polyps: beginning at age 50. 2. Cervical cancer: screening (testing) should begin at age 21.
question
What is the cell mechanism and growth of a normal cell?
answer
When cells are destroyed, cells of the same type reproduce until the correct number have been replenished.
question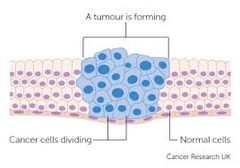
What is the cell mechanism and growth of a cancer cell?

answer
Instead of limiting their growth to meet specific needs, they continue to reproduce in a disorderly and unrestricted manner.
question
What is the cell mechanism and growth of a neoplasm?
answer
1. Uncontrolled or abnormal growth of cells 2. Benign: Not recurrent or progressive; nonmalignant 3. Malignant: Growing worse and resisting treatment; cancerous growths; tumors
question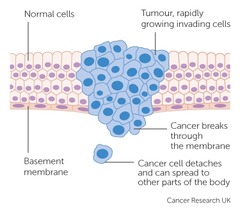
What is metastasis?

answer
When tumor cells spread to distant parts of the body.
question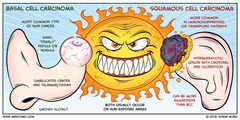
What is carcinoma?

answer
Malignant tumors composed of epithelial cells (line the cavities and surfaces of blood vessels and organs throughout the body.); tend to metastasize.
question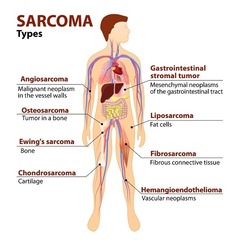
What is sarcoma?

answer
Malignant tumor of connective tissues, such as bone or muscle.
question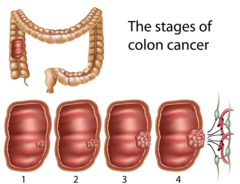
What is the purpose of staging cancer?

answer
It indicates tumor size, spread to lymph nodes, and extent of metastasis Stage 0: Cancer in situ Stage I: Tumor limited to the tissue of origin Stage II: Limited local spread Stage III: Extensive local and regional spread Stage IV: Metastasis
question
Some of the diagnostic tests for cancer include?

answer
1. Biopsy: Incisional, excisional, needle aspiration. Biopsies are performed to obtain a sample of tissue from the body. 2. Endoscopy. 3. Diagnostic imaging: Bone scanning, Tomography Computed tomography (CT), Ultrasound testing, Magnetic resonance imaging.
question
Laboratory tests performed in diagnosing cancer include?
answer
1. Serum alkaline phosphatase - the level of alkaline phosphatase is elevated in the presence of liver disease or metastasis to the bone or liver. 2. Serum calcitonin - Calcitonin is a hormone secreted by the thyroid gland in response to a rise in serum calcium level. The level is increased in the blood of people who have cancer of the thyroid. It may be elevated with breast cancer and oat cell cancer of the lung. 3. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) - normally, production of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) stops before birth, but it may begin again if a neoplasm develops. CEA level can be elevated for other reasons, such as smoking cigarettes or the presence of inflammation. CEA is found in increased amounts in the blood of people with colorectal cancer. 4. PSA and CA125 - prostate-specific antigen (PSA) for prostate cancer, CA-125 for ovarian cancer, and CA-19-9 for pancreatic or hepatobiliary cancer. PSA is the only tumor marker for prostate cancer. Although PSA levels are usually elevated when cancer is present, PSA level alone is not diagnostic of prostate cancer. CA-125 is a cancer antigen detected in the blood and peritoneal ascites. The normal level is 35 units/mL. The CA-125 level may be elevated in patients with gynecologic cancers (including ovarian cancer) and cancer of the pancreas. CA-19-9 antigen, a tumor marker, is used in the diagnosis, monitoring, and surveillance of patients with pancreatic or hepatobiliary cancer. 5. Stool examination for blood - it is essential that the person not ingest red meat, turnips, melons, aspirin, or vitamin C for 4 days before the test because this may result in a false-positive result.
question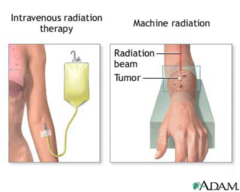
Cancer therapies include?

answer
1. Surgery: Preventive, Diagnostic, Curative, Palliative. 2. Radiation therapy: External radiation therapy, Internal radiation therapy.
question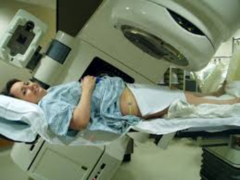
What kind of therapy is the women in the picture receiving?

answer
External radiation therapy
question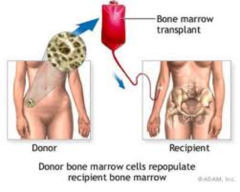
What is bone marrow transplantation?

answer
Process of replacing diseased or damaged bone marrow with normally functioning bone marrow.
question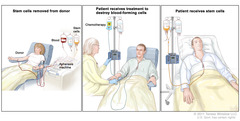
What is peripheral stem cell transplantation?

answer
Alternative to bone marrow transplant. Circulating stem cells are capable of repopulating the bone marrow.
question
Pain management in advanced cancer includes?
answer
1. Opioids: Morphine, hydromorphone, fentanyl, methadone Sustained-release morphine - MS Contin, Roxanol SR. 2. Administration of IV drips, intrathecally, and epidurally. 3. Patient self-control: Distraction, massage, relaxation, biofeedback, hypnosis, and imagery
question
Problems that arise in nutrition with advanced cancer include?
answer
Malnutrition, Anorexia, Altered taste sensation, Nausea/vomiting, Diarrhea.
question
Terminal prognosis in advanced cancer:

answer
Most patients with advanced cancer know they are dying Honesty and openness are the best approaches Spiritual activities may provide mental and emotional strength Social worker assists the patient and family in planning for home care Hospice services can be arranged—efforts are directed toward relief from pain and other problems
question
What are the leading sites of primary cancer in men and women?
answer
The leading sites of primary cancer in men are the prostate, lungs, colon, and rectum. The leading sites of primary cancer in women are the breasts, lungs, colon, and rectum.
question
What is the overall percentage of cancer affecting people?
answer
Overall, it affects people of all ages, but most cases (76%) are diagnosed in people older than 55
question
Cancer incidence is higher amongst which cultural race?
answer
Cancer incidence is higher among African Americans than among members of any other race.
question
Which type of cancers have a better cure and survival rate? Why?
answer
Other cancers, such as breast and prostate, occur more often than lung cancer, but they have better cure and survival rates because of early detection and treatment.
question
The incidence of cancer increases with what factors?
answer
The incidence of cancer increases with aging, possibly as a result of decreased effectiveness of the immune system and changes in DNA.
question
The most common types of cancers observed in older adults are?
answer
The most common types of cancers observed in older adults are prostate, lung, breast, and colorectal cancer. Cancers of the skin, urinary bladder, vagina, and vulva are seen primarily in older adults. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and multiple myeloma are seen more frequently in older adults than in younger people.
question
Which ethnic groups have the lowest rate of death from cancer?
answer
Of all ethnic groups, Asian Americans have the lowest rate of death from cancer.
question
The highest rate of invasive cervical cancer of any ethnic group (other than Vietnamese) goes to?
answer
Hispanic women have the highest rate of invasive cervical cancer of any ethnic group other than Vietnamese, and the incidence rate is twice as high as that in non-Hispanic white women.
question
Which ethnic group is less likely to develop breast cancer, but die from the disease if acquired?
answer
Although African American women are less likely than white women to develop breast cancer, they are more likely to die from the disease if they develop it.
question
In the United States which ethnic group has the lower incidence of cancer, but poor survival rate when they do develop cancer?
answer
Native Americans have a lower incidence of cancer than any other ethnic group in the United States but have the poorest survival rate when they do develop cancer.
question
What is carcinogenesis?
answer
Carcinogenesis is the process by which normal cells are transformed into cancer cells.
question
Cancer may be caused by what factors?
answer
Cancer may be caused by external factors (infection, chemicals, radiation, and tobacco use) and internal factors (genetic mutations, immunologic conditions, and hormones).
question
Primary prevention of cancer consists of what?
answer
Changes in lifestyle habits to eliminate or reduce exposure to carcinogens, substances known to increase the risk for developing cancer.
question
The most preventable cause lung cancer is what?
answer
Smoking: 80% of people who die from lung cancer are smokers. Other cancers associated with smoking are acute myeloid leukemia and cancers of the bladder, kidney, mouth, lip, stomach, colorectum, nasopharynx, larynx, paranasal sinuses, esophagus, pancreas, uterus, ovary, and cervix.
question
Which type of diets are associated with cancer development?
answer
Diets that are high in fat and low in fiber, as well as inadequate nutrient intake, are associated with cancer development.
question
Obesity is a risk factor for what types of cancer?
answer
Breast, prostate, gallbladder, ovarian, and uterine cancer.
question
Foods to Reduce Cancer Risk include:
answer
Vegetables from the cabbage family, such as the following: •Broccoli •Cauliflower •Brussels sprouts •All types of cabbage and kale •Vegetables and fruits high in beta-carotene, such as the following: •Carrots •Peaches •Apricots •Squash •Broccoli •Rich sources of vitamin C, such as the following: •Grapefruit •Oranges •Cantaloupe •Strawberries •Red and green peppers •Broccoli •Tomatoes
question
A risk factor in basal cell, squamous cell skin cancers, and melanoma is?
answer
Excessive exposure to the sun's ultraviolet rays is a factor, indoor tanning beds, and radiation commonly used for medical diagnosis and treatment.
question
What are the effects of smokeless tobacco?
answer
Use of smokeless tobacco increases the risk of cancer of the mouth, larynx, pharynx, and esophagus. Long-term snuff users have an increased risk for cheek and gum cancers
question
What is the percentage of hereditary cancers?
answer
About 5% of cancers are hereditary. Hereditary cancers arise from germline mutations.
question
What are germline mutations?
answer
Changes in egg or sperm cells that are then incorporated into the DNA of each body cell of the children produced.
question
Multiple cancers are often seen how? and what areas of the body?
answer
In location, they are more likely to be bilateral, in unusual organ combinations, such as breast cancer and sarcoma, breast and thyroid cancers, and leukemia and brain tumors.
question
What is the incidence of developing postmenopausal breast cancer and premenopausal breast cancer?
answer
The incidence of postmenopausal breast cancer is three times higher, and the incidence of premenopausal breast cancer is five times higher, in women with a family history of this disease.
question
Explain the BRCA1 gene:
answer
Women who have either of the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 have a 60% risk of having breast cancer during their lifetime.
question
Explain breast cancer in Asian women vs white women?
answer
Breast cancer is rare in Asian women and common in white women.
question
Explain the incidence of leukemia in twins?
answer
Is higher in an identical twin of a person with the disease.
question
Explain the frequency of neuroblastoma amongst siblings?
answer
The frequency of neuroblastoma is increased among siblings.
question
A history of breast cancer in women may also develop what other type of cancer?
answer
Colon cancer is more likely to occur in women who have a history of breast cancer.
question
Explain the diagnostic procedure and age requirement for cancer of the cervix:
answer
Women, ages 21-65. A Pap test; human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA test is performed. 1. women ages 21-29, screening should be done every 3 years with conventional or liquid-based Pap tests. 2. women ages 30-65, screening should be done every 5 years with both the HPV test and the Pap test (preferred), or every 3 years with the Pap test alone (acceptable). 3. Women aged 65+ who have had ? 3 consecutive negative Pap tests or ? 2 consecutive negative HPV and Pap tests within the last 10 years, with the most recent test occurring within 5 years, women who have had a total hysterectomy should stop cervical cancer screening.
question
Explain the diagnostic procedure and age requirement for colorectal cancer in men and women:
answer
Men and women, age 50+ 1. a stool DNA test: Intervals of test performance is uncertain. 2. flexible sigmoidoscopy (FSIG): every 5 years. 3. double contrast barium enema (DCBE): every 5 years. 4. colonoscopy: every 10 years 5. CT colonography: every 5 years.
question
Explain the diagnostic procedure and age requirement for endometrial cancer:
answer
Women, at menopause. Symptoms of endometrial cancer should be strongly encouraged to reported such as unexpected bleeding or spotting.
question
Explain the diagnostic procedure and age requirement for prostate cancer:
answer
Men, ages 50+ A digital rectal examination (DRE) and prostate-specific antigen test (PSA) screening is performed.
question
A cancer related check up should include a thorough assessment of what body systems/organs?
answer
Examination for cancers of the thyroid, testicles, ovaries, lymph nodes, oral cavity, and skin.
question
S/S to look for in a breast self examination (BSE) include:
answer
Any abnormality—such as discharge from the nipples; puckering, dimpling, peau d'orange (skin appearance of an orange peel), or scaling of the skin; and the palpation of a lump or thickness should be reported to a medical professional.
question
S/S to look for in testicular cancer examination include:
answer
Some clinical manifestations of testicular cancer include a lump in or enlargement of either testicle, a heavy feeling in the scrotum, dull aching in either the groin or the lower abdomen, fluid collection in the scrotum, and tenderness or enlargement of the breasts (this results from hormones produced by cancer cells). Blood in the urine, difficulty starting to urinate, a weak flow of urine, and other urination problems should be reported to the health care provider for evaluation.
question
What happens when a cell is destroyed?
answer
When cells are destroyed, the remaining cells of the same type reproduce until the correct number has been replenished. This orderly replacement of cells is governed by a control mechanism that stops when the loss or damage has been corrected
question
What is the responsibility of the immune system in cell production?
answer
The immune system aids in preventing the development of cancer by destroying the abnormal cells. On occasion, the immune system fails to recognize these abnormal cells, and cancer develops.
question
The term proliferation means?
answer
The rapid reproduction of a cell, part, or organism. Proliferation is not always indicative of cancer, however.
question
Abnormal cellular growth is classified as?
answer
Nonneoplastic growth and neoplastic growth.
question
What are the four common nonneoplastic growth patterns?
answer
The four common nonneoplastic growth patterns are hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia, and dysplasia. Although not neoplastic conditions, these may precede the development of cancer.
question
What is a neoplasm?
answer
a group of cells whose growth is uncontrolled or abnormal. Neoplasms may be benign or malignant.
question
The term anaplasia means what?
answer
Anaplasia means "without form" and is an irreversible change in which the structures of adult cells regress to more primitive levels.
question
What ability does a malignant neoplasm contain?
answer
The ability to spread to other body sites and resist treatment, as in cancerous growths.
question
Growths may also be referred as?
answer
Growths are also referred to as tumors, which means "swelling" or "enlargement." They may be localized or invasive.
question
How can metastasis occur?
answer
Metastasis can occur by (1) diffusion to other body cavities or (2) circulation via blood and lymphatic channels.
question
What is the function of a T cell?
answer
Some T cells are responsible for immunosurveillance (the immune system's recognition and destruction of newly developed abnormal cells). When a cell becomes malignant, its membranes carry a tumor-specific antigen that is recognized by the body as nonself and is destroyed.
question
What happens to suppress a T cell rejection after organ transplant?
answer
To suppress T cell rejection of a transplanted organ, steroids and other drugs are given.
question
How are cancers described?
answer
Cancers are described according to the original site of the primary tumor.
question
How do cancers originate?
answer
Carcinomas originate from embryonal ectoderm (skin and glands) and endoderm (mucous membrane linings of the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal [GI] tract, and genitourinary tract)
question
What is the TNM cancer staging classification system?

answer
Histopathology: G3 - poorly differentiated (high grade). G4 - Undifferentiated (high grade).
question
Where do lymphomas and leukemias originate?
answer
Lymphomas and leukemias originate from the hematopoietic system.
question
Sarcomas may affect what body organs?
answer
Sarcomas may affect bone, bladder, kidneys, liver, lungs, parotid glands, and the spleen.
question
What are the stages of tumors?
answer
Stage 0: cancer in situ Stage I: Tumor limited to the tissue of origin; localized tumor growth. Stage II: Limited local spread. Stage III: Extensive local and regional spread. Stage IV: Metastasis
question
What are radioisotope studies and what do they require?
answer
Radioisotope studies require the injection or ingestion of a radioactive substance. A scanning device is then used to identify the distribution of the substance in different areas of the body. Concentration of the radioisotope in a specific organ, such as the thyroid gland or the brain, is indicative of a tumor in that location (it may be primary or metastatic).
question
An example of a radioisotope study is?
answer
Bone scanning
question
Bone scanning detects what in cancer patients?
answer
Bone scanning is indicated to detect metastatic tumors that have spread into the bone. All malignancies capable of metastasis may reach the bone, especially malignancies of breasts, kidneys, lungs, prostate, thyroid gland, and urinary bladder.
question
Ultrasonography in cancer patients is used for what?
answer
It is most helpful in distinguishing between cystic and solid tumors.
question
What is an magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)?
answer
This test is currently used in the diagnosis of intracranial and spinal lesions and of cardiovascular and soft tissue abnormalities. The procedure also provides information about changes within the cells of soft tissues, arteries, veins, the brain, and the spinal column.
question
Contraindications for an magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) include?
answer
During the test, the patient must not have any metallic materials on the body, including jewelry. MRI cannot be performed on patients with metallic implants, such as a pacemaker, orthopedic nail, or aneurysm clip.
question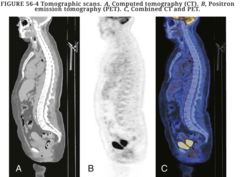
What is the function of a PET scan?

answer
PET can demonstrate glucose metabolism, oxygenation, blood flow, and tissue perfusion for any designated area. Alterations in the normal metabolic process in pathologic conditions are diagnosed during PET
question
What glands may be surgically removed to help control the growth and spread of malignancies?
answer
The pituitary, adrenal glands, ovaries, or testes may be surgically removed to help control the growth and spread of malignancies caused by hormonal stimulation.
question
Why must nutritional status be assessed before and after surgery?
answer
Nutritional status has been found to be a significant factor in the amount of surgery that can be tolerated, the rate of recovery, the patient's role performance, and the adequacy of wound healing.
question
What are some of the side effects of radiation therapy?
answer
skin damage and burning. Skin atrophy, changes in pigmentation, and chronic dermatitis may result. Frequent assessment and monitoring of the skin's condition are needed. When external radiation is planned, the specific area on the body is marked to indicate the port at which external radiation will be directed. These markings must not be washed off.
question
Management of the skin area marked for radiation should include what?
answer
•Keep the skin dry. If the area becomes wet during bathing, pat the skin dry with an absorbent towel. •Do not apply lotions, ointments, creams and powders in marked areas. Any lotions or creams designed to specifically manage drying skin must be prescribed by the physician. •Protect the radiated area from direct sunlight. •Avoid applications of heat or cold because these would increase erythema, drying, and pruritus of the skin, which is common over an irradiated area.
question
What dietary interventions should be focused during radiation therapy?
answer
Dietary interventions should focus on the ingestion of foods high in protein and calories. This helps promote healing and tissue regeneration. Fluid intake to maintain hydration is needed.
question
What are some of the special precautions the nurse should take when taking care of the cancer patient with an unsealed internal radiation?
answer
The nurse should stand as far away as possible from the site where an internal radiation device is in the patient's body. In addition, the nurse should limit the time needed for close contact near the irradiated site. If direct, prolonged care is needed, the nurse should wear a lead apron. Children younger than 18 years and pregnant women should not be allowed to visit implant recipients. Periods of visitation are limited to 10 minutes. Visitors are asked to stand as far away from the patient as possible.
question
How is unsealed internal radiation administered?
answer
intravenously or orally, so that it is distributed throughout the patient's body.
question
The term "Leukopenia" refers to?
answer
The reduction in the number of circulating white blood cells (WBCs) as a result of depression of the bone marrow is a common problem for patients receiving chemotherapy. It can lead to life-threatening infections.
question
What is the normal range for WBCs?
answer
The normal number of WBCs ranges from 5000/mm3 to 10,000/mm3. A patient with a total WBC count of less than 4000/mm3 is considered to be leukopenic.
question
What is the normal range of neutrophils?
answer
The normal number of neutrophils ranges from 60% to 70%, or 3000/mm3 to 7000/mm3. When the neutrophil count is less than 1000/mm3, neutropenia is considered present, and when the count is less than 500/mm3, neutropenia is severe.
question
What are neutropenic precautions?
answer
A patient with neutropenia should be placed on neutropenic precautions, which is sometimes referred to as protective precautions or reverse isolation.
question
What happens if there is not enough neutrophils?
answer
Without enough neutrophils, the body's first line of defense collapses, paving the way for the development of pneumonia, septicemia, or other potentially overwhelming infections.
question
Nursing considerations for a patient on neutropenic precautions include:

answer
Safety
question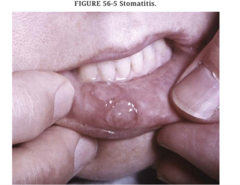
One of the most common complications of chemotherapy is?

answer
Stomatitis (inflammation of the oral mucosa) is one of the most common complications of chemotherapy and can lead to severe swallowing problems and systemic infections
question
To reduce the risk of an oral Candida infection, the health care provider may prescribe what?
answer
prophylactic antifungal medications such as an oral nystatin (Mycostatin) suspension, clotrimazole (Lotrimin) lozenges, or fluconazole (Diflucan). A bland soft or liquid diet may also be ordered.
question
Organisms can also grow along catheter tracts and infect the blood, resulting in septicemia. What are some of the S/S to look for?
answer
Signs and symptoms of a central line-associated infection in the blood stream include tenderness around the catheter site and pain.
question
Why should injections be avoidable on a patient placed on neutropenic precautions?
answer
Subcutaneous or intramuscular injections should be limited because they may cause abscesses in patients with neutropenia. These patients are also at risk for excessive bleeding because of the potential for an associated decrease in platelets and other formed elements in the blood.
question
When assessing for pulmonary function on the a patient placed on neutropenic precautions the nurse should be aware of what?
answer
Neutropenic patients with lung infections do not exhibit common clinical manifestations, such as sputum production or infiltrates demonstrable on chest radiographs. The nurse should assess the patient for other indications of a possible infection, such as changes in breath sounds, elevated respiratory rate and rhythm, and labored breathing. The patient may also complain of pain during inspiration or expiration.
question
Straining during a BM on a patient placed on neutropenic precautions should be contraindicated why?
answer
Straining can cause ulcerations or fissures in the rectum, which creates ports of entry for bacteria. Avoid the use of enemas, rectal medications, and rectal thermometers. They can abrade the mucosal lining creating an entrance for pathogens. Neutropenia also predisposes patients to rectal abscesses. If the patient complains of perirectal pain, the nurse should notify the health care provider immediately.
question
What are colony-stimulating factors (CSFs)?
answer
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) have been very helpful when treating patients with neutropenia. CSFs are commercially made. They are the only therapy that can prevent and manage neutropenia. CSFs are given subcutaneously or intravenously. Although CSFs are extremely expensive, they are administered prophylactically to patients at increased risk for neutropenia, such as those with a history of developing severe or prolonged neutropenia after chemotherapy.
question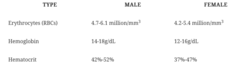
What are the normal values for the patient with anemia?
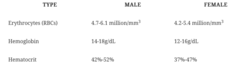
answer
Anemia is a reduction in the number of circulating red blood cells (RBCs), hemoglobin, or hematocrit as a result of depression of the bone marrow.
question
How do you distinguish between mild, moderate, and severe anemia?
answer
Hemoglobin levels of 10 to 14 g/dL indicate mild anemia, levels of 6 to 10 g/dL indicate moderate anemia, and levels lower than 6 g/dL indicate severe anemia.
question
Explain Recombinant human erythropoietin, or epoetin alfa (EPO; Epogen, Procrit):
answer
Recombinant human erythropoietin, or epoetin alfa (EPO; Epogen, Procrit), was initially approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1987 for management of chronic anemia associated with end-stage renal disease. In 1993, the FDA approval was expanded to include management of chemotherapy-related anemia.
question
When is the transfusion of packed RBCs indicated?
answer
Transfusion of packed RBCs is indicated if there is evidence of cardiac decompensation or if hemoglobin levels are low in combination with low platelet counts. The transfusion improves the patient's oxygen-carrying capacity, allows for a more efficient use of blood components, and lowers the risk of volume overload.
question
What is thrombocytopenia?
answer
Thrombocytopenia is a reduction in the number of circulating platelets as a result of the depression of the bone marrow. Normal platelet values are 150,000 to 400,000/mm3. When the platelet count is less than 20,000/mm3, spontaneous bleeding can occur.
question
Which chemotherapeutic drugs are most frequently associated with the development of stomatitis?
answer
Methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin, dactinomycin, and bleomycin are the chemotherapeutic drugs that are most frequently associated with the development of stomatitis.
question
What medications is used when stomatitis becomes intolerable?
answer
lidocaine (Xylocaine)
question
What is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)?
answer
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)—a chemical found in marijuana—taken in pill form produces an antiemetic effect in some patients who have not benefited from the commonly prescribed prochlorperazine (Compazine).
question
What are the effects of metoclopramide?
answer
Metoclopramide blocks dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the central nervous system, stimulates motility of the upper GI tract, and accelerates gastric emptying.
question
diphenoxylate with atropine (Lomotil) is prescribed under what circumstance?
answer
If diarrhea becomes marked or persistent, an antidiarrheal medication such as diphenoxylate with atropine (Lomotil) may be prescribed.
question
What is tumor lysis syndrome?
answer
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) is an oncologic emergency with rapid lysis of malignant cells.
question
Explain the concept of "tumor lysis syndrome?"
answer
The syndrome develops when chemotherapy or irradiation causes the destruction (or lysis) of a large number of rapidly dividing malignant cells. As malignant cells are lysed, intracellular contents are quickly released into the blood stream. This results in high levels of potassium (hyperkalemia), phosphate (hyperphosphatemia), and uric acid (hyperuricemia). These conditions, plus secondary hypocalcemia, all increase the risk for renal failure and alterations in cardiac function.
question
Clinical manifestations for tumor lysis syndrome include:
answer
Early clinical manifestations include nausea, vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea, muscle weakness, and cramping. Later signs and symptoms may include tetany, paresthesias, seizures, anuria, and cardiac arrest.
question
What is the best way to prevent TLS?
answer
The best way to prevent TLS is to recognize which patients are at risk and to initiate prophylactic measures before antineoplastic therapy begins.
question
When preventing TLS when should hydration begin and for how long?
answer
Hydration should begin 24 to 48 hours before treatment and continue for at least 72 hours after treatment.
question
What is the purpose of diuretics in preventing TLS?
answer
Diuretics may be used to promote the excretion of phosphate and uric acid, to prevent volume overload, and to promote the excretion of potassium in the urine.
question
What is the purpose of allopurinol in preventing TLS?
answer
Allopurinol prevents uric acid formation; administration is initiated a few days before treatment and should be continued for 3 to 5 days after treatment is completed.
question
What is the purpose of sodium bicarbonate and sodium polystyrene (Kayexalate)?
answer
Sodium bicarbonate is used to maintain alkalinity of the urine (pH over 7), which prevents uric acid crystallization. Cation-exchange resins, such as sodium polystyrene (Kayexalate), bind with potassium, and so their administration enables excretion of potassium through the bowel.
question
What is the purpose of calcium gluconate in preventing TLS?
answer
Calcium gluconate is administered intravenously to correct hypocalcemia. Cardiac monitoring is required.
question
What happens when all measures to prevent TLS fail?
answer
When these measures are not successful, renal failure may occur, and renal dialysis is necessary.
question
Signs and symptoms of TLS, including the following:
answer
Hyperkalemia: electrocardiographic changes, muscle weakness, twitching, paresthesia, paralysis, muscle cramps, nausea, vomiting, lethargy, and syncope Hyperphosphatemia: azotemia, oliguria, hypertension, and renal failure Hypocalcemia: electrocardiographic changes (heart block, dysrhythmias, and cardiac arrest), tetany, confusion, and hallucinations Hyperuricemia: renal failure, nausea, vomiting, flank pain, gout, and pruritus
question
What is the focus of care when treating TLS?
answer
Preventing renal failure
question
How do biologic response modifiers (BRMs) work?
answer
In three different ways. One type of BRM increases, restores, or modifies the host defenses against the tumor (CSFs, filgrastim, erythropoietin, GM-CSFs). Other BRMs are directly toxic to tumors (interleukins, bacille Calmette-Guérin vaccine [BCG]) or modify biologic features of the tumor (interferons alpha, beta, and gamma).
question
What are the common side effects in patients receiving BMRs?
answer
fatigue, flulike symptoms, leukopenia, nausea, and vomiting.
question
How is bone marrow obtained?
answer
Most bone marrow used for transplantation is obtained by multiple needle aspirations from the posterior iliac crest while the patient is under general or spinal anesthesia. The anterior iliac crest and sternum may also be used.
question
How much bone marrow is extracted for the average adult?
answer
The amount of marrow extracted ranges from 600 to 2500 mL for the average adult.
question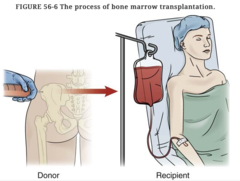
How is bone marrow given to the patient?

answer
After processing, the marrow is given to the patient intravenously through a transfusion bag, or it can be frozen (cryopreservation). Marrow may be kept for 3 years or more.
question
What is allogenic bone marrow?
answer
Bone marrow transplant that came from someone else.
question
What are the three types of allogenic bone marrow?
answer
Three types of allogenic bone marrow transplants are (1) syngeneic (donation from the patient's identical twin), (2) related (donation from a relative, usually a sibling), and (3) unrelated (donation from a nonrelative).
question
The procedure of peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT) its based on what fact?
answer
An emerging and promising alternative to bone marrow transplant (BMT) is peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT). This procedure is based on the fact that peripheral or circulating stem cells are capable of repopulating the bone marrow.
question
What is leukapheresis?
answer
When tubing from the donor for a peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT) enters a cell separator machine that is used to remove the peripheral stem cells; then the blood is returned to the donor. This procedure usually takes 2 to 4 hours.
question
A change in taste during treatment of cancer is called what?
answer
Cancer treatments may cause the patient to experience an alteration in the sweet, sour, bitter, and salty taste sensations. This change in taste is known as dysgeusia.
question
What are the most common concerns voiced by the patient with cancer?
answer
(1) fear of recurrence, (2) chronic or acute pain, (3) sexual problems, (4) fatigue, (5) guilt for delaying screening or treatment, (6) behavior that may have increased the risk for cancer, (7) changes in physical appearance, (8) depression, (9) sleep problems, (10) change in role performance, and (11) being a financial burden on his or her loved ones.
question
The nurse-patient relationship should be based on what?
answer
trust and confidence; the nurse must be open, honest, and caring in the approach.
question
What is the primary focus of hospice?
answer
The primary focus of a hospice is enhancing the patient's quality of life, not prolonging it. Efforts are directed toward relief from pain and other problems.
question
A nurse is caring for a patient receiving chemotherapy who complains of severe nausea and vomiting that interferes with eating and drinking. Which medication would the nurse expect to administer? 1. Morphine 2. Ondansetron (Zofran) 3. Dexamethasone (Decadron) 4. Diphenoxylate with atropine (Lomotil)
answer
2. Ondansetron (Zofran) The nurse should anticipate administering Zofran for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Decadron can be used for nausea and vomiting but can suppress the immune system and so should not be given to a patient receiving chemotherapy. Morphine is used for pain, not nausea and vomiting. Diphenoxylate with atropine (Lomotil) is used to treat diarrhea, not vomiting.
question
A nurse is caring for a patient receiving chemotherapy who has been vomiting for 3 days and has poor oral intake. The patient's electrolyte levels were found to be normal by testing of the patient's blood. For which complication of nausea and vomiting is the patient at risk? 1. Falls 2. Clotting 3. Infection 4. Bleeding
answer
3. Infection The patient with impaired nutritional intake is at risk for infection, especially when combined with neutropenia, which, in general, follows chemotherapy treatment. If the patient had a fluid deficit (which the laboratory results show is not the case), the patient would be at an increased risk for falls. Impaired nutritional intake does not put the patient at an increased risk for clotting or bleeding.
question
A nurse is providing education to a patient receiving chemotherapy. Which statement, if made by the patient, indicates a need for further teaching? 1. "I'll tell my family to bring me books instead of fresh flowers as gifts." 2. "I can't believe I'll never have hair again. I guess I'll start buying wigs now." 3. "I'll miss eating fresh fruit and vegetables, but I'll look forward to eating them after treatment." 4. "I'll remember to request antiemetic medication an hour before mealtimes to help prevent nausea and vomiting."
answer
2. "I can't believe I'll never have hair again. I guess I'll start buying wigs now." Although chemotherapy can cause complete alopecia, the hair will most likely grow back after treatment has stopped. The patient should avoid fresh fruits and flowers. Prophylactic antiemetic therapy can help increase the patient's appetite and caloric intake.
question
A patient with neutropenia from chemotherapy complains to the nurse of burning with urination and urinary frequency. On assessment of the urine, the nurse notes cloudy yellow urine with a foul odor. What should the nurse's response be? 1. Call the health care provider 2. Obtain a clean urine specimen for culture 3. Catheterize the patient to ensure the bladder is completely empty of urine 4. Instruct the patient to start the stream of urine not in the specimen cup, stop the stream, and restart the stream into the specimen cup
answer
1. Call the health care provider The nurse should first call the health care provider to alert him or her to the patient's symptoms, which may indicate infection. The nurse should anticipate obtaining a urine specimen for analysis and culture, but would first need an order. Catheterization should be avoided to prevent trauma to the urinary tract and introduction of bacteria into the bladder from the urethra.
question
A nurse is caring for a patient with neutropenia from chemotherapy. Which instruction would be important to help prevent pneumonia in this patient? 1. Use an electric razor when shaving 2. Cough and deep breathe every hour while awake 3. Wear sequential compression devices while in bed 4. Sit on the side of the bed for 5 minutes before standing
answer
2. Cough and deep breathe every hour while awake To prevent lung infection, the nurse should instruct the patient to cough and deep breathe frequently. The nurse should instruct the patient to use an electric razor when shaving to prevent bleeding and skin or bloodstream infections. Sequential compression devices should be worn while in bed to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Sitting on the side of the bed for 5 minutes before standing helps to limit orthostatic hypotension and prevent falls.
question
A nurse is caring for a patient with neutropenia from chemotherapy. The nurse knows to be vigilant for which early signs of pneumonia or other lung infection? 1. Increased temperature 2. Increased blood pressure 3. Increased respiratory rate 4. Increased sputum production
answer
3. Increased respiratory rate Patients with neutropenia do not have the same signs as an otherwise healthy person would have with a lung infection, such as increased sputum production or fever. Blood pressure is not necessarily elevated. The nurse should be aware of respiratory rate and lung sounds.
question
The nurse asks a patient who is receiving internal radiation therapy for cervical cancer to wear antiembolism stockings. What complication is the nurse trying to prevent in the patient? 1. Risk of infection 2. Nausea and vomiting 3. Implant dislodgement 4. Deep vein thrombosis
answer
4. Deep vein thrombosis Internal radiation therapy for cervical cancer involves the insertion of a radioactive implant into the vagina. The procedure involves the patient lying in the supine position for prolonged periods. Therefore patients are advised to wear antiembolism stockings or pneumatic compression boots to prevent the stasis of blood in the lower extremities and the risk of deep vein thrombosis. Risk of infection is manifested by a temperature higher than 100° F (37.7° C). Antiembolism stockings do not have any effect on body temperature. Nausea and vomiting are the common manifestations of chemotherapy. Antiembolism stockings do not have any impact on these symptoms. The patient is kept on strict bed rest and is restricted from turning from side to side to prevent the radioactive vaginal implant from getting dislodged.
question
The results of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test of a patient are found to be elevated. Which diagnostic testing would be useful to establish prognosis of cancer in the patient? 1. Shave biopsy 2. Thin-needle biopsy 3. CA-125 tumor marker 4. Calcitonin stimulation testing
answer
2. Thin-needle biopsy The PSA test is a screening tool used for the detection of prostate cancer in men over the age of 50. A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of living tissue from an organ and is used to confirm the diagnosis and establish the prognosis of a disease. Prostate cancer can be diagnosed with the help of a thin-needle biopsy. A shave biopsy is useful to assess the suspected lesions of the skin that are cancerous. Tumor markers such as CA-125 are used to detect the recurrence of ovarian cancer. Calcitonin stimulation testing is a diagnostic procedure to confirm thyroid cancer.
question
A nurse is providing education to a patient about prevention and detection of cancer. What is the most appropriate information for the nurse to include when educating this patient? Select all that apply. 1. Seek out stress to fully experience life. 2. Know the seven warning signs of cancer. 3. Perform monthly breast self-examination only if you are female. 4. Eat a balanced diet that includes vegetables, fruit, whole grains, and fiber. 5. Seek immediate medical care if you notice a change in what is normal for you.
answer
2. Know the seven warning signs of cancer. 4. Eat a balanced diet that includes vegetables, fruit, whole grains, and fiber. 5. Seek immediate medical care if you notice a change in what is normal for you. A balanced diet that includes vegetables (green, yellow, and orange), fresh fruit, whole grains, and adequate amounts of fiber helps prevent certain types of cancer. Other important dietary teaching points include reducing the amount of fat and preservatives consumed, including smoked and salt-cured meats. The seven warning signs of cancer are important to know. These are a change in bowel or bladder habits; a sore that does not heal; unusual bleeding or discharge; thickening or a lump in the breast or elsewhere; indigestion or difficulty swallowing; obvious change in a wart or mole; and nagging cough or hoarseness. Seek immediate medical care if a change in what is normal for you is noticed; it is an important strategy in early cancer detection. Early detection of cancer has a positive impact on the prognosis. Better advice for the patient is to eliminate, reduce, or change the perceptions of stressors in one's life and enhance the ability to cope effectively with stressors. Monthly breast examinations are important both for men and women in detecting breast cancer at an earlier stage.
question
What statement reflects accurate information regarding the use of radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer? 1. Nursing care includes limiting time in the room. 2. Unsealed internal radiation is also known as brachytherapy. 3. A patient with a radioactive implant will have radiation in the urine. 4. Skin care for the patient receiving external radiation therapy includes the use of powder or ointment on the marked area where the external radiation will be directed.
answer
1. Nursing care includes limiting time in the room. The nurse should follow the principles of time, distance, and shielding when caring for a patient with a radioactive implant. Directions supplied by the hospital related to the radioactive substance being used should be followed. In general, nursing care for the patient with a radioactive implant should be carried out as quickly as possible, with the time spent in the patient room limited. The area on the body where the external radiation will be directed must be kept clean, dry, and protected. No lotions or creams should be used unless specifically prescribed by the primary health care provider (and usually only if the skin is becoming excessively dry from the radiation treatments). The area should also be protected from direct sunlight and the application of heat or cold. The use of sealed internal radiation is also known as brachytherapy. These are implants that are temporarily or permanently inserted into hollow cavities, within body tissues, or on the body's surface. The radioactive source delivers a specific radiation dose continuously over hours or days. The highly concentrated dose of radiation is delivered in or near a tumor. A patient who is treated with unsealed internal radiation (administered intravenously or orally) will have radiation in the urine and other body fluids because it is distributed throughout the body. Special precautions must be taken to prevent exposure to radiation from direct contact with the patient or any body tissue or fluid.
question
A patient with cancer is about to undergo surgery. Which is the most accurate statement regarding the role of surgical interventions in the treatment of cancer? 1. If cancer has already metastasized to other areas of the body, surgery is pointless. 2. A radical surgical approach to operable tumors is considered to be the standard of care. 3. The use of a laser beam as an alternative to some surgical procedures has the drawback of excessive bleeding. 4. When surgery may result in an altered body image, the patient may benefit from talking with another patient who has undergone a similar operation.
answer
4. When surgery may result in an altered body image, the patient may benefit from talking with another patient who has undergone a similar operation. When surgery may result in an altered body image, such as with a mastectomy, laryngectomy, or the formation of an ostomy, the patient may benefit from talking with another patient who has undergone a similar operation. The American Cancer Society sponsors support groups and prepares volunteers to visit people who need these types of surgeries. If cancer has already metastasized to other areas of the body, surgery may provide palliation by relieving some of the associated problems, such as obstruction, ulceration, hemorrhage, and pain. A radical surgical approach to operable tumors is no longer routinely used because of more sensitive and accurate diagnostic methods, a greater variety of surgical procedures, more sophisticated staging techniques, and more available advanced treatment options. The use of a laser beam as an alternative to some surgical procedures is increasing. It vaporizes tissue with little bleeding and low risk of infection. The major uses for laser surgery are in ophthalmology, gynecology, urology, neurosurgery, and otolaryngology.
question
An older adult patient tells the nurse, "All of my friends have cancer, it seems. Why is that?" In formulating a response, the nurse recalls which true statement about cancer and the older adult? 1. The incidence of cancer increases with age. 2. Breast and lung cancers are rarely seen in older adults. 3. It is easy to distinguish between cancer and normal changes of aging. 4. Multiple myeloma is seen more frequently in younger adults than in older adults.
answer
1. The incidence of cancer increases with age. The incidence of cancer increases with aging, possibly as a result of the decreasing effectiveness of the immune system and changes in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Breast and lung cancers are among the types of cancers often seen in older adults, as are prostate and colorectal cancer. Other cancers often seen in the older adult include cancers of the skin, bladder, vagina, and vulva. Multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia are seen more frequently in older adults than in younger people. Many of the early signs and symptoms of cancer may be misdiagnosed as normal changes of aging. The importance of routine medical screening and self-examination should be stressed to the aging individual.
question
When caring for a female patient with cancer, the nurse notices that the patient's daughter is worried about her mother, as well as herself, and her own cancer risk. On what knowledge will the nurse base responses to the daughter's questions about hereditary cancers? 1. About 50% of cancers are inherited. 2. Hereditary cancers are usually diagnosed at an advanced age. 3. Smokers are more likely to develop lung cancer if they have a family history of the disease. 4. The incidence of breast cancer is the same whether or not there is a family history of the disease.
answer
3. Smokers are more likely to develop lung cancer if they have a family history of the disease. The incidence of lung cancer in smokers with a family history of this disease is greater than in smokers without a family history of the disease. Hereditary cancers are usually diagnosed at an earlier age—usually 15 to 20 years earlier than cancers that are not inherited. Often, several relatives have the same or related cancers; they are more likely to be bilateral, and multiple cancers are seen in single individuals. The incidence of postmenopausal breast cancer is three times higher and the incidence of premenopausal breast cancer is five times higher in women with a family history of the disease. Breast cancer is rare in Asian women and common in white women. About 10% of cancers are inherited. Hereditary cancers are those cancers that arise from germline mutations.
question
Which dietary choice is most associated with risk factors for cancer? 1. High-fiber, low-fat diet 2. Frequent heavy consumption of alcohol 3. Excessive consumption of fruits and vegetables 4. Consumption of eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day
answer
2. Frequent heavy consumption of alcohol Frequent heavy consumption of alcohol is a risk factor for cancer of the esophagus, larynx, throat, and liver, as well as oral cancer. The National Cancer Institute has launched a program called "5 a day for Better Health," which aims to show how adding five servings of fruits and vegetables can help reduce cancer risk. Approximately 20% of the United States population consumes five daily servings of fruits and vegetables. Obesity is a risk factor for breast, prostate, gallbladder, ovarian, and uterine cancers. Diet plays a role in the development of cancer of the colon, rectum, and breast. A diet high in fiber and low in fat is recommended to reduce the risks of these cancers. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays of the sun is a factor in the development of basal and squamous cell cancers and melanoma. Adequate amounts of water consumption are recommended.
question
The nurse is teaching a patient about cancer warning signs. Which signs/symptoms does the nurse include? Select all that apply. 1. A sore that heals quickly 2. Unusual bleeding and discharge 3. Nagging cough or a hoarse voice 4. Change in bowel or bladder habits 5. Long-lasting warts without any observable change
answer
2. Unusual bleeding and discharge 3. Nagging cough or a hoarse voice 4. Change in bowel or bladder habits Unusual bleeding and discharge can be a warning sign for the onset of cancer. A change in bowel or bladder habits may be indicative of a malignancy in the intestine and urinary bladder, respectively. A nagging cough or hoarseness can indicate a malignancy of the respiratory airways. A sore that heals quickly indicates an effective wound-healing mechanism, while a non-healing sore can be a cancer warning sign. Long-lasting moles or warts with observable changes may be a warning sign for cancer.
question
Which dietary modifications can the nurse recommend to a patient for preventing cancer development? Select all that apply. 1. Increase broccoli intake. 2. Consume more dietary bran. 3. Eat more sausage and bacon. 4. Increase red meat consumption. 5. Restrict alcohol consumption to less than 2 drinks per day.
answer
1. Increase broccoli intake. 2. Consume more dietary bran. 5. Restrict alcohol consumption to less than 2 drinks per day. The dietary modifications that can help reduce cancer development include eating broccoli, cauliflower, sprouts, cabbage, and dietary bran. Restricting alcohol consumption to less than 2 drinks per day also reduces the risk of developing cancer. Consuming animal fats like red meat, sausage, and bacon increase the risk for developing cancer, so their consumption should be restricted.
question
While waiting for her mammography, a patient asks the nurse about factors that may cause breast cancer. What would the nurse respond? 1. "Breast cancer is caused due to the mutation in APC gene." 2. "Breast cancer is caused due to the mutation in MLH1 gene." 3. "Breast cancer is caused due to the mutation in MSH2 gene." 4. "Breast cancer is caused due to the mutation in BRCA2 gene."
answer
4. "Breast cancer is caused due to the mutation in BRCA2 gene." The BRCA2 gene mutation is known to increase the risk for breast cancer. BRCA1 is also known to increase the risk for breast and ovarian cancer. These are inherited gene mutations. The APC, MLH1, and MLSH2 genes increase the risk for colon cancer.
question
The nurse is teaching a group of workers about the prevention of lung cancer. What does the nurse tell them? 1. Avoid environmental asbestos exposure. 2. Avoid a diet that is high in fat and low in fiber. 3. Use skin protection during exposure to the sun. 4. Limit the intake of alcohol to one ounce per day.
answer
1. Avoid environmental asbestos exposure. The nurse should inform the group of workers to avoid exposure to asbestos, which is known to cause cancer. They must use personal protective equipment that reduces direct contact with the substance. The use of skin protection when exposed to the sun helps reduce the incidence of skin cancer. There is an increased incidence of cancer in people who consume alcohol, because alcohol is mildly carcinogenic; long-term exposure can lead to cancer. Alcohol acts as a co-carcinogenic with tobacco; when taken together, they enhance each other's carcinogenic activity. A diet that is high in fat and low in fiber is known to cause colon cancer.
question
A patient who is undergoing a diagnostic workup for cancer expresses anxiety about the results. Which is the best nursing response? 1. "It is probably nothing." 2. "Let's discuss that later." 3. "Everyone feels that way." 4. "Let's talk about your concerns."
answer
4. "Let's talk about your concerns." During the diagnostic workup of cancer, it is common for patients to be anxious. The nurse should actively listen to all concerns expressed. The nurse should not use communication patterns that may hinder exploration of feelings and meanings. "It is probably nothing," may indicate that the nurse is giving false reassurances. "Let's discuss that later," may mean that the nurse is delaying the discussion, and "Everyone feels this way," means that the nurse is generalizing the patient's concern. By using these strategies, the nurse may deny patients the opportunity to share the meaning of their experience.
question
A nurse is caring for a patient who has breast cancer with axillary lymph node involvement who will undergo a bilateral mastectomy and removal of the axillary lymph nodes. Interventions to prevent which complication will be most important after surgery? 1. Infection 2. Lymphedema 3. Impaired self-esteem 4. Impaired skin integrity
answer
1. Infection The most important interventions after surgery will be related to preventing infection. The patient will also require interventions for lymphedema, impaired self-esteem, and impaired skin integrity.
question
What diagnostic test is useful for diagnosing cervical cancer and is recommended after a woman turns age 18? 1. Colposcopy 2. Culdoscopy 3. Papanicolaou (Pap) test 4. Dilation and curettage (D;C)
answer
3. Papanicolaou (Pap) test The diagnostic test that is useful for early detection of cervical cancer and is recommended after a woman turns age 18 is a Pap test, or Pap smear. This is a simple smear method of examining stained exfoliative peeling and sloughed off tissue or cells. The tissue sample is placed on a slide, sprayed with fixative, and sent to the laboratory for analysis. A colposcopy is a procedure that provides direct visualization of the cervix and vagina. Tissue is visualized for growths or other abnormalities or vascularity, and samples can be obtained for analysis. A culdoscopy is a procedure that provides direct visualization of the uterus and adnexa and is performed with use of local, spinal, or general anesthesia. The area is examined for tumors, cysts, and endometriosis; removal of eroded or infected tissue may also be performed. D;C is a procedure performed for a biopsy, to correct cervical stricture, and to treat dysmenorrhea. The cervix is dilated and the inside of the uterus is scraped with a curette.
question
While counseling a patient with lung cancer, the nurse advises the patient to do leg and feet exercises regularly. What could be the possible reason for this advice? 1. To reduce nausea 2. To prevent atelectasis 3. To promote coughing 4. To avoid deep-vein thrombosis (DVT)
answer
4. To avoid deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) Patients with lung cancer are encouraged to do leg and feet exercises regularly to prevent deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) that may occur due to pulmonary embolism. Leg and feet exercises are not useful in reducing nausea. Antiemetics are used for nausea. Changing positions frequently and early ambulation helps to prevent atelectasis and mobilize secretions. Providing necessary splints helps to facilitate coughing.
question
A patient with cancer of the head of the pancreas is admitted to the hospital. What are the manifestations that a nurse might expect to find in this patient? Select all that apply. 1. Clay-colored stools 2. Itching and irritation of the skin 3. Ulcers on the back and abdomen 4. Swelling of the face and extremities 5. Extreme pain in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back
answer
1. Clay-colored stools 2. Itching and irritation of the skin 5. Extreme pain in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back Tumor of the head of the pancreas will obstruct the common bile duct where it passes through the head of the pancreas to join the pancreatic duct and empty at the ampulla of Vater into the duodenum. The stools will be clay-colored when bile is not able to enter the duodenum. Pruritus is also a common symptom in cancer of the pancreas; hence, the patient may complain of itching and irritation of the skin. Severe pain is also present. The pain generally depends on the part affected and severity. Edema and ulcers are not common manifestations of pancreatic cancer.
question
A patient with breast cancer had a left mastectomy 2 days ago. There is a prescription for the blood pressure to be taken every 4 hours. Which nursing action would compromise safety in this patient? 1. Taking the blood pressure in the left arm 2. Obtaining the blood pressure in the right leg 3. Assessing the blood pressure in the right arm 4. Retaking the blood pressure after a high reading
answer
1. Taking the blood pressure in the left arm The cuff should not be applied in the following situations: an arteriovenous shunt is present; a catheter is in an antecubital fossa and fluids are infusing; breast or axillary surgery has been performed on that side; the arm or hand has been traumatized or diseased; or a lower cast or bulky bandages are place. Taking the pressure in the leg is not necessary because the right arm would be a better option. Taking the pressure in the right arm and retaking the pressure after a high reading are appropriate measures associated with taking a blood pressure.
question
A cancer patient with radioactive implants rings the call bell and states, "I feel like something fell out of my vagina." The nurse assesses the patient and sees the implant lying on the bed. What should the nurse do next? 1. Instruct the patient to replace the implant 2. Gently replace the device to the original position 3. Calmly leave the room to prevent radiation exposure 4. Place the device in a glove and remove it from the room
answer
3. Calmly leave the room to prevent radiation exposure Hospitals have strict guidelines for the care of patients receiving radioactive materials and the handling of these materials. To reduce the amount of exposure the nurse must limit the amount of time spent with the source, keep as great a distance from the source as possible, and use shielding devices such as a lead apron. Therefore, the nurse should leave the room to prevent exposure to the radioactive material. The nurse and the patient should not try to reinsert the device. The device should not be placed into a glove and removed because there are protocols for removing the implants.
question
A patient with cancer has decided to use alternative medicine as the primary treatment for the disease. Which treatment is the patient less likely to use in the treatment of the disease? 1. Music 2. Surgery 3. Imagery 4. Massage
answer
2. Surgery Alternative therapies include exercise, music, imagery, massage, prayer, biofeedback, reflexology, creative therapies such as art, and dance. Also included are chiropractic therapy, acupuncture, and relaxation strategies. Alternative therapy often replaces traditional therapy. Surgery is traditional allopathic medicine and not alternative in nature.
question
A patient is experiencing acute pain due to cancer. The nurse discusses the pain with the patient's family. Which statement by the nurse is appropriate in this condition? 1. "Drugs that block neurotransmitter uptake are used for such pains." 2. "Guided imagery and distraction may be effective for such pains." 3. "Such type of pains is caused due to damage to the tissues." 4. "Analgesics and opioids alone usually do not relieve such pains."
answer
4. "Analgesics and opioids alone usually do not relieve such pains." Pain caused by cancer is generally neuropathic pain. The nervous system gets altered due to neuropathic pain. Analgesics and opioids alone usually do not relieve such pains. It is sometimes managed with common analgesics such as those in the NSAID family. Currently, adjuvant medications such as tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and corticosteroids are increasingly used. Drugs that block neurotransmitter uptake are used for the modulation phase of nociceptive pain. Guided imagery and distraction are non-pharmacological treatments that may be effective for nociceptive pains in the perception phase. Damage to tissues generally causes nociceptive pain and not neuropathic pain.
question
A terminally ill patient with breast cancer has severe pain. What would be an ideal nursing intervention related to pain management for this patient? 1. Provide medication on a round-the-clock basis 2. Educate the patient about the risk of addiction. 3. Discourage the use of pain medication for minimal pain. 4. Educate the patient about the risk of respiratory depression.
answer
1. Provide medication on a round-the-clock basis In managing cancer-related pain, pain medication should be administered on a round-the-clock basis to ensure a painless death. Most cancer patients die with uncontrolled pain due to undertreatment with pain medication. Telling the patient that the medication will cause addiction may make the patient more anxious. Pain management is a priority instead of a concern about future addiction. Pain medication should not be discouraged for fear of respiratory depression, a secondary concern.
question
The nurse is caring for a female patient with ovarian cancer. The patient refused to sign the informed consent and requests that the nurse to wait for her spouse to arrive before getting the signature. To which community does the patient likely belong? 1. Islamic community 2. Quaker community 3. Presbyterian community 4. Roman Catholic community
answer
1. Islamic community People in Islamic communities practice patriarchy. According to this system, the male member of the family makes decisions on health care and medication. In this community, the patient's spouse signs the informed consent. Consent from the male individuals in the family is not prominent in the Quaker, Presbyterian and Roman Catholic communities. Women belonging to this community usually make their own health care decisions and generally sign their informed consent form.
question
A terminally ill cancer patient who is on opioids for pain relief develops constipation. What are the direct nursing measures that would be helpful to this patient? Select all that apply. 1. Using laxatives 2. Promoting exercise 3. Using stool softeners 4. Encouraging a high-fiber diet 5. Encouraging fluid intake
answer
2. Promoting exercise 4. Encouraging a high-fiber diet 5. Encouraging fluid intake Constipation is a side effect of opioids. Promoting exercise to an acceptable level is one way to help the patient with constipation. A high-fiber diet may help to increase the bulk of stool and relieve constipation. Increased fluid intake may prevent stools from hardening and facilitate easy passage. However, before promoting the use of laxatives or stool softeners, the nurse should consult the health care provider.
question
A patient with advanced cancer wishes to have a natural death without much medical intervention. How can this patient execute this wish when unable to express it during the dying process? 1. Write a diary to mention the wish. 2. Get a court order for this wish. 3. Use an advance directive to convey the wish. 4. Keep the family members informed about the wish.
answer
3. Use an advance directive to convey the wish. Advance directives would be helpful to spell out the patient's wishes for health care at the time when he or she is unable to indicate the choice. A diary is not a legal document, whereas an advance directive is. Getting a court order is not a practical approach; rather an advance directive would be useful. Rather than informing family members, the patient may appoint any person to carry out the wish as expressed in the advance directive through the durable power of attorney for health care.
question
A nurse is completing a health history and physical assessment on a patient. Vital signs reveal a slightly elevated blood pressure. The patient admits to having a family history of arthritis, breast cancer, and hypertension. Based on the patient's history and blood pressure, which dietary restriction can the nurse anticipate the primary health care provider will implement for this patient? 1. Sodium 2. Flouride 3. Selenium 4. Phosphorous
answer
1. Sodium Sodium, which is found in salt and processed food, is responsible for fluid and acid-base balance. In excessive amounts sodium leads to hypertension in susceptible individuals. Because of a slightly elevated blood pressure and a family history of hypertension, the patient is at risk for developing hypertension. Fluoride is related to tooth decay, selenium may be associated with cardiomyopathy, and phosphorous is an essential component of bone.
question
A 28-year old patient underwent a mastectomy for breast cancer and is depressed. The community center nurse asks the patient to join a program that would assist in coping with the loss. What are such programs called? 1. Grief analysis 2. Grief therapy 3. Grief work 4. Grief coping
answer
2. Grief therapy Grief therapy is a mental health treatment aimed at helping a patient deal with the pain of loss. This program assists the bereaved in coping with the loss. Grief analysis deals with the classification of grief based on the factors affecting it. The process of adapting to and mourning a loss is called grief work. After a loss, serious emotional, mental, and social problems may occur if a patient does not perform grief work.
question
A patient with colon cancer being admitted to hospice care does not have an advance directive. Which elements does the nurse include in the discussion with the patient and family about advance directives? Select all that apply. 1. Portable Do-Not-Resuscitate (DNR) order 2. Instruction about life-sustaining treatment 3. Instructional directive for health care professionals 4. Durable power of attorney for health care (DPOAHC) 5. Instruction that an advance directive cannot be changed once it is filed
answer
1. Portable Do-Not-Resuscitate (DNR) order 2. Instruction about life-sustaining treatment 3. Instructional directive for health care professionals 4. Durable power of attorney for health care (DPOAHC) At the time of admission to hospice care the nurse should document the presence of an advance directive by the patient. An advance directive is a legal document or directive about the patient's decisions regarding life-sustaining treatment when he or she loses decision-making capacity. Living wills and medical directives such as DNR orders are instructional directives that help health care professionals make the appropriate decision(s) as per the patient's will. A portable DNR order or a DNR order written in advance is an advance directive. A patient can appoint a health-care proxy by providing a DPOAHC regarding their health care to make decisions for the patient in the event of loss of decision-making capacity. An advance directive can be altered once it is filed, but will need to be witnessed again.
question
A terminal cancer patient is experiencing nausea and vomiting. What should be the first intervention when caring for this patient? 1. Small servings of food 2. Antiemetics 3. Favorite homemade food 4. Frequent mouth washes
answer
2. Antiemetics Antiemetics are the first choice for managing nausea and vomiting in terminally ill patients. Small servings of food, favorite homemade foods, frequent oral care, and mouth washes are various nonpharmacologic comfort measures effective to manage nausea and vomiting but are not the first interventions.
question
The nurse is caring for a cancer patient with acute lymphoid leukemia who has neutropenia. Which measure should the nurse take to ensure patient safety? 1. Serve small snacks or meals when the patient is hungry. 2. Avoid administering methotrexate (Trexall) intrathecally. 3. Monitor the patient's temperature and maintain hygiene. 4. Avoid administering prednisone (Deltasone) to the patient.
answer
3. Monitor the patient's temperature and maintain hygiene. Cancer (acute lymphoid leukemia) patients have neutropenia or reduced white blood cell count. Neutropenia compromises the patient's immune system, increasing the risk of infections. Infection is manifested as increased body temperature; therefore, the nurse should monitor the patient's temperature regularly. The nurse should maintain hygiene in the patient's surroundings to prevent infection. Offering small and frequent meals helps patients who experience anorexia and vomiting; it is unrelated to neutropenia. Methotrexate (Trexall) is administered intrathecally to reduce the risk of cerebral leukemia and is not avoided if the patient is neutropenic. Prednisone (Deltasone) is the principal drug used to treat acute lymphoid leukemia.



