Classification: Taxonomy & Cladistics – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Taxonomy
answer
The naming of organisms based on a system
question
Goal of modern taxonomy
answer
Describe phylogeny
question
Phylogenetic Systematics
answer
Taxonomy based on phylogeny
question
Why study phylogenies?
answer
1. Knowledge about one group allows for inferences to be made about related groups. Photosynthesis first worked out in a single cell green algae. 2. Medical Considerations: If you want to develop new types of antibiotics what sort of microbe should you explore?
question
Taxon
answer
Group of related organisms
question
The only taxon with a biological bases is
answer
the species
question
Hierarchical arrangement of taxons
answer
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species.
question
Binomial Nomenclature
answer
The scientific name of a species. Humans are called Homo sapiens.
question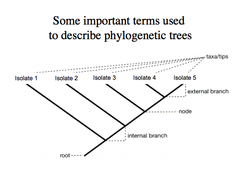
Phylogenetic Trees

answer
Graphical presentation of phylogeny ex. evolutionary relatedness. Phylogenetic systematics established the rolling tree for life on Earth.
question
Henning Principle: Homologous Traits
answer
are due to descent from a common ancestor ex. forelimbs of fish and mammals
question
Henning Principle: Synapomorphies
answer
Homologous traits that differ between groups are due to divergent evolution. ex. forelimbs vs. legs. Thus, the evolutionary most related species will share the greatest number of homologous traits.
question
What creates synapomorphies between homologous traits?
answer
Divergent evolution. Homologs: forelimbs Synapomorphies: fins vs. legs
question
Homologous Traits used include:
answer
1. Morphology -skeletal arrangements -flower parts -embryonic or larval developmental patterns 2. Biochemistry -DNA sequences -Protein sequences -Metabolism
question
Characters used to infer phylogeny
answer
Assumptions: 1. most closely related species share the greatest number of traits. 2. traits are shared because homologous (common ancestry) Traits to use should be: 1. under genetic control 2. show variation between talons (synapomorphy) and similar within taxon. 3. traits being studied are independent of each other.
question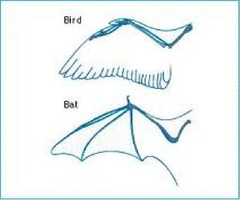
Homoplasy:

answer
apparent homology not consistent with other homologies.
question
Convergent evolution
answer
similar traits arising independently in not closely related organisms.
question
Revertance:
answer
mutation and selection back to the ancestral form ex. antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
question
Making phylogenetic trees Phenetics:
answer
derived from phenotype, relationships among a group of organisms based on their similarity ex. the most similar organisms are grouped together. -resulting trees are called phonograms.
question
cladistics
answer
identifying groups based on a shared derived characteristics. ex. identifying the pathway of evolution. -resulting trees are called cladograms
question
phenograms and cladograms
answer
-sometimes phonograms are cladograms produce identical looking trees -sometimes phenograms and cladograms produce different looking trees ex. similar organisms produced are in different groups.
question
Parsimony
answer
adoption of the simplest assumption in the formulation of a hypothesis -parsimonious cladograms produce a phylogenetic tree with the fewest number of evolutionary changes.
question
Taxon Domain:eukaryote
answer
synapomorphy: nucleus and organelle
question
Taxon kingdom: animalia
answer
synapomorphy: multicellular, eukaryotic heterotrophs, embryos
question
Taxon phylum: chordata
answer
synapomorphy: closed circulatory system
question
Taxon class: mammalia
answer
synapomorphy hair, mammary glands
question
Taxon order: Primate
answer
synapomorphy forward facing eyes, nails, hands, feet
question
Taxon family: hominid
answer
synapomorphy bipedal walk by two feet
question
Taxon genus: homo
answer
synapomorphy smaller face, larger brain
question
Taxon species: Homo sapiens
answer
reproduction



