Diarrhea – Flashcard
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Normal stooling patterns
answer
varies from 3 BMs/week to 3 BMs/day
question
Definition of diarrhea
answer
Any of the following: -> 3 loose stools / day -a definite decrease in consistency of stool and increase in frequency based upon individual baseline -stool weight > 200 g/d
question
Classifications of diarrhea
answer
Duration: -Acute (4 weeks) Pathophys: -Osmotic -Secretory -Inflammatory -Malabsorptive Specific stool features
question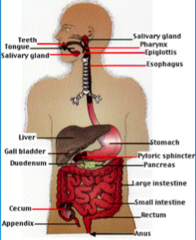
Amt of fluid in GI tract that is oral, salivary, gastric, pancreatic/biliary/small intestines

answer
2 liters oral 1 liter salivary 2 liters gastric 4 liters pancreatic, biliary and small intestines = TOTAL 9 liters in S.B.
question
Nutrients absorbed in mouth
answer
glucose
question
Amt of nutrients absorbed in esophagus & stomach
answer
Esophagus: None Stomach: Minimal
question
Nutrients absorbed in duodenum
answer
calcium, iron, folic acid, magnesium, vitamins A, D, E, K
question
Nutrients absorbed in jejunum
answer
Vitamins C & B, carbs, fats, proteins, [net secretion of water]
question
Nutrients absorbed in ileum
answer
Jejunal functions plus: Vitamin B12 (cobalamin), bile acids (if not absorbed properly could lead to malabsorption later), [net absorption of water]
question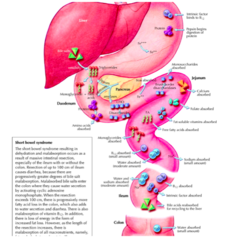
Nutrients absorbed in colon

answer
short chain fatty acids, water
question
Normal physiology of fluid intake/output
answer
-9 L of fluid flow daily (intake + secretion) -8 L (~90%) absorbed by jejunum and ileum -900 cc absorbed by colon -RESULT: Only ~100 cc of fluid is excreted in the stools daily ... 99% efficiency
question
Key points in hx taking of diarrhea
answer
DURATION Volume Fecal incontinence Steatorrhea - fatty, greasy stools that float Presence of blood Tenesmus - painful rectal spasms with a strong urge to defecate but little passage of stool Color Weight Loss - how much?? Medications (recent antibiotics, sorbitol, laxatives) Previous surgeries (gallbladder, ileum resection) Previous radiation
question
When is evaluation indicated for diarrhea?
answer
> 72 hours, bleeding, dehydration
question
Epidemiology of acute diarrhea
answer
1 of 5 leading causes of death worldwide In U.S. often self limited
question
Typical etiology of acute diarrhea
answer
-Usually an infectious source -Infectious agent usually not identified: Stool Culture positive 1.5% to 5.6%
question
Etiologic agents of traveler's diarrhea
answer
Hepatitis A Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) Parasites (Giardia and Cryptosporidium) Cases of food poisoning
question
Etiologic agents of diarrhea in daycares
answer
Rotavirus, Norovirus, Giardiasis, cryptosporidium
question
Etiologic agents of diarrhea in Institutionalized patients
answer
Norovirus, hepatitis A
question
Presentation of acute diarrhea when small bowel is the source
answer
Fluid/enzyme secretion nutrient absorption: -Watery large volume -Cramps bloating and weight loss -Ileum
question
Presentation of acute diarrhea when colon is the source
answer
Storage and water reabsorption: -Frequent -Small volume -Painful -Fever -Blood
question
Rotaviruses epidemiology
answer
most common cause in children (453,000 deaths worldwide in 2008)
question
Rotaviruses presentation
answer
check for recent respiratory illness green, profuse diarrhea
question
Rotaviruses dx
answer
rotazyme test positive on stool
question
Norwalk epidemiology
answer
most common cause in adults
question
Norwalk transmission
answer
-transmission by fecal-oral route -shellfish or contaminated water are also routes for transmission
question
Parasite pathogens of acute diarrhea
answer
Cyclospora Giardia Cryptosporidium Entamoeba histolytica (Amebiasis) - Immunocompromised Host Cryptospiridium Microspiridium
question
MC bacterial pathogens in acute diarrhea
answer
Salmonella 37% Campylobacter 31% Shigella 20% Escherichia coli 0157 3% Cryptosporidium 3% Yersinia, Listeria, Vibrio 1% (severe infxn often bacterial)
question
Stool tests for diarrhea
answer
Fecal leukocytes Culture: Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter Stool for C. Diff Ova and Parasites Protozoal and viral antigens
question
Sn/Sp of fecal leukocyte test
answer
70% sensitivity, 50% Specificity. Presence suggest enteroinvasive organism, or possibly IBD / ischemic / radiation-induced colitis
question
Etiologic agents for whom antimicrobial therapy is always indicated
answer
V cholerae, Shigella species, and G lamblia
question
You should not give anti-motility agents when what sx are present?
answer
febrile or bloody stools - can aggravate the problem
question
Acute diarrhea tx agents for cholera
answer
Doxycycline, Azithromycin, Ciprofloxacin
question
Acute diarrhea tx: shigella, ETEC
answer
Ciprofloxacin, Ceftriaxone
question
Acute diarrhea tx: giardiasis, amebiasis
answer
Metronidazole
question
Acute diarrhea tx: e. coli O157:H7
answer
DO NOT TREAT
question
Acute diarrhea tx: campylobacter
answer
Azithromycin, Fluoroquinolones
question
Acute diarrhea tx: Cryptosporidium, Microsporidium, Isopora
answer
Nitazoxanide
question
Sx that are indications for abx
answer
severe febrile, bloody diarrhea, elderly, immunocompromised, or prolonged course. NOT O157:H7
question
Classifications of chronic diarrhea
answer
Osmotic Malabsorptive Steatorrhea Secretory Inflammatory Dysmotility Fictitious
question
Causes of osmotic type diarrhea
answer
-Disaccharidase deficiency: Lactose Intolerance -Small intestinal mucosal disease: Celiac Sprue, Infections (Tropical sprue, Whipples, viral gastro), Infiltrative diseases (amyloidosis and lymphoma) -Pancreatic insufficiency -Bile Salt malabsorption: Ileal resection, Crohn Disease -Certain laxatives (sorbitol, PEG, magnesium)
question
Dx tests for osmotic type diarrhea
answer
-Fasting Trial: Diarrhea ; symptoms ? with fasting -Osmotic gap: involving measurement of electrolytes Stool Osmotic Gap = Stool Osm - (2 * (Na + K) ) ; 100 : osmotic ;50 secretory
question
Define Lactose Intolerance
answer
Inability to break down lactose due to low lactase levels or activity
question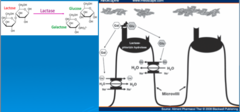
Mechanism of dietary lactose breakdown

answer
Dietary lactose must be hydrolyzed to a monosaccharide in order to be absorbed by the small intestinal mucosa
question
What happens to unabsorbed lactose?
answer
The osmotic load of the unabsorbed lactose causes secretion of fluid and electrolytes until osmotic equilibrium is reached
question
Causes of lactose intolerance
answer
-Primary Lactase Deficiency -Secondary Lactase Deficiency -Lactase Deficiency in Disease: May occur after any process affecting small-bowel mucosa; Celiac disease, Crohns, radiation enteritis, small-bowel resection, Viral or bacterial gastroenteritis
question
Sx of lactose intolerance
answer
Abdominal pain Diarrhea Borborygmi Bloating Flatulence
question
Complications of lactose intolerance
answer
osteopenia
question
Tests for lactose intolerance
answer
-Primarily a Clinical Diagnosis -Lactose Hydrogen breath test : 80-95% Sensitivity, 100% specificity, -Stool Reducing substances ? -Stool pH ?
question
Tx of lactose intolerance
answer
Avoid milk, OTC enzyme products available
question
Definition of celiac dz (Celiac sprue)
answer
A genetic autoimmune enteropathy
question
Incidence of celiac dz
answer
-1 in 120 to 300. More common in Celtic descent and females -Variation in presentation (up to 40% no GI sx), makes it diff to dz
question
Presentation of celiac dz

answer
Dermatitis herpetiformis (IgA deposits)
question
Tests to diagnose celiac dz ; corresponding Sn
answer
*IgA - When suspicion high you should rule out IgA Deficiency
question
Define Steatorrhea
answer
Fatty, bulky, foul smelling stools
question
Causes of Steatorrhea
answer
Chronic pancreatitis Mucosal malabsorption
question
Test for Steatorrhea
answer
Fecal Fat measurement: -24- or 72-hr stool collection on daily 100g fat diet -;7g fat is normal
question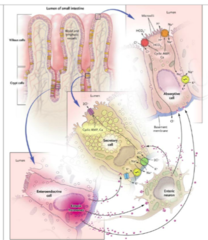
Secretory Type diarrhea pathophys

answer
-Derangements of fluid and electrolyte transport -Absorptive and secretory processes are regulated by both the enteric nervous system and enteric hormones.
question
Causes of secretory diarrhea
answer
-Hormonal: gastrinoma, carcinoid, VIPoma, -Neoplasia: medullary thyroid cancer (calcitonin) -Infections producing enterotoxins: Vibrio cholera, Enterotoxigenic E coli, Rotavirus, clostridium perfringens, S. aureus -Inflammatory mucosal diseases: Collagenous and lymphomatous colitis -Medications: laxatives (senna), ricin -Ileal resection: ? absorption bile salts
question
Presentation of secretory type diarrhea
answer
Diarrhea and symptoms do not decrease with fasting
question
Inflammatory type diarrhea causes
answer
-Inflammatory bowel disease: Ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Lymphocytic or collagenous colitis, Ulcerative jejunoileitis (rare complication of celiac sprue) -Infections: Invasive bacterial infection (Clostridium difficile, E.Coli 0157:H7, Whipples, others -Ischemic Colitis -Microscopic Colitis -Radiation enterocolitis -Neoplasia: colon carcinoma, lymphoma
question
Fecal _____ are important in inflammatory diarrhea
answer
leukocytes
question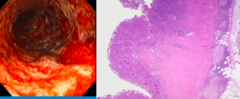
Presentation of inflammatory bowel dz

answer
-Bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss, fevers, skin lesions, arthritis, superimposed diarrheal infections -Anemia -Vitamin deficiency -Malabosrpotion
question
Testing for inflammatory bowel dz
answer
-Stool Studies: VERY IMPORTANT -Colonoscopy + Ileoscopy : sensitivity of 74% / specificity of 100%, p of 100% as a diagnostic test
question
When should you not use a colonoscopy with IBD?
answer
ACUTE SETTING : risk of perforation
question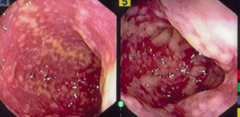
Pseudomembranous Colitis epidemiology

answer
-14,000 deaths per year. -Deaths related to C. difficile increased 400% between 2000 and 2007, in part because of a stronger bacteria strain that emerged.
question
Risk factors for Pseudomembranous Colitis
answer
IBD Antibiotic use Hospitalization
question
Presentation of Pseudomembranous Colitis
answer
-Mild to moderate watery diarrhea -Cramping abdominal pain, Anorexia, Dehydration -Lower abdominal tenderness -Fever, abdominal tendereness in severe cases
question
Motility Disorders
answer
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Hyperthyroidism Diabetes Hormone-secreting tumors
question
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) pathophys

answer
Altered motility and hypersensitivity to intestinal distension without known pathology
question
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) epidemiology
answer
Females>males
question
Forms of IBS
answer
diarrhea predominant form constipation predominant form pain/spasm predominant form alternating diarrhea-constipation predominant form
question
Compare different predominant forms of IBS: diarrhea vs constipation vs pain/spasms vs alternating
answer
-Diarrhea: loose frequent stools typically in AM, after meals, or with stress -Constipation: hard pellet-like stools, difficult to pass with sense of incomplete evacuation -Pain/spasm: crampy abdominal pain, dull to sharp, spasm-like -Alternating diarrhea-constipation: changing bowel habits
question
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) sx that can present with all forms
answer
-fecal mucus -flatulence, belching, and abdominal distention -patients frequently report symptoms involving other organs particularly genitourinary and musculoskeletal -exacerbations with menses and stress
question
Treatment of Constipation predominant IBS
answer
high fiber diet supplemental fiber osmotic laxatives for severe cases
question
Treatment of diarrhea predominant IBS
answer
loperamide lomotil levsin or bentyl (antispasmodics) supplemental fiber is occasionally helpful
question
What is Factitious Diarrhea?
answer
Patient self-induced: -Munchausen Syndrome -Eating disorder



