Dermatology Lecture – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Which antibiotics could be used to treat cellulitis in the previous picture? 1.Cephalexin (Keflex) 2.Cefadroxil (Duricef) 3.Amoxicillin (Amoxil) 4.Cefdinir (Omnicef)
answer
1. Cephalexin (Keflex) (methicillin sensitive staff infection). (MSSA). see them back in 48 hours. mark it with pen and if the redness is increased then change abx.
question
Which antibiotics could be used to treat purulent cellulitis in the previous picture? Select all that apply. 1.Cephalexin (Keflex) 2.TMPS (Bactrim) 3.Doxycycline 4.Ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
answer
Staph infection: use Bactrim, Doxycycline do not use Rocephine-ceftrioxone or cephlexine to treat MRSA. MRSA is usually is purulent when it pus about then let it out, always purulent present, I&D is the first action. Doxycycline, Bactrim, clindamycin.
question
When should you see a person in the office after cellulitis txmt or starting of abx?
answer
48 hours.
question
A 20 year old plays in the college marching band. She has beenbitten on the practice field several different times by "mosquitoes". Today she presents with pruritic bites on her legs and arms consistent with mosquito bites. There is crusting around most of the bites. What condition does this describe? 1.Cellulitis 2.Pyoderma (impetigo) 3.Contact dermatitis 4.Bullous impetigo
answer
2.Pyoderma (impetigo). Example of staph infection. Gram +.
question
What could be the cause of this? Select all that apply. 1.Poor hygiene 2.Elevated glucose levels 3.HIV infection 4.Inhaled steroid for asthma
answer
1.Poor hygiene 2.Elevated glucose levels 3.HIV infection What's the most likely pathogen?Staph
question
Bites: Cat, Dog, Human
answer
Pasturella Gram negative, Staph, Strept
question
A patient was bitten b y a dog about 2 hours ago. There are puncture marks and a small laceration on the right anterior thigh. What should be done at this time? Select all that apply 1.Clean and flush bite thoroughly 2.Prescribe amoxicillin-clavulanate for 7-10 days 3.Order tetanus,rabies prophylaxis if needed 4.Suture the lacerated area
answer
1. Clean and flush bite thoroughly not number 2 as we should only treat the patient propholaxis for only 3-5 days, not longer than that. 3.Order tetanus,rabies prophylaxis if needed 4.Suture the lacerated area-never do this one as bugs need to clear off
question
Fungal Infections: Dermatophytosis
answer
Tinea capitis (head) •Tinea corporis (bodysurfaces) Tinea cruris ("jock itch") •Tinea pedis (foot) •Tinea unguium (nail
question
What is commonly used to confirm diagnosis of fungal infections? 1. Clinical presentation 2.Response to treatment 3. KOH slide preparation 4.Fungal culture
answer
1. Clinical presentation, 3. KOH slide preparation
question
Onychomycosis
answer
Fungal nail infection •Terbinafine 73-79%cure rate (treat for 6 -12 weeks) •Others are less effective •Watch for hepatotoxicity, drug-drug interactions •Topical are poorly effective
question
A patient presents with a vesicular rash on the lateral neck with acute neuritis. This is: 1.bullous impetigo. 2.post-herpetic neuralgia. 3.motor neuropathy. 4.Varicella zoster virus
answer
4. Varicella zoster virus. known as shingles. it is darn common. we got exposed to the chicken pox virus, if something awakens it, what ever dermatome it harbors in then exacerbation happens only in that dermatome. Unilateral. Your trunk, thoracic region is loaded with nerve endings, therefore lot of pain is involved.
question
HERPES ZOSTER (Shingles)
answer
A reactivation of the varicella-zoster (chickenpox) virus that has lain dormant in nerve cells. This involves the skin of a single dermatome or less commonly, several dermatomes
question
Pharmacologic Management
answer
NSAIDs or narcotic analgesics for pain •Antiviral agents if patient presents within 72 hours of symptoms (acyclovir, famciclovir, valacyclovir) •Antiviral agents to all immunocompromised patients •Treatment Post Herpetic Neuralgia (PHN): TCAs, gabapentin, pregabalin (Lyrica), Capsaicin® cream, others
question
What is the most common complication of herpes zoster infection? 1.Bacterial skin infection 2.Post-herpetic neuralgia 3. Motor neuropathy 4.Meningitis
answer
2.Post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN), it creates month or years of pain. Occures in 10-15% of the people and these patients are absolutely miserable for months and years.
question
Herpes Zoster Vaccine
answer
-ACIP recommends for all immunocompetent (because its a live vaccine persons >60 years -32% of adults will have this once in lifetime -Reduces risk of shingles and post-herpetic neuralgia
question
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
answer
more women then men in childbearing age. Chronic inflammatory disease that affects the skin, joints, kidneys, lungs, nervous system, serous membranes •Course is variable: characterized by remissions and relapses •More common in women in 20's, 30's
question
Symptoms of Lupus: lupus on the inside such as joint aches, myalgias
answer
-Fatigue most common complaint (80-100% of patients) •joint aches(hands) and myalgias(90%) •Eye: keratoconjunctivitis sicca •Butterfly rash, malar rash (very prominent in the sun, its a photosensitive rash) -Discoid lupus: lupus on the outside, very distinct rash •Oral and nasal ulcers(12-45%): painless ulcers •Renal involvement: 50% •Hematologic: Leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia •Gastritis, peptic ulcer
question
A 25 year old female is suspected of having lupus. Lupus is characterized by: 1.thrombocytopenia. 2.anemia. 3.presence of Howell Jolly bodies. 4.production of antinuclear antibodies
answer
4.production of antinuclear antibodies (clue to order a test ANA, don't order without a good reason, because there are lot of false positive. if the titer is 1 to 160 that means something is going on, refer them to reheumotologist.
question
Lupus: what diagnostic workup is required for the diagnosis of Lupus
answer
ANA positive with titer (1:160 or higher) Lots of false lupus positives and other diseases at lower titers (Sjogren's syndrome is dry mouth and dry eyes, scleroderma, RA, Mixed connective tissue disease, undifferentiated connective tissue disease, others Refer to rheumotologise
question
Acne Rosacea? Chronic what is the treatment for it? topical metronidazole
answer
orally: tetracycline, it is a chronic condition.
question
SKIN CANCER:Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) Locations: Sun exposed areas oHead and neck 55% oDorsum of the hands/forearms: 18% oLegs: 13% oShoulder, back: 4% oLower lip is common location in smokers, scrape it gently with a tongue blade, and common characteristic of squamous cell is that it bleeds very easily.
answer
Head and Neck anything exposed to sun Presents as papules, plaques, nodules, smooth, hyperkeratotic or ulcerative lesions •May bleed easily •Definitive diagnosis always with biopsy or excision of specimen
question
Basal Cell Carcinoma: 40X more common than squamous cell
answer
Common in fifty and sixty year olds •Most common sites are head and neck •Usual appearance is pearly domed nodule with overlying telangiectatic vessels, later, central ulceration and crusting •Occurs 40x more common than squamous cell •Particularly common in Caucasians •Uncommon in dark skinned populations •Most important risk factor is sun exposure •Definitive diagnosis always with biopsy or excision of specimen •Presentations: nodular, superficial, other presentations •70% occur on the face •Nodular: Typically present on face as a pink or flesh colored papule
question
Malignant Melanoma ABCDE pneumonic(AAD, ACS) ABCDE pneumonic (AAD, ACS)
answer
A=asymmetry •B=border is irregular •C=different colors within the same region •D=diameter>6mm (pencil eraser) •(in whites primarily on lower legs and back; in African Americans, on hands, feet and nails) •E =Enlargement (evolution)
question
Glasgow 7-point Checklist
answer
Major Features: Change in size, color, shape (Refer for any major feature) -Minor Features: Presence of inflammation oBleeding or crusting oSensory change oLesion diameter > 6mm
question
ITCHY THINGS A 66 year old male has Parkinson's disease. What is a common skin manifestation of this? 1.Atopic dermatitis 2.Seborrheic dermatitis 3.Contact dermatitis 4.Dyshidrotic eczema
answer
Seborrheic dermatitis
question
Seborrheic dermatitis:Dermatological Disorders How might this manifestation be described? 1.Maculopapular 2.Extremely pruritic 3.Scaly, greasy 4.Burning
answer
Scaly, greasy
question
What is seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp termed?
answer
Dandruff
question
Atopic Dermatitis(eczema)
answer
Clinical diagnosis,pruritis is predominant symptom •Clues: chronic and recurring •Family history of allergic disease (Asthma, allergic rhinitis runs together with Atopic dermatitis.
question
Contact Dermatitis:
answer
Trigger induces an immune response (T cell media ted response) •May be allergic or irritant-induced •Example: Poison ivy It means we need to give a systemic agent: oral steroid, or oral antihistamine.
question
Dyshidrotic Eczema (pompholyx or dyshidrosis)
answer
Vesicular dermatitis •Intensely pruritic •Chronic •Involves palms, soles what else should be in differentials: Scabies.
question
Itchy Things: Systemic
answer
Renal, liverdisease •Connective tissue disorders •Post-herpetic neuralgia •Multiple sclerosis •Psychogenic itch •Burns/Scar
question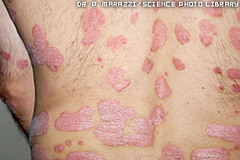
PSORIASIS: its always bilateral, silvery scalses

answer
Plaque psoriasis , always itching most common variant
question
Pharmacologic Management for Psoriasis
answer
Emollients to hydrate skin luberaderm, Eucerin. •Topical steroids(lowest strength that eradicates symptoms) for small places. •Methotrexate •Systemic agents prescribed by derm **always use low potency steroids, use it <5 days, never use longer than 5 days especially on the face.
question
A topical steroid may be most appropriately delivered to the thin skin of an older adult via a(n) 1. gel (3) 2.cream.(2) 3.ointment.(4) 4. lotion (1)
answer
4.lotion vehicle: is what you place the drug in, Gel would be way too much potent, lotion would way less potent. Older adults should be used the weakest vehicle. treating something on scrotum use lotion 1. lotion 2. cream 3. gel 4. ointements.
question
Which organism listed below may be diagnosed using the "scotch tape test ape" test? 1.Pinworms 2.Bed bugs 3.Pubic louse 4.Scabies
answer
1.Pinworms
question
A patient has scabies. Which contacts listed below should be treated? Select all that apply 1.Household contacts 2.Sexual contacts 3.Office mates 4.Close personal contacts
answer
1.Household contacts 2.Sexual contacts 4.Close personal contacts
question
What Dermatologic conditions are these associated with? Honey colored crusts
answer
Impetigo
question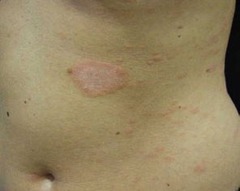
Herald patch

answer
Pityriasis rosea (PR)
question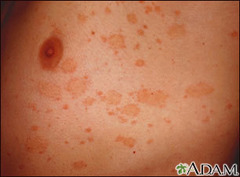
Christmas tree pattern rash

answer
Pityriasis rosea (PR)
question
Burrows
answer
scabies
question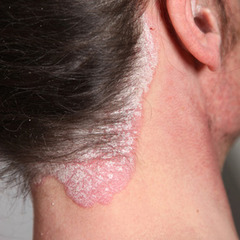
Well circumscribed lesion found on the trunk

answer
Tinea corpus, or PR or Hives
question
Sandpaper textured rash
answer
Strep infection
question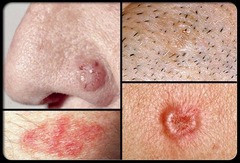
Pearly domed nodule

answer
basal cell carcinoma
question
Bright, beefy red rash
answer
Candida Albicanas
question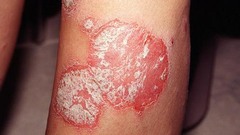
Silvery scales

answer
Psoriasis
question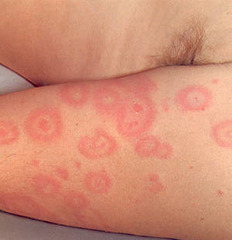
Bull's eye lesion

answer
lyme disease
question
Nits

answer
head lice
question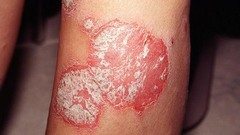
Plaques

answer
psoriasis
question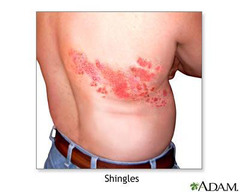
Dermatomal rash

answer
Shingles (varicella Zoster)
question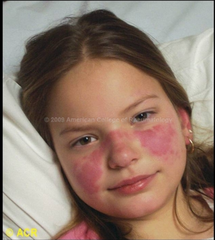
Butterfly rash

answer
Lupus
question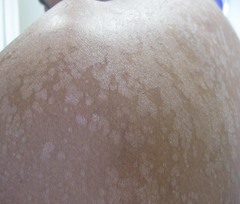
Tinea Versicolor:

answer
Tinea versicolor is typically visualized during the spring and summer months when a patient has become tanned. The areas that are infected do not tan and so become very noticeable. The chest and back are common areas to observe tinea versicolor. There can be 100 or more in some infections. This can be treated with ***topical selenium sulfide or an oral antifungal agent****.
question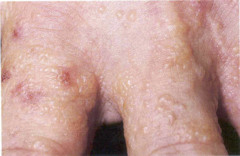
Dyshidrotic dermatitis

answer
small vesicles on the lateral edges of his fingers and intense itching. On close inspection, there are small vesicles on the palmar surface of the hand.
question
Basal Cell Carcinoma: P: Pearly papule U: ulcerating T: telangiectasia O: on the face, scalp, pinnae N: Nodules slow growing
answer
Slow growing perlie or waxy apperence nodules wth relatively distict border.
question
Squamous cell carcinoma: N: nodular O: opaque S: sun exposed areas U: ulcerating N: non distinct borders
answer
can arise from actenic keratosis, red conical hard lesion with or without ulceration, less distict border.



