CISSP Domain 3: Information Security Governance and Risk Management – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Confidentiality Integrity Availability
answer
CIA Triad
question
Ensures reliability and timely access to data and resources to authorized individuals. Ways to provide: -RAID -Clustering -Load Balancing -Redundant data and power lines -Software and data backups -Disk shadowing -Co-location and off-site facilities -Roll-back functions -Fail-over configs
answer
Availability
question
Upheld when the assurance of the accuracy and reliability of information and systems is provided and any unauthorized modification is prevented. Ways to provide: -Hashing (data integrity) -Config Mgmt (system integrity) -Change Control (process integrity) -Access controls (physical and technical) -Software digital signing -Transmission CRC functions
answer
Integrity
question
Ensures that the necessary level of secrecy is enforced at each juncture of data processing and prevents unauthorized disclosure. Level of confidentiality should persist with data at rest, devices within network, data in flight, and once data reaches its destination. Can be provided by: -encrypting data at rest (whole disk, database encryption) -encrypt data in transit (IPSec, SSL, PPTP, SSH) -strict access control and data classification (physical and technical) -training personnel
answer
Confidentiality
question
When one person tries to trick another into sharing confidential information (such as posing as a person who already is authorized to have access to information).
answer
Social Engineering
question
Valuable resources you are trying to protect: -data -systems -people -buildings -property
answer
Asset
question
Lack of a countermeasure or a weakness in a countermeasure that is in place. Weakness in: -software -hardware -procedural -human Basically, a weakness that allows a threat to cause harm.
answer
Vulnerability
question
Any potential danger that is associated with the exploitation of a vulnerability. The threat is that someone or something will identify a specific vulnerability and use it against the company or individual. Anything that potentially can cause harm to an asset.
answer
Threat
question
The entity that takes advantage of a vulnerability.
answer
Threat Agent
question
The likelihood of a threat agent exploiting a vulnerability and the corresponding business impact. Risk ties the vulnerability, threat, and likelihood of an exploitation to the resulting business impact. RISK = THREAT x VULNERABILITY
answer
Risk
question
The severity of the damage, sometimes expressed as dollars. RISK = THREAT x VULNERABILITY x IMPACT (COST)
answer
Impact
question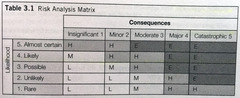
Uses a quadrant to map likelihood of a risk occurring against a consequence (or impact) the risk would have.

answer
Risk Analysis Matrix
question
An instance of being exposed to loss.
answer
Exposure
question
According to Deloitte... 1. Market Approach: Assumes that the fair value of an asset reflects the price which comparable assets have been purchased in transactions under similar situations. 2. Income Approach: Based on premise that the value of a security or asset is the present value of the future earning capacity that an asset will generate over its useful life. 3. Cost Approach: Estimates the fair value of the asset by reference to the costs that would be incurred in order to recreate or replace the asset.
answer
Calculate value of intangible asset
question
Sometimes referred to as a "countermeasure" and is put into place to mitigate (reduce) the potential risk. May be a software configuration, hardware device, or procedure. Examples: -strong passwords -firewalls -security guards -access control mechanisms -encryption -security-awareness training
answer
Control
question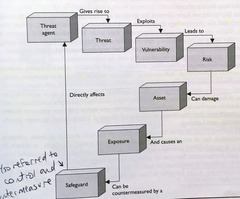
See image for diagram.

answer
Security Definitions Relationship
question
-Administrative -Technical -Physical
answer
3 Types of Control Categories
question
"Soft Controls" Management-oriented Examples: -Security Documentation -Risk Management -Personnel Security -Training
answer
Administrative Control Type
question
"Logical Controls" Software or hardware components Examples: -Firewalls -IDS -Encryption -Identification and Authentication mechanisms -Antimalware
answer
Technical Control Type
question
Controls put in place to protect facility, personnel, and resources. Examples: -Security Guards -Locks -Fences -Lighting
answer
Physical Control Type
question
Coordinated use of multiple security controls in a layered approach. The more sensitive an asset, the more layers of protection put in place.
answer
Defense in Depth
question
Deterrent -Intended to discourage a potential attacker Preventive -Intended to avoid an incident from occurring -Should be number 1 consideration for security structure of an environment -Should implement with detective Corrective -Fixes components or systems after an incident occurred Recovery -Intended to bring the environment back to regular operations Detective -Helps identify an incident's activities and potentially an intruder -Should be implemented with preventive Compensating -Controls that provide and alternative measure of control -Alternate control that provides similar protection as the original control, but has to be used because it is more affordable or allows specifically required business functionality.
answer
6 Types of Control Functionalities
question
These frameworks OUTLINE the necessary components of an organizational security program. BS7799 ISO/IEC 27000 Series
answer
Security Frameworks
question
-British Standard BS7799 -Developed in 1995 by U.K. -Outlines how an Information Security Management System (ISMS) --aka security program--should be built and maintained. -Goal was to provide guidance to organizations on how to design, implement, and maintain policies, processes, and technologies to manage risks to its sensitive assets.
answer
BS7799 Security Framework
question
-Built on top of already established BS7799 -Industry best practice -Follows PDCA cycle: --Plan (establish objectives and make plans) --Do (implementation of plans) --Check (measure results to see if objectives are met) --Act (how to correct and improve plans to better achieve success) ISO 27000: Overview/Vocabulary ISO 27001: ISMS requirements ISO 27002: Code of practice in info security mgmt ISO 27003: Guidelines for ISMS implementation ISO 27004: Guidelines for ISMS measurement and metrics ISO 27005: Guidelines for info security risk mgmt ISO 27006: Guidelines for audit and certification of ISMS ISO 270011: Guidelines for telecommunications ISO 27031: Guidelines for business continuity ISO 27033-1: Guidelines for network security ISO 27799: Guidelines for health organizations
answer
ISO/IEC 27000 Series Security Framework
question
Encompasses the essential and unifying components of an organization. Expresses the enterprise structure (form) and behavior (function). It embodies the enterprise's components, their relationships to each other, and to the environment. When developing an architecture, first identify stakeholders. Then create views that illustrate the information in a way conducive to the parties looking at the architecture. Should allow one to understand the company from several different views and to understand how a change at one level will affect items at another level. Enterprise Architecture is needed to present information in a way in which all consumers of the information can understand.
answer
Enterprise Architecture
question
Zachman Framework TOGAF DoDAF MODAF
answer
Enterprise Architecture Frameworks
question
Created by John Zachman Two dimensional model using 6 basic communication interrogatives (what, how, where, who, when, and why) intersecting with different viewpoints (Planner, Owner, Designer, Builder, Implementer, and Worker) to give a holistic understanding of the enterprise. Goal of the model is to be able to look at the same organization from different views (Planner, Owner, Designer, Builder, Implementer, and Worker). This framework is NOT security oriented.
answer
Zachman Architecture Framework
question
Origins in U. S. DOD Provides an approach to design, implement, and govern an enterprise information architecture. Develops the following architecture types: -Business Architecture -Data Architecture -Applications Architecture -Technology Architecture Creates individual architectures through use of its Architecture Development Method (ADM). This allows an analyst to understand organization from 4 different views (business, data, applications, technology).
answer
The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF)
question
DoDAF military-oriented framework Focus is on command, control, communications, computers, intelligence, surveillance, and recon systems and processes. Helps ensure all systems, processes, and personnel work in concerted effort to accomplish its missions.
answer
Dept. of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF)
question
MODAF military-oriented framework Based on DoDAF Crux of framework is to be able to get data in the right format to the right people as soon as possible.
answer
British Ministry of Defense Architecture Framework (MODAF)
question
Helps us integrate the requirements outlined in our security program. Subset of enterprise architecture and defines the information security strategy that consists of layers of solutions, processes, and procedures and the way they are linked across an enterprise strategically, tactically, and operationally. Main reason to develop an enterprise security architecture is to ensure that security efforts align with business practices in a standardized and cost effective manner.
answer
Enterprise Security Architecture
question
Similar to Zachman Framework Layered model with first layer defining business requirements from a security perspective. Framework and methodology for enterprise security architecture and service management.
answer
Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture (SABSA)
question
Strategic Alignment -Business drivers and the regulatory and legal requirements are being met by the security enterprise architecture. Business Enablement -Core business processes are integrated into the security operating model--they are standards-based and follow a risk tolerance criteria. Process Enhancement -Organization must take a close look at their business processes that take place on an ongoing basis. Security Effectiveness -Metrics -SLA -ROI -baselines -dashboards -scorecards
answer
What's Needed in Enterprise Security Architecture to be Effective
question
Enterprise architecture addresses the structure of and organization. System architecture addresses the structure of software and computing components.
answer
Enterprise versus System Architectures
question
CoBiT NIST 800-53 COSO
answer
Security Controls Development
question
Control Objectives for Information and related Technology Private Sector Derived from COSO. COSO is model for corporate governance, CobiT is model for IT governance. Security framework that acts as a model for IT governance and focuses more on operational goals. Framework and set of control objectives developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) and the IT Governance Institute (ITGI). It defines goals for the controls that should be used to properly manage IT and to ensure that IT maps to business needs. Broken down into four domains -Plan and Organize -Acquire and Implement -Deliver and Support -Monitor and Evaluate Provides checklist approach to IT governance by providing a list of things that must be thought through and accomplished when carrying out different IT functions. CobiT provides the objectives that the real-world implementations (controls) you chose to put in place need to meet. Where ISO27000 would say "Unauthorized Access should not be permitted", CobiT would define the specific objectives that must be met to satisfy this. Most security auditing practices used today in the industry are based off CobiT.
answer
CoBiT
question
U. S. government control objectives Outlines controls that agencies need to put in place to be compliant with Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002. Control categories (families) are the Management, Operational, and Technical controls prescribed for an information system to protect confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system and its information. i.e. (family--class) Access Control--Technical Audit and Accountability--Technical Risk Assessment--Management Security Assessment and Authorization--Management Contingency Planning--Operational Maintenance--Operational Government auditors use SP 800-53 as their "checklist" approach for ensuring that government agencies are compliant with government-oriented regulations.
answer
NIST 800-53
question
Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (of Treadway Commission in 1985) Created to deal with fraudulent financial activities and reporting. Made up of the following components: Security framework that acts as a model for corporate governance and focuses more on strategic goals. -Control Environment -Risk Assessment -Control Activities -Information and Communication -Monitoring Model for corporate governance (where CobiT is model for IT governance). Deals with more with none-IT items such as company culture, financial and accounting principles, board of director responsibilities, and internal communication structures. SOX is based on COSO.
answer
COSO
question
ITIL Six Sigma Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI)
answer
Process Management Development
question
De facto standard of best practices for IT service management. Was created because of the increased dependence on IT to meet business needs. Focus is more toward internal SLA's between the IT departments and the "customers" it serves.
answer
ITIL
question
Process improvement methodology. It is the "new" and improved TQM. Goal is to improve process quality by using statistical methods of measuring operation efficiency and reducing variation, defects, and waste. Developed by Motorola with goal of identifying and removing defects from it manufacturing processes.
answer
Six Sigma
question
OMB Circular A-130 was developed to meet information resource management requirements for the federal government. According to this circular, independent audits should be performed every three years.
answer
OMB Circular A-130
question
Came from security engineering world Model is also used within organizations to help lay out a pathway of how increment improvement can take place. Crux of CMMI is to develop structured steps that can be followed so an organization can evolve from one level to the next and constantly improve its processes and security posture. Developed by Carnegie Mellon
answer
Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI)
question
Top-down: Initiation, support, and direction come from top management, work through middle management and then reach staff members. Bottom-up: Staff (usually IT) try to develop a security program without getting proper management support. Bottom-up is far less effective than top-down approach.
answer
Top-down vs. Bottom-up Approach to Security Program
question
1. Plan and organize --Establish management commitment. --Establish oversight steering committee. --Assess business drivers. --Develop a threat profile on the organization. --Carry out a risk assessment. --Develop security architectures at business, data, application, and infrastructure levels. --Identify solutions per architecture level. --Obtain management approval to move forward. 2. Implement --Assign roles and responsibilities. --Develop and implement security policies, procedures, standards, baselines, and guidelines. --Identify sensitive data. --Implement the following blueprints: -----Asset identification and management -----Risk management -----Vulnerability management -----Compliance --Identity management and access control --Change control --Software development life cycle --Business continuity planning --Awareness and training --Physical security --Incident response --Implement solutions. --Develop auditing and monitoring solutions. --Establish goals, service level agreements (SLAs), and metrics. 3. Operate and maintain --Ensure that all baselines are met. --Complete internal and external audits. --Complete tasks outlined in the blueprints. --Manage SLAs as outlined in the blueprints 4. Monitor and evaluate --Review logs, audit results, collected metric values, and SLAs per blueprint. --Assess accomplishments --Carry out quarterly meetings with steering committees. --Develop improvement steps and integrate into the Plan and Organize phase.
answer
Security Program Lifecycle
question
Think of ISO27000 mainly working at the policy level as a DESCRIPTION of the type of house you want to build (two-story, five bedroom, three bath). Security enterprise framework is the ARCHITECTURE layout of the house (foundation, walls, ceilings). Blueprints are the detailed descriptions of specific components in the house (window types, security system, electrical and plumbing). Inspector (auditor) uses checklists to inspect house like and auditor uses checklists (CobiT/SP 800-53) to ensure that you are building and maintaining your security program securely. Once house is built, procedures for running the house day in and day out are implemented. This is where ITIL comes into play. Optimizing daily activities occurs with Six Sigma.
answer
Putting the pieces together
question
In the context of security, it's the possibility of damage happening and ramifications of such damage should it occur. Information Risk Management (IRM) is the process of identifying and assessing risk, reducing it to a acceptable level, and implementing the right mechanisms to maintain that level. Types of Risk -Physical damage -Human interaction -Equipment malfunction -Inside and outside attacks -Misuse of data -Loss of data -Application error
answer
Risk Management
question
Requires strong commitment from senior management, document processes supporting organization's mission, and an IRM policy, and delegated IRM team. IRM policy provides the foundation and direction for the organization's security risk management processes and procedures.
answer
IRM Policy
question
Overall goal is to ensure the company is protected in the most cost-effective manner. Should have one person assigned to lead the IRM team and devote at least 50-70% of their time to this.
answer
Risk Management Team
question
Is a method of identifying vulnerabilities and threats and assessing the possible impacts to determine where to implement security controls. Used to GATHER DATA Risk assessment calculates the probability of a vulnerability being exploited and the associated business impact. In contrast, a vulnerability assessment are jut focused on finding the vulnerabilities (the holes).
answer
Risk Assessment
question
Helps companies prioritize their risks and shows management the amount of resources that should be applied to protecting against those risks in a sensible manner. Four Main Categories: 1. Identify asset and value to organization 2. Identify vulnerabilities and threats 3. Quantify probability and impact of threats 4. Provide economical balance between impact of threat and cost of control Provides cost/benefit comparison--this compares the annualized cost of the control versus the potential cost of loss. A control's cost should generally not exceed the potent loss. Used to EXAMINE the gathered data and PRODUCE RESULTS that can be acted upon.
answer
Risk Analysis
question
Should include individuals from many or all departments to ensure that all the threats are identified and addressed. Must include people who understand individual process in their department(s)
answer
Risk Analysis Team
question
Determined by the importance the asset has to the organization.
answer
Asset Value (AV)
question
What the company would lose if a threat agent actually exposed a vulnerability.
answer
Loss Potential
question
Loss that occurs well ofter the vulnerability is exploited. Loss of market share Reputation damaged Civil suits
answer
Delayed Loss
question
NIST SP 800-30 FRAP OCTAVE AS/NZS 4360 ISO 27005 FMEA CRAMM
answer
Methodologies of Risk Assessment
question
Named Risk Management Guide for IT Systems Considered U.S. federal government standard Specific to IT threats and how they relate to IT security risks. Mainly focused on computer systems and IT security issues. Covers IT and operations Does not cover larger threats like natural disasters, succession planning, etc.
answer
NIST SP 800-30
question
Facilitated Risk Analysis Process Qualitative methodology Focus only on systems needing assessing to reduce time and cost obligations. Used if limited budget. Stressed pre-screening so only those systems needing risk assessments are carried out. Used to analyze one system, application, or process at a time. Does not support calculating exploitation probability or annual loss expectancy.
answer
FRAP
question
Operationally Critical Threat, Asset, and Vulnerability Evaluation Created by Carnegie Mellon Methodology intended to be used in situations where people manage and direct the risk evaluation for information security within the company. Puts people that work inside the company in position to make decisions on what the best approach is to secure organization. Uses facilitated workshops. Stresses self-directed team approach. Used to analyze All systems, ALL applications, and ALL processes (FRAP just analyzes individual systems, applications, and processes). Three-phase process: 1. Identify staff knowledge, assets, threats 2. Identify vulnerabilities and evaluates safeguards 3. Conducts Risk Analysis and develops risk mitigation strategy
answer
OCTAVE
question
Broad approach to risk management Used to understand company's financial, capital, human safety, and business risk decisions. Focused on health of a company from a business point of view, not security.
answer
AS/NZS 4360
question
Risk methodology that can be used to integrate into organization's security program that address all threats an org could be faced with. International standard on how risk management can be carried out in ISMS. Covers IT and softer items, like documentation, personnel security, training, etc.
answer
ISO 27005
question
Failure Modes and Effect Analysis Used for determining functions, identifying functional failures, and assessing cause of failure and their failure effects through a structured process. Used to dig into details of specific systems. Commonly used in product development and operational environments. Goal is to identify where something is most likely to break and either fix the flaw or implement controls to reduce the impact of the break. Failure Modes (how something can break or fail) Effects Analysis (impact of that break or failure) First developed for systems engineering with purpose of examining potential failures in products and the process involved with them. Not useful in discovering complex failure modes that may be involved in multiple systems or subsystems.
answer
FMEA
question
Approach to identify failures that can take place within more complex environments and systems. Used to dig into details of specific systems.
answer
Fault Tree Analysis
question
Central Computing and Telecommunications Agency Risk Analysis and Management Method Created by U.K., and tolls sold by Siemens. Three stages: 1. Define Objectives 2. Assess Risks 3. Identify Countermeasures
answer
CRAMM
question
Quantitative Qualitative
answer
Risk Analysis Approaches
question
Used to assign monetary and numeric values to all elements of the risk analysis process. Example: Organization would be as risk of losing $100,000 if a buffer overflow was exploited on a web server.
answer
Quantitative Risk Analysis
question
Single Loss Expectancy. Quantitative analysis equation used to assign a dollar amount to a single event/asset, that represents the company's potential loss amount of a specific threat were to take place. Asset Value x Exposure Factor (EF) = SLE Exposure Factor (EF) represents the percentage of loss a realized threat could have on a certain asset. Example: Data warehouse asset value = $150,000 If fire, 25% would be lost Asset Value ($150,000) x EF (25%) = SLE ($37,500)
answer
SLE
question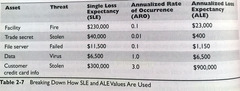
Annual Loss Expectancy. Tells company the annual amount of exposure, in terms of dollars, that could be expected for a loss of a single asset. SLE x Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO) = ALE ARO is value that represents the estimated frequency of a specific threat taking place within a 12-month timeframe. Range for ARO: 0.0 (never) 1.0 (once per year) > 1 (several times per year) Examples: 3 times / year = 3.0 Once every 10 years = 0.1 Once every hundred years = 0.01 ALE Example: Fire in data warehouse causes SLE of $37,500 Expected to occur once every 10 years SLE ($37,500) x ARO (.1) = ALE ($3,750) So company could spend $3,750 or less annually on controls to mitigate fire destruction of the data warehouse asset. Spending more than $3,750 would not make sense.

answer
ALE
question
TCO= total cost of a mitigating safeguard. It combines upfront costs (often a one-time capital expense) plus annual costs of maintenance, including staff hours, vendor maintenance fees, software subscriptions, etc. ROI=the amount of money saved by implementing a safeguard. If TCO is less than ALE, you have a positive ROI (good decision). If TCO is higher than ALE, you have a negative ROI (bad decision).
answer
TCO and ROI
question
Uses a "softer" approach to the data elements of the risk analysis process. Does not quantify that data, which means that is does not assign numeric values to the data so that they can be used in equations. Ranks the seriousness of threats and validity of different possible countermeasures based on opinions. Examples on gathering data: -Brainstorming -Story boards -Meetings -Focus groups -Surveys -Delphi (group decision making where people submit their ideas individually (not during a group activity). This helps reduce group pressures. Example Scenario: Risk of a buffer overflow exploitation on a web server would be rated as red, yellow, or green. A scale could also be used, such as a scale of 1-5. No monetary values are assigned.
answer
Qualitative Risk Analysis
question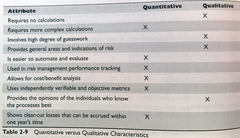

answer
Quantitative versus Qualitative
question
(ALE before implementing safeguard) - (ALE after implementing safeguard) - (annual cost of safeguard) = value of safeguard to the company Example: ALE threat hacker brings down web server: $12,000 ALE after implementing safeguard = $3,000 Annual cost of safeguard = $650 $12,000 - $3,000 -$650 = $8,350 (annual value of safeguard)
answer
Cost-benefit Analysis
question
Residual Risk: risk that remains after company has provided some level of countermeasure for a risk. Sometimes expressed as: total risk - countermeasures = residual risk --or-- Threats x vulnerabilities x assets x (control gap) = residual risk Total risk: Risk company faces if it chooses not to implement any safeguard. Expressed as: Threats x vulnerabilities x assets = total risk Handling risk: -Risk Transfer: purchase insurance -Risk Avoidance: terminate activity that's introducing risk -Risk Mitigation: Reduce risk to acceptable level (i.e. implement firewalls, training, IDS/IPS) -Risk Acceptance: Simply lives with the risk and not implement countermeasures.
answer
Risk
question
A security policy is an overall general statement produced by senior management (or a selected policy board or committee) that dictates what role security plays within the organization. A security policy defines the technology that should be used to control access to a company's network or buildings. -organizational policy -issue-specific policy -system-specific policy.
answer
Security Policy
question
Policy where management establishes how a security program will be setup, lays out the program's goals, assigns responsibilities, shows the strategic and tactical value of security, and outlines how enforcement should be carried out. Formulated by the management, this security policy defines the procedure used to set up a security program and its goals. It identifies the major functional areas of information and defines all relevant terms. The management assigns the roles and responsibilities and defines the procedure used to enforce the security policy. A security policy is developed prior to the implementation of standard operating procedures. The organizational polices are strategically developed for a long term. Referred to as Master Security Policies
answer
Organizational Security Policy
question
Also called a Functional Policy. Addresses specific security issues that management feels needs more detailed explanation and attention to make sure a comprehensive structure is built and all employees understand how they are to comply with these security issues. An issue-specific security policy involves the detailed evaluation of security problems and addresses specific security issues. An issue-specific security policy ensures that all employees understand these security issues and that they comply with the security policies defined to address these security issues. Example: Email security policy stating management has right to read employee's emails residing on a server, but not when they reside on a user's workstation.
answer
Issue-Specific Policy
question
Presents management's decisions that are specific to the actual computers, networks, and applications. A system-specific policy defined by management describes the rules governing the protection of information processing systems, such as databases, computers, and other infrastructure equipment. A system-specific policy is strategic in nature and is designed with a long-term focus. This policy restricts the use of software to only those approved by management and further defines the policies and guidelines for system configuration, implementation of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network and virus scanners. A system-specific policy is used to implement security configuration settings that have been determined to provide optimum security to the infrastructure assets. It should include a statement of senior executive support and a definition of the legal and regulatory controls. Example: Policy that outlines how a database containing sensitive info should be protected, who has access, and how auditing will take place.
answer
System-Specific Policy
question
Classification of information is typically part of an information policy. A company usually has at least two information classifications: public and proprietary. Public information can be revealed to the public, and proprietary information can only be shared with individuals who have signed a non-disclosure agreement. Some companies also use the restricted classification. Only a small group of individuals within a company can gain access to restricted information. The cornerstone of a well-defined information policy is to limit individual access to that information which the individual 'needs to know' to perform required functions.
answer
Information Policy
question
Regulatory: policy that ensures company is following standards such as SOX, G:BA, HIPAA, etc. Advisory: Strong advisement of following a policy. List possible ramifications if not followed. Might describe how to handle medical or financial information. Informative: Informs employees of certain topics. Not enforceable. Stuff like how a company interacts with its partners, company's goals, etc.
answer
Types of Policies
question
-Purpose -Scope -Responsibilities -Compliance
answer
4 Things All Program Policies Should Have
question
High-level management directives. Does not go into specifics. Policy is mandatory. Policy would not use terms like Windows or Linux. Instead, server policy would state things like protecting confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system.
answer
Policy
question
Detailed step-by-step tasks that should be performed to achieve a certain goal. How to install an OS, configure security parameters, setup new user accounts, etc.
answer
Procedures
question
Mandatory activities, actions or rules. Gives a policy its support and reinforcement in direction. Describes the specific use of technology: --All employees receive a Windows 7 -based desktop with 2.8Ghz CPU, 16GB RAM, and 2TB hard drive. Standards are mandatory.
answer
Standards
question
Recommended actions and operational guides to users, IT staff, operations staff, and others when a specific standard does not apply. Deals with methodologies of technology, personnel, or physical security. Discretionary. Not mandatory.
answer
Guidelines
question
Refers to a point in time that is used as a comparison for future changes. Consistent reference point. Used to define minimum level of protection required. Unified ways to implement a safeguard and discretionary.
answer
Baselines
question

answer
Policy/Procedure/Standard/Guideline/Baseline Example
question
Security Policy indicates confidential info should be protected Supporting standard mandates all customer info be held in database and be encrypted with AES256. Procedures explain exactly how to implement AES and IPSec. Once configuration completed, system is now at baseline.
answer
Security Policy Flow
question
Need to classify information to organize i according to its sensitivity to loss, disclosure, or unavailability. Primary purpose is to indicate the level of confidentiality, integrity, and availability protection that is required for each type of data set. Ensures data is protected in the most cost-effective manner. Common levels of sensitivity for Commercial businesses -Confidential -Provate -Sensitive -Public Common levels of sensitivity for Government -Top secret -Secret -Confidential -Sensitive, but unclassified -Unclassified
answer
Information Classification
question
Group of individuals who are elected by the shareholders of a corporation to oversee the fulfillment of the corporation's charter. Goal is to ensure shareholder's interests are being protected and that corporation is running properly.
answer
Board of Directors
question
CEO/CFO Responsible for informing stakeholders of firm's financial condition and health.
answer
Executive Management
question
Responsible for strategic use and management of information systems and technology within the organization. Ultimately responsible for the success of the security program.
answer
CIO
question
Responsible for ensuring that customer, company, and employee data are kept safe. Often reports to CSO
answer
CPO
question
Responsible for undertaking the risks that the company faces and for mitigating these risks to an acceptable level. Must understand the organization's business drivers, creating a security program, security compliance, etc.
answer
CSO
question
Privacy: Indicates the amount of control an individual should be able to have and expect as it related to the release of their own sensitive information. Security: Is the mechanisms that cane put in place to provide this level of control.
answer
Privacy versus Security
question
Responsible for making decisions on tactical and strategic issues within an enterprise as a whole and should not be tied to a specific business unit. CEO should head this committee. Should meet at least quarterly.
answer
Security Steering Committee
question
Appointed by Board of Directors to evaluate the company's internal operations, internal audit system, and the transparency and accuracy of financial reporting. Goal is to provide open an independent communications between the Board of Director's and the company' management, internal/external auditors.
answer
Audit Committee
question
Member of management in charge of specific business unit and ultimately responsible for protection and use of specific subset of information. Can be held responsible for data. Decides on data classification, backups, disclosure, approves access requests. Delegates responsibilities to Data Custodian.
answer
Data Owner
question
Responsible for maintaining and protecting data. Fulfilled by IT or Security department. Implements the controls necessary for protecting, backing up, maintaining security controls, etc.
answer
Data Custodian
question
Responsible for one or more systems, each of which may hold and process data owned by different data owners. Ensures systems are properly assessed for vulnerabilities and reports incidents to team and data owner.
answer
System Owner
question
Responsible for implementing and maintaining specific security network devices and software in the enterprise. Include things like IDS, IPS, antimalware, proxies, data loss prevention, etc. Includes new user account creation, implementing new security software, testing security patches, and issuing new passwords.
answer
Security Administrator
question
Strategic level employee who helps develop policies, standards, and guidelines along with setting baselines. Design level person.
answer
Security Analyst
question
Usually business unit mangers. Responsible for dictating who can and cannot access their applications.
answer
Application Owner
question
Also called a user manager. Responsible for all user activities and any assets created and owned by these users.
answer
Supervisor
question
Responsible for approving or rejecting requests to make changes to the network, systems, or software.
answer
Change Control Analyst
question
Responsible for ensuring that data is stored in a way that makes sense to the company and individuals who need access to and work with the it.
answer
Data Analyst
question
Responsbile for properly defining, improving upon, and monitoring processes.
answer
Process Owner
question
Works with the business unit managers, data owners, and senior management to develop and deploy a solution to reduce the company's pain points.
answer
Solution Provider
question
Any individual who routinely uses the data for work-related tasks.
answer
User
question
Role that understand business drivers, business processes, and the technology that is required to support them. Evaluates various markets, works with vendors, and advises management on proper solutions needed to meet their goals.
answer
Product Line Manager
question
Ensures correct controls are in place and are being maintained securely. Goal is to make sure the organization complies with its own policies and the applicable laws and regulations.
answer
Auditor
question
Makes sure one person cannot complete a critical task by them self. Preventative Administrative control to reduce fraud.
answer
Separation of Duties
question
When at least two people work together to cause some sort of destruction or fraud.
answer
Collusion
question
Control in which no one person has all the knowledge necessary to complete a task. Example: Bank vault that requires two sets of codes to open he vault (each person has only their code).
answer
Split Knowledge
question
Control in which two individuals must be available to perform a task. Example: Two officers must perform identical key-turn in order to launch a missile.
answer
Dual Control
question
Administrative Detective control put in place to uncover fraudulent activities. Person is rotated to different positions frequently in order to uncover activities that would show up if the person was no longer performing their same duties.
answer
Rotation of Duties
question
Control to uncover fraudulent activities. Person is required to take vacation and any fraudulent activities might show up when the person is on vacation.
answer
Mandatory Vacation
question
Put in place to modify employee's behavior and attitude toward security. Security Awareness Program created for 3 types of audiences: 1. Management 2. Staff 3. Technical Employees Should happen during hiring and at least annually thereafter. Integrate into employee performance reports.
answer
Security Awareness Training
question
Awareness changes use behavior. --Reminding users to never share account passwords is an example of awareness Training provides a skill set. --Training service desk to open/close new tickets --training staff to configure a router
answer
Security Awareness versus Training
question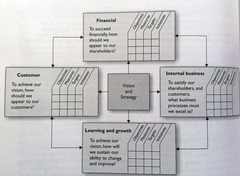
Framework that allows for the security goals of an organization to be set and expressed by senior management, communicated throughout the different levels of the organization, grant power to the entities needed to implement and enforce security, and provide a way to very the performance of these necessary security activities. Strong management support necessary. There has to be established policies, procedures, and standards to measure against. Measurement activities need to provide quantifiable performance-based data that is repeatable, reliable, and produces results that are meaningful. Balanced scorecard.

answer
Security Governance
question
Inernational standard used to assess the effectiveness of an ISMS and the controls that make up the security program. Breaks individual metrics down into: -base measures -derived measures -indicator values. ISO 27001 tells you how to BUILD the security program, ISO 27004 tells you how to measure it.
answer
ISO 27004:2009
question
U.S. Government standard covering performance measurement for information security. Breaks metrics down into -implementation -effectiveness/efficiency -impact values.
answer
NIST 800-55
question
Due Care: doing what a rinsable person would do. Informal. Due Diligence: is the management of due care. Follows a process.
answer
Due Care/Due Diligence
question
Certification: Detailed inspection that verifies whether a system meets the documented security requirements. Accreditation: Is the data owner's acceptance of the risk represented by that system. NIST 800-37 specifies 4-step Certification and Accreditation process: 1. Initation phase 2. Security certification phase 3. Security accreditation phase 4. Continuous monitoring phase
answer
Certification versus Accreditation
question
Operational Goals=Daily Tactical Goals = more time than operational, but not as long as strategic. Milestones within a project. Strategic Goals=1 year or longer goals
answer
Goal Types
question
Information security is a continuous process of securing the business operations of an organization. The security starts with the establishment of a security policy and standards, is followed by the implementation of hardware and software through standard operating procedures, and ends by imparting security awareness training to employees. The security awareness training covers the acceptable use of resources and the risks that the threats might pose to the business operations.
answer
Information Security
question
The purpose of information assurance is to ensure that the access control mechanisms correctly implement the security policy for the life cycle of an information system. Assurance procedures should be developed based on the organization's security policy.
answer
Information Assurance
question
A security template should cover: -account policies -user rights and permissions -registry permissions, and system services. Other areas that should be covered include: -event log settings -restricted groups -file permissions -auditing settings
answer
Security Template



