Colorectal cancer – chapter 56 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
-refers to the colon and rectum, which makes the colon -this is often not a death sentence although it may be perceived that way -colonic mucosa forms polyps that can transform into malignant tumors, these polyps are often removed -liver is the most common sight of mets but can also include lungs, brains, bones, adrenal glands
answer
colorectal information
question
occurs when surgical resection occurs of a tumor and cancer cells break off and go into the peritoneal cavity. for this reason special techniques are used during any resection surgery
answer
peritoneal seeding
question
-bowel obstruction or perforation or fistula formation from the bladder or the vagina -tumor is growing in size and can cause obstructions and distention -frank bleeding can occur -pressure on neighbor organs like the uterus, urinary bladder, ureters and cause symptoms that mask those of cancer
answer
complications due to colorectal cancer
question
major risk factors: 50+ genetic predisposition family history of cancer crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (for 10 years high risk) some infections like JC and HPV smoking, obesity, inactive, alcohol consumption high fat diet, low fiber, red meats, lots of carbs
answer
etiology and genetic risk
question
-third most common cause of cancer death in the U.S -it is not common before the age of 40 -incidence has decreased over the past 20 years due to better screening -more common in black people due to lack of screening
answer
incidence and prevalence
question
-when you turn 40 discuss screening with your doctor -50 without a family history of issues = start screening -decrease fat, carbs, low fiber foods -encourage baked or broiled foods, high in fiber -brassica veggies, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, sprouts because these foods protect mucosa of the intestines -stop excessive drinking or smoking, exercise
answer
health promotion and maintenance
question
-personal history of breast, ovarian, endometrial cancer because these can spread -UC, crohn's, polyps, family history of CRC -vomiting and changes in bowel elimination are huge signs -fatigue, abdominal fullness, vague discomfort, unintentional weight loss, are all symptoms
answer
history gathering
question
most common signs: rectal bleeding, anemia, change in stool consistency or look -stools may be dark with blood or red, or microscopic lose
answer
physical assessment / clinical manifestations
question
obstruction ribbon like stool tenesmus (i need to go bad) gas pains, cramping, straining to pass stools bleeding more common on the left side
answer
tumors on the left side: (rectum and descending colon)
question
abdominal pain and discomfort cramping, n/v, weight loss, anemia, mass, melena (dark stool) -can grow large without disruption of bowl patterns because the stool is liquid in the right side (beginning) -anemia secondary to blood loss
answer
tumors on the right side:
question
-distention or masses may be noted -visible peristaltic waves with high pitched tinkling sounds indicate a partial obstruction -total absence of bowel sounds = complete obstruction
answer
abdominal examination
question
-hematocrit and hemoglobin can be decreased from bleed -liver enzymes can be off due to mets
answer
laboratory assessment
question
-should not be done with a specimen from a rectal exam because it is not reliable, tissue trauma may occur from exam -this should indicate bleeding in the tract -avoid taking: aspirin, vitamin C, red meat for 48 hours, anti inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, corticosteroids, salicylates) -two or three samples taken for 3 consecutive days -negative result does not completely rule out CRC
answer
fecal occult blood test (FOBT) every 5 years
question
-is often elevated in people with CRC -normal value is less than 5 -protein is not specific to cancer, but it may be elevated in presence of other malignant diseases and smokers -CEA is often used to monitor effectiveness of treatment
answer
carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
question
-double contrast barium enema (q 5 years) (air and barium instilled into the colon) or colonoscopy provides visualization of polyps or small lesions than does a barium enema alone -colonoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing and should be done every 10 years
answer
imaging assessment
question
-radiation therapy has not been shown to improve survival rates, can provide local control of disease FOR COLON CANCER -may be used to control pain for palliative treatment and radiation FOR COLON CANCER - FOR RECTAL CANCER, radiation therapy is going to be part of the treatment plan
answer
nonsurgical management radiation
question
-after primary surgery is recommended for patients with stage 2 or 3 of disease
answer
nonsurgical management chemotherapy
question
-most common is colon resection (removal of tumor) with reanastomosis, (MIS via laparscopy) colonectomy (colon removal) with colostomy ileostomy/ileoanal pull through abdominoperineal (AP) resection (rectal tumors)
answer
surgical management
question
surgical creation of an opening of the colon onto the surface of the abdomen
answer
colostomy
question
reattachment of the colon with the cancered part removed and no longer part of the intestine so you attach two ends together
answer
anastomosis
question
-talk about any concerns and pain management -low rectal surgery = risk for sexual dysfunction and urinary incontinence after surgery due to nerve damage -bowel prep may be used but not all Dr. support this due to discomfort and in older people easily dehydrated -reduce risk for infection = one dose oral antibiotics -NGT may be used for decompression after surgery but is not used with MIS
answer
preoperative teaching
question
usually in the transverse colon and a external rod may be used to support the loop that is commonly used until the intestinal tissue adheres to the abd wall
answer
temporary stoma
question
usually in the descending or sigmoid colon
answer
permanent stoma
question
-not very common type of colostomy -dividing the bowel and bringing both proximal ends to the abd surface creating two stomas
answer
double barrel stoma
question
-allows for complete tumor removal with adequate surgical margin removal of all cancer and lymph nodes -several small incisions are made -this way takes longer than conventional procedure
answer
MIS colon resection or total colectomy
question
-should be reddish pink and moist, protrude 3/4 inch -small amount of bleeding at the stoma is common -should start functioning 2-3 days post op -empty it at 1/3 or 1/2 full and watch for gas collection - ascending = liquid / transverse = pasty / descending = solid
answer
colostomy management post op
question
-AP resection, perineal wound is surgically closed and suction drains are placed in the wound. drains help prevent collection within the wound and usually left in place for several days -phantom sensation to poop is common -rectal pain and itching = benzocaine, warm compresses
answer
wound management for AP resection
question
-normal appearance of a stoma (reddish pink) -s/s of complications (purple stoma?) -measurement of the stoma (2cm or 3/4 inch protrude) -barrier cream around the stoma to avoid irritation -use mild soap and water to clean stoma before placing an appliance -don't use moisturizing soaps because it can affect adhesion -broccoli, beans, spicy foods, onions, peas often cause gas, cucumbers, mushrooms, beer, skipping meals, chewing gum, -crackers, toast, yogurt, buttermilk, cranberry = prevent gas
answer
colostomy care
question
--------------------------SLIDES BEGIN---------------------
answer
----------------------CHAPTER ENDS-----------------------
question
-understand treatment for colorectal cancer -know which medications will be used -know the changes that occur with this cancer -know the s/s -understand nursing care for these patients -different types of ostomies for these patients -understand nursing diagnosis
answer
GOALS
question
-involves the rectum and large intestine most tumors are found in the distal portion of the intestine an increase has been seen in right sided (cecum) -2nd leading cause of death in U.S -incidence has decreased in the U.S (better screening) -with early detection, it is very curable (remove the cancer) -mets to liver is the biggest risk
answer
colorectal cancer
question
family history genetic predisposition (uncommon) polyps (these things need to be removed) IBD for more than 10 years (UC specifically) high fat and a low fiber diet with tons of carbs obesity, physical inactivity, alcohol, smoking
answer
risk factors for CRC
question
type 2 DM - 30% increased risk low fruit and veggie intake processed meats age (over 50) industrialized countries
answer
more risk factors
question
-sessile (flat growth) and pedunculated (elongated stalk) -small growths on the colon wall -removed, I.D by colonoscopy
answer
what are polyps
question
-removal of parts of the colon is the most invasive procedure that can occur -body image changes -pre and post op concerns and teachings
answer
colorectal cancer and removal
question
-rectal bleeding (big sign) -changes in consistency or shape of stool (big sign) -blood in stool -fatigue, weight loss, n/v -anemia (blood loss), changes in bowel habits, mets
answer
clinical manifestations of colorectal cancer
question
abd pain cramping n/v weight loss anemia palpable mass melena
answer
right sided CDC (beginning of colon)
question
obstruction ribbon like stool tenesmus gas incomplete bm's mucous in stool
answer
left sided CDC (ending of colon)
question
-history gathering (smoke, alcohol, family history) -clinical manifestations will depend on location of CRC -complaints of straining (obstruction, new onset difficulty) -distention, pain, discomfort -high pitched BS, turns to absent with complete obstruction
answer
assessment for colorectal cancer
question
screening: colonoscopy, barium, occult stool testing labs: FOBT, h+h, CEA imaging: colonoscopy is #!
answer
diagnostics
question
-staging of tumors 1-4 -nonsurgical procedures radiation (works well for rectal not colon) chemotherapy (adjunct therapy post surgery) -surgical intervention colectomy (removal of the colon) resections -surgery is most likely to occur -chemo helps survival rate in stages 2 and 3
answer
management of CRC
question
resections (remove a piece 2 ends connected) exploration (colonoscopy) removal of lymph nodes restoration of continuity prevent complications
answer
goals of surgery
question
- pre op includes: teaching, ostomy care, bowel prep, medications, consults
answer
nursing considerations
question
-stoma appearance (reddish pink) -peristomal skin appearance (any lesions, pain, discomfort) -monitor for pain and NG tube placement -3 to 4 days for colostomy to begin to work -flatulence needs to be released
answer
post op care
question
-time to regain strength -do not strain, stool softeners -resume activities 1-2 weeks for MIS 4-6 for open surgery -support groups for colostomy -flatulence is normal and can be managed
answer
teaching includes:
question
-patient may be embarrassed and stays home all the time -fear, anxiety, anger, grief -let them participate in their own care to regain control
answer
patient psycho social changes
question
-high fiber, low fat diets -stop smoking or drinking alcohol -screen every 10 years colonoscopy or 5 for barium -40 with issues = colonoscopy begins -50 with no issues = colonoscopy begins
answer
nursing interventions to prevent issues
question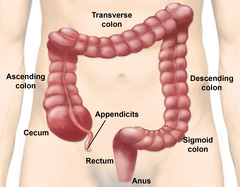

answer
large intestine
question
-----------------------EVOLVE BEGINS----------------------
answer
------------------------SLIDES END-------------------------
question
Dark red and firm stoma A dark red and firm stoma are signs of ischemia and should be reported to the provider. It is normal for the stoma to be reddish-pink, moist, slightly edematous, with small amounts of bleeding.
answer
The nurse is caring for a client who is 2 days postoperative for a colostomy placement. Which assessment finding does the nurse report to the health care provider?
question
"I need to check for leakage underneath my colostomy." The pouch system should be checked frequently for evidence of leakage to prevent excoriation. A purplish stoma is indicative of ischemia and necrosis. Redness or scratched skin around the stoma should be reported to prevent it from beginning to break down. An overly tight fit may lead to necrosis of the stoma.
answer
The home health nurse is teaching a client about the care of a new colostomy. Which client statement demonstrates a correct understanding of the instructions?
question
"I will make certain that I always have an extra bag available." The statement that the client will be certain to bring an extra bag is the only statement illustrating that the client is taking responsibility to care for the colostomy. Using a towel is not an acceptable or effective way to cope with leakage. It is not realistic that the home health nurse can make frequent visits for the purpose of colostomy care.
answer
The Certified Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nurse (CWOCN) is teaching a client with colorectal cancer how to care for a newly created colostomy. Which client statement reflects a correct understanding of the necessary self-management skills?
question
"The only way to know whether you are predisposed to CRC is by genetic testing." Genetic testing is the only definitive way to determine whether the client has a predisposition to develop CRC. A higher incidence of the disease has been noted in families who have a history; however, it is not the responsibility of the nurse to engage in genetic counseling, and this client might not be predisposed to developing CRC. Asking the client what the health care provider thinks is an evasive response by the nurse and does not address the client's concerns.
answer
A male client's sister was recently diagnosed with colorectal cancer (CRC), and his brother died of CRC 5 years ago. He asks the nurse whether he will inherit the disease too. How does the nurse respond?
question
Ask the client to describe feelings about having a colostomy. Clients' reactions to colostomy surgery often include fears about not being accepted by others, grieving over disturbances in body image, and concerns about sexuality; therefore, the nurse should help the client explore feelings about the colostomy. Reassuring the client that the surgery was successful and giving information about support groups assumes that the client is worried about the cancer. Providing teaching about the colostomy will be necessary for home management, but is not appropriate while the client is expressing feelings of grief.
answer
A client has a new colostomy after a partial colectomy for colon cancer in which the surgeon was able to completely remove the colorectal tumor. The client is crying and keeps saying, "Nothing will ever be the same." Which action by the nurse is best?
question
Every 10 years The screening recommendation for those over the age of 50 is every 10 years for a colonoscopy or every 5 years for a double-contrast barium enema or sigmoidoscopy.
answer
A 50-year-old client comes to an outpatient clinic for a colonoscopy and asks how often the procedure needs to be performed. What does the nurse tell the client?
question
To prevent the adjacent skin from becoming raw Stoma paste or powder is often used to prevent rawness of the adjacent skin. Skin sealants are used to facilitate the removal of adhesive. If fungal infection occurs, powder (not paste) is recommended. Stoma paste is not used as an adherent.
answer
In home colostomy care, what is the purpose of stoma paste?



