Dysrhythmia Interpretation and Management/EKG – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Automaticity
answer
Cardiac muscle can generate its own electrical activity
question
Cardiac cycle
answer
Two activities: 1. Electrical (caused by automaticity) 1a. Depolarization = active --> stimulates contraction 1b. Repolarization = resting 2. Mechanical (muscular) = contraction 2a. Systole-contraction 2b. Diastole-relaxation
question
Depolarization process
answer
Leads to systole/contraction • Na+ outside, K+ inside • Change cell permeability • Na+ enters, K+ exists • Ca2+ slowly enters cells • ATP needed to move electrolytes back to resting state
question
Cardiac Conduction Pathway
answer
Begins in SA node (60-100 bpm) → Atrial contraction → AV node (60-80 bpm) → Bundle of His → L and R Bundle branches → Ventricles (Purkinje fibers) (15-40 bpm)
question
Interpreting the EKG steps
answer
1. Determine the heart rhythm 2. Measure the heart rate 3. Examine the P waves 4. Examine the P to QRS ratio 5. Measure the PR interval 6. Examine the QRS complex 7. Interpret the rhythm
question
P wave
answer
• Represents electrical firing from SA node • Atrial depolarization • Not to exceed 3 boxes high
question
PR segment/interval
answer
• Atrial depolarization/delay in AV node • Results from short pause in electrical conduction as the wave of depolarization slows down while traveling through AV junction • Normal: 0.12-0.20 second • 0.20 seconds = First-degree AV block
question
QRS complex/interval
answer
• Ventricular depolarization 1. Q wave = First negative (downward) deflection after P wave 2. R wave = First positive (upward) deflection after P wave 3. S wave = Negative waveform after R wave • Not everyone has traditional QRS • Normal: 0.06-0.10 seconds (narrow complex) • Wider complex = Further away from SA node
question
Pathologic Q waves
answer
• ≥ 1 box (0.04 seconds) in width • More than 1/4 of R wave amplitude Indication of myocardial infarction/tissue death and necrosis (In an acute MI, you won't see the Q wave until tissue has been necrotic)
question
ST Segment
answer
• Look for depression or elevation • ST elevation = Myocardial injury • ST depression = Reciprocal changes, digoxin, and ischemia
question
T wave
answer
• Ventircular repolarization • Follows QRS complex • Bigger than P wave, but no greater than 5 small boxes high • Peaked T wave = Hyperkalemia • Inverted T wave = Ischemia in myocardium
question
QT Interval
answer
• Beginning of QRS complex to end of T wave • Normal: 0.32-0.50 seconds • >0.40-0.45 = Look at drugs that prolong QT interval causing escape rhythms/beats (i.e. amiodarone); longer when HR is slower
question
U Wave
answer
• Sometimes after T wave • Unknown origin • May be normal or hypokalemia
question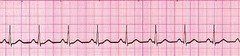
Normal Sinus Rhythm

answer
• Regular rhythm • Rate: 60-100 bpm • Normal P wave • P wave before each QRS • Normal PR, QRS, and QT
question
Sinus Dysrhythmia
answer
• Sinus rhythm • Rate varies with respirations • Inspire = Increase • Expire = Decrease • Rarely affects hemodynamic status • Speeds up, slows down, speeds up, etc.
question
Sinus Tachycardia
answer
• Sinus rhythm • Rate: 100-150 bpm • Causes: Stimulants, exercise, fever, alterations in fluid status • N/I: Assess for s/s of low cardiac output
question
Sinus Bradycardia
answer
• Sinus rhythm • Rate: <60 • Causes: Vagal maneuvers (i.e. bearing down, icing), ischemia, elevated intracranial pressure (ICP), and athletes (normal) • Produces various hemodynamic responses
question
Sinus Arrest or Exit Block
answer
• Sinus node fails to initiate impulse • Causes: Vagal responses, heart disease, drugs that slow HR • HR can be normal or slow • Irregular rhythm • Decrease cardiac output
question
Atrial Dysrhythmias: Defintion + causes
answer
• Increased automaticity in the atrium • Generally have P-wave changes • Causes: -Stress -Electrolyte imbalances -Hypoxemia -Atrial injury -Digitalis toxicity -Hypothermia -Hyperthyroidism -Alcohol -Pericarditis
question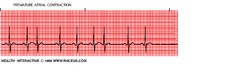
Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC)

answer
• Early beats initiated by atrium • P waves and PR interval may vary • Non-compensatory pause • P wave may be found in T wave
question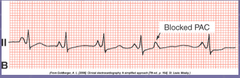
Blocked Premature Atrial Contractions

answer
• Pause noted on rhythm strip • Premature P wave • May alter cardiac output
question
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
answer
• SA node not fully in control; May give some beats but mostly ectopic (outside stimuli) • Varying configurations of P waves (since different areas of atrium) • At least 3 different looking P waves must be seen • HR < 100 • PR interval varies • Irregular rhythym
question
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
answer
• Similar to wandering atrial pacemaker but faster (>100 bpm)
question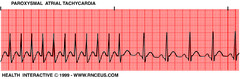
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT, PSVT)

answer
• Without warning, sudden onset of very fast tachycardia • HR 150-250 bpm • Regular rhythm • P waves (if present) may merge in T waves • AV block • Ectopic foci in atria rapidly fluttering • QRS complex is normal • Hemodynamic effects vary • S/S: Sudden onset palpitations, racing heart • Tx: 1. Adenosine (blocks atrial beats for 6 seconds so SA can reset as primary pacemaker) 2. Beta blockers (slow down heart rate)
question
Atrial flutter
answer
• Ectopic foci in atria, heart disease • Classic "sawtooth" pattern • Atrial rate fast and regular (250-350 bpm) with AV block • Degree of conduction varies; may be 3 P waves: 1 QRS complex
question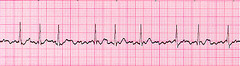
Atrial fibrilation

answer
• Erratic impulse formation in atria • No discernible P wave • Irregular R-R intervals* • Aberrant (normal) ventricular conduction can occur • Results in loss of atrial kick = decreased cardiac output, pooling blood • High risk for pulmonary or systemic emboli • New onset patients feel weak, lightheaded • Maintain with anticoagulants
question
Junctional (Nodal) Rhythms
answer
• Regular rhythm • PR interval low end of normal • P-wave changes - May be absent or retrograde (because stimulus from AV node) • Normal rate: 40-60 bpm • Decreased CO possible
question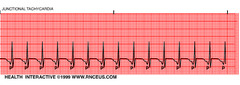
Junctional tachycardia

answer
• Rate 60-100 bpm for accelerated junctional rhythm • Rate 100-150 bpm for junctional tachycardia
question
Premature junctional contractions (PJC)
answer
• P-wave changes • PR interval shorter than normal (because closer to ventricle) • Usually noncompensatory pause • QRS complex that is irregular with the rest of the waves and changing P waves
question
Ventricular dysrhythmias + causes
answer
• Impulses initiated from lower portion of heart (i.e. Bundle of His) • Depolarization occurs, leading to abnormally wide QRS complex • Ectopic and escape beats • Common causes: 1. Myocardial ischemia, injury, and infarction 2. Low potassium or magnesium 3. Hypoxemia 4. Acid-base imbalances
question
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)
answer
• Wide and bizarre beats • Compensatory pause • Patterns: -Bigeminy and trigeminy -Couplets and triplets • Uniforcal vs multifocal (depends on morphology) • QRS complex >0.10 second • Irregular rhythm (d/t early beats and compensatory pause) • Absent P waves • Assess and treat cause: 1. Hypoxia 2. Ischemia 3. Electrolyte imbalance • May need antiarrhythmic agents
question
Ventricular tachycardia
answer
• Rapid, life threatening • Three or more PVCs in a row • Fast rate (>100 bpm) • Initiated by ventricles • Wide QRS, no P waves before each beat • Usually regular • May or may not have a pulse --> Treat pulseless same as v-fib • Significant loss of cardiac output • Hypotension • Tx: Cardioversion w/ external defibrilator or medications
question
Ventricular fibrilation
answer
• Chaotic pattern • No discernible P, Q, R, S, or T waves • Coarse versus fine • No cardiac output; life threatening • Emergent defibrilation
question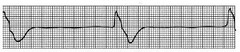
Idioventricular rhythm

answer
• Hallmark = Very slow • Escape from Purkinje fibers • Rate: 15-40 bpm • Regular rhythm • Wide QRS interval • No P waves
question
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
answer
• Same as idioventricular rhythm • Rate > 40 bpm • Hemodynamic effects correspond to heart rate
question
Ventricular standstill (asystole)
answer
• No P, Q, R, S, T waveforms • Assess in two leads (EKG may be off) • No cardiac output • Death
question
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
answer
• EKG rhythm but no pulse • Causes: H's & T's
question
H's & T's
answer
H: 1. Hypoxia 2. Hypovolemia 3. Hypothermia 4. H+ ions (acidosis) 5. Hypokalemia or hyperkalemia T: 1. Tablets (overdose) • Tamponade (cardiac) • Tension pneumothorax • Thrombosis (coronary) • Thrombosis (pulmonary)
question
Atrioventricular blocks (AVB)
answer
• Block of conduction from atria to ventricles • Causes: 1. Coronary artery disease 2. Myocardial infarction (eg inferior wall) 3. Infections 4. Enhanced vagal tone 5. Drug effects (eg digoxin toxicity)
question
Normal EKG intervals
answer
• PR interval = 0.12-0.20 seconds • QRS <0.12 seconds (0.06-0.10 seconds) • QT interval = 0.32-0.50 seconds



